International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1M.Tech Scholar, Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Nims University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
2 Asst. Professor, Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Nims University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
3 Asst. Professor, Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Nims University, Jaipur, Rajasthan, India
4Jrf, Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering, Nims University, Rajasthan India ***
Abstract –
Themainobjectiveofthisresearchworkistofocusonthe subjective and comparative performance of batteries in termsofvariousparametersthemethodusedisasubjective and comparative study of car batteries available in the market.Thevariousparametersstudiedforthesebatteries are:B-S,B-P,B-C-TandB-C.Thestudyanddatacollection revealed that the ranking of the batteries was based on poweroutputandchargingtime,asthesetwoparameters areconsideredcritical.Followingthehigh-rankingbatteries were mapped for future analysis of a battery combining thesetwohigh-rankingbatteries.TheS-N-C-BandtheA-I-B have the highest performance for each factor, i.e., "power capacity" and "B-C-T". S-N-C-B and A-I-B offer maximum powerandminimumchargingtimebecausetheyhavehigh power output and low charging time. A combined experimental study of these two batteries is essential for high performance and optimized batteries for automotive applications. Their high energy density enables best efficiencybatteriestopowercomplex.
Key Words: Subjective and Comparative, Battery Mapping, B-S, B- P, B-C-T, B-C, Ranking and Score
Batteriesgavetheprimarywellspringofpowerbeforethe improvement of electric generators and electrical lattices around the finish of the nineteenth hundred years. Progressive upgrades in battery innovation worked with majorelectricaladvances,fromearlylogicalexaminationsto the ascent of transmits and phones, in the long run promptingconvenientPCs,cellphones,electricvehicles,and numerous other electrical gadgets Researchers and architects fostered a few monetarily significant sorts of battery."Wetcells"wereopencompartmentsthatheldfluid electrolyte and metallic anodes. At the point when the terminalsweretotallyconsumed,thewetcellwasrecharged bysupplantingtheanodesandelectrolyte.Openholdersare unsatisfactoryforversatileorconvenientuse.Wetcellswere utilizedfinanciallyinthemessageandphoneframeworks.
Early electric vehicles involved semi-fixed wet cells one significant arrangement for batteries is by their life cycle. "Essential" batteries can deliver flow when gathered, howeverwhenthedynamiccomponentsareconsumed,they can'tbeelectricallyre-energized.Theimprovementofthe lead-corrosive battery and resulting "auxiliary" or "chargeable"typespermittedenergytobereestablishedto thecell,expandingthe existenceofforevergatheredcells. Thepresentationofnickelandlithiumbasedbatteriesinthe last50%ofthetwentiethcenturymadetheadvancementof countless versatile electronic gadgets doable, from strong spotlightstocellphones.Extremelyenormousfixedbatteries discoverafewapplicationsinframeworkenergycapacity, assisting with settling electric power conveyance organizationsInviewofcertaindiscoveriesbyLuigiGalvani, Alessandro Volta, a companion and individual researcher, acceptednoticedelectricalpeculiaritieswerebroughtabout bytwouniquemetalscombinedbya clammydelegate.He confirmedthisspeculationthroughtestsanddistributedthe outcomes in 1791. In 1800, Volta created the primary genuine battery, which came to be known as the voltaic heap.Thevoltaicheapcomprisedofsetsofcopperandzinc platesheapedontopofoneanother,isolatedbyalayerof material or cardboard absorbed saline solution (i.e., the electrolyte).NotatallliketheLeydencontainer,thevoltaic heapdeliveredconstantpowerandstablecurrent,andlost littlechargeaftersometimewhennotbeingused;however hisinitialmodelscouldn'tcreateavoltagesufficientlyableto deliver flashes. He explored different avenues regarding differentmetalsandfoundthatzincandsilvergavethebest outcomes.Voltaacceptedthecurrentwastheconsequence oftwouniquematerialsessentiallycontactingeachotheran outdatedlogicalhypothesisknownascontactpressure-and nottheaftereffectofcompoundresponses.
Wehavestudiedaround50articlesrelatedtothebatteries outofwhich20relevantarticleshasbeenshortlistedfora detailedandsubjective,comparativelystudiedondifferent parameters efficiently performance of the batteries .The study of various batteries is done both subjectivelyand
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
comparatively.[1]RafaelB.Araujoet.al,ChalmersUniversity ofTechnology8April2021,Towardsnovelcalciumbattery electrolytesbyefficientcomputationalscreeningwhichwas presentedscreeningstrategyisinitiallybasedonacombined density functional theory (DFT) and conductor1like screening model for real solvents (COSMO-RS) approach, whichallowsfora rationalselectionofelectrolytesolvent based on a set of physico-chemical and electrochemical properties.Recommendedasa timeandeffortsaving tool prior to undertaking any experimental studies to fast evaluateCaconductingelectrolytecandidates.[2]MengLiao et.al Fudan University2019, Extraction of oxygen anions fromvanadiumoxidemakingdeeplycyclableaqueouszinc ionbattery,itwaspresentedstabilityover200cycleswith high specific capacity of ~400 mAhg -1 , achieving 95% utilizationofitstheoreticalcapacity,andlongcyclelifeupto 2000cyclesathighutilizationof67%.Thisworkopensupa new avenue to synthesize novel cathode materials for advancedbatteriesbydesigningoxygendeficientstructure, [3]SefukitaronkaSiirtUniversityturkeyJanuary2022,leadacid battery it was presented a recent study on economic andenvironmentalimpactsuggeststhatlead-acidbatteries are unsuitable for domestic grid-connected photovoltaic systems. [4] Cesar a.c. sequeira1, Mario r. pedro2 02 June 2014.Lead-acidbatterystorageitwaspresented.Thispaper includesa few pertinent commentsonthese rechargeable systemsintheirpresentstagesofresearchanddevelopment. [5]YiqunLiu,Y.GeneLiaoandMing-ChiaLaiWayneState University27January2020Lithium-IonPolymerBatteryfor 12-Voltage Applications: Experiment, Modeling, and Validation it was presented Modeling, simulation, and validationofthe12-voltbatterypackusinga20Ahlithium–nickel–manganese–cobalt–oxidecellinthispaper,influence ofambienttemperatureandcharging,dischargingcurrents onthebatteryperformanceintermsofdischargingvoltage and usable capacity. The proposed simulation model providesdesignguidelinesforlithium-ionpolymerbatteries inelectrifiedvehiclesandstationaryelectricenergystorage applications. [6] D. U. Sauer et. al ,University, Germany, 2003(1)SliBatteryspecificationandcapacity12vor6volt DC which was used for automobile application and its life spanshouldbe3to4yearsanditscostaround112/pices high current discharge, low internal resistance, and ultralonglifewithacyclelifeofmorethan100,000times.[7]S.R. Nelatury and P. Singh, 621-625 (2002) lead-acid the pure leadatthenegativesideandthePbO2onthepositiveside, plustheaqueoussulfuricacid.UPSsystems,starting lighting and ignition power sources for automobiles, and its life span should be 3-4 years its cost should be 7500 large current capability Tolerant to abuse, Tolerant of overcharging,itcanbechargedslowelyittakes14-16hours. ItslimitedlifespanitwasusedinhybridvehiclesFordand Volkswagen.[8]Deng,D.,M.G.Kim,J.Y.Lee,andJ.Cho.Sic 2009[9]lithium-ionbatteriesmaximalcapacityof1339C/g (372mAh/g)spectrum-fromenergystorageisabouttwoto three years or 300 to 500 charge cycles its high energy
densitysensitivetohightemperatures.itwasusedintesla model’s.[10] Ying, T. K., ET. Al, 31, 525-530. Studies on rechargeable NiMH batteries it was provided 3.2–3.7 V nominal voltNiMH hydride batteries are used in hybrid automobilebatteriesitscostshouldbearound14000NiMH batteries and operate around ambient temperature. For example,theToyota™Prius(II-Vmodels)usesealedNiMH batteries, which are estimated to have a 150,000 mile battery life based on the manufacturer′s More complex chargealgorithmHighself-discharge typically50%higher thanNiCd.
Themethodadoptedissubjectiveandcomparativestudyof automobile batteries existing in the market. Around 50 articles were studied and out of which 20 articles were rankedfrom1to20basedontheirrelevancetothisstudy. Thevariousparametersstudiedonthesebatteriesare:
• BatterySpecification
• Batterypower
• Chargingtime
• Costofbattery
Limitations From the study and data collection, ranking of batteries is done based on (a) Power output, and (b) Charging time, as these two are observedascriticalparameters.Followingrankings, thehighrankedbatteries weremappedforfuture analysis of a battery combining these two high rankedbatteries.
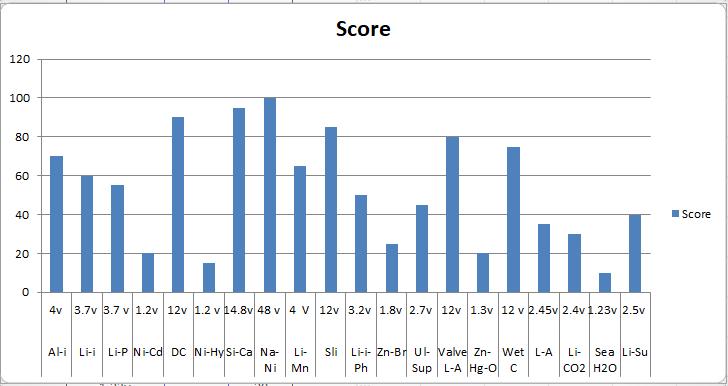
Table -1: Max.PowerandMinimumTimeCharge
Battery Max. Power v
Battery Minium time charge
AluminumIon 4v AluminumIon 1
Lithium-Ion 3.7v Lithium-Ion 2 L-P-B 3.7 LithiumPolymer 3
NickelCadmium 1.2v Nickel-Cadmium 1.3
DeepCycle 12v DeepCycle 2
N-M-H-B 1.2V N-M-H-B 15
SilverCalcium 14.8v SilverCalcium 4 S-N-C-B 48V S-N-C-B 5-6 L-M-S-B 4V L-M-S-B 4-6
SliBattery 24v SliBattery 12
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
L-I-P-B 3.2v L-I-P-B 4 Z-B-F-B 1.8v Z-B-F-B 7 U-S-B 2.7v U-S-B 10
V-R-L-A-B 12v V-R-L-A-B 12 Z-M-O-B 1.3v Z-M-O-B 9
WetCellBattery 12V WetCellBattery 7
LeadAcid 2.45v LeadAcid 8 L-C-D-B 2.4v L-C-D-B 6 S-W-B 1.23v S-W-B 4 LithiumSulfur 2.5v LithiumSulfur 6
S-N-C-B 1 11
L-P-B 7 5 L-M-S-B 8 9 N-C-B 19 2
DeepCycle 4 4 SilverCalcium 3 6 L-I-P-B 10 7 Z-B-F-B 15 13
UltraSuper 11 17
V-R-L-A-B 5 18
Z-M-O-B 16 16
WetCell 6 14
AluminumIon 20 1 L-C-D-B 14 10
SeaWater-B 17 8 LithiumSulfur 12 12
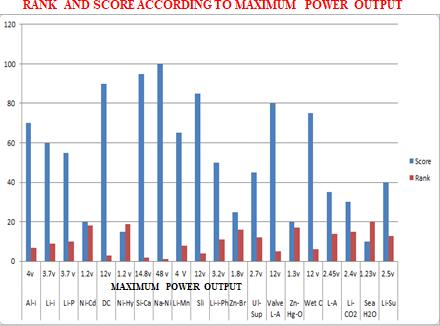
AmappingofMaximaxpowerandMiniminchargingtimeis carriedoutfromthedetailsfurnishedinthetabletofindthe batteriesdeliveringmaximumpowerandminimumcharging time,whichhappensto bebattery-sodiumnickelchloride andBattery–AluminumionBattery
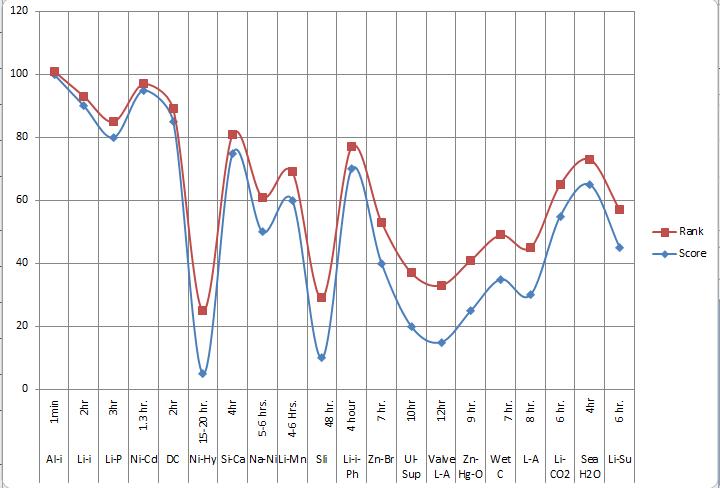
S-N-C-B 48V 1 S-N-C-B 1min
L-I-B 3.7v 2 L-I-B 2hr
L-P-B 3.7v 3 L-P-B 3hr
N-C-B 1.2v 4 N-C-B 1.3hr
D-C-B 12v 5 D-C-B 2hr
N-M-H 1.2v 6 N-M-H 15-20hr
S-C-B 14.8v 7 S-C-B 4hr
S-N-C 48v 8 S-N-C 5-6hr
L-M-S-B 4-5V 9 L-M-S-B 4-5hr
SLI-B 24v 10 SLI-B 12-16hr
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
11 L-I-P-B 3.2v 11 L-I-P-B 4hr 12 Z-B-F-B 1.8v 12 Z-B-F-B 7hr 13 U-S-B 2.7v 13 U-S-B 10hr 14 V-R-L-A 12v 14 V-R-L-A 12hr 15 Z-M-O 1.3v 15 Z-M-O 9hr 16 W-C-B 12v 16 W-C-B 7hr 17 L-A-B 2.45v 17 L-A-B 8hr 18 L-C-D-B 2.4v 18 L-C-D-B 6hr 19 S-W-B 1.23v 19 S-W-B 4hr
Chart -2:RankandScoreAccordingmaximumPowerOutput
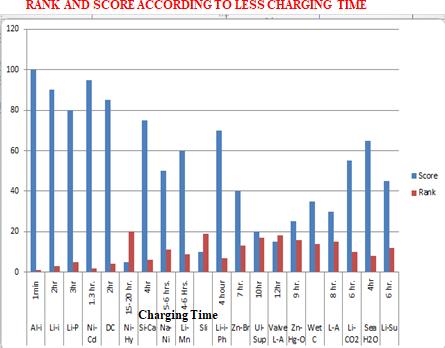
Chart -1:RankandScoreaccordingtoLessChargingTime
Table -4: ChargingTimeinMinutefor48Volts
NameofBattery PowerinVolts Charging Time in Minfor48volt
SLIBattery 48v 360min L-I-B 48v 1560min L-A-B 48v 4800min N-M-H-B 48v 48000min S-N-C-B 48v 360min L-P-B 48v 2340min L-M-S-B 48v 3456min A-I-B 48v 12min D-C-B 48v 480min S-C-B 48v 779min
Factor value: 7.529
Chart -3:Rankandscoreaccordingtolesschargingtime
Chart -4:Scoreaccordingtomaximumpoweroutput 3.2 COMPARATIVE STUDY ON MAPPING
1. Sodium battery is taking 360 minutes for 48V charging capacity, but Aluminum-Ion-battery is taking only 12 minutesfor48Vchargingcapacity.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
2. Lithium-ion batteries are taking 1560 minutes for 48V chargingcapacity.
3. Lead acid battery batteries aretaking 4800 minutes for 48Vchargingcapacity.
4. Lithiummanganesespinelbatteryistaking3456minutes for48Vchargingcapacity.
ThesodiumnickelchloridebatteryandaluminumionBattery havemaximumperformanceoneachfactor,thatis,“power capacity”and“lesschargingtime”.Acombinedexperimental study of these two batteries is mandatory for a high performanceandoptimizedbatteryforenergysources.
Conclusion of the studies It also recharge quickly and hold their charge longer S- C -B and A-I-B revels maximumpowerandminimumchargingtimebecauseits highpoweroutputandlowchargingtime.itshighenergy density allows batteries efficiency them to power complexenergysources.
1.Ihavedonestudiesaround50articlesonlyduetoless accesstojournalsandperiodicals.
2.Ihavereadarticlewiththehelpofinternetwithout visitingotherlibrariesandreferencesourcesinIITsand otherpremierinstitutions.
3.Somedatahasbeencollectedfromothersourcessuchas mediaandnewspapers.
4.Ihavenotperformedtheexperimentalworkduetolack oftime.
The rechargeable batteries should be most recommendedbecausetheyseemlikeagoodideaasthey aremoreeco-friendlyfortheenvironmentatfirstglance howeverwehavetestedcommonlyavailablerechargeable batterieswehaveidentifiedthattheirchargingtoshouldbe more fasterthanliquidcellbatteriesanditsperformance should be goodAnd its manufacturing cost should be minimum and price should be affordable foreveryone.
ThecheapBatteriescanbefound but greatcaretoneeds to be taken using low qualitybatteries can lead to early batteryfailureandshortbatterylife.
[1]D.U.Sauer,„OptimierungdesEinsatzesvonBlei-SäureAkkumulatoren in Photovoltaik- Hybrid-Systemen unter spezieller Berücksichtigung der Batteriealterung“, Ph.D. thesis,UlmUniversity,Germany,2003.
[2] S. R. Nelatury, P. Singh, “Extracting equivalent circuit parameters of lead-acid cells from sparse impedance measurements”,J.PowerSources,112,621-625(2002).
[3] Deng,D.,M.G.Kim,J.Y.Lee,andJ.Cho.2009.Green energy storage materials: Nanostructured TiO2 and Snbasedanodesforlithium-ionbatteries.Energy.Environ.Sci. 2:818–837.
[4]Levine,S.2010.TheGreatBatteryRace.ForeignPolicy 182:88–95.
[5] Battery Technology for Data Centers and Network Rooms:U.S.FireSafetyCodesRelatedtoLeadAcidBatteries, SchneiderElectric–DataCenterScienceCenter,WhitePaper 31,2012BatteryTechnologiesforDataCentersandNetwork Rooms:VentilationofLead-AcidBatteries,Schneider.
[6] Ying, T. K., GAO, X. P., Hu, W. K., Wu, F., & Studies on rechargeableNiMHbatteries.InteHydrogenEnergy,31(4), 525-530.
[7] Aghazadeh, M., Golikand, A. N characterization, and electrochemistnanoparticles.InternationalJourn8679.
[8]M.TarasconandM.Armand,Nature,2001,414,359–367.
[9] L.Cheng,J.Yan,G.N.Zhu,J.Y.Luo,C.X.WangandY.Y. Xia,J.Mater.Chem.,2010,20,595–602
[10] Crompton, T. R. (20 March 2000).Battery Reference Book(thirdEd.). Newnes. p.Glossary ISBN978-0-08049995-6Retrieved18March2016.Ashcroft,N.W.;Mermin (1976).SolidStatePhysics.N.D.Belmont,CA:Brooks/Cole.
[11]Leisch,JenniferE.;Chernyakhovskiy,Ilya(September 2019).Grid-Scale Battery Storage Frequently Asked Questions(PDF)(Report). National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) & greeningthegrid.org. Retrieved21 May2021.
[12]Pan,AQ;Li,XZ;Shang,J;Feng,JH;Tao,YB;Ye,JL;Yang, X; Li, C; Liao, QQ (2019).The applications of echelon use batteriesfromelectricvehiclestodistributedenergystorage systems.2019InternationalConferenceonNewEnergyand Future Energy System (IOP Conf. Series: Earth and Environmental Science). Vol.354. IOP Publishing Ltd.doi:10.1088/1755-1315/354/1/012012.012012.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[13]Brudermüller, Martin; Sobotka, Benedikt; Dominic, Waughray(September2019).InsightReport aVisionfora SustainableBatteryValueChainin2030:UnlockingtheFull Potential to Power Sustainable Development and Climate ChangeMitigation(PDF)(Report).WorldEconomicForum& GlobalBatteryAlliance.pp.11,29.Retrieved2June2021.
[14]ColumbiaDryCellBattery" NationalHistoricChemical Landmarks.AmericanChemicalSociety.Archivedfromthe originalon23February2013.Retrieved25March2013.
[15]Bellis,Mary.BiographyofAlessandroVolta,Inventorof theBattery.About.com.Retrieved7August2008
[16] Battery History, Technology, Applications and Development.MPower Solutions Ltd. Retrieved 19 March 2007.
[17] Fascinating facts about the invention of the Electric BatterybyAlessandroVoltain1800.TheGreatIdeaFinder Retrieved11August2008.