International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1,2,4B. Tech Scholars, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Sreenidhi Institute of Science and Technology Hyderabad, Telangana, India 3Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Sreenidhi Institute of Science and Technology Hyderabad, Telangana, India ***
Abstract - The biggest cause of death in children under five years old worldwide is pneumonia. Radiologists with the necessary training examine chest X-rays to identify pneumonia. But it is time-consumingandexhausting. Medical image analysis has a lot of potential applications for biomedical image diagnostics techniques. This studysuggests a model for diagnosing pneumonia that is trained on chest Xray pictures. Finding a large enough dataset for detection tasks was extremely difficult, hence data augmentation techniques were utilized to expand the training dataset. The models are additionally trained via transfer learning. The proposedapproach might help radiologists'clinicaljudgment and assist in the early diagnosis of illnesses. The model was statistically validated after being checked for overfitting and generalization errors. To evaluate the effectiveness of the suggested model, various metrics including testing accuracy, F1, recall, precision, and AUC score were constructed.
Elderlyandyoungchildrenaremorelikelythanotherstodie frompneumonia.Sincefewpeopleareawareofitpolitically andsocially,itisknownas"thesilentkiller"incomparison to other diseases. Children's pneumonia is an illness with rootsinpoverty.Itsprimarycausesincludealackofaccess tobasichealthcare,inadequateeducation,andinadequate childcare.Adultpneumoniamaybeviewedasapublichealth problemthatneedsmoreproactivetreatment. Twomajor factorsdrivingacademicstoincreaselearningratesarethe availability of vast datasets and the development of more potentGPUs.Foravarietyofmedicalimagingtasks,suchas the diagnosis of pneumonia, the detection of arrhythmias, the classification of skin cancer, the detection of diabetic retinopathy, and the identification of bleeding, resourceintensive models are now feasible with performance superiortothatofhumanexperts.Deeplearningmethods akintoCNNarehencetheresearchers'chosentechnology for disease categorization and diagnosis from medical imaging.
For example, chest X-rays, chest MRIs, chest ultrasounds, lung needle biopsies, computed tomography of the lungs, and chest X-rays are all techniques that can be used to diagnose pneumonia. X-rays are the most widely used diagnostic imaging tool. Radiotherapists find it difficult to examine chest X-rays. Pneumonia on the patient's X-ray might occasionally be challenging to diagnose. Disease predictionbecomestoughsinceitisdifficulttoidentifythe traits that identify the presence of the disease. The X-ray picturesinthedatasetwerewronglycategorizedmostlydue tothis.IthasbeendemonstratedinthepastthatseveralCAD systemsarebeneficialinthemedicalfield,particularlyinthe identificationoflungnodulesandbreastcancer.
The most effective and popular Machine Learning (ML) methodfordiseasediagnosisingeneralandradiography,in particular, continues to be deep learning. The accuracy of disease prediction using deep learning algorithms has alreadybeendemonstratedtobeonparwiththatofatypical radiologist. At this time, trained physicians cannot be replaced by deep learning-based algorithms in medical evaluation.Therefore,deeplearning-basedcomputer-aided diagnosis techniques can be employed as an addition to clinicaldecision-making.
Severalauthorshavealreadypresentedvariousbiomedical image detection methods. Authors in [1] talked about diagnosingpneumonia.Thedifficultieswithmedicalimaging technologies were discussed by Razaak et al. [2]. Various approaches were put forth by numerous writers for the identificationofnumerousdiseases[3].Forinstance,Andre presentedadeepCNN-basedInceptionv3architectureinhis paperfortheclassificationofskincancer[4],Milletarialso worked on a method for CNN-based prostate detection in MRIvolumes[5],GrewalapplieddeeplearningtoCTscans toidentify brainhemorrhages[6],and Varun developed a method for the detection of diabetic retinopathy [7]. In comparison to DNN, CNN is a lot superior breakthrough sinceitcaneasilyworkwith2-Dand3-Dimagesandextract thefeaturesneededtocategorizethedisease.Becausethe max-pooling layer in CNN is so effective and because it is
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
coupledwithsomeweights,thisisconceivable.Astheyuse gradient-basedlearningwhiletheyarebeingtrained,CNNs also deal with the serious issue of the declining gradient. CNN'sidentifydifferentchestX-raysandaccuratelyclassify themusingtheinformationretrievedbythevariouslayers. SomealgorithmsweredevisedearlierinthepapersofShin for data mining [10,11] and the paper of Boussaid also proposed that labels are predicted by the extraction of features and application of segmentation techniques from radiologyimagesofchestX-rays [12].ThestudiesbyShin [10,11]andBoussaid[12]bothprovidedcertainalgorithms for data mining, and Boussaid's work also suggested that labels are predicted by the extraction of features and application of segmentation techniques from radiology picturesofchestX-rays.
The initial dataset from the Guangzhou Women and Children'sMedicalCenterhad5836imagesaltogether.Both healthyindividualsandpneumoniapatientsweredepicted in the pictures. There were 1583 photographs of healthy chest X-rays and 4273 images of chest X-rays with pneumonia.Atrainingsetwith5136imagesandatestset with700imageswerecreatedfromtheentiredataset.The figureshowsthefirsttwoexampleimagesfromthedataset.
case, just the images of the normal case needed to be enhancedtwice.Therewere3849normalpicturesand3873 photosofpneumoniafollowingaugmentation.Imagesfrom thetestsetwerenotenhanced.
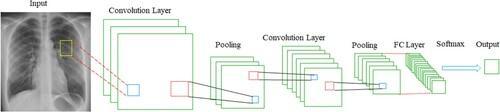
Undoubtedly, the most well-known deep learning architecture is CNNs. They fall under the heading of feedforwardnetworks.CNN'sabilitytotakelocalityintoaccount isbyfaritsgreatestbenefit.TheCNN'sconvolutionallayer, whichgivesthenetworkitsname,isitscorecomponent.The convolutionallayerextractsthecharacteristicsfromaninput image.Eachinputmap'sdimensionalityisdecreasedviathe pooling layer while critical data is kept. The network architecture is represented in Figure 1 as a sequence of variousconvolutionalandpoolinglayers.Thesoftmaxlayer isutilizedforpictureclassificationatthenetwork'send.The maindrawbackofdeeperCNNsisofvanishinggradients.
This research suggests an ideal strategy for detecting pneumoniafromchestX-rays.Toexpandthesmalldataset, dataaugmentationtechniqueswereused.
Theinputphotoswerefirstreducedinsizeto224*224and used to train the model. A sizable dataset is necessary for efficientneuralnetworktraining.Becausethedeepnetworks cannotgeneralizewhentrainedonasmallerdataset,testing accuracysuffers.Oneapproachtosolvingthisissueisdata augmentation,whichextendsandeffectivelymakesuseof the current dataset. There were 1283 healthy chest X-ray images and 3873 pneumonia-infected chest X-ray case imagesinthetrainingdatasetusedinthisstudy.Sincethe datasetalreadycontainedadequatephotosofthepneumonia
Figure3:ArchitectureoftheCNN.
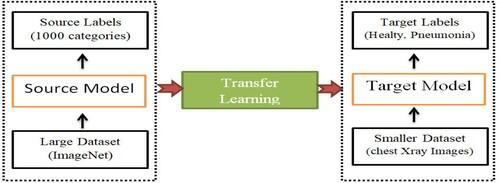
In general, larger datasets are needed to train CNNs. CNN performsbadlyin generalizationwhen trained onsmaller datasets.Inthesesituations,transferlearningisanoption. TheprocessoftransferlearningisdepictedinFigurewhere knowledge gathered by the model while resolving one problemisappliedtoresolveanother.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
detection and picture analysis. The Google Inception Convolutional Neural Network, which was first presented during the ImageNet Recognition Challenge, is in its third iteration. Inceptionv3 was created to enable deeper networks without allowing the number of parameters to becomeunmanageablylarge;itcontains"under25million parameters,"asopposedto60millionforAlexNet.
Figure4:Themechanismoftransferlearning.
DenseNet(DenseConvolutionalNetwork)isanarchitecture thatfocusesonmakingdeeplearningnetworksgodeeper while also making them more efficient to train by using shorter connections between the layers. DenseNet is a convolutional neural network in which each layer is connectedtoallotherlayersdeeperinthenetwork,i.e.the firstlayerisconnectedtothesecond,third,fourth,andsoon, andthesecondlayerisconnectedtothethird,fourth,fifth, andsoon.Thisisdonetoallowformaximuminformation flowbetweennetworklayers.Tomaintainthefeed-forward nature,eachlayerreceivesinputfromallpreviouslayersand passesonitsfeaturemapstoallsubsequentlayers.
2014's ILSVR (Imagenet) competition was won using the convolutionneuralnet(CNN)architectureVGG16.Oneofthe bestvisionmodelarchitecturestodate,accordingtomany. The most distinctive feature of VGG16 is that, rather than concentrating on having many hyper-parameters, they concentrated on having convolution layers of a 3x3 filter with a stride 1 and always used the same padding and maxpoollayerofa2x2filterwithastride2.Convolutionand maxpoollayersarearrangedinthismannercontinuously throughouttheentirearchitecture.ItfinisheswithtwoFC (completely connected layers) and a softmax for output. Thereare16layerswithweights,asindicatedbythe16in VGG16. There are around 138 million parameters in this network,makingitasizablenetwork.
AcommonstartingpointfortransferlearningisResNet-50,a shrunken-downversionofResNet152.Therearefivestages intheResNet-50model,eachofwhichhasaconvolutionand identity block. The identity blocks and each convolution block have three convolution layers. The ResNet-50 has morethan23milliontrainableparameters.
INCEPTION V3
ConvolutionalneuralnetworkInceptionv3wasdeveloped as a plugin for GoogLeNet and is used to support object
Inception aids in the classification of items in the field of computer vision, much like ImageNet can be seen as a database of categorized visual objects. Numerous applications have utilized the Inceptionv3 architecture, frequentlyusing"pre-trained"datafromImageNet.
Pneumonia is a life-threatening infectious disease. For patientsover75years,the mortalityrateofpneumonia is 24.8%.Inthispaper,analgorithmthatcanfurthersupport the computer-aided diagnosis of pneumonia has been proposed.Thedeepresidualnetwork,proposedinthepaper, has a more complex structure but fewer parameters and higher accuracy. Furthermore, this model was scaled up efficiently using the method of compound scaling. Data augmentationandtransferlearninghavealsobeenusedto tackle the obstacle of the insufficient training dataset. Differentscores,suchasrecall,precision,andaccuracy,were computedtoprovetherobustnessofthemodel.Thefuture worksinvolvedevelopinganalgorithmthatcanlocalizethe partsofthelungaffectedbypneumonia.
Instatistics,accuracyisanimportantmeasuretoestimate theperformanceofaclassifier.Accuracyistheproportionof thesumofTP(truepositive)andTN(Truenegative)overa totalnumberofpredictionsthatisthesumofTP,TN,FP,and FNwhichisasfollows.
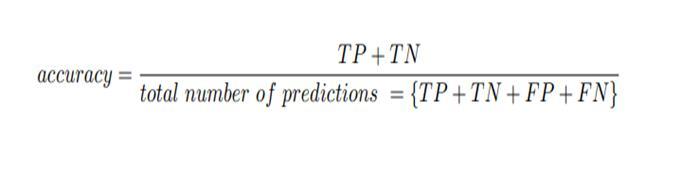
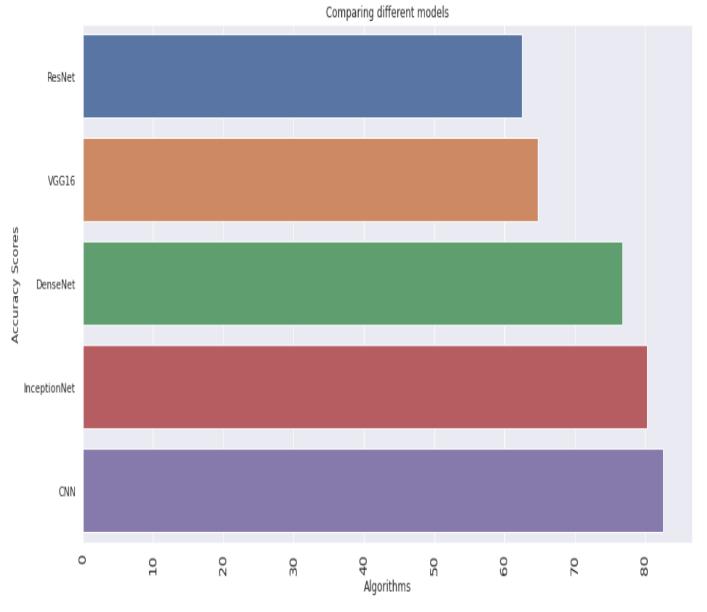
Table1:TrainingaccuracyandTestingaccuracyof differentmodels.
Models TrainingAccuracy TestingAccuracy CNN 9323 8253 DENSENET121 7970 7676 VGG16 81.77 64.74
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

References
1. GonçalvesPereiraJ,ConceiçãoC,PóvoaP.Communityacquiredpneumonia:identificationandevaluation ofnonresponders.TherAdvInfectDis.2013;1(1):5–17.[Crossref],[GoogleScholar]
2. RazzakMI,NazS,ZaibA.Deeplearningformedical image processing: overview, challenges, and the future.2017.[Crossref],[GoogleScholar]
3. ShenD,WuG,Suk HI.Deep learning in medical image analysis. Annual review of biomedical engineering.2017;19:221–248.doi:10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071516044442 [Crossref],[Web of Science ®],[Google Scholar]
4. AndreE,BrettK,RobertoA, et al.Dermatologistlevelclassificationofskincancerwithdeepneural networks. Nature.2017;542(7639):115–118.[Crossref],[Web of Science ®],[Google Scholar]
5. MilletariF,NavabN,AhmadiS.V-net: fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. 2016 fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV); Stanford, CA; 2016:565–571. doi:10.1109/3DV.2016.79.[Crossref],[Google Scholar]
6. GrewalM,SrivastavaMM,KumarP, et al.2017. Radiologistlevelaccuracyusingdeeplearningfor
hemorrhage detection in CT scans. arXiv preprint arXiv:1710.04934.[Crossref],[GoogleScholar]
7. VarunG,LilyP,MarcC, et al.Development and validationofadeeplearningalgorithmfordetection of diabetic retinopathy in retinal fundus photographs. JAMA.2017;316(22):2402–2410.[WebofScience®],[GoogleScholar]
8. LakhaniP,SundaramB.Deep learning at chest radiography:automatedclassificationofpulmonary tuberculosis by using convolutional neural networks. Radiology.2017;284(2):574–582.[Crossref],[Web of Science ®],[Google Scholar]
9. BarY,DiamantI,WolfL, et al. Chest pathology detection using deep learning with non-medical training.2015IEEE12thInternationalSymposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI); New York (NY); 2015:294–297. doi:10.1109/ISBI.2015.7163871.[Crossref],[Google Scholar]
10. ShinHC,LuL,KimL,etal.Interleavedtext/image deep mining on a very large-scale radiology database. Proceedings of the Conference on ComputerVisionandPatternRecognition(CVPR); Boston (MA); June 2015. [Crossref],[Google Scholar]
11. ShinHC,LuL,KimL, et al.Interleaved text/image deepminingonalarge-scaleradiologydatabasefor automated image interpretation. J Mach Learn Res.2016;17(40):1–31.[GoogleScholar]
12. BoussaidH,KokkinosI.Fast and exact: ADMMbased discriminative shape segmentation with loopy part models. Proceedings of Conference on ComputerVisionandPatternRecognition(CVPR); Columbus (OH); June 2014.[Crossref],[Google Scholar]