International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Veer Singh Rawat1 , Gaurav Shrivastava2
1M.E. Student - Department of Civil Engineering, VITM College, Gwalior (M.P.), India
2Asst. Professor - Department of Civil Engineering, VITM College, Gwalior (M.P.), India ***
Abstract: Today's big structures are constructed with more flexibility and lighter materials. This has a minimal damping. When there is an earthquake, the buildings tremble, making people uncomfortable. The latest building earthquake resistant strategies also include energy dissipation device technologies. There are three types of systems: Active, Passive, and hybrid and semi-active system. Buildings may utilize a passive energy dissipation device to enhance seismic responsiveness during an earthquake. Many tall buildings in earthquake-prone areas have tuned mass dampers and viscous fluid dampers fitted as the simplest energy dissipation mechanisms.
keywords: Seismic analysis, damping and dissipation device.
This earthquake Tectonic plate motions cause energy to be released, and this energy is transferred through the ground as waves.Thesewaves,whichvariedinintensityandenergylevel,cameatdistinctpointsthroughouttime.apassivedevicethat absorbs some of the input energy and transmits the forces created in reaction to the structure's motion. Therefore, the structural system does not need an external power source to contribute energy. Some examples of passive energy control mechanismsarebaseisolation,tunedmassdampers(TMD),tunedliquiddampers(TLD),metallicyielddampers,andviscous fluid dampers. Software for structural analysis is called Etabs. Structural frame seismic loads have been examined using Etabswithoutdampersandwithdamper.
Adjusted mass dampers are passive devices that are installed at the top of buildings and have additional mass attached to themaswellastunedfrequenciesofthestructures.Itishungatthetopofthestructureandissettooneprimaryfirstmode frequency. The Having a calibrated mass damper allows dampers to also overcome the inertia of mass. They needed the building's top to be widely dispersed, thus a single TMD or several tiny TMDs were installed to efficiently manage the structure's response. loads with a TMD, VFD, and loads without a damper Both linear and nonlinear time history analyses have been performed. One of the dampening mechanisms utilised often in military and aerospace applications as well as lately embraced for use in structures is viscous fluid dampers. A piston in the damper housing that is filled with a silicon compoundoroiltypicallymakesupaviscousfluiddamper.FluidViscousDampersfromTaylorDevicesmaybeusedonboth permanent and base separated structures, including as buildings, bridges, and life support systems. These research studies makeuseofdiagonalbracedampers.Inthisequation,thereisnospringforce.Thesolevariableindamperforceisvelocity. The force will be the same at any point in the stroke for any fixed velocity. The structure itself must resist all static force becausethedamperdidnotsupplyanyrestoringforce.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
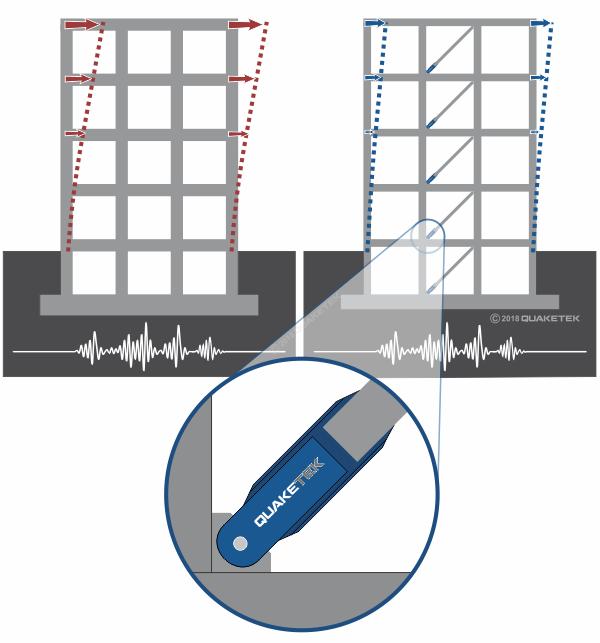
On the investigation of seismic damping structures, various works are provided. This audit document contains text from briefsprovidedbyawiderangeofstudentsandscientists.
Manuel Aguirre1 (1991) In this paper, The device permits controlled exchange of the structure burdens to the establishmentheaps,tosuchanextentthatthestructureneithersettlesnorarisesasfortheencompassingground,inregions where the dirt is profoundly compressible, with no guarantees that of Mexico City. Moreover, the device disperses energy whenthestructureencountersshakingmovementundertheactivityofseismictremorpowers.Thedeviceisfixedtothetop ofeveryoneoftheestablishmentheaps,whichgounreservedlythroughthebuildingbasechunk.Likewise,thedeviceisfixed to the base section, to such an extent that it gives, through deformable components that go through a rolling-twisting movement,avariablelengthassociationbetweenestablishmentheapsandbuilding.
Maria Q. Feng (1995) Thisframeworkexploitstheallegedmegasubstructuredesign,whichisparticularlywellknownintall structures. Bases contained in the mega structure fill in as energy safeguards so no extra mass is needed for the expected vibration control as found in the traditional mass damper frameworks. The proposed framework normally settle the hardships in expanding damping limits of tall structures related with the high unbending nature and disfigurement in the prevailing bowing mode. Dynamic qualities of the proposed control framework including the recurrence reaction and the energy stream are explored. Ideal upsides of underlying boundaries like the damping proportion and firmness of the foundation still up in the air. The attainability and viability of this one of a kind control framework in working on human solacefurthermore ensuringstructuresunder both breezeandquakeloadsareshownthroughinsightful and mathematical analysis.
Lih-Shing Fur (1996) In this review, a second-request dynamic controller planned witassembled sensors/actuators is introduced for the vibration control of tall structures under seismic and wind excitation. The review incorporates three illustrative models, to be specific, dynamic base disengagement of a structure displayed as a shear shaft, AMD control of a three layered structure with erraticisms under quake excitation, and AMD control of a tall structure displayed as a planar edge exposed to wind loads. Through the models, the control framework dependent on this controller has been demonstrated to be more compelling in the decrease of dynamic reaction than utilizing detached control alone. Since the controller configuration as introduced is genuinely broad, the powerful controller configuration might be applied straightforwardly to structures displayed as a multi-level of-opportunity frameworks invigorated by more broad loads. In any case, for every actuator introduced, there is a relating level of opportunity added to the entire framework due to the powerful controller. In this way the use of such a control framework is especially appropriate for structures which have dynamicreactionoverwhelmedbyacoupleofvibrationmodes.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Gina J. Lee-Glauser (1997) In this paper, an inactive isolator, a functioning vibration safeguard, and a coordinated aloof/dynamic(hybnd)controlarereadupfortheirviabilityindiminishingprimaryvibrationunderseismicexcitation.For the inactive isolator, a covered elastic bearing base isolator, which has been considered and utilized broadly by specialists and seismic plan is considered. A functioning vibration safeguard idea, which can give ensured shut circle soundness with minimum information on the controlled framework, is utilized to diminish the inactive isolator displacement and to stifle vibration.Athree-storybuildingmodelisutilizedforthemathematicalreenactment.Theexecutionofafunctioningvibration safeguard and a crossover vibration controller in diminishing pinnacle primary reactions is contrasted and the inactively disconnected primary reaction under the NOOW part of the El Centro 1940 and N90W part of the Mexico City 1985 quake excitationrecords.
Franklin Y. Cheng (1998) A hypothetical review is done for ideal controller situation and viability of a mixture seismic reaction control framework including a viscous liquid damper and a servovalve-controlled water powered actuator. A stochasticseismicreactionofcontrolledconstructionsisfirstexaminedwithnonorthogonaldampingalsofirmness;then,at thatpoint,afactualstrategyforidealpositionofcontroldevicesonseismic-safeconstructionsiscreated.Withsuchposition, a mixture framework can accomplish more noteworthy execution in that amount less control power is needed to decrease primary seismic reaction to a given level. This concentrate likewise shows the half and half framework is better than both dynamicandlatentcontrolframeworksincontrollimit. Mathematicalreenactmentfortheseismic reactionofa structureis introducedtoexhibittheviabilityoftheproposedcontrolprocedure.
Takayuki Teramoto (2000) As of not long ago, as a quake countermeasure, seismic structures have been planned over eighty years in Japan. Then again, numerous structures with underlying control frameworks have been developed in these fifteen years. These plan techniques mean to lessen the underlying reaction brought about by powerful data sources includingseismictremors. Theseframeworksarecharacterizedastheframeworkswhichcontrol thereaction movementof structures,underlyingcomponentsandfacilitiesinsidethestructures,byintroducingaspecificframeworkorcomponent.As per this definition, the primary control framework is a strategy which controls a wide range of vibration brought about by wind,traffic,apparatusstacks,etc.Inthispaper,theblueprintofthestructuremodelswithunderlyingcontrolframeworksin Japan is presented. The quantity of models is around 200. The underlying control frameworks which are examined, are frameworksutilizinghysteresisdampers(steelplatewithcut,steelchimetypeandleaddamper),grindingdampers,viscous dampersincludingvisco-versatiledampers,tunedmass dampersand dynamiccontrol frameworksincludingdynamicmass dampersandhalfandhalfmassdampers.Alsothesubtletiesoftheseframeworksarepresentedgenerally
Narito Kurata (2001) We havefostereda constantlyfactorsemi-dynamicpressuredrivendamperthatcreatesthecontrol powerupto 1000kN with anouter power supplyof just70watts. Thisdamperwasappliedto a real five-storyworkingin 1998.Thisistheworld'sfirstutilizationofthepersistentlyfactorsemi-dynamicunderlyingcontrolframeworkforenormous seismic tremors. The semi-dynamic underlying control framework controls a structure's reaction by changing the damping elementofthevariabledampingparts,Thispapertracesthecreatedsemi-dynamicdamperframeworkandthestructureto which it was applied. It too portrays the control execution of the framework dependent on an assessment of constrained vibrationtestsledaftertheframeworkwasintroduced,andtheseismicperceptionrecords.
Akira Fukukita (2004) Inthispaper,weconcentrateonthecontrolimpactfora20-storybenchmarkconstructingandapply aloofandsemiactivecontroldevicestothestructure.Tobeginwith,wetakeviscousdampingdividersasaninactivecontrol devicewhichcomprisesoftwoexternalplatesandoneinwardplate,confrontingeachotherwithalittleholeloadedupwith viscous liquid. The damping power is connected with the interstory speed, temperature, and the shearing region. Then, we acceptavariableoildamperasasemiactivecontroldevicewhichcancreatethecontrolpowersbyminimalelectricalpower. Weproposeadampermodelwherethedampingcoefficientchangesasindicated bythereactionofthedamperandcontrol powers determined by the controller dependent on a direct quadratic Gaussian control hypothesis. It is exhibited from the consequencesofcertainreenactmentsthatbothinactivedeviceandsemiactivedevicecanviablydecreasethereactionofthe constructionindifferentseismictremormovements.
Osamu Yoshida (2004) This paper tends to the third-age benchmark issue on underlying control, and spotlights on the control of a full-scale, nonlinear, seismically energized, 20-story building. A semi active plan is created in which magneto rheological dampers are applied to decrease the underlying reactions of the benchmark building. Control input assurance dependsonacutidealcontrolcalculationwhichutilizesoutrightspeedincreasecriticism.AphenomenologicalmodelofaMR damper,inlightofaBoscawencomponent,isutilizedintheanalysis.ThesemiactiveframeworkutilizingtheMRdamperis
© 2021, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page832

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
contrastedwiththepresentationofafunctioningframeworkandanidealsemiactiveframework,whichdependonasimilar ostensible controller as is utilized in the MR damper control calculation. The outcomes show that the MR damper is successful,andaccomplishescomparativeexecutiontothedynamicandoptimalsemiactiveframework,whilerequiringvery littlepower.
Claudia Mara Dias Wilson (2005) The review said A sort of semi-dynamic control device, the magnetorheological (MR) damper, comprises of a water powered chamber containing micron-sized, attractively polarizable particles suspended in a fluid like water, glycol, mineral or engineered oil. The damping capacities of this device can be immediately fluctuated by changingthethicknessoftheMRliquidfromviscoustosemi-strongthroughthepresentationofanattractivefield.Thegoal of this examination is to foster a fluffy controller to manage the damping properties of the MR damper. Since fluffy control utilizes master information rather than differential conditions, it takes into consideration the advancement of basic calculations.Itdoesn'tneedexactdataonunderlyingandvibrationqualitiesoftheframeworkandisinthiswayanappealing optionforcomplexandadditionallynonlinearframeworks.
Y. L. Xu (2005) thispapertoinvestigatethechanceofutilizingmagnetorheologicaldamperstoassociatetheplatformdesign to the multistory structure to forestall the whipping impact. The multistory structure was built as a slim 12-story building model,whiletheplatformstructurewasworkedasamoderatelyfirm three-storybuildingmodel.AMRdamperalongwitha currentcontrollerwasutilizedtoconnectthethree-storyworkingtothe12-storybuilding.Theuniqueattributesofthetwo structureswithnexttonoassociationandwithaninflexibleassociationwerefirstrecognized.Thetwostructuremodelswith next to no association and with the inflexible association were then tried under the scaled El Centro 1940 north–south groundmovement.Atlast,thetwostructuremodelsassociatedbytheMRdampercontrolledbyastaggeredrationalecontrol calculationweretriedunderthepredefinedgroundmovement.TheexploratoryoutcomesshowthattheMRdamperwiththe staggered rationale control calculation could essentially moderate the seismic whipping impact and diminish the seismic reactionsofboththemultistorystructureandplatformstructure.
Taichi Matsuoka (2008) The focal point of this paper is use of the model huge scope VCD to a genuine construction. Two newVCDsthathaveapowerlimitinthescopeof15kNhavebeenmadeandtransportedtotheNationalCenterforResearch onEarthquakeEngineering(NCREE)inTaiwanfortestingonathree-storystructurethatisenergizedbyahugeshaketable. ToexploredynamicpropertiesoftheVCD,executiontestsarecompletedandtheopposingpowerattributesofthedeviceare estimated.Then,vibrationtestsareledonthedesignbya shaketablewiththeVCDsintroduced.Seismic reactionsatevery story level are estimated for the Imperial Valley, El Centro north-south part of movement. A control law that depends on limiting the Lyapunov work is utilized alongside bang-bang activity of the VCD. The impacts of vibration concealment utilizingtheVCDaredemonstratedtobeaffirmed.
J.L. Zhang, (2008) Theidealboundariesofthedampingdevicescanbegottenbyutilizingthesimpleximprovementstrategy and the perplexing enhancement technique separately in the energy record of the three-layered design. The ideal number and situation of damping devices can likewise be gotten by the presentation record of control devices. Mathematical outcomes show that the ideal plan strategy proposed in this paper is viable and adaptable. It might clearly diminish the reactionsofbuildingstructures.
H. Qian (2010) This paper presents a survey of primary vibration control in structural designing, featuring brilliant constructions with shape memory combinations (SMAs). SMAs are a class of novel practical material that have exceptional properties, including shape memory impact, super elasticity impact, uncommon weakness opposition, high consumption obstruction, high damping qualities and Young's modulus-temperature relations, which made them incredible potential for seismic vibration control in structural designing. Then again, the somewhat significant expenses, practices subject to outer andinnerboundaries,lackofdefinitionofthethermomechanicalhandlingandtheissueofholdingpost-tensioningpowers whenutilizingafewkindsofSMAsarethehindrancestogrowtheutilizationofSMAs.
L. Huo (2012) The review said A creative ideal plan technique dependent on H∞ standard is introduced for the seismic reactioncontrol ofcapricious structurestructuresutilizingfluid dampers. The H∞ standard ofthe exchange work fromthe beginning to the primary reaction is chosen as the ideal target. A mathematical discretionary methodology is completed by utilizing Genetic Algorithms (GAs) to arrive at an ideal arrangement. The settling of condition of movement for the control frameworkispointlessintheidealplanprocessandtheacquiredidealboundariesofdampersarenotsubjecttotheground movementrecords.A12-storyunconventionaldesignischosenforinstance.Theresultsshowedthatthefluiddamperswith
© 2021, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page833

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
ideal boundaries procured through the proposed technique can viably lessen the underlying reaction in various site conditions.
D. T. R. Pasala (2012) In this paper an insightful review is carried on an inelastic multistoried shear working to show the viabilityofsettingNSDsanddampersatvariousareasalongthetallnessofthestructure.Ithasbeenshownthatbyputtinga NSDinaspecificstorythesuperstructureoverthatstorycanbeconfined.Ithaslikewisebeendisplayedthroughrecreation concentrates on that the NSD will restrict how much energy sent to the superstructure starting from the earliest stage. Basically,NSDgoesaboutasavibrationisolator.
Peng Zhang (2012) Grid transmission towers are indispensable parts of transmission line frameworks, which play an significantjobintheactivityofelectricalpowerframeworks.Thispaperproposesanothersortoftunedmassdamper(TMD), the beating tuned mass damper (PTMD), to redesign the seismic safe execution of a transmission tower. In the PTMD, a restricting collar with viscoelastic material bound on the internal edge is introduced to limit the stroke of the TMD and to disseminateenergythroughcrash.ThebeatingpowerisdemonstrateddependentontheHertzcontactlawwhilethebeating firmness β is assessed in a limited scale test. A multi-mass model of a 55m pinnacle is set up to confirm the viability of the PTMD mathematically. Consonant excitation and time history analysis exhibit the PTMD's predominance over the conventionalTMD.Atlast,aparametricreportisperformedfortheidealplan.
A. A. Sarlis (2013) This paper portrays a negative firmness device (NSD) that can copy debilitating of the underlying frameworkwithoutinelastictripsandextremelydurabledistortions.TheNSDmimicsyieldingbydrawinginatanendorsed relocation and by applying a power at its establishment level that goes against the primary reestablishing power. The NSD comprisesof(a)anindependentexceptionallycompactedspringinatwofoldregrettablefirmnessamplificationcomponent; and (b) a hole spring get together (GSA) system which postpones the commitment of negative solidness until the primary framework goes through an endorsed removal. The NSD utilizes twofold chevron supports that self-contain the enormous verticalpowersrequiredfortheadvancementoftheevenregrettablesolidnesswithoutmovingthesepowerstothedesign. ThispaperreportstheturnofeventsandactivityoftheNSDandpresentsscientificandcomputationaldevicesthatportray theconductofthedevice.
Rakesh Patwa (2018) This present paper dependent on the latent energy scattering tools. These gadgets are directed the movementof design bysettingtool ofadjustingmassanddampingor both. Thispresentonexhibitionoftobe specific two kindsofdamper(tunedmassdamperandviscousfluiddamper)notwithstandinginnatedampingofR.C.outlinebuilding.The 16storyunsymmetricalstructuremodularwithpracticallynodamperwithTMDandwithVFDaredissectedbytimehistory techniqueunderrudraprayag(2005)timehistoryinformation.ThisworkisconsideredtodotheadequacyofTMDandVFD which are intended for same damping esteem. The outcome of model frequencies, bury story float, dynamic reaction like speed increase, speed, uprooting and base shear will be thought about of three model. It closed the reactions of building is additionallydecreasesbyinvolvingVFDofSameDampingcoefficientasTMD,andBuildingwithoutDampers.
Lekshmi Suresh (2019) Thisreviewpresentsadifferenttunedmassdamper(MTMD)framework,whichisbasicandmore successful than a traditional single TMD framework. The framework comprises of various more modest dampers dispersed insidethe design either consistently,shifting straightly, orinviewofthejudgment ofthe planner.TMDs tuned tothe main, second, and third normal frequencies are utilized to control vibrations, consequently empowering a more extensive data transmissionofvibrationcontrolandaccomplishingexceptionaldecreasesinfloorremovals,floorspeedincreases,andbase shear. A MTMD framework was explored for various base excitations, specifically consonant and seismic. A three-levels ofopportunity outline model and three mass dampers tuned to every one of the three regular frequencies of the framework werecreated.
Athanasia K. Kazantzi (2020) Arestorationplanisintroducedforatwo-storymodernsteelstructureinIran.Thestructure wasfoundtohave unacceptable execution:The main floor two-waycomposite piecewas inclined to wildvibrationsduring typical activity (forklift vehicles), and the parallel burden opposing framework didn't agree with current seismic code arrangements. Eminently, a new vibration restoration endeavor applied to a practically indistinguishable construction had added sections and swaggers of almost 120 tons of steel with little improvement. To determine this twofold issue while regarding the base disturbance necessity for an office that works almost 24=7 and the stature/width freedom limitations because of existing modern apparatus and vehicle traffic, a consolidated recovery plot was suggested that included: (1)
© 2021, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page834

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
keeping the additional sections of the bombed restoration conspire, (2) solidifying the joists, (3) embracing switch support dampersinthefundamentalbraces,and(4)fortifyingthecurrentsidelongX-supportsandtheirassociations.
These reviews indicate that various energy dissipation technologies are crucial for regulating a building's reaction to an earthquake.TheTMDaidsinreducingthestructure'sdeformation,drift,baseshear,andfirstmodefrequency.Buttheissue withTMDisthateachstructuremusthaveauniquedesignbasedonitsmassandstiffness. ofconstruction.Despitethefact thatVFDisreadilyaccessibleandcomesinavarietyofmassesanddamping,theywerealsoinneedofthecorrectapproach to build weak stories above the structure that had to be rigid. VFD also aids in lowering the total distortion and responsivenessonthebuilding.
[1] Manuel Aguirre (1991) " Device For Control Of Building Settlement And For Seismic Protection" J. Geotech. Engrg. 1991.117:1848-1859.
[2] Maria Q. Feng (1995) " Vibration Control Of Tall Buildings Using Mega Subconfiguration " Journal Of Engineering Mechanics
[3] Lih-ShingFur,HenryT.Y.Yang,zandSeshasayeeAnkiredde (1996)"VibrationControlOfTallBuildingsUnderSeismic AndWindLoads"JournalOfStructuralEngineering.
[4] Gina J. Lee-Glauser; Goodarz Ahmadi and Lucas G. Horta (1997) " Integrated Passive/Active Vibration Absorber For MultistoryBuildings"JournalOfStructuralEngineering.
[5] FranklinY.Cheng,FellowandHongpingJiang(1998)"HybridControlOfSeismicStructuresWithOptimalPlacementOf ControlDevices"PerspectivesinScienceJournalOfAerospaceEngineering
[6] Takayuki Teramoto (2000) " Japanese Structural Control System for Building" Advanced Technology in Structural EngineeringASCE.
[7] NaritoKurata(2001)"ActualSeismicResponseControlBuildingwithSemi-activeDamperSystem"ASCE.
[8] Akira Fukukita, Tomoo Saito and Keiji Shiba (2004) " Control Effect for 20-Story Benchmark Building Using Passive or SemiactiveDevice"JournalOfEngineeringMechanics©Asce
[9] OsamuYoshidaandShirleyJ.Dyke(2004)"SeismicControlofaNonlinearBenchmarkBuildingUsingSmartDampers"J. Eng.Mech.2004.130:386-392
[10] Claudia Mara Dias Wilson (2005) " Some Structural Vibration Reduction Using Fuzzy Control of Magnetorheological Dampers"ASCE
[11] J.L.Zhang,J.S.Jiang(2008)" AnOptimalVibrationControlandDampingDevicesDesignforThreeDimensionalBuilding Structures"Earth&Space2008.
[12] H.Quian(2010)"Seismicvibrationcontrolofcivilstructuresusingshapememory"EarthandSpace2010:Engineering, Science,Construction,andOperationsinChallengingEnvironments©2010ASCE.
[13] D.T.R.Pasala (2012)"NegativeStiffnessDeviceforSeismicResponseControlofMultistoryBuildings"20thAnalysis& ComputationSpecialtyConference©2012ASCE
[14] Peng Zhang, Gangbing Song, Hong-Nan Li and You-Xin Lin (2013) " Seismic control of power transmission tower using PoundingTMD"JournalofEngineeringMechanicsdoi:10.1061/(ASCE)EM.1943-7889.0000576
© 2021, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page835
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[15] Ras, A. and Boumechra , N. (2016) “Seismic energy dissipation study of linear fluid viscous dampers in steel structure design.”AlexandriaEngineeringJournal55,2821–2832
[16] Rakesh Patwa (2018) " Comparative Study of Seismic Analysis of Dampers in Asymmetrical R.C. Frame Building" International Journal for Research in Applied Science & Engineering Technology (IJRASET) ISSN: 2321-9653; IC Value: 45.98;SJImpactFactor:6.887Volume6IssueVIII
[17] Athanasia K. Kazantzi and Dimitrios Vamvatsikos (2020) " Seismic and Vibration Performance Rehabilitation for an IndustrialSteelBuilding"Pract.Period.Struct.Des.Constr.,2020,25(2):05020001.
© 2021, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page836
