International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
1PG Scholar (Structural Engineering)
2Professor & HOD (Civil Engineering Department)
Chalapathi Institute of Technology, Andhra Pradesh, India. ***
ABSTRACT :- Many reinforced concrete frame structures in India were designed and built previous to 2002. The seismiclawIS1893wasrevisedin2002.Hence,structures built previous to 2002 don't comply with the codal demand. Further, some of the India structures built over the once many times indeed after 2002 are seismically deficient because of lack of mindfulness of builders regarding the seismic geste of structures. utmost of the being structures in this megacity are designed for gravenessloadsonly.utmostofthestructureswhichhave infilledwallshaven'tconsideredinfillsintheirdesign.
A large number of being structures in India need seismic evaluation due to colorful reasons similar as, resistance withthecodalconditions,streamliningoflaw,poordesign practice and change in the use of the structure. still, the being deficient structures in India some regions are in Zone III can be upgraded with some recuperation to sustaintheanticipatedperformanceposition.
Thestudyhighlightstheseismicevaluation of the existing hostel structure, grounded on the geste of G 2 reinforced concrete bare frame and infill frame structure subordinated to Zone- III position earthquake forces. The three dimensional reinforced concrete structures are anatomized by nonlinear static analysis( Pushover Analysis) using SAP2000 software. The analysis results showed the performance situations, geste of the factors, failuremediumandsequenceofhingeconformationofthe structure.
Inflexibility of ground shaking at a given position during an earthquake can be minor, moderate and strong. fairly speaking, minor shaking occurs constantly; moderate shaking sometimes and strong shaking infrequently.
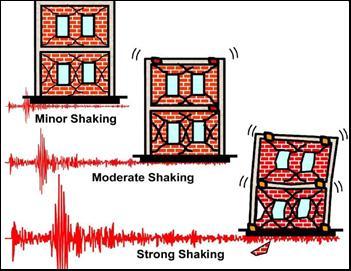
The masterminds don't essay to make an earthquake evidence structure that won't get damaged indeed during the rare but strong earthquake; similar structures will be too robust and also precious. rather, the engineering intention is to make structures earthquake resistant; similar structures repel the goods of ground shaking, although they may get damaged oppressively but would not collapse during the strong earthquake. therefore, safety of people and contents is assured in earthquakeresistantstructures,andtherebyadisasterisavoided.This is a major ideal of seismic design canons throughout the world.
The consequences of damage have to be kept in view inthedesigngospel.Forillustration,importantstructures, like hospitals and fire stations, play a pivotal part inpostearthquake conditioning and must remain functional incontinently after the earthquake. These structures must sustainveritablylittle damageandshould bedesignedfor aadvancedpositionofearthquakeprotection.Thecollapse of heads during earthquakes can beget flooding in the downstream rung, which itself could lead to a secondary disaster. thus, heads( and also, nuclear power shops) should be designed for a still advanced position of earthquakestir.
Figure1PerformanceoftheBuilding
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Objectives:- This study aims to investigate the effect of brickmasonryinfillwallonareinforcedconcretemoment resisting frame conventionally designed as a bare frame, usingavailablemacromodel.Thespecificobjectivesofthe studyare:
1. To study the effect of brick masonry infill wall on existing reinforced concrete moment resisting frame, subjected to earthquake induced by the lateralload.
2. To study the effect of an existing reinforced concrete moment resisting bare frame, subjected toearthquakeinducedbythelateralload.
Theresearchworkhadbeencarriedoutinthreephases.In theFirstphase of thestudy isthe creation andanalysisof the model has to evaluate the performance of a typical selected deficient existing building having different types of lateral load resisting systems such as R.C. frame and In filledframebehaviorwithrespecttoseismicvulnerability. For this evaluation, a pushover analysis had been performed. The analysis result showed the performance levels,behaviorofthecomponentsandfailuremechanism of the building. It also provided the sequence of hinge formation. Based on the analysis the elements which neededretrofittingwereidentified.
The Second phase of the study involved the seismic strengthening of the existing bare framestructure basedontheSAP2000analysisresults.Forstrengthening of the existing building Glass Fiber Reinforced Polymer Composite (GFRP) was used extensively to address the strength requirements related to flexure and shear in the structuralsystem.Thisphasehighlightedthebehaviorand performance of composite beams by the moment –rotationrelationandtheductilityofthetestedbeams.The testresultshowedthatthebeamsstrengthenedwithGFRP wrappedexhibitedbetterperformance.
EVALUATION OF SEISMIC PERFORMANCE:- To select an appropriate retrofitting method, an accurate evaluation of the seismic performance and the condition of an existing structureisnecessary.Basedonthisevaluation,engineers canchoosethemosteffectiveretrofittechniqueamongthe various intervention techniques and optimize the improvement in seismic performance for an existing structure. Seismic deficiencies should first be identified throughaseismicevaluationofthestructure.Theselection of an appropriate intervention technique based on the
structural type and its deficiencies is the most important step in retrofitting. Seismic evaluation consists of gatheringas-builtinformationandobtainingtheresultsof a structural analysis based on collected data. The Prestandard and Commentary for the Seismic Rehabilitation of Buildings – FEMA 356 (2000) provides guidance for evaluating the seismic performance of existing structures and determining the necessary retrofittingmethodstoachievetheperformanceobjectives ASCE(2000).
The present study was to evaluate the behavior of G+2 reinforced concrete bare frame and infill frame building subjected to zone III level earthquake forces. The three dimensionalreinforcedconcretestructureswereanalyzed by nonlinear static analysis (Pushover Analysis) using SAP2000 software. The analysis results showed the performance levels, behavior of the components and failure mechanism of the building. It also showed the sequence of hinge formation. Based on the analysis, the elementswhichneedretrofittingwereidentified.
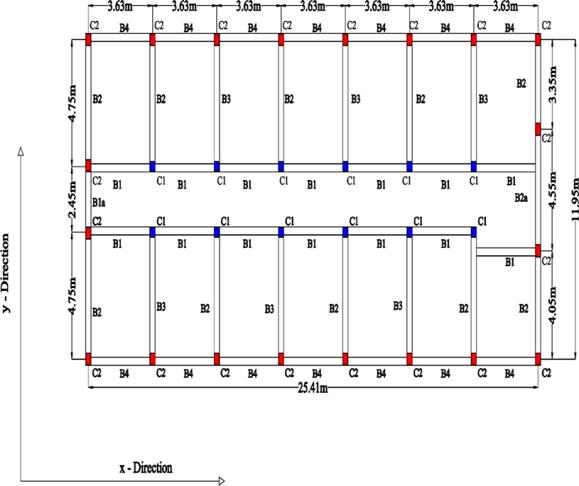
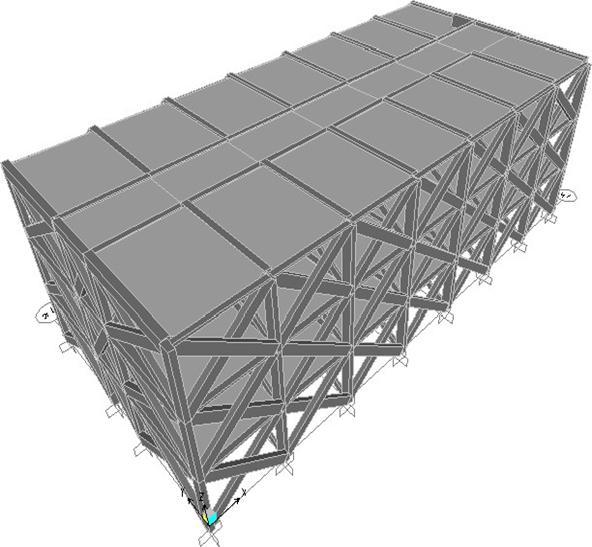
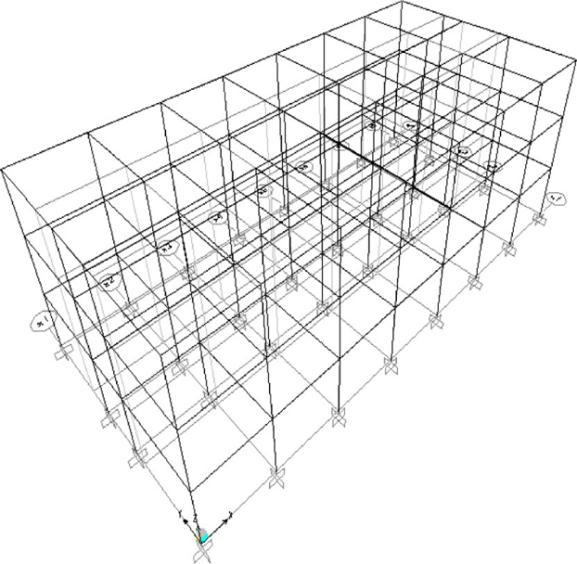
The three dimensional frame of the selected building having different types of lateral load resisting systems suchasR.C.bareframeandInfilledframewereconsidered in this study. Figure 3.4 shows the plan of the building representingtheXandYdirectionusedforanalysis.Figure 3.5 shows a three dimensional line sketch of the frame in the X, Y and Z direction. Figure 3.4 shows a typical longitudinal bare frame (in the X direction in XZ plane). Figure 3.5 shows a configuration model of braces representing infills. Figure 3.6 shows an elevation of the existing study hostel building. The building exists in India and is a typical example of many such buildings in this region.
Figure2PlanoftheExistingHostelBuilding
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The basic computer model (without the pushover data) in the usual manner was created. The graphical interfaceofSAP2000makesthisaquickandeasytask.
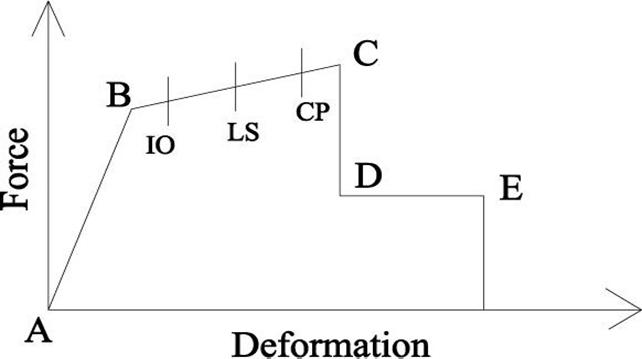
The properties and acceptance criteria for the pushoverhingesweredefined.
The program includes several built-in default hinge properties that are based on average values from ATC-40 (1996) for concrete members and average values from FEMA-273 (1997) for steel members. These built in properties were used for preliminary analyses but userdefinedpropertieswereusedforfinalanalyses.
The pushover hinges on the model were located byselectingtheframemembersandassigningthemoneor morehingepropertiesathingelocations.
The pushover load cases were defined in SAP2000, where more than one pushover load case could
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
be run in the same analysis. Also a pushover load case could be started from the final conditions of another pushover load case that was previously run in the same analysis. Typically the first pushover load case is used to apply gravity load and then subsequent lateral pushover loadcasesarespecifiedtostartfromthefinalconditionsof the gravity pushover. Pushover load cases can be force controlled, that is, pushed to a certain defined force level, ortheycanbedisplacementcontrolled,thatis,pushedtoa specifieddisplacement.
Typically a gravity load pushover is force controlled and lateral pushovers are displacement controlled.SAP2000allowsthedistributionoflateralforce usedinthepushovertobebasedonauniformacceleration ina specifieddirection,a specifiedmodeshape, ora userdefinedstaticloadcase.
Initially the basic static analysis was made to run in SAP 2000 and then the static nonlinear pushover analysis.
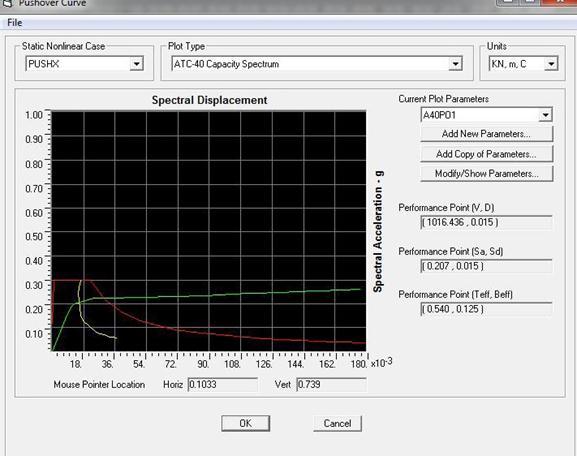
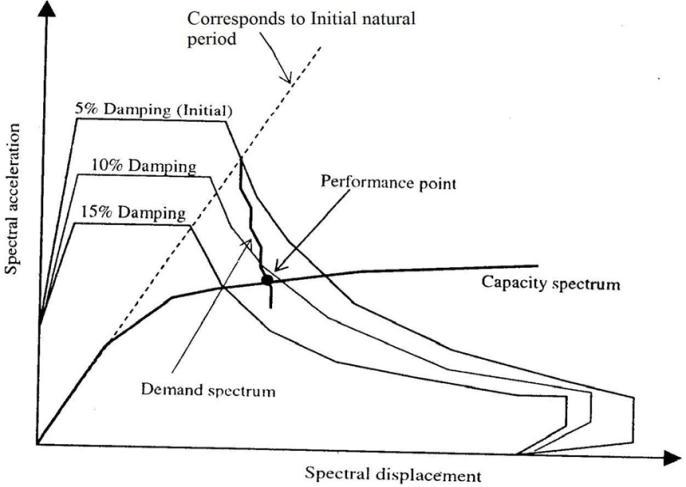
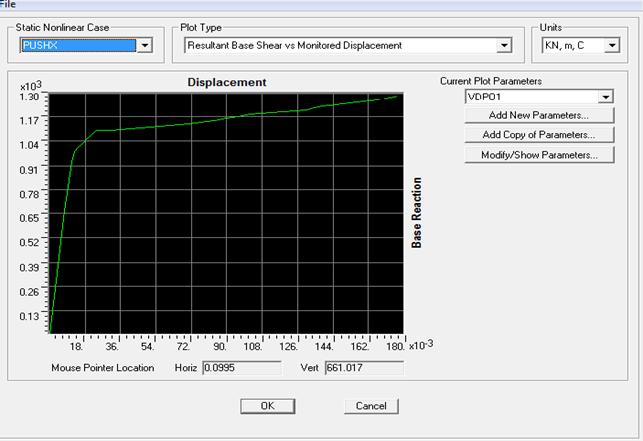
Capacity Spectrum and Building Performance Level:Capacityspectrumis the capacitycurve transformedfrom base shear versus roof displacement co-ordinates into spectral acceleration versus spectral displacement (Sa Vs Sd) co-ordinates. The performance point is obtained by superimposing demand spectrum on capacity curve transformed into spectral coordinates. To have desired performance, every structure has to be designed for the spectral acceleration corresponding to the performance point.
Figure
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
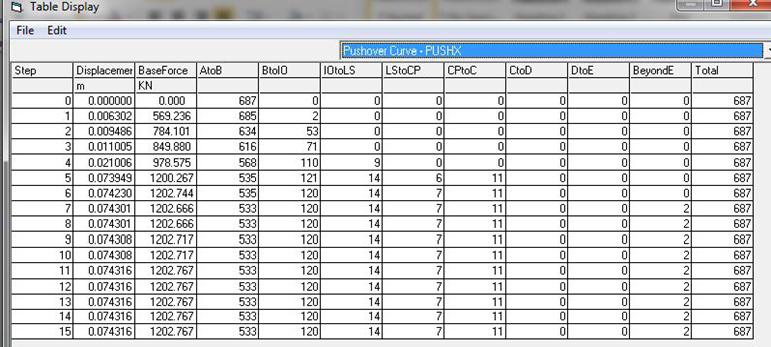
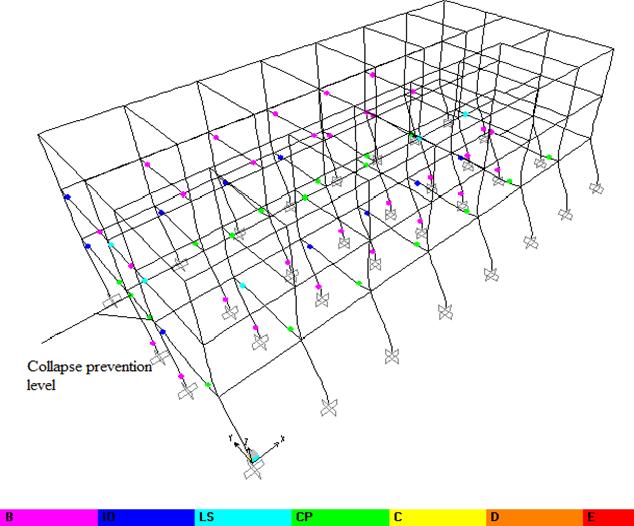
Figure12HingesFormationinX-DirectionatPerformance Level
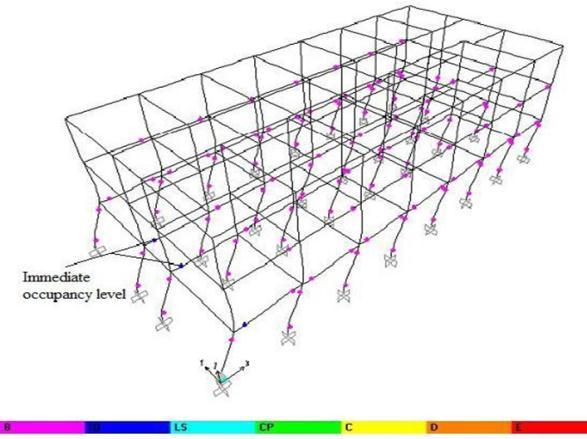
Figure14 HingesFormationinYdirectionatPerformance Level
Figure13CapacitySpectrumforBareFrameinY-direction
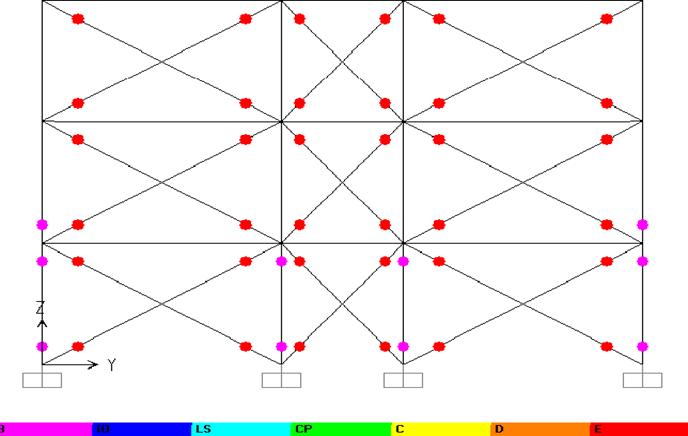
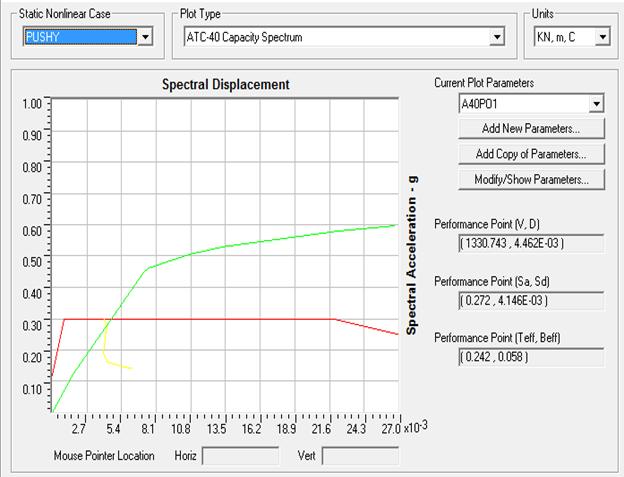
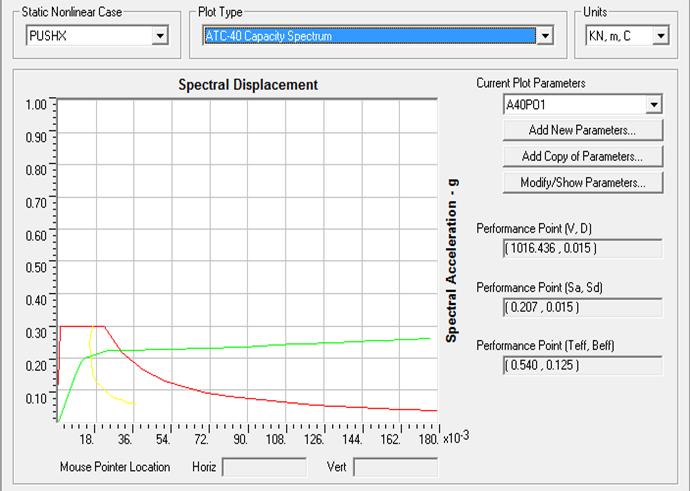
Figure15SequenceofHingesFormationinY-Direction
The structural designers of the India designed the buildings considering them as bare frame or bare frame with infill. In case of buildings designed as bare frame, when the first hinge occurs the beam collapse first in the event of an earthquake in the city. This is the case for the existingbuildingselectedfortheresearchwork.
The study involved the creation and analysis of the model and evaluation of the performance of a typical selected building which has different types of lateral load resisting systems such as R.C. bare frame and Infilled frame behavior with respect to seismic vulnerability. For this evaluation, a pushover analysis had been performed. The analysis results showed the performance levels, behavior of the components and failure mechanism of the
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
building. It also showed the sequence of hinge formation. Based on the analysis the elements which needed retrofittingwereidentified.
The bare frame analysis predicts a beam failure mechanismfirst.InIndia manybuildingshaveinfills.Infill frameanalysispredictscolumntofailbeforebeamfailure. Therefore,theinfillbuildingshadaweakness.
To avoid premature collapse of the column, the columnshadtoberetrofittedtohaveadequatestrengthso that at the performance point columns do not reach yield level.
Therefore weak columns in X and Y directions must be strengthened by using locally practiced strengtheningtechniques,beforeanearthquake.
Alexander G.Tsonos, “Effectiveness of CFRPJackets and RC-Jackets in Post-Earthquake and Pre-Earthquake Retrofitting of Beam–Column subassemblages”, Engineering Structures, Vol.30, Issue3,pp.777–793,2008.
AshrafHabibullah,S.E.andStephen,S.E.“Practical Three dimensional Nonlinear Static Pushover Analyses”, Published in Structure Magazine, winter,1998.
ATC 40. “Seismic Evaluation and Retrofit of ConcreteBuildings”,AppliedTechnologyCouncil”, 1996.
Binay Charan Shrestha, “Effect of Unreinforced Full and Partial Infilled Brick Masonry Wall in RC Frame under Seismic Loading”, Graduate School, KasetsartUniversity,2008.\
Cengizhan Durucan and Murat Dicleli, “Analytical Study on Seismic Retrofitting of Reinforced Concrete Buildings Using Steel Braces with Shear Link”,EngineeringStructures,Vol.32,Issue10,pp. 2995–3010,2010.
Ei-Sokkary, H. and Galal, K. “Analytical Investigation of the Seismic Performance of RC Frames Rehabilitated using Different Rehabilitation Techniques”, Engineering Structures, Vol. 31,pp.1955-1966,2009.
Elnashai, A.S. “Advanced Inelastic Static (pushover)AnalysisforEarthquakeApplications”, Journal of Structural Engineering and Mechanics, Vol.12,No.1,pp.51-69,2001.
FEMA 398, “Incremental Seismic Rehabilitation of MultifamilyApartmentBuildings”,WorldInstitute forDisasterRiskManagement,Alexandria,2004.
FEMA 399, “Incremental Seismic Rehabilitation of RetailBuildings”,WorldInstituteforDisasterRisk Management,Alexandria,2004.
Gopen Paul and Pankaj Agarwal, “Experimental Verification of Seismic Evaluation of RC Frame BuildingDesignedasperPreviousISCodesbefore and after Retrofitting by Using Steel Bracing”, Asian Journal of Civil Engineering (Building And Housing)Vol.13,No.2,pp.165-179,2012.
IS: 456, “Plain and Reinforced Concrete- code of Practice, Bureau of Indian Standards, Manak Bhavan, 9, Bahadur Shah Zafer Marg, New Delhi, 110002,India,2000.
IS: 875, “Code of practice for Design Loads (other thanearthquake)forBuildingandStructures-Part 2", Imposed loads Indian Standards, New Delhi, 1987.
Kunnath, S.K., Hoffmann, G., Reinhorn, A. M. and Mander, J. B. “Gravity Load-Designed Reinforced Concrete Buildings - Part II: Evaluation of Detailing Enhancements”, ACI Structural Journal, Vol.92,No.4,pp.470-478,1995.
Murty, C.V.R. “What is Seismic Design Philosophy for Buildings?” Learning Earthquake Design and Construction,EarthquakeTip8,IndianInstituteof TechnologyKanpur,India,2002a.
Pankaj Agarwal and Manish Shrikhande, “Earthquake Resistant Design of Structures”, PrenticeHallofIndia private limited,NewDelhi, 2008.
Pavan Kumar, V.S.R., Rayaprolu1 and Polu Raju P. “Incorporation of Various Seismic Retrofitting TechniquesandMaterialsforRCFramedBuilding Using SAP2000”, International Journal of
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
EmergingtrendsinEngineeringandDevelopment, Issue2,Vol.32012.
Park,J.M.,Hong,S.N.,OH,M.H.,Kim,T.W.andPark, S.K. “Evaluation of Behavior and Ductility of Reinforced concrete Beams Strengthened with AFRP”, International Conference of International Institute for FRP in Construction for Asia pacific Region,2009.
Sadjadi, R., Kianoush, M. R. and Talebi, S. “Seismic Performance of Reinforced Concrete Moment ResistingFrames”,EngineeringStructures,Vol.29, pp.2365-2380,2007.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page760
