International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume 9 Issue 12, Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072


International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume 9 Issue 12, Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

Sumera Anjum1 , T. Uma Devi2 , K.K. Namish3 , B. Vasundhara Devi4
4
1,2,3
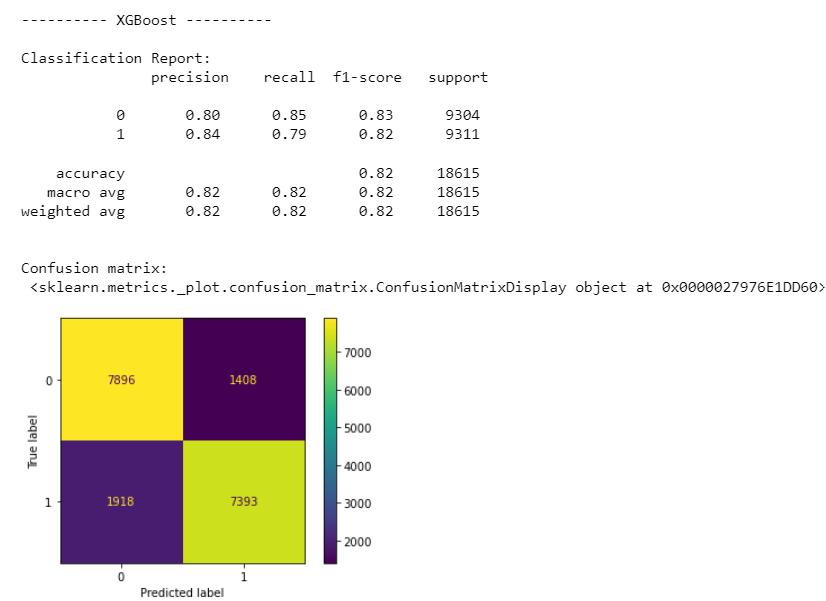
Abstract - One of the largest and most potent cyber hazards today is phishing, which costs thousands of millions of dollars in damages resulting from data breaches that happen every year. Due to the frequent change andshort lifespanofphishing websites, several pattern recognition approaches have been explored and developed to address phishing attacks, but none of them are effective in detecting web phishing activities. Among the most pragmatic ways to solve this challenge is with machine learning since it can attain statistics and handle the changing nature of online fraud. In this project, we illustrate using an ensemble machine learning technique, the Extreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost) Algorithm, to detect malicious URLs with high precision and efficacy using the Uniform Resource Locators. In XGBoost, the target variable yi is predicted using training data xi repeatedly until the model's parameters are improved by merging the trees and boosting. As determined by the confusion matrix createdbythe XGBoost model's performance, it accurately predicted 7393 positive terms and 7930 negative terms with the set of features identified from the Kaggle dataset. Its merits encompass substantial regularisation capabilities that reduce overfitting, great speed and performance since trees are created in parallel, and flexibility because of costume optimization.
Key Words: Phishing, Website, XGBoost, ensemble, Extreme Gradient Boosting, Uniform Resource Locator
Upsurgeinwebusers,phishingthreatshavegrowntobea seriousproblem.Morethan80%ofsecurityincidentsthat havebeenreportedentailphishingattacks.Thesephishing portals are cyber snoopers attempting to gather data covertlybycoercingusersintodivulgingprivateinformation like their passwords and credit card details. Attackers generallyemployspoofingtolureconsumerstomalicious websites by mimicking the names and designs of trusted websiteslikeMyntra,Flipkart,Amazon,andZomato.Hence, itischallengingforthecommonpersontotellthem apart fromlegitimatewebsites.AUniformResourceLocator(URL) incorporatesdifferentcomponents,includingtheprotocol, domain name, port, path, query, etc. A phishing website's URL maybedifferentiatedfromauthenticones byusinga fewspecificcharacteristics.Although,itmaynotbealways reliabletoclassifyawebsitesimplybylookingattheURL. Phishershaveemployedavarietyofsophisticatedstrategies to trick unsuspecting consumers, including the usage of
***
social engineering techniques and technology to offer carefully designed URLs that lead users to believe that websitesaretrustworthy.Thereareseveralapproachesto combatphishing,includingtechnological,educational,and legal means, and numerous research on the subject have beenconducted.Acredibleandplausiblesolutionmustbe providedtoavoidjeopardizingtheusers'privacy.Sincethe methodologiesfrommachinelearningcanidentifypossible threats by learning provided data and building predictive models,itisaviablefieldtohandletheprobleminthiscase. Singlemodelsthateffectivelyprocessthetrainingdataand produce substantially accurate predictions are most commonlyimplemented.Thealgorithmpredominantlyisa collection of Decision Trees, which are used by ensemble machinelearningapproachestotrainseveralcategorization models[4].Thefinalresultisgeneratedthroughacombining method, such as voting (majority wins), weighted voting (certain classifiers have more authority than others), and averagingtheresults,aseachconstituentlearningalgorithm willhaveitsownseparateoutput[4].
In this section, we have articulated several well-known examplesbecauseextensivestudyandresearchhavebeen doneonphishingdetection.Fordetectingattacks,thereare severalmethodsandabroadrangeofdatatypesinacademic researchandcommercialservices.URL-based,domain-based, page-based, and content-based features gathered from academic research for phishing domain identification through machine learning approaches [10]. Traditional machinelearningtechniqueslikeNaveBayes,SupportVector Machine,andDecisionTreewereusedinthemajorityofthe research on the topic. Software called "Anti Phishing Simulator"wasdevisedatFiratUniversitytomakeiteasierto identify phishing and spam emails by looking at the email content [3].As encouragedby Cisco, fogcomputing makes useoffeaturessuchasuniformresourcelocator(URL)and internet activity to identify phishing websites based on a designedneuro-fuzzyframework(dubbedFi-NFN),andan anti-phishing model was created to transparently monitor and defend fog users from phishing attacks [1]. To some extent,approachesbasedonvisualresemblancecanidentify phishing websites. The majority of web information is not consistent, though, and when a web page's characteristics change, the approach encounters a detection problem. Blacklisting techniques are the basic and most commonly
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume 9 Issue 12, Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

usedstrategiesinthebusinesstostopphishingassaults[6]. CheckingwhethertheURLofthematchedwebsiteisonthe blacklistisoneofthephishingdetectiontechniquesusedby Google Safe Browsing [6]. CANTINA is a content-based phishingdetectionmethodthatwasproposedbyZhangetal. ThefirstfivephrasesbasedonTF-DFareforwardedtothe searchunitforcomparisonwiththeresultsreturnedbythe searchunitutilizinglinkablelinksintheauthors'approach foridentifyingphishingwebsites[5].
In this part, the working of the proposed solution is explainedinwhichthedatacollectionanditsprocessingis thefirststep.Theprocessed data isthenusedtotrainthe modelwithanensemblealgorithm.Testingdataisusedto test the accuracy and precision of the model developed whichisdisplayedthroughtheconfusionmatrix.Intheend, the user can enter any URL to classify it as a phishing websiteoralegitimatewebsitewhichisgeneratedasoutput bytheXGBoostparadigm.
The dataset which is used in this project is obtained from Kaggle. Kaggle provides the public dataset consisting of 71677 unique values. This data is fetched from google's whoisAPIwhichtellsusmoreaboutthecurrentstatusofthe URL'sregistration[2].Thefirststepfollowingdecidingonan algorithmisdatacollection,oftenknownastherequirements stage.Despite,thefactthatthisstepisonlybeginning,itisthe mostimportantandtime-consuming.Becausethemodule's main objective is to learn about and apply cutting-edge technology, this section pays particular focus to this componentoftheproject.Fromfourprimarycategories,17 factorsaretakenoutandincorporatedintothesystem.The featuresareextractedandstoredintheCSVfile.Theresulting CSVfileisuploadedtothisnotebookandstoredinthedata frame.
It's appropriate toconstructthe model when the essential datahasbeenobtainedandexamined.Thedevelopmentof themodel'sarchitecture,thecreationoforderlyyetsecure codes,andmodeltrainingcomprisethedesignportionofthe project as it is now being presented. Python is being leveraged throughout the project, thus important libraries thataremostlyusedfordatascienceareimported,andthe scripts are either created from scratch or drawn from the web.ExtremeGradientBoost,oftenknownasXGBoost,isa machinelearningtechniquethatemploysextremegradient boosting and is based on Decision Trees. The gradient boosting method was improved by integrating parallel processing, tree pruning, missing value handling, and normalizationtogetridoferrorsandinaccuracies[11].It'sa lethalcombinationofhardwareandsoftwaremetaheuristics that uses the least amount of processing resources while
achievingbettersignificantresults.Thefundamentalpurpose ofthisworkistoestablishcertaindatasetparametersthat themodelwilluseinthefuturetodeterminewhetheraURL isgenuineornot.Here,eachparametertransformsintoatree andincreasesthedecidingfactor[11].Althoughthesetrees mightnotperformaswellasanticipated,bymergingthese trees and boosting them, the prediction might noticeably enhance.InXGBoost,thetargetvariableyiispredictedusing trainingdataxirepeatedlyuntilthemodel'sparametersare improved.
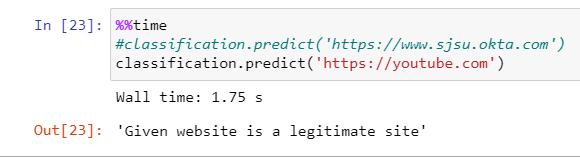
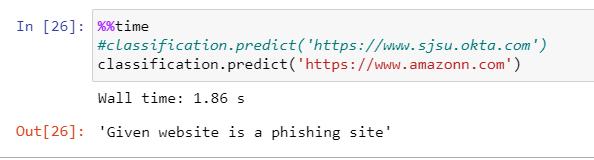
The developed paradigm is saved and tested for accuracy withthetestingdata.Thisparadigmcanbeusedinreal-time toclassifytheURLsintolegitimateorphishing,givenbythe userasinput.
Theoutputscreenshotsdisplaytheuserinputsclassification and the confusion matrix shows the performance of the XGBoostphishingwebsiteidentificationmodel.
Fig -1: Phishingwebsitedetectionoutput1
Fig -2: Phishingwebsitedetectionoutput2
Fig -3: ConfusionmatrixofthedevelopedXGBoostmodel
oftenupdated and do notlastforever. With the use ofthe Ensemble Algorithm XGBoost and a feature set well stipulated, phishing detection using website URLs is predicted to generate highly accurate results with a reasonablebias-variancetrade-offinarobustandefficient manner.Accordingtotheabovemodels'assertions,XGBoost Classifierhasthefinestmodel performanceat86.4%.The Pythonpicklemodulehasbeenusedtoretainthismodelas the regression design and demonstrates how reliable and accuratethemodelisatinterceptingwebphishing.
[1] ChuanPham,LuongA.T.Nguyenz,NguyenH.Tran,EuiNam Huh, Choong Seon Hong, “Phishing-Aware: A Neuro-Fuzzy Approach for Anti-Phishing on Fog Networks”,IEEETransactionsonNetworkandService Management,2018
[2] Aman Nagariya; https://www.kaggle.com/aman9d/phishing-dataR.
[3] M.Baykara,Z.Z.Gürelr,6thInternationalSymposiumon DigitalForensicandSecurity,1(2018)
[4] DharaniM,Soumya Badkul,Kimaya Gharat,Amarsinh Vidhate,andDhanashriBhosale,“DetectionofPhishing WebsitesUsingEnsembleMachineLearningApproach”, Mar2021
[5] Zhang, Y.; Hong, J.I.; Cranor, L.F. Cantina: A contentbased approach to detecting phishing web sites. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on WorldWideWeb,Banff,AB,Canada,8–12May2007;pp. 639–648
[6] Jain, A.K.; Gupta, B. Comparative analysis of featuresbased machine learning approaches for phishing detection.InProceedingsofthe20163rdInternational Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development (INDIACom), New Delhi, India, 16–18 March2016;pp.2125–2130
[7] Lin,Y.;Liu,R.;Divakaran,D.M.;Ng,J.Y.;Chan,Q.Z.;Lu,Y.; Si, Y.; Zhang, F.; Dong, J.S. Phishpedia: A Hybrid Deep LearningBasedApproachtoVisuallyIdentifyPhishing Webpages.InProceedingsofthe30th{USENIX}Security Symposium({USENIX}Security21),VirtualEvent,11–13August2021.
Fig -4: PrecisiongraphfordevelopedXGBoostmodel
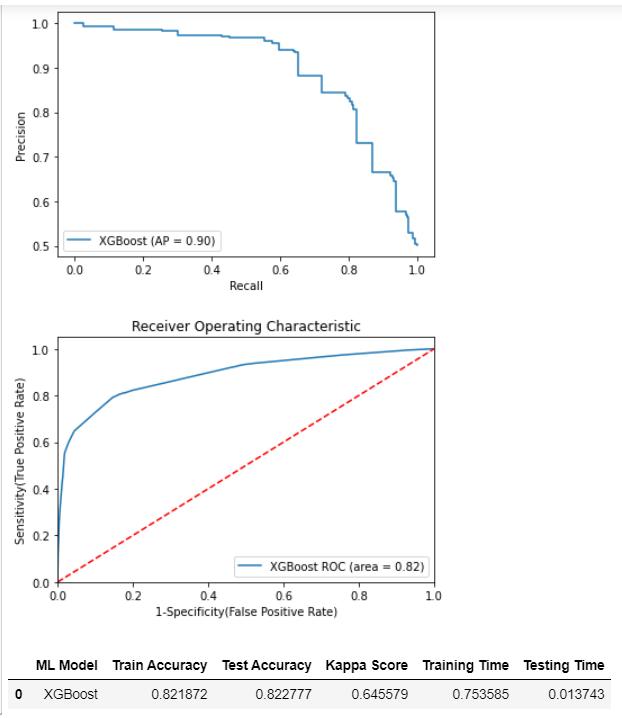
Today there are more uncontrolled websites than ever before due to a mammoth increase in internet users. Phishingvariegatesovertimesincefraudulentwebsitesare
[8] Jiaqi Gu; Hui Xu; An Ensemble Method for Phishing WebsitesDetectionBasedonXGBoost,15March2022
[9] Musa Hajara; A.Y. Gital;Fatima Umar Zambuk; Jamilu Usman Waziri; A comparative analysis of phishing website detection using XGBOOST algorithm; March 2019
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume 9 Issue 12, Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1366

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume 9 Issue 12, Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[10] EbubekirBüber;“PhishingURLDetectionwithML”; https://towardsdatascience.com/phishing-domaindetection-with-ml-5be9c99293e5,Feb2019
[11] NishantNityanandNaik;“ModellingEnhancedPhishing detection using XGBoost”; https://norma.ncirl.ie/5512/1/nishantnityanandnaik.p df,Aug2021
[12] AliAhmadAminu;AbdulrahmanAbdulkarim;Amatullah Yahaya Aliyu; Muhammad Aliyu; Abdulkadir Maigari Turaki;“DetectionofPhishingWebsitesUsingRandom Forest and XGBOOST Algorithms”; http://www.smrpi.com/images/journals/IJPAS/20.pdf; Sep2019
[13] Ali Aljofey, Qingshan Jiang, Abdur Rasool, Hui Chen, WenyinLiu,Qiang Qu& Yang Wang;“Aneffective detectionapproachforphishingwebsitesusingURLand HTML features”; https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-022-108415;May2022
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal
