International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Comprehensive Study on Deployment Models and Service Models in Cloud Computing.
Dhanashri Ravi Patil1 , Prof. Chetan S. Arage2, Pratik S. Gaikwad31, 3 Research Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, 2 Professor Department of Computer Science and Engineering, 1,2,3 Sanjay Ghodawat University ***
Abstract - Since its inception Cloud Computing is making a paradigm shift in the worldof computingtechnology.Basedon pay-peruse principle it provides a variety of services to both individual and industry. The services it provides include Platform-asa-Service (PaaS), Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) and Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS) and it isstillmaking its way to other similar services. These services models have certain requirements to be met and other security and design issues. This paper aims at discussing these three services models, important factors for these models and challenges currently faced by these services models.
Key Words: Cloud Computing, Service Models in Cloud, DeploymentsinCloudComputing.
1. INTRODUCTION
Cloudcomputingisatypeofinternet-basedcomputingthat allows computers and other devices to share different processingresourcesanddata.Cloudcomputingisathriving technology that offers a variety of services such as computers, databases, storage, virtual machines, servers, analytics, machine intelligence, and many more. Cloud computingdeliverstheseservicesovertheinternet,making it scalable and allowing businesses to save capital expendituresonhardwarepurchases.TheNationalInstitute ofStandardsandTechnologydefinescloudcomputingas"a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, or demand networkaccesstoasharedpoolofconfigurablecomputing resourcesthatcanberapidlyprovisionedandrelatedwith minimal management effort or service provider interaction."[1]
Cloudmodelsareclassifiedintotwotypes:servicemodels and deployment models. Service models are categorised based on the sorts of cloud services supplied, whereas deploymentmodelsareclassedbasedonhowandbywhom thecloudservicesareused.Therearethreetypesofservice models:IaaS(InfrastructureasaService),PaaS(Platformas aService),andSaaS(SoftwareasaService)(Softwareasa Service).NISTofficiallyrecognisesthesethreemodels.There are several additional well-known cloud services, such as MBaaS (Mobile Backend as a Service), DaaS (Data as a Service),MaaS(MonitoringasaService),andsoon.Public cloud,privatecloud,communitycloud,andhybridcloudare all deployment methods. There are various cloud
deploymentmodels,suchasIntercloud,Distributedcloud etc.
2. CHARACTERISTICS OF CLOUD COMPUTING
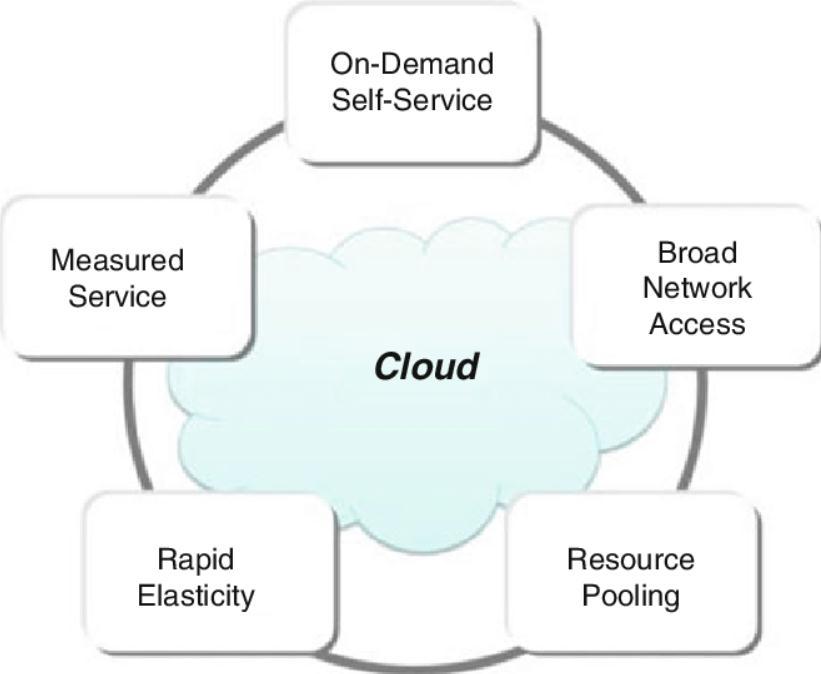
Therehasbeensubstantialdebateinindustryandacademics over what exactly cloud computing entails. [2][3][4].The NationalInstituteofStandardsandTechnology(NIST)inthe United States has created a working definition that encompasses the most widely accepted characteristics of cloudcomputing.Cloudcomputingisdefinedas"amodelfor providing convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks,servers,storage,applications,andservices)that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal managementeffortorserviceproviderinteraction."Cloud computing has the following five fundamental qualities, accordingtothisdefinition:
1) On-demandself-service.
2) Broadnetworkaccess. 3) Resourcepooling. 4) Rapidelasticity. 5) MeasuredService.
Cloudcomputingisanewdistributedcomputingparadigm that promises to provide consumers with cost-effective, scalable on-demand services without requiring massive upfrontinfrastructureinvestments[5].Oneoftheprimary reasons for cloud computing's success is the role it has playedin removing the scaleof a businessasa significant component in its economic success. An outstanding illustrationofthisshiftistheconceptofdatacentres,which eliminatestheneedforsmallbusinessestoinvestheavilyin infrastructureinordertogainaworldwideclientbase[6].
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
deployment make it an excellent choice for test environments.
Fig1Source:internet
3. CLOUD COMPUTING DEPLOYMENT MODEL
It is necessary to discuss the fundamental cloud service deployment capabilities of each architecture right away. Fourfundamentaltypesofcloudcomputingaredefinedby NIST[NationalInstituteofStandardsandTechnology]:
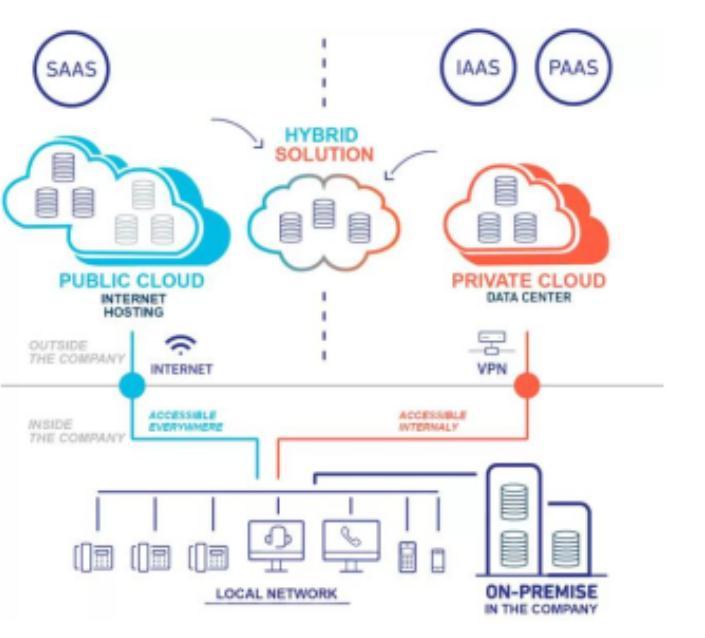
Fig3:Source:Internet BenefitsofPublicCloud
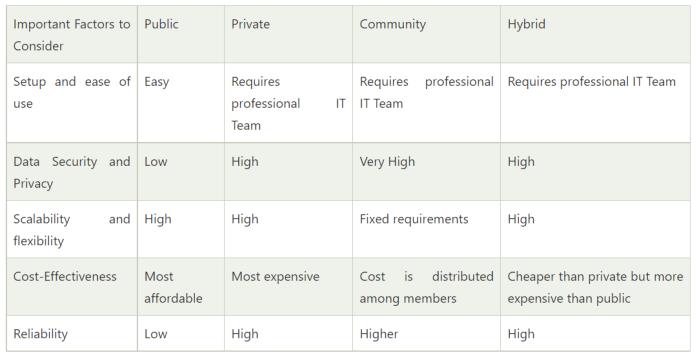
Minimal Investment - As a pay-per-use service, there is no large upfront cost and is ideal for businesseswhoneedquickaccesstoresources
NoHardwareSetup - Thecloudserviceproviders fullyfundtheentireInfrastructure
No Infrastructure Management - This does not requireanin-houseteamtoutilizethepubliccloud.
LimitationsofPublicCloud
Data Security and Privacy Concerns - Since it is accessible to all, it does not fully protect against cyber-attacksandcouldleadtovulnerabilities.
ReliabilityIssues-Sincethesameservernetworkis open to a wide range of users, it can lead to malfunctionandoutages
Service/LicenseLimitation-Whiletherearemany resourcesyoucanexchangewithtenants,thereisa usagecap.
3.2PrivateCloud–
Fig2Source:https://www.padok.fr/
3.1PublicCloud–
Thenameisself-explanatory.Itisopentothepublic.Public clouddeploymentstrategiesareidealforenterpriseswith changeable and rising demands. It is also an excellent alternativeforbusinesseswithfewersecurityconcerns.Asa result, you pay a cloud service provider for networking, computingvirtualization,andstorageonthepublicinternet. Itisalsoanexcellentdeliverymechanismfordevelopment and testing teams. Its rapid and simple configuration and
Factor value:
The public cloud deployment paradigm is diametrically opposedtotheprivateclouddeploymentmodel.Itisaoneon-one setting for a single user (customer). It is not necessarytoshareyourhardwarewithanyone.Thecontrast between private and public cloud is in how all of the hardware is handled. The capacity to access systems and serviceswithinacertainborderororganizationisreferred toasthe"internalcloud."Thecloudplatformisdeployedina securecloudenvironmentsecuredbyrobustfirewallsand overseenbyanorganization'sITstaff.
The private cloud allows for better control over cloud resources.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Fig4Source:Internet
BenefitsofPrivateCloud
DataPrivacy-Itisidealforstoringcorporatedata whereonlyauthorizedpersonnelgetsaccess
Security - Segmentation of resources within the sameInfrastructurecanhelpwithbetteraccessand higherlevelsofsecurity.
Supports Legacy Systems - This model supports legacysystemsthatcannotaccessthepubliccloud.
LimitationsofPrivateCloud
Higher Cost - With the benefits you get, the investmentwillalsobelargerthanthepubliccloud. Here, you will pay for software, hardware, and resourcesforstaffandtraining.
Fixed Scalability - The hardware you choose will accordinglyhelpyouscaleinacertaindirection
High Maintenance - Since it is managed in-house, themaintenancecostsalsoincrease.
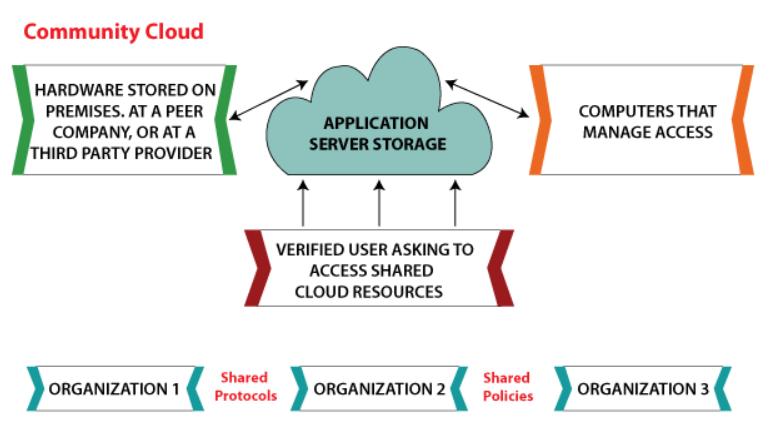
3.3CommunityCloud
It enables a number of businesses to access systems and services.Itisadistributedsystemmadebycombiningthe functionsofmanycloudstomeettheuniquerequirementsof a neighbourhood, sector, or company. The community's infrastructuremightbesharedbyorganisationswithsimilar interestsorduties.Itisoftenhandledbyathirdpartyora collaborationofoneormorecommunityorganisations.
3.4HybridCloud
Fig5Source:Internet
Hybridcloudisasolutionthatcombinesaprivatecloudwith oneormorepubliccloudservices,withproprietarysoftware enabling communication between each distinct service. A hybrid cloud strategy provides businesses with greater flexibilitybymovingworkloadsbetweencloudsolutionsas needs and costs fluctuate. Hybrid cloud services are powerfulbecausetheygivebusinessesgreatercontrolover theirprivatedata.Anorganizationcanstoresensitivedata onaprivatecloudorlocaldatacenterwhilesimultaneously leveragingtherobustcomputationalresourcesofamanaged publiccloud andmanageitallinasingleplaneofglass.
Fig6Source:Internet
BenefitsofHybridCloud
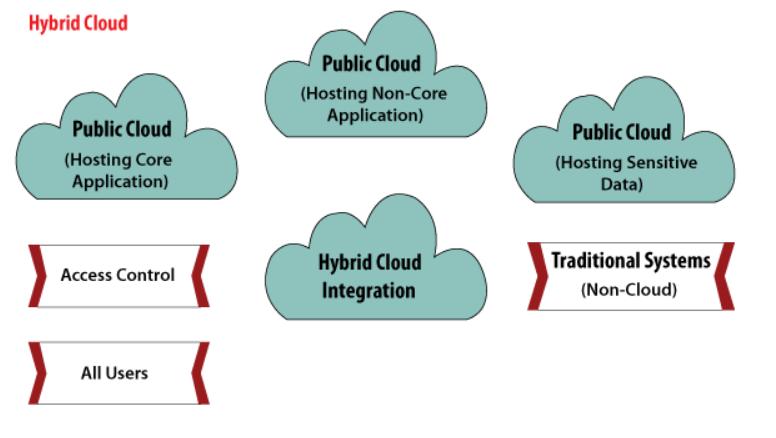
Cost-Effectiveness - The overall cost of a hybrid solutiondecreasessinceitmajorlyusesthepublic cloudtostoredata.
Security - Since data is properly segmented, the chancesofdatatheftfromattackersaresignificantly reduced.
Flexibility - With higher levels of flexibility, businessescancreatecustomsolutionsthatfittheir exactrequirements
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
LimitationsofHybridCloud
Complexity-Itiscomplexsettingupahybridcloud since it needs to integrate two or more cloud architectures
SpecificUseCase-Thismodelmakesmoresensefor organizationsthathavemultipleusecasesorneed toseparatecriticalandsensitivedata
Chart -1:AComparativeAnalysisofCloudDeployment Models
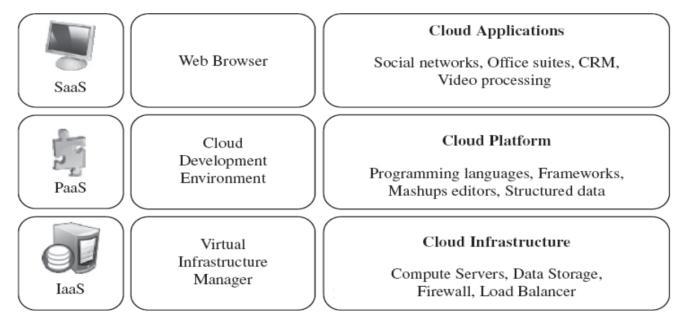
4. CLOUD COMPUTING SERVICE MODELS
Thistechnologyparadigmhasgonethroughseveralstages throughout the years. Grid, utility, and on-demand computing were older kinds of computing that before currentcloudcomputing.Theearlytypesofcontemporary cloud computing, such as Software as a Service (SaaS), PlatformasaService(PaaS),andInfrastructureasaService (IaaS), originated as a technological byproduct of falling computer and server hardware prices. Individual servers mightbepurchasedbyuserstomeettheircomputingneeds.
Thecloudparadigmoriginatedwhensoftwareandhardware providerscollaboratedtointegratemanyserversinaneffort toharnessthemassivecomputationalcapacitycreatedbya grid(ornetwork)oflinkedservers.Concurrently,therecent advancement of digital networking technologies that underpintheWorldWideWebformalisedthepresentidea of"cloudcomputing."Inrecentyears,technologyvendors haveparlayedcloudcomputingsystemsintonumeroustiers ofservice,includingSaaS,PaaS,andIaaS.
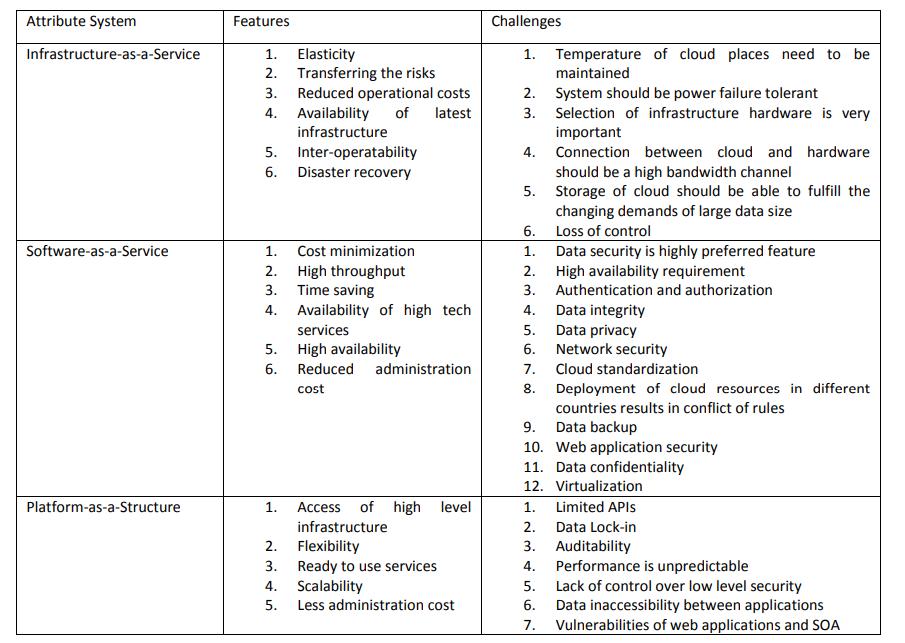
Cloudcomputingisabletoprovideavarietyofservicesat themomentbutmainthreeservicesareInfrastructures-AService, Platform-As-A-Service and Software-As-AService alsocalledasservicemodelofCloudcomputing
4.1
Fig7Source:Medium.com
Infrastructure-As-A-Service[laaS]
Thecorecomputingresourcesarehardwareandsoftware components.Theylaythefoundationsofevery computing infrastructure.Infrastructure-as-a-Structureserviceofcloud computing provides these services to cloud end users. In otherwordsIaaSismakinguserfreeoftheseservices.End userscanhireanyoftheseservicesattheleveltheydesire. Userhastopayonlyfortheusageofhisresources.IaaSisto provide computing infrastructure and operating middleware. Grid/Cluster architectures provide high performance infrastructures to the organizations on rent bases and make them free from their own resources. So organizationscanputtheirattentiononmanufacturingand quality concerns. The main concept behind IaaS is the resourcevirtualization.It allowsthe user tohave his own guestoperatingsystemontopofinfrastructureprovidedby the cloud provider. This concept leads to automatic deploymentofinfrastructurewhichisbothdistributedand scalable.Theadministration,deployment,andmaintenance istheresponsibilityoftheserviceprovider.
4.2Software-As-A-Service(SaaS)
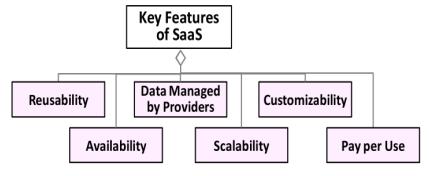
SaaS is the top layer of cloud computing services. It is different than traditional software services, where traditional software need own hardware and software components,WhereSaaSmakesusers,independentoftheir ownresources.Usersusetheintegratedservicesprovided bycloudoperator.OneofthebestexamplesofSaaSisGoogle Docs
QualityModelofSaaS
Fig8Source:Internet
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
4.3Platform-As-A-Service(PaaS)
Platformasaserviceprovidesadevelopmentplatformtoits users so that they can develop and maintain their applicationsandcloudspecificutilities.Itisdifferentfrom SaaSbecauseSaaSisadevelopedanddeployedapplication and PaaS provides a platform or ground to develop those applications.PaaSprovidesdevelopmentenvironmentand platform, so all supporting material i.e. programming environment,developmenttoolsandinfrastructureetc.must beprovidedbycloudprovider
[2] D.Plummer,T.Bittman,T.Austin,D.Cearley,andD. Smith,“Cloudcomputing:Defininganddescribing an emerging phenomenon”, Technical report, Gartner,2008.
[3] J.Staten,S.Yates,F.Gillett,W.Saleh,andR.Dines, “Is cloud computing ready for the enterprise?”, Technicalreport,ForresterResearch,March2008
[4] M.Armbrust,A.Fox,R.Griffith,A.D.Joseph,R.Katz, A. Konwinski, G. Lee, D. Patterson, A. Rabkin, I. Stoica,andM.Zaharia,“Aviewofcloudcomputing,” Commun.ACM,53:50–58,April2010.
[5] D.Agrawal,A.ElAbbadi,F.Emekci,andA.Metwally, “DatabaseManagementasaService:Challengesand Opportunities,”InICDE,1709–1716,2009.
[6] Aniruddha S. Rumale, D.N.Chaudhari, ” Cloud Computing: Infrastructure as a Service,” InternationalJournalofInventiveEngineeringand Sciences(IJIES)ISSN:2319–9598,Volume-1,Issue3,February2013.
Chart -2:Featuresandchallengesofcloudcomputing servicesmodels
3. CONCLUSIONS
Cloud computing is an emerging technology which introduced itself as a service oriented technology. It is working on the principle of on demand service and scalability.Itisprovidingservicesinmanywaysincluding software,platformandinfrastructureandmakingtheusers freeofinstallingandadministeringtheseservices.Inspite the fact that cloud computing provide high performance, high available, fault tolerant services; the issues it comes witharealsoveryseriousinnature.Oftheworthmentioning aredataandnetworksecurity,dataauthenticityandaudit ability, lack of user control over data and security polices and virtualization problem. In order to attract the organizations and build the confidence of customer, these issuesneedtobewellresearchedandresolved
REFERENCES
[1] L.Gonzalez,L.Merino,J.Caceres,andM.Lindner,“A Break intheClouds:Towardsa CloudDefinition”, ComputerCommunicationReview,39(1),2009.
