International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
P Ramu1 , P Suketh Reddy2 , B Anjali Reddy3 , Sriraj Katkuri4 , M Sathyanarayana5
1,5 Professor, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, SNIST, Hyderabad501301, India
2,3,4 B.Tech Scholars, Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering Hyderabad-501301, India ***
Abstract :- The survival of a nation’s wellbeing greatly depends on the availability of freshwater. An essential step in managing freshwater assets is the evaluation of the quality of the water. According to the World Health Organization's annual report, people across all walks of life fall prey to the lack of access to safedrinking water. This occurs as a result of mismanagement and inefficient methodologies to prevent the occurrence of harmful water. Before using water for any purpose, it is crucial to assess its quality to ensure it is potable and hence can be used safely. For examining the safety levels of water sources, analysis of water and its underlying components is essential. A water's readiness for a particular use based on its physical, chemical, and biologicalcharacteristics is referred to as its quality.
Keywords: Machine learning; potability; entropy; Gini index
Each cell in the body receives its energy mostly from water, which also controls all the body's functions. 80% of the cerebrum is made up of water. Extreme dehydrationmayresultinmentalimpairmentsandaloss of the ability to clearly think. One of the most important regular resources for the survival of all species on Earth iswater.Waterisusedformanydifferentthings,suchas drinking, washing, and water systems, due to its nature. Water is essential for both living things and plants. Simply put, all organic living things require a huge quantityandexceptionalqualityofwatertoexist.
Freshwater is a fundamental asset to horticulture and industry for its essential presence. Water quality observation is a key stage in the administration of freshwater assets. As indicated by the yearly report of WHO,manyindividualsarekickingthebucketbecauseof the absence of unadulterated drinking water parti. It is critical to check the nature of water for its expected reason, whether it be animals watering, compound showering,ordrinkingwater.
A tool called water quality testing can be used to locate puredrinkingwater.Thismeansthatfortheprotectionof pure and clean water, the proper water testing is quite important. Water testing is crucial in determining the
proper operation of water sources, evaluating the safety ofdrinking waterand deducingthe measurestocurbthe menace.
Wecanrespondtoquestionslikewhetherthewaterisfit for drinking, washing, or water systems, to name a few applications,bytestingthe natureofa water body.Itcan usetheresultsofwaterqualityteststoexaminethenature of water in a location, a state, or the entire country, starting with one water body and moving on to the next. Since irresistible illnesses caused by pathogenic bacteria, infections, helminths, and other parasites are the most well-known and pervasive health danger associated with drinking water, microbiological quality is typically the mosturgentissuetobeaddressedduringthisprocess.
When certain synthetic compounds are present in drinking water in excess, health risks result. These synthetics contain nitrate, fluoride, and arsenic. To the client should be given safe drinking (consumable) water for drinking, meal preparation, personal hygiene, and cleaning. To ensure purity at the point of client supply, thewatermustadheretostandardqualitystandards.
Iran's Dez Catchment is one of its major watersheds. There are several sporadic and perennial streams in the watershed. One of the primary perennial streams of this basin is the Tireh River, which flows through the two largest cities and is located in the province of Lorestan. tireh River's coordination To determine the stage discharge relation and monitor the water quality components, the regional water authority (RWA) in Lorestanprovince(Iran)constructedhydrometrystations alongthisriver.ConstructedhydrometrystationsbyRWA are shown by triangular symbols. Measuring the stage dischargerelationandwaterqualitycomponentsbyRWA wasconductedmonthly.
It is interesting that a number of measurements have beentakenalmosteverymonth.Morethan55yearshave passed since the sampling began. The river is still being monitorednow after the first measurement was reported in 1960. The components of the water quality measured by RWCA are listed in summary form. measurement parameters include temperature (T), pH, specific C–1), sulfates (SO4–2), chlorides (Cl), total dissolved solids

e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
(TDS), sodium (Na+), magnesium (Mg+2), calcium(Ca+2).
After understanding the data, processing some attributes,andanalyzingthecorrelationsandpredictive potential of the attributes, the major goal of any data science project is model construction. like it was explainedintheearlierchapters.Creatingamodelusing the decision tree technique is one of the most straightforward and effective ways of predicting informationbasedontestvalues.
A categorization paradigm called a decision tree, which resembles a flowchart, is frequently employed. Each internal node (non-leaf node) of a decision tree represents a test on an attribute, each branch a test result, and each leaf node (orterminal node) a class label.Therootnodeisthetopmostnodeinatree.
Tree induction, which is the learning or creation of decisiontrees from a class-labeled training dataset, is a method for creating decision trees. Deduction is the process of classifyingatestdatasetusingadecisiontree that has alreadybeen built. The method of deduction involves applying the test condition to a record or data samplestartingattherootnodeofadecisiontree,then, depending on the results of thetest, the appropriate branch is proceeded to. This step leads to either a leaf node or to another internal node for which a new test condition is applied. The record or data sample is subsequently given the class label associated with the leafnode.
Decision trees facilitate decision-making under certain conditions and enhance communication. The idea that different actions can result in different operational nature of the situation is easier for computational purposes. Making the best choice possible is beneficial. Wheninstancesarerepresentedbyattributevaluesand trainingdatacontainserrors,themethodperformswell. In cases where the target function contains discrete outputvalues,itisalsorelevant.
It automatically screens variables, and prepares data with comparatively little user work. Non-linear relations are simple to comprehend and have little impactontheperformanceoftrees.Thedecisiontreeis helpfulforexploringdataandhighlysuggestedwhenthe requirementtopredictdataisbasedonexpectations
Thenon-parametricsupervisedlearningapproachused for classification and regression applications is the
decisiontree.Itisorganizedhierarchicallyandhasaroot node,branches,internalnodes,andleafnodes.
Adecisiontreehasarootnodeatthebeginningthathas noincoming branches. The internal nodes, sometimes referredto as decision nodes, are fed by the root node's outgoing branches. Both node types undertake assessments based onthe available attributes to create homogenous subsets, which are represented by leaf nodes or terminal nodes. All the outcomes within the datasetarerepresentedbytheleafnodes.
Decision tree learning employs a divide and conquer strategy by conducting a greedy search to identify the optimal split points within a tree. This process of splitting is then repeated in a top-down, recursive manner until all, or the majority of records have been classifiedunderspecificclasslabels.
Someofthepresumptions whenutilizingadecisiontree are:
The entire training set is first regarded as the root.
Categorical feature values are desired. If the values are continuous, they must first be discretizedbeforethemodelcanbeconstructed.
Basedonattributevalues,recordsaredispersed recursively.
Using a statistical approach, properties are arrangedto serve as the tree's root or internal node.
To construct a decision tree, the flowing parameters aretakenintoconsideration:
Probability is defined as the possibility of the occurrenceofavalueoutofthetotalintheoutputdata set that is considered while constructing a decision tree.
P(playgolf=yes)=9/14;P(playgolf-no)=5/14;
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Step3:SubsettheStoincludepotentialvaluesforthebest qualities.
Step 4: Create the decision tree node that has the best attribute.
Step 5: Use the selections of the dataset generated to iterativelydevelopnewdecisiontrees
Step 6: Continue along this path until you reach a point when you can no longer categorize the nodes and you refertothelastnodeasaleafnode
Entropyisametricusedindatasciencetoassesshow "mixed"acolumnis.Itisspecificallyusedtoquantify disorder.
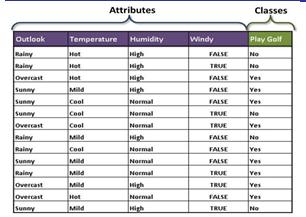
Entropy=-P(class1)xLog(P(class1))-P(class2)X Log(P(class2))wherePdenotesprobability.
E(S)=[(9/14)log(9/14)+(5/14)log(5/14)]=0.94
The primary factor used to determine whether a feature should be used to split a node is information gain. The feature that results in the maximum information gain at a decision tree node, or the featurewith the best split, is utilized to divide the node.
Informationgain=Entropy(s) -[(Weightedaverage) X (Entropyofeachfeature)
IG(S,outlook)=0.94-0.693=0.247
IG(S,Temperature)=0.940-0.911=0.029
IG(S,Humidity)=0.940-0.788=0.152
IG(S,Windy)=0.940-0.8932=0.048
TheGiniIndex,alsoknownasImpurity,calculatesthe likelihood that a randomly selected instance will be incorrectly classified. The likelihood of misclassificationisbasedonthisparameter.
Gini Impurity= 1 (Probability of ‘Class 1’) ²(Probabilityof‘Class2’)²
Step1:AccordingtoS,startthetreeattherootnode, whichhastheentiredataset.
Step 2: Utilize the Attribute Selection Measure to identifythedataset'stopattribute(ASM).
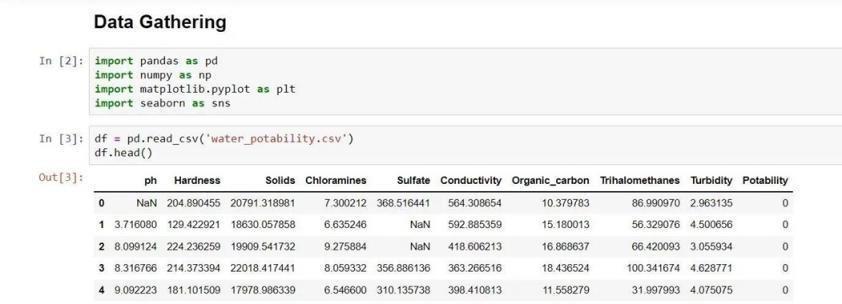
Importallthenecessarylibrariesthatareneededfordata visualization or to train the model. The top five rows of thedata set should then be displayed after loading the datasetusingthePandasmethodreadcsv().
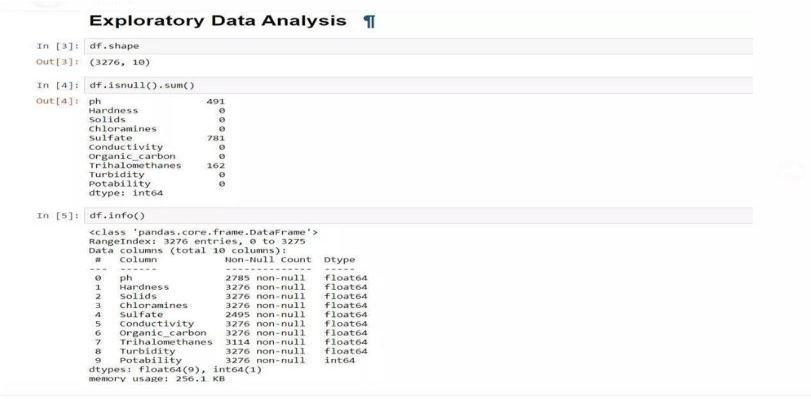
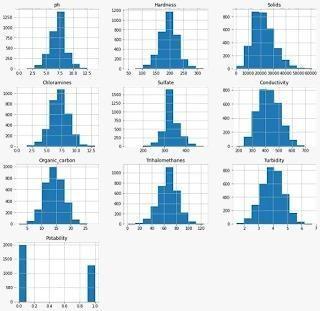
ExploratoryDataAnalysisshouldthenbedone.Checkthe dataset'sshapefirstinEDA.Checktoseeifthereareany NULL values, as you can see in the image below for ph, Sulfate, and Trihalomethanes. then verify the dataset's information.

e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The dataset that displays the lowest value, maximum value, mean value, count, standard deviation, etc. is nowdescribed.
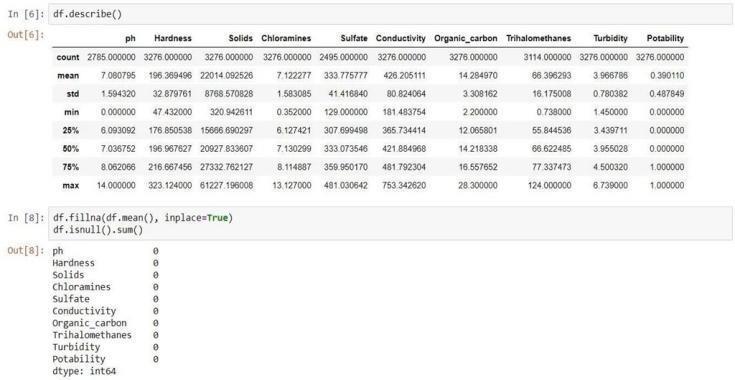
Finally,wetakecare of the missing data. Weused the meanvalueofeachfeaturetofillinthemissingvalues in our features' data, handling missing data by filling in the mean value. Next, confirm whether any null valuesarepresent.
Visualize every aspect of the data set as shown below.
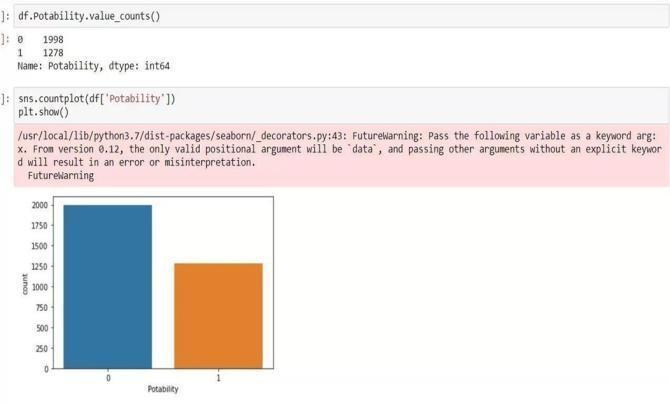
Verify the potability value counts for our target feature.thenmakeuseofseaborn'scountplotfunction toillustrateportability.
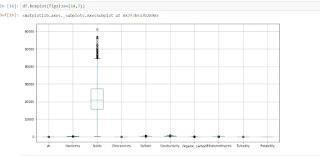
Nowuseaboxplotfunctiontoviewtheoutlier.Youcan see that the Solid feature has outliers, but we are unable to eliminate them because doing so would make the Solid feature unusable. Water will therefore always be safe to drink. We will know whether the water is safe ornot since it contains an anomaly that makesthewater unclean.Watermaybedangerous to drinkifthesolidcontentishigh.
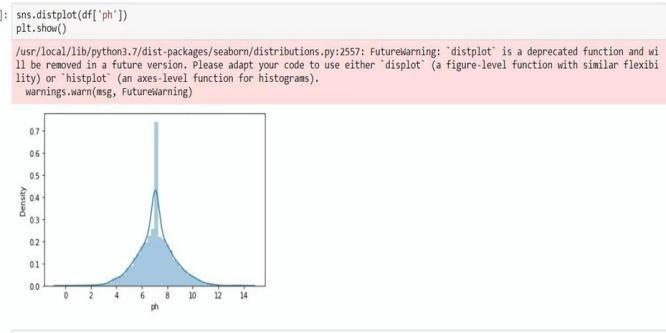
To determine whether the pH value has a normal distributionornot,depictitusingthedistplotfunction. Sinceitisanormaldistribution,youcanobservethat.
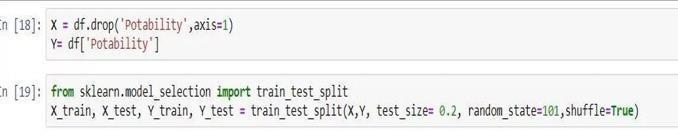
The data set needs to be prepared now. Separate the featuresthatareindependentanddependentfromthe data. Except for Potability, which is our dependent characteristic,theyareallindependentfeatures.
Usingthetraintestsplitfunction,whichyieldsfourdata sets, divide the data set into the training and testing sets.
Thedecisiontreeclassifier model will now be defined, andthedataset(Xtrain,Ytrain)willbeusedtotrainthe model.
Utilizing the test data set (Xtest,YTest), we furthertest themodel.

e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
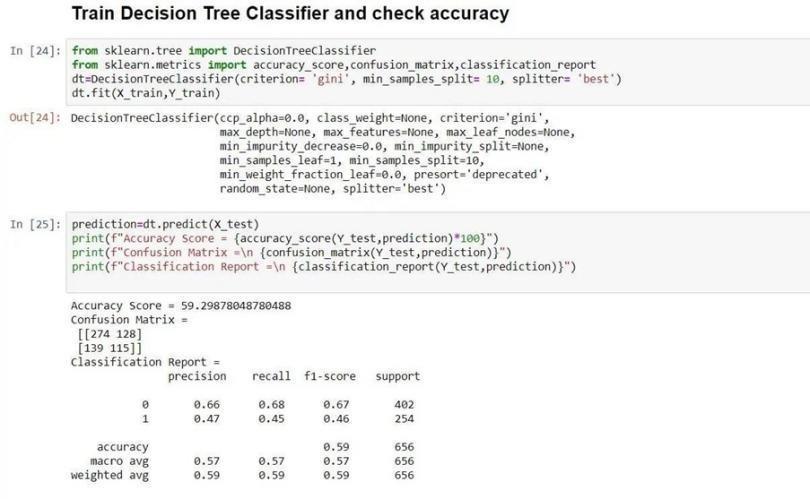
It's time to assess the model using the classification report, confusion matrix, and accuracy score. The actual data and theexpecteddata arethetwoparametersused inevaluationmethodologies.Andyoucanseethat59%of thetimeisaccurateoverall.
The sequence diagram, which is also known as an event diagram,showshowmessagesmovethroughthesystem.
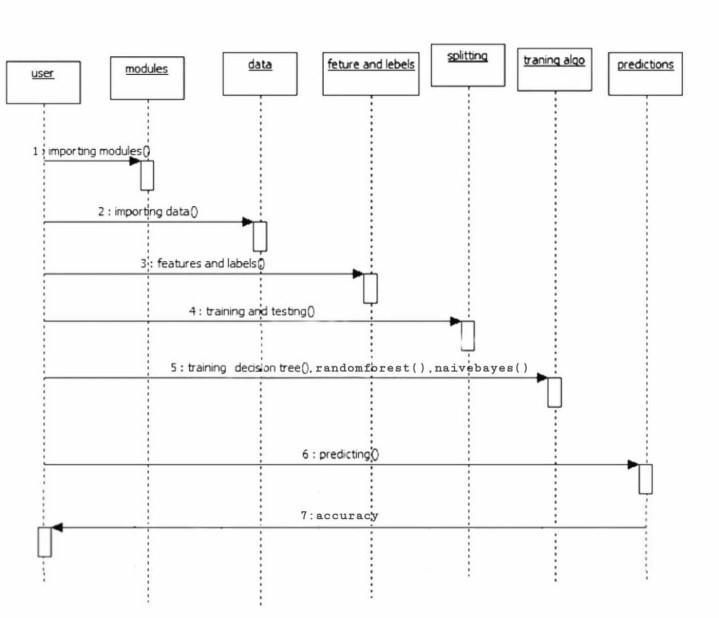
Itaidsincreatingavarietyofdynamicsettings.Itdepicts communication between any two lifelines as chronologicallyorderedseriesofactivities, implyingthat these lifelines were active at the moment of communication
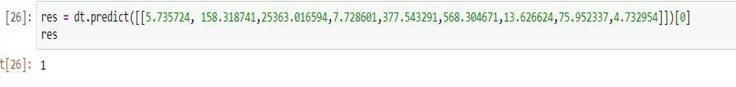
Themodelisthentestedusingauniquedataset, andthe resultsareshowninthegraphicbelow.
Themodelisthentestedbasedonagivensetofvaluesto predict the potability of water. As per the given values, themodelpredictsthewatertobefitfordrinking.
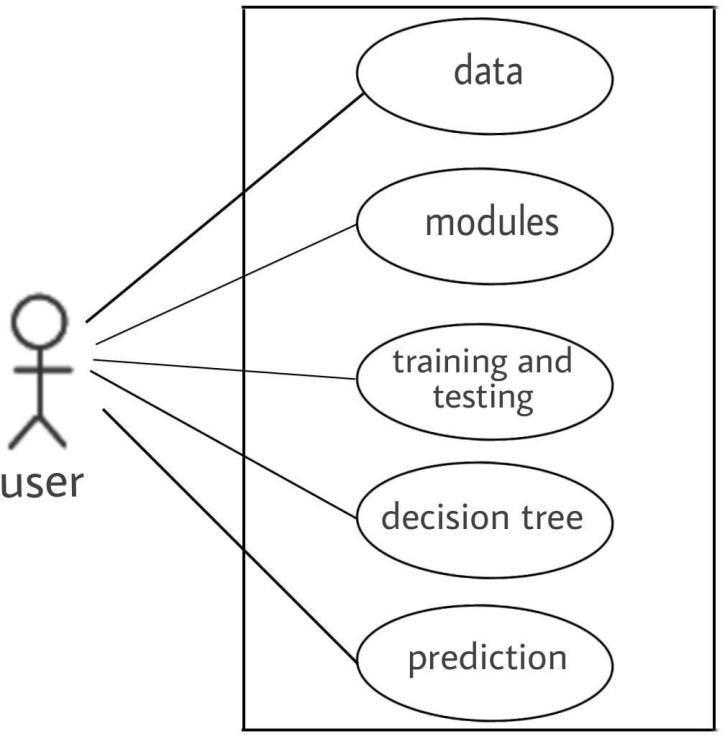
The dynamic behavior of a system is represented by a use case diagram. It incorporates use cases, actors, and their interactions to encapsulate the functionality of the system. It simulates the duties, services, and operations neededbyasystemorapplicationsubsystem.Itshows a system'shigh-levelfunctionalityandalsodescribeshow auserinteractswithasystem.
This research investigated how well machine learning approaches predicted the water quality elements of a water quality dataset. For this, the most well-known dataset variables, including conductivity, ph, tcm, nitrate, and organic salts, were acquired. The results showed that the implemented decision tree model performs well in predicting the parameters of water quality, with an accuracy of 59%. To increase the effectivenessoftheselectionprocess,additionalresearch will be conducted to create models that incorporatethe suggested method with other methods and deep learningapproaches.
International Research Journal of Engineering
Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
A decision tree has the important benefit of requiring the consideration of all potential outcomes and tracing each path to a conclusion. It generates a thorough analysis of the outcomes along each branch and pinpoints decision points that require additional research.
They provide each problem, option, and result a particular value. Costs and advantages are made clear whenexpressedinmonetaryterms.Thismethodreveals the financial repercussions ofvariouscoursesofaction, lowers confusion,eliminates ambiguity, and highlights the pertinent decision paths. They also employ probability for circumstances to put choices in perspective with one another for straightforward comparisonswhenfactualinformationisunavailable.
Weareallawareofhowvitalwateristohumanhealth. Knowing the water's quality is crucial because if we consumewaterwithoutfirst makingsureitissafetodo so, we run therisk of getting sick. Numerous illnesses that are transmitted through water exist and if we consume non-drinkable water, we risk contracting hazardous diseases. Consequently, the most crucial factor is understanding the water's quality. But this is wheretherealissueis.We musttestthewaterata lab, which is expensive and time-consuming in addition to beingnecessary for determining the water's quality. In this study, wethereforeprovidea differentstrategyfor predictingwaterqualityusingartificialintelligence.
[3] Kangabam, R.D.; Bhoominathan, S.D.; Kanagaraj, S.;Govindaraju,M.Developmentofawaterquality
[4] The Environmental and Protection Agency, “Parameters of water quality,” Environ.Prot., p.133,2001.
[5] Kangabam, R.D.; Bhoominathan, S.D.; Kanagaraj, S.; Govindaraju,M.Developmentofawaterquality.
[6] Jiang, J.; Tang, S.; Han, D.; Fu, G.; Solomatine, D.; Zheng, Y. A comprehensive review on the design and optimization of surface water quality monitoring
[7] Manish Kumar Jha,Rajni Kumari Sah, M.S. Rashmitha, Rupam Sinha, B. Sujatha. Smart Water Monitoring System for Real-Time WaterQualityandUsageMonitoring,2018
[8] Ashwini K,D. Diviya,J.JaniceVedha,M.Deva Priya. IntelligentModelForPredictingWaterQuality
[9] Priya Singh,Pankaj Deep Kaur. Review on Data Mining Techniques for Prediction of Water Quality,2017
[10] HadiMohammed,IbrahimA.Hameed,RazakSeidu. Machine Learning: Based Detection of Water Contamination in Water Distribution systems,2018.
Decision trees' relative instability in comparison to other decision predictors is one of their drawbacks. A minor change in the data can have a significant impact on the decision tree's structure, which can express a differentoutcome than what users would receive in a typicalevent.Hencebetterpredictionmodelscanreplace formorerobustresult
thisalgorithm
WewouldliketothankMr.PRamuandMSatyanarayana for their wise advice, wise counsel, andmoral support throughoutthewritingofthiswork.
[1] Jayalakshmi, T.; Santhakumaran, A. Statistical normalization and back propagation for classification.Int.J.Comput.TheoryEng.2011.
[2] Park, J.; Kim, K.T.; Lee, W.H. Recent advances in information and communications technology (ICT) andsensortechnologyformonitoringwaterquality.