International
(IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

p-ISSN:2395-0072

International
(IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

p-ISSN:2395-0072
1Associate Professor and Head, Department of Computer Science, Thanthai Periyar Government Arts and Science College (Autonomous), Tiruchirappalli
Assistant Professor and Head, Department of Computer Science, Sri Vasavi College, Erode
Abstract:- Cloud Computing is a recent developmental paradigm in the field of computing offering huge power to next-generation computers. The dynamic provisioning acts as a base for cloud computing facilitating and supporting the network services. It focuses on making the vision of utility computing a reality with pay as you go. It offers immense potential to bloom the world with applications and products focusing on greater resource utilization and scalability. This paper presents the survey on the basics of cloud computing, the concepts of load balancing, and the scheduling of tasks in the cloud. It elaborates on the existing load scheduling algorithms with their merits and demerits, suitability in the cloud, heterogeneous computing environment, and proposes a new perspective for better results as per desired parameters.
Keywords
balancing,
Optimization, Response time, Scheduling Algorithms.
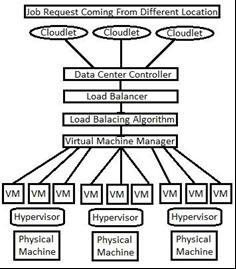
Loadbalancingisthereapportionoftheworkloadequallyacrossallprocessors,sothatnoprocessorisoverloaded Aload balancerisaphysicaldevice,runningonaspecializedhardwareorsoftwareprocessanditacceptsmultiplerequestsfrom usersanddistributesthemevenlyacrossservers[20] Loadbalancingincreasesthroughputandtherebyreducesresponse time Loadbalancinginclouds,distributestheexcessdynamiclocalworkloadevenlyacrossallthenodes Itensuresbetter serviceprovisioningandresourceutilizationratio,andinturn,improvestheoverallperformanceofthesystem Incoming tasks,which arereceivedfrom different locations, arereceived by theload balancer and arethendistributed tothedata centerfortheproperloaddistribution Figure(1)showsthetypicalloadbalancingmechanism
pointfailuredoesnotaffectthe provisioning of
issue prevails in centralized systems, when the central node fails, then the whole system conkout So,loadbalancingalgorithmsshouldbedesignedwithhighavailabilitytoovercomethisproblem
1.
cloudisreferredtoasasubscriptionbasedservicewherecomputingresourcesand storagespaceinthenetworkcaneasilybeaccessed.Thecloudsactasvirtualizeddatacenters[1,22].Theplatformsused incloudcomputingaredynamicallybuiltusingvirtualizedsoftware,hardware,data,andnetworks Thus,cloudcomputing isanewandupcomingcomputingparadigmthatsupportsdataandcomputationaloutsourcing[27] Figure(2)showsthe typicalarchitectureofloadbalancingincloudenvironment
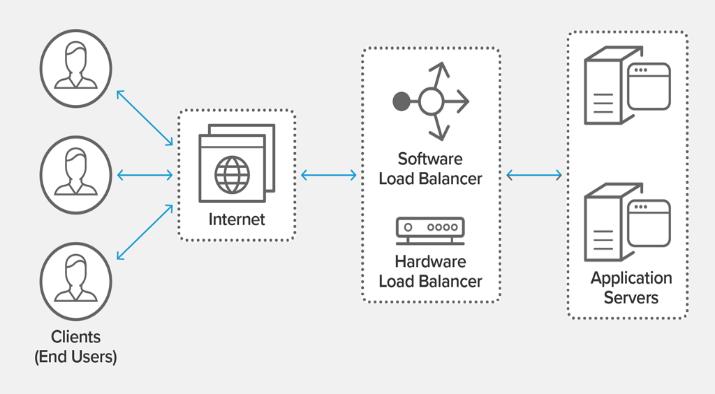
Cloudcomputingisascalableanddistributedsystemrequiringtheallocationofresourcestoseveralusers Thiscouldlead tocongestionorimbalancedallocationofthesystem[3] So,aloadbalancingstrategyisneededtodealwiththeimbalance in the network Load balancing is the mechanism used for distributing the load for optimal resource utilization on the systemprocessesorvirtualmachines Theloadreferstothetaskneededtobedoneonthesystemandbalancingrefersto thehandlingorthemanagementoftheload Loadbalancingisappliedtotheresourcesinthesystemwhichcanbedisks, drivers,memorybuffers,processors,networksimulators,etc.[4].Theloadbalancingisperformedandappliedtoachieve minimumresponsetime,maximumthroughput,andthereductionoftheoverheadsproducedbythesystem.Themainaim istoprocesstheuser’srequestbytheefficient,andeffectiveutilizationoftheresourcespresentinthesystem[23].
Loadschedulingtherebytheloadbalancingisattained,isacomputernetworkingtechniquetodistributeworkloadacross multiplecomputersorcomputerclusters,diskdrives,networks,[28]centralprocessingunits(CPUs)andotherresources incitedduetoscalabilityforachievinghigherthroughput,optimalresourceutilization,lesserresponsetime,andavoiding

overloadingofthesystem[1]
multiplecomponentswithload
[14]insteadofasinglecomponent,increases thereliabilitywiththehelpofredundancy Thetaskofprovidingtheloadbalancingserviceisdonebydedicatedsoftware andhardware,suchasaDomainNameSystemserver.Loadbalancingplaysanimportantroleinthedistributedcomputing system.Theloaddistributioninanetworkisperformedamongservers.Loaddistributionisthemethodofreallocatingthe totalavailableloadtothespecificandsinglenodeavailableonthenetworkforefficientutilizationofresources,improving theresponsetimeofthetask,andremovingthesituationofnodeoverloadingaswellunderloadinginthesystem.Theload balancerisasoftwareservicethatlistensontheporttoavailservicesbyconnectingwithexternalusers.Theloadbalancer intern forwards requests to the servers located at the backend and the feedback data is passed to the load balancer and thenbacktotheuser Theuserreceivesthereplyfromtheloadbalancer,buttheuserisunawareoftheinternalseparation orabstractionoffunctions[12,15] Italsopreventstheuser’sdirectcontactwiththebackendservers,therebyincreasing the benefits obtained from security by the inner network’s structural abstraction, and preventing attacks on the service portsandnetworkstackofthekernel
3. 1. Major goals of the load balancing:
a) Toenhancethesystemperformance.
b) Tohaveabackupplanreadyifanyfailureoccursinthesystem.
c) Toupholdthesystemstability.
d) Toallowfurthermodificationsinthesystem.
e) Todistributetheloadeffectivelyandobtaincost effectiveness

The load scheduling, as well as the task scheduling algorithms that are currently available in the cloud environment, are discussedbelowandtabularizedinTable(1)
In this algorithm, firstly a set of minimum execution time M is computed The task having a total maximum completion time amongst elements of M is selected and allocated to the corresponding machine is called the Max min strategy The recentlymappedtask, T isremovedfromtheset M andtheprocedureisrepeatedtillthesystemmapstheremainingtasks [1,16,19].Theminimizingalgorithmattemptstominimizethedegreeofshortcomingsincurredforperformingtaskswith longerexecutiontimes.Itoffersbettermappingthantheshortertasksthatgetexecutedfirst,followedbytheexecutionof long running tasks while several machines remain idle waiting for resources. Thus, the Max min heuristic provides mappingwithamorenicelybalancedloadacrossmachinesandabettermakespan(completiontime).
It is the simplest algorithm enduring as a base for existing [1, 16, 21, 30] cloud scheduling algorithms It is fast and provideshigherandbetterperformancethanothersbyschedulingbyconsideringthebestcasefirst Itbeginsusingaset of completely unmapped tasks, S Then, the resource R having a minimum completion time for all tasks is found and the task T withtheminimumsizeisselectedandassignedtothecorrespondingresource R Lastly,fromthesetofunmapped tasks, S executedtask, T isremovedandtheprocessgoesonrepeatingusingMin minalgorithmtillalltaskedarefinished Assuming [29] we have a set of n tasks (Tn) that need to be scheduled onto m available resources (Rm) We denote the Expected CompletionTime fortask i startingfrom 1 to n onresources j from 1 to m as CTij and RTj represents theReady Timeofresource Rj. ETij representstheExecutionTimeofthetask Ti onresource Rj.So,thecompletiontimeis CTij = ETij + RTj.
ThisalgorithmsortsthetasksbasedonETCs(EstimatedTimetoComplete)[17] Thetasksaresortedbasedonthesorting key using an ordered list by the trade off factor N in average ETC, minimum ETC, or the maximum ETC After this, segments with equal size using a trade off factor N are created using the task list partitioning scheme The larger task segments are scheduled and executed first followed by the smaller tasks ie in decreasing order Min min is applied to
It is a search technique based on a binary tree beginning at the root node (null solution) As the tree propagates, nodes represent partial mappings where a subset of the tasks is assigned to machines [1] The partial mapping (solution) of a child node has one more task mapped than the parent node The children are generated by the parent node with the possibleadditionaltask’smapping(ta)andthentheparentnodebecomesinactive Pruningisappliedtokeeptrackofthe executiontimeandatatimerestrictiononthemaximumnumberoftree’sactivenodes Eachnodecontainsacostfunction Itschildrenreplacethenodehavingaminimumcostfunction Thisprocesscontinuesuntilacompletemappingisdoneor aleafnodeislocated
This algorithmdetermines theaverage execution time ofthe tasks andaveragecommunicationtime among resources of the consecutive tasks [24]. Then, the algorithm orders the tasks, based on the rank function in the workflow i.e. higher rankvaluetaskisawardedhigherpriority.Theschedulingoftasksoccursdependingonthepriorityorderand resources areassignedtotaskstocompletethemattheearliesttimeintheallocationphase.
This algorithm works on multiple workflows and many Quality of Service parameters [6] This strategy involves minimizing the makespan (the time difference between the beginning and end of a job or task sequence) and the cost of workflows for a cloud computing platform This algorithm also leads to an increase in the scheduling access rate in the system
Inthisalgorithm,aprioriisusedinaheterogeneousenvironment,whichisdefined,bythemeta taskssizeandthenumber of machines [4, 5] These are static heuristics, therefore on each machine, the task expected execution time for accurate estimationisknowntobepriorlyandstoredinanETCmatrixwhereETC(ti, mj)denotestheestimatedexecutiontimeof the task i on machine j The scheduling is accomplished using the Min min approach In this, we allocate a number of independent jobs to the available resources, there is a sufficient number of machines available for allocating tasks and workloadandprocessingcapabilityofeachjobandresources(inmillionsofinstructionspersecondMIPS)aretakeninto account
This algorithm adds QoS (Quality of Service) constraints like bandwidth, time, and memory [2, 10] to the basic Min min heuristic. In this, some tasks require high network bandwidth, whereas others could be contented with low network bandwidth.ItassignstaskshavinghighQoSrequestparametersfirstsimilartotheMin minheuristic.Intheworstcase,all tasksgenerallyneedeitherlowQoSorhighQoS.
This algorithm is used for efficient mapping of tasks to resources in the cloud [8, 10] It measures the computational performance and the resource cost incurred in the system, thereby helping in the improvement of the computational or communicationratio

Thisalgorithmaimstoobtaincompleteoptimizationorsub optimizationinthecloud.Itsupportsmultipleinstancesinthe cloud for processing the user requests, bewaring the cost and performance. It supports an automated scheduling policy andusesanImprovedGeneticAlgorithm(IGA)[14,31]toincreasetheresourceutilizationrateandspeedofexecutionin thesystem.

This algorithm uses particle swarm optimization based heuristics to schedule applications to the resources present in cloud by taking into consideration the cost of computation and the data transmission [7, 18]. It is used for a workflow applicationbydecreasingtheapplications’computationalaswellascommunicationcostswithsignificantcostsavingsand optimalworkloaddistributionoftheresourcesinthesystem.
This algorithm is based on Max min and Min min task scheduling algorithms and is referred to as Resource Aware Scheduling Algorithm (RASA) [8] It utilizes the benefits of both Max min and Min min algorithms and hides their disadvantages byoutperforming the existingscheduling algorithms inlarge scaledistributedsystems andthen usingthe bettersolution[16] Itisadjustedtoexploittheconditions,withminimaloverheadandhigherperformanceeitherbyMax minorMin min
Itis a static anddecentralized algorithm[29]usedon webservers.Theprocesses aredividedamongtheprocessors ina round robin fashion using a particular timestamp The allocation order of the resources to the processors is locally maintainedirrespectiveofremoteones Theypossessequaldistributionofworkloadamongtheprocessorsanddifferent processingtimesoftasksforprocessors Butthepay offisthatnodesbecomeoverloadedandtimesbecomeunderloaded [13]
In this algorithm, the weights are assigned in a particular order to every task in the system to allocate resources for optimalutilizationofresources[13,29].Afterassigningtheweights,theallocationofthedatacentersoccursdependingon thetimequantumortimeslotintheround robinfashion
This algorithm schedules the workflow elastically on a cloud computing environment with the benefits of the Heterogeneous Earliest Finish Time algorithm (HEFT) which also induces scalability [6, 25] The parameters act as a meansforschedulingtheresourcesandtasks Thescalabilityisgenerallydeterminedbyaddingalargenumberofsystems for resources It outpaces other workflow scheduling algorithms to obtain an optimized execution time and provides the abilitytoelasticallyscaleresourcesatruntime
This algorithm [20] considers the characteristics of cloud computing to provide multiple instances for performing computation on the system and implementing intensive cost constraint workflows by compromising or lessening the executiontimeandcostwiththehelpoftheuserinputenabledonthefly.
Thisalgorithmschedulestheworkflowinacloudenvironmentbyfindingasolutionbymeetingthequalityofservicelike bandwidth,memoryconstraintsusedbytheuserandperformsoptimalworkflowexecution[9,15] Thereby,achievingan importantimprovementandbetterresultsintermsofCPUutilizationandthecostsincurred
International
Volume:
Table
Algorithm
Min MinScheduling Algorithm
30]
Max MinScheduling Algorithm[1,19]
SegmentedMin Min SchedulingAlgorithm [17]
A*Scheduling Algorithm
MultipleQoS Constrained SchedulingStrategy ofMultiWorkflows [6,15]
ADoubleMin Min AlgorithmforTask Scheduling[4]
QoSGuidedMin Min Algorithm[2]
Manycasesused,
completiontime
Multiplecases, Speed,Maximum completiontime
Multiplecases, Speed,Resource Utilization
Groupapproach,
Utilization
Tasks
execution
1. Resourcecostandcomputational performanceiscalculated
2. Higherutilizationrateofresources
OptimizedResource SchedulingAlgorithm [31]
Improvedcost based algorithmfortask scheduling[10]
AcompromisedTime CostScheduling Algorithm[20]
Heterogeneous EarliestFinishTime algorithm(HEFT) [25]
VariousCases, Speed,Utilization
Segmentsaremade, ResourceUtilization
Resources
to tasks
Request
Segmentation
Unscheduledtaskgroups, Pruningisdone
Segmentsaremade, ResourceUtilization QualityofService, Constraintsare considered
1. Computationalperformanceandresource costareevaluated
2. Greaterresourceutilization
1. Measuresbothresourcecostand computationperformance
2. Theutilizationrateofresourcesishigh
1. Completethetaskattheearliesttime
2. Obtaininglowermakespanandcost.
3. Betterallocation.
1. Optimizesexecutiontime
2. Allowselasticscalingofresourcesin workflowexecution
Requestallocation similartoMin min
QualityofService, Constraintsconsidered
1. Measuresbothresourcecostand computationperformance
2. Theutilizationrateofresourcesishigh
1. SimilartoMin minalgorithmwithsub policies
2. Resourcesarescaledelasticallyin executionwithahigherutilizationrate
Multipleinstances, Speed,Resource Utilization
Allocationofresourcesas requestedbytheuser
Multiplecases,Cost, Performance Taskgroupsare unscheduled
1. Speedishigher.
2. TheGeneticAlgorithmimprovesresource utilizationrate.

1. Measuresbothresourcecostand computationperformance
2. Improvesthe computation/communicationratio
Manycases,Cost andtime, Constraintsofcost applied
Dependency Method,Execution time,Scalability
Jobcasesarecreatedby consideringservicelevel scheduling
Groupoftasksordered byrankfunction
1. Optimizesandreducescostandtime
2. Reducestheexecutiontime
1. Optimizesexecutiontime
2. Resourcesarescaledelasticallyduring execution
RoundRobin Algorithm[13,29]
ResourceAware Schedulingalgorithm [8,16]
WeightedRound RobinAlgorithm[13, 29]
AParticleSwarm Optimizationbased HeuristicAlgorithm [18]
SHEFTworkflow schedulingalgorithm [6,25]
OptimalWorkflow SchedulingAlgorithm [9]
Jobsmade,Cost, Weightsassignedto eachtask
Manycasesused, UsesbothMin min &Max min Scheduling
Jobscreated, Weightsare Assignedtoeach task,Costandtime
Dependencymode, Resourceutilization, Time
Jobsassignedto resourcesbasedontime value
Executiontimeand completiontimeoftasks
1. Reducescostandtimebyround robin fashion
2. Reducingthedebtorcost
1. Measuresbothresourcecostand computationperformance.
2. Theutilizationrateofresourcesishigh.
Jobsassignedto resourcesbasedontime valueandweights
Demanddistribution strategy, Tasksaregrouped
1. Reducescostandtimeduetoweighted stamps
2. Weightsreducethedebtorcost
1. Offershighercostsavings
2. Gooddistributionoftheworkloadonto resourcesisperformed
Areliablemethod, Executiontime, Scalability
CreationofVirtual clusters,Makespan, Cost,CPUtime
Groupoftasksordered byrankfunction
Schedulingbasedon servicelevelandquality ofserviceconstraints
1. Optimizesexecutiontime
2. Resourcesarescaledelasticallyduring execution
1. Minimizestheoverallrunningcost.
2. Optimizesthemakespanandcost.
In this appraisal paper, we briefly discoursed the load and task scheduling algorithms implemented in various heterogeneous cloud servers. These algorithms are constrained by assorted scheduling parameters and strategies. For example, a higher utilization rate was achieved by using min min, segmented min min, double min min, and max min algorithms TheETCfactorcompletesataskattheearliesttimeandtheweighted round robinreducescomputationcost The exploration was served for greaterresourceutilization, reduced cost and debt toachievemaximum throughput,and higher performance Even though the existing load balancing techniques doing well but not enough to fulfill the current demand from the different cloud environments So, in future work, we have to concentrate on the existing problems to sussouttheseinthecloudcomputingenvironmentwithbetteracuminationsubjectivetoresourceconstraints Thefuture proposed papermust bedesigned toimprovetheoptimized loadbalancing incloud computingenvironment forefficient utilization of resources, the improved response time of tasks and refining the situation of node congestion, overloading, andunderloadinginthedistributedcloudenvironment
[1] Braun, Tracy D, et al., “A comparison of eleven static heuristics for mapping a class of independent tasks onto heterogeneous distributed computing systems”, in Journal of Parallel and Distributed computing, Volume 61, Issue6,Pages810 837,2011.
[2] He,XiaoShan,XianHeSunandGregorVonLaszewski,“QoSguidedMin minheuristicforgridtaskscheduling”,in JournalofComputerScienceandTechnology,Volume18,Number4,Pages442 451,2013
[3] Wang, Shu Ching, et al., “Towards a load balancing in a three level cloud computing network”, in 3rd IEEE InternationalConferenceComputerScienceandInformationTechnology(ICCSIT),Vol 1,Pages108 113,2019
[4] DDH Miriam, KS Easwarakumar, “A Double Min min Algorithm for Task Metascheduler on Hypercubic P2P Grid Systems”,inInternationalJournalofComputerScienceIssues,Vol 7,Issue4,Pages8 18,2010

2395 0072
[5] Kong, Xiangzhen, et al, “Efficient
virtualized data centers with fuzzy prediction”, in JournalofNetworkand
Issue4,Pages1068 1077,2011
[6] Hirales Carbajal,Adán,etal.,“MultipleWorkflowSchedulingStrategieswithUserRunTimeEstimatesonaGrid”, inJournalofGridComputing,Volume10,Number2,Pages325 346,2012.
[7] W Chen, J Zhang, “An Ant Colony Optimization Approach to a Grid Workflow Scheduling Problem with Various QoSRequirements”,inIEEETransactionsonSystems,ManandCyberneticsPartC:ApplicationsandReviews,Vol 39,No 1,January2009,Pages29 43
[8] Saeed Parsa, Reza Entezari Maleki, “RASA: A New Task Scheduling Algorithm in Grid Environment”, in Special IssueofComputer&IT,WorldAppliedSciencesJournal,Vol 7,Pages152 160,2009
[9] J.YuandR.Buyya,“Workflow Scheduling Algorithms forGridComputing”,inTechnical Report,GRIDS TR 2007 10,GridComputingandDistributedSystemsLaboratory,TheUniversityofMelbourne,Australia,May2017
[10] Mrs. S. Selvarani, G. and Mr. S. Sadhasivam, “Improved cost based algorithm for task scheduling in Cloud computing”, in IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research (ICCIC), Pages1 5,28 29December2010.
[11] Y Yang, K Liu, J Chen, X Liu, D Yuan, H Jin, “An Algorithm in SwinDeW C for Scheduling Transaction Intensive Cost Constrained Cloud Workflows”, in Proceedings of 4th IEEE International Conference on E Science, Pages 374 375,USA,December2018
[12] Meng Xu, Lizhen Cui, et al, “A Multiple QoS Constrained Scheduling Strategy of Multiple Workflows for Cloud Computing”, in IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing with Applications, 10 12 August2009,Pages629 634
[13] Bhathiya Wickremasinghe, Rodrigo N. Calheiros and Raj Kumar Buyya, “CloudAnalyst: A CloudSim based Visual ModellerforAnalysingCloudComputingEnvironmentsandApplications”,in24thIEEEInternationalConference onAdvancedInformationNetworkingandApplications,20 23April2010,Pages446 452.
[14] A Khiyaita, El Bakkali, M Zbakh, Dafir El Kettani, “Load Balancing Cloud Computing: State of Art”, in IEEE TransactionsonSoftwareEngineering,978 1 4673 1053 6,2012,Pages106 109
[15] Cui Lin, Shiyong Lu, “Scheduling Scientific Workflows Elastically for Cloud Computing”, in IEEE 4th International ConferenceonCloudComputing,2011
[16] K. Etminani and M. Naghibzadeh, “A Min min Max min selective algorithm for grid task scheduling”, in 3rd IEEE/IFIPInternationalConferenceinCentralAsia,26 28September2017,Pages1 7
[17] M. Wu, Wei Shu and Hong Zhang, “Segmented Min min: A static mapping algorithm for meta tasks on heterogeneouscomputingsystems”,inHCW9thHeterogeneousComputingWorkshop,Page375,Washington,DC, USA,2000,Pages375 385.IEEEComp.Society.
[18] Suraj Pandey, Rajkumar Buyya, et al, “A Particle Swarm Optimization based Heuristic for Scheduling Workflow ApplicationsinCloudComputingEnvironments”,in24thIEEEInternationalConferenceonAdvancedInformation NetworkingandApplications,20 23April2010,Pages400 407
[19] M Hosaagrahara and H Sethu, “Max min Fair Scheduling in Input Queued Switches”, in IEEE Transactions On ParallelandDistributedSystems,Vol 19,No 4,Pages462 475,April2018
[20] SenSu, JianLi, Qingjia Huang, etal.,“Cost efficient task schedulingfor executing large programs in the cloud”,in JournalofParallelComputing,Elsevier,Vol.39Pages177 188,2013.
[21] Doulamis et al., “Fair Scheduling Algorithms in Grids”, in IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, Vol 18,No 11,November2007,Pages1630 1648

[22] Luiz F Bittencourt, Edmundo R M
[23]Chun WeiTsaiandJoelJ P C
Nelson L S da Fonseca, “Scheduling in Hybrid Clouds”, in IEEE
“MetaheuristicSchedulingforCloud:ASurvey”,inIEEESystemsJournal, Vol 8,No 1,March2014,

279
[24] Haluk Topcuoglu et al., “Performance Effective and Low Complexity Task Scheduling for Heterogeneous Computing”,inIEEETransactionson
[25]Dr.A.ShaikAbdulKhadir,V.Manochitra(2021).
DistributedSystems,Vol 13,No 3,Pages260 274
ofmilkprocessingsystemusingautomatedrule
4775 4787 retrieved from http://www.thedesignengineering.com/index.php/de/article/view/2917
[26] M Srinivas and L M Patnaik, “Genetic
A survey”, in IEEE Journal of Computing, Vol 27, No 6, June 1994,Pages17 26
[27]http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cloud_computing
[28]http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Load_balancing_(computing)
[29] Divya Chaudhary and RS Chhillar, “A New Load Balancing Technique for Virtual Machine Cloud Computing Environment”,inInternationalJournalofComputerApplications69(23)Pages37 40,May2013.
[30] Huankai Chen, Wang, F., Helian, N., Akanmu, G, “User priority guided Min Min scheduling algorithm for load balancingincloudcomputing”,in2013IEEENationalConferenceonParallelComputingTechnologies,21 23Feb 2013,Pages1 8,ISBN978 1 4799 1589 7
[31] Dr A Shaik Abdul Khadir, V Manochitra (2021) A survey on optimized milk distribution process using hybrid rule generation techniques in milk big data servers Design engineering, 308 313 retrieved from http://wwwthedesignengineering.com/index.php/de/article/view/2277
[32] Dr.K.Saravanan,T. Thamaraiselvan (2021).Anefficient clustering onhybriditemdependency using SCFCM and SVM techniques. Design engineering, 2275 2286 retrieved from http://www.thedesignengineering.com/index.php/de/article/view/2596.
[33] Cui Lin and Shiyong Lu, “Scheduling Scientific Workflows Elastically for Cloud Computing”, in 2011 IEEE 4th InternationalConferenceonCloudComputing,Pages746 747,2011.
[34] Hai Zhong, Kun Tao, Xuejie Zhang, “An Approach to Optimized Resource Scheduling Algorithm for Open source CloudSystems”,inFifthAnnualChinaGridConference,Pages124 129,16 18July2010
1Mr T Kannadasan, designated as Associate Professor in Computer Science in the Tamil Nadu State Government Collegiate Education Service from October 1998. Pursuing the Ph.D. Degree in Computer Science (Part Time) in Bharathiar University, Coimbatore under the guidance and supervision of Dr.R.PragaladaninCloudComputing

2Dr R.Pragaladan conferredthePh.D.Degree inComputerScience byBharathiarUniversity,Coimbatore through Erode Arts and Science College under Faculty Development fellowship Programme (FDP) for Teacher by UGC, Erode Tamilnadu, India in the year 2018. Currently, he is designated as Assistant ProfessorinComputerScienceandHeadoftheDepartmentofComputerScience,SriVasaviCollege,Erode affiliated with Bharathiar University. He has been a supervisor and mentor for several students in B.Sc (CS),M.Phil.,andPh.D programsallaroundforthepast14years.Hehasvastexperienceandpublished5 papers at Conferences and more than 15 papers in reputed Journals His principal domain of fascination includesCloudComputing,InternetofThings,Bio Informatics,CyberSecurity,andComputerNetworks.
