International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
2
, S. Harish Krishnan3, Vaishali Nirgude41,2,3Student, Department of Computer Engineering, Thakur College of Engineering and Technology, Kandivali (East), Mumbai – 400101, Maharashtra, India
4Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Engineering, Thakur College of Engineering and Technology, Kandivali (East), Mumbai – 400101, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - In recent years, the premise of entertainment and experience has been recognized in the field of education, as it has in other fields. It is indicated that subjects incorporating entertainment attract consumers’ attention more, and events providing consumers with a perception are more permanent and recollective. Education is among the fields in which entertainment is quite active. As a result of these specific advancements in this collaborative field, global knowledge now incorporates ‘edutainment’ as a concept of interest. Edutainment is a term that refers to the combination of entertainment and education, or subjectively, the marriage of education and entertainment. The primary goal of this combination is to supplement education along with the evergrowing field of entertainment. The use of video games in teaching practice is studied multifaceted, along with formats and requirements of educational games, methods for effectiveness assessment, and the effect of games on students. The controversial nature of game-based learning effect on students requires deeper research, as the increase in motivation and learning efficiency cannot be disputed, as well as the negative impact of long gaming on cognitive abilities, emotional state and social skills of students.
In pushing forward this ideology into existence, productivity and adaptability factors with respect to the specific methodof throughput play a role of high priority. To help predetermine the possible outcomes of the developed system on hand, this paper provides a review specifically on the ‘educational gaming’ industry in respect of aforementioned factors and beneficial collaborative opinions.
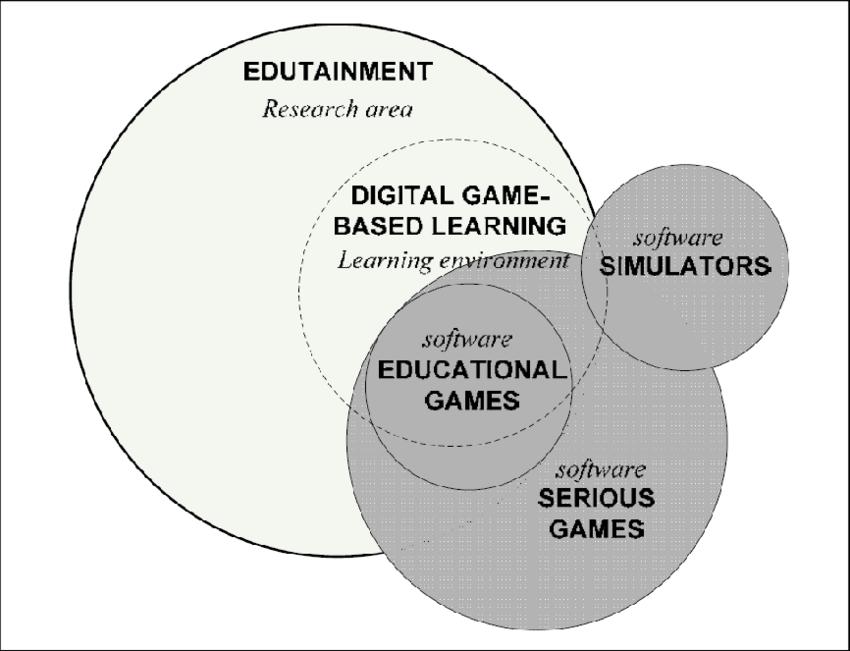
When it comes to educators' responsibility, instructional media are viewed as an effective alternative to complementing traditional teaching methods in terms of motivatingandencouragingpupilstostudy.Manyofthese dutiesgounfulfilledinscientificclassessinceengagingand motivating learners to engage in class is a difficult undertaking,asseveralstudieshaveshown.Students,onthe other hand, are more excited about learning when it is engaging and interactive. Learning and teamwork can be enhanced using educational games that are interactive. Activelearningcanbeachieved throughtheuseofgames, whichfeatureinteractiveanduniqueelements.Inadditionto making the learning process more enjoyable, they also inspirepupilstoparticipateinclassandpromoteapositive attitude toward education. As a result, students who are engagedandactivelyinvolvedintheeducationalprocessare morelikelytoretaintheinformationtheylearn,makingit easiertorecollectlateron.Educationalgamescanbeusedin a variety of ways by teachers to reinforce previously acquired material, introduce new ideas, or just get their pupilsmoreinvolved.Thebeginningandfinishofaclasscan both benefit from the inclusion of learning programmes. Students'interestanddrivetostudycanbesparkedbythese activities,andtheycanalsoservetoreview,reinforce,and testpreviouslytaughtmaterial.
KeyWords: Educational games, Edutainment, Serious gaming, Teaching, Learning
Duetotherapidevolutionoftechnology,instructionalgames andsimulationsarenowfrequentlyusedinschoolsacross thenation.Thereisalreadyasubstantialcorpusofresearch that examines the relationship between gaming and education. Games enabled by the internet have become increasinglypopularinrecentyears.Students,teachers,and game designers all have a vested interest in this area of researchbecauseofitsrelevancetoonlineeducation.Video games, virtual worlds, and Massive Multiplayer Online Games (MMPOGs) are becoming increasingly popular instructionaltoolsforeducatorsandpolicymakers.
Several aspects of student performance, engagement, and desire for learning are impacted differently by games and simulations. This research does not provide a
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
comprehensiveoverviewofhowthesetoolsmightbeusedin differentacademicsettingssinceitfocusessolelyonspecific fields.Asaresult,ateacher'sdiscretionisoftenrequiredin determininghowwellinteractiveexerciseslikegamesand simulationsfitintothecurriculum.
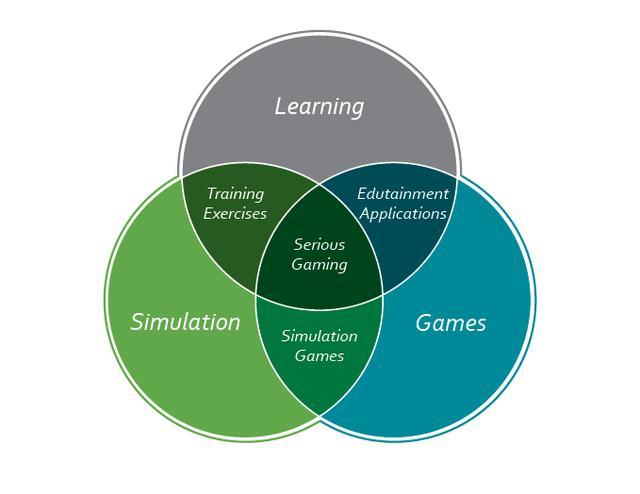
Inaccordancewiththesolefocusofthissection,thepurpose of this paper is to undertake a meta-analysis of scientific researchontheeducationalvalueofgames,andtodisclose thetypesofresearchandtheirinferences.Thereisaclear needtoexaminehowgame-basedlearninghasbeenstudied andhowtheresultsofsuchstudiescaninformpractitioners due to the widespread use of educational games. For educationalgamepractitioners,thereisapressingneedto not only demonstrate the value and effectiveness of educationalgames,butalsotoprovideusefulinputonhow toimplementeducationalgamesinpractise.Anothergoalis to give a general overview of the various types of studies thatevaluateeducationalgamesandtoidentifytrendsinthe fieldofseriousgamesresearch.Finally,weevaluatewhether the results of observational assessments in the field of complexgamesarelinkedtotheinvolvementoftheassessor asastakeholderinthedesignanddevelopmentprocess.
opencharacterization,suchastheoneprovidedbyPrensky, which includes the element rules, goals and objectives, outcomesandfeedback,conflictandcompetitionalongwith opposition and interaction, as well as representation or narrative, in order to better understand the situation. It is also crucial to consider the concept of collaboration when playing games;there are many games that do not place a strong emphasis on competitive features or winning in particular.
Toconfirmtheouttakesof whatthisresearchcontributes towards,resultsintheformofsurveyanswersarestudied andsynthesizedintothefinalreviewofhowrevolutionary thisparticulardomaincouldpotentiallyturnouttobe.
Thereisaplethoraofdefinitionsforcomputergames,aswell as widely accepted broad concepts of what videogames represent. [4] For instance, Salen and Zimmerman outline eight alternative meanings that each emphasize different aspectsofthetermandarriveataverysimplifieddefinition: "Agameisasysteminwhichplayersengageinanartificial conflict that is specified by rules and that results in a quantifiable outcome,". Particularly restrictive is the constraint on quantifiable outcomes, which is a significant limitationofthedefinition.Itisoftenbeneficialtousemore
Seriousgames,whichweconsidertobea collectivename, compriseavarietyofinstructionalgamesaswellasgamesfor avarietyofotherobjectives,suchastraining,recuperation, advertising, and supportive behaviors. Serious games are becoming increasingly popular. [6] According to Zyda, the word"seriousgames"means“amentalcontestthatisplayed withacomputerinaccordancewithspecificrules,andthatis usedtofurthergovernmentorbusinesstraining,education, health,publicpolicy,andstrategiccommunicationobjectives throughtheuseofamusement."Althoughthisdefinitionis very wide, its emphasis on amusement can occasionally conflict with what is sold as serious games in the marketplace.Theterm"seriousgames"referstoacontinuum between games with a purpose and experiencing environmentsforapurpose,whichMarshdescribesthrough anexampleas:manyseriousgameapplications,ratherthan relying on the game play component, make use of the technology that are normally associated with videogames. These applications, which are referred to as virtual environments and digital media, do not have any of the qualitiesassociatedwithtraditionalgaming.Specifically,for thesakeofourresearch,seriousgamesrefertogamesthat involve the player and contribute to the achievement of a definedgoalratherthansheerenjoyment.Whenitcomesto seriousgames,thepurposecanbedefinedeitherbytheuser orbythegame'sdesigner,whichmeansthatacommercialoff theshelf(COTS)gamethatisutilizedforpurposesotherthan enjoymentcanbecalledaseriousgame.Inthisregard,itis important to note that the use of game and visualization technologies, simulations, and virtual worlds for reasons otherthanamusementmightbeincludedwithinthescopeof thisterm.Whilethisdefinitionencompassesbothdigitaland non-digitalgames,itshouldbenotedthatthevastmajorityof referencestoseriousgamesare,inreality,todigital-based seriousgames.
[1]Acomprehensiveoverviewofstudiesoncomputergames is presented by Tobias et al., who assess the evidence regarding the effectiveness of computer games as instructionaltools.95studiesaredividedintogroupsbased on their purpose and knowledge claim. The following classificationshavebeenidentified:
Thetransferofknowledge,abilities,andattitudesgained fromgamestoreal-worldworkisamajorgoal.
Cognitive processes such as visual attention, spatial visualization,andproblemsolvingareaffected.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Improvingperformanceandlearninginavarietyoftopics.
Theapplicationofgamesineducationalcircumstances.
Theimpactofplayinggamesonstudents'abilitytolearn inschool.
of cognitive abilities or the modification of attitudes. Furthermore,theyonlyincluderesearchthatgivesstatistical findings and evaluate the difference between regular classroom instructionandcomputer gaming orinteractive simulationinstruction.Thisdemonstratesthewiderangeof possibilitiesinthefield.
Effectsonaggression,animosity,andmotivation.
Ashiftinone'sattitude.
Tobiasandcolleagues conclude thatthefindingsof the studies reviewed indicate that instructional games have potential.However,sincetheyidentifiedanumberofareasin whichadditionalresearchandtheoreticaladvancementare required,theseclaimsareregardedasprovisional."Thereis significantlymoreenthusiasmfordescribingtheaffordances ofgamesandtheirmotivatingcharacteristicsthanthereisfor conductingresearchtodemonstratethattheseaffordances are being used to attain instructional aims or to resolve problemsidentifiedinpriorresearch,"Tobiasandcolleagues conclude[1].Oneinterpretationofthisissueisthatthereisa desire within the community to produce and evaluate prototypes rather than devoting greater resources to the actualuseoftheprototypesineducationalsituations.
Egenfeldt-Nielsen provides an overview of the instructional usage of computer games by studying the fundamental learning theories that underpin these games' development.Thereisapaucityofunderstandingaboutthe ramificationsofemployinggamesineducationalsituations, owingtothefactthatthisparticularsubjecthasitsownsetof issues in terms of techniques, emphasis, and appropriate studyquestions.Whenitcomestoeducationalgamedesign, he points out that all of the main learning techniques (philosophy,cognitivism,constructionism,andsocio-cultural approaches) have something to offer, and that there are namesouttherethathighlighteachofthem.Asaresult,there isnosilverbullet,andtheworldofeducationalgamesisnot uniforminitsapproach.
Hays provides an analysis of 48 empirical research publicationsontheeffectivenessofinstructionalgamesthat were published between 1982 and 2005, and draws the conclusion that empirical studies on the instructional effectiveness of games are scattered and not necessarily methodologicallysound.Furthermore,thereisnoevidenceto suggestthatgamesarethemosteffectiveinstructionaltoolin all circumstances. This suggests that the educational atmosphereaswellastheinstructional activitiesthattake placeinconjunctionwiththegamearecritical.
[12] Vogel and colleagues report a meta-analysis of computergamesandsimulationsforeducationalpurposes. They assert that it is difficult to define the nature of the relationshipbetweengamesandlearningsincethereisno consensus on which abilities and domains should be considered when analysing the relationship. This is addressedbyfocusingonstudiesinvolvingthedevelopment
[10] In Ke's opinion, empirical research on instructional games is scattered. Ke also points out that much of the evaluation of games has been anecdotal, descriptive, or judgemental in nature, citing Dempsey et al. as sources of information.Kegivesanexaminationofthemethodologies thathavebeenemployedandtheoutcomesoftheempirical researchthathasbeencarriedout.Itisnoteworthythatno consideration is given to the evaluator's independence or whethertheevaluatorhasashareholderinthedevelopment ofthegame.
The work proposed in this paper addresses the following concerns:
i)Toidentifysubstantialpiecesofputtingforwardauserefficientedutainmentproduct.
ii)Tocategorizeandlookoverthevarietyofissuesfacedby developers in selecting the ideal mode of presenting the productofinterest.
iii)Toinfersuppositionsregardingproductlikeabilityand provide a logical outlook on the existence of potential growthintheedutainmentdomain.
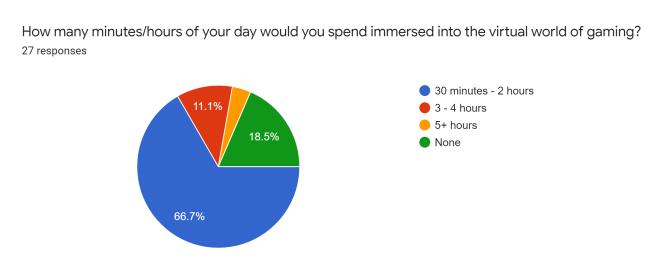
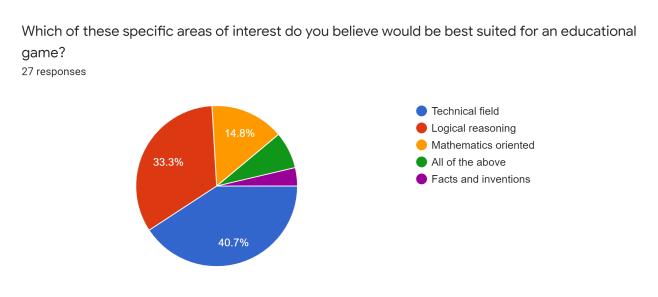
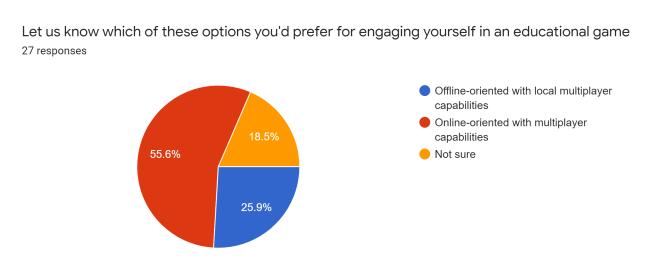
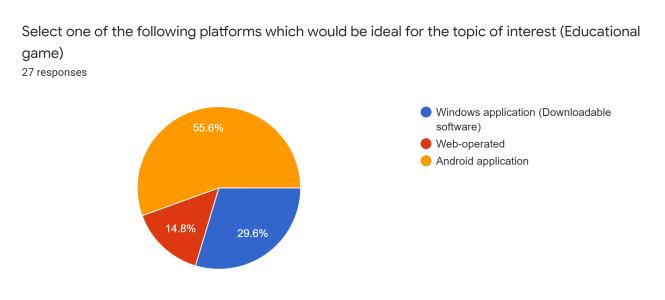
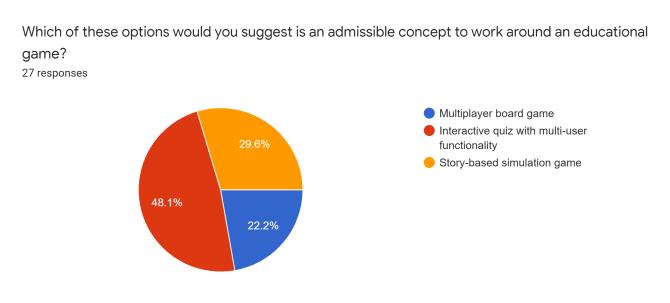
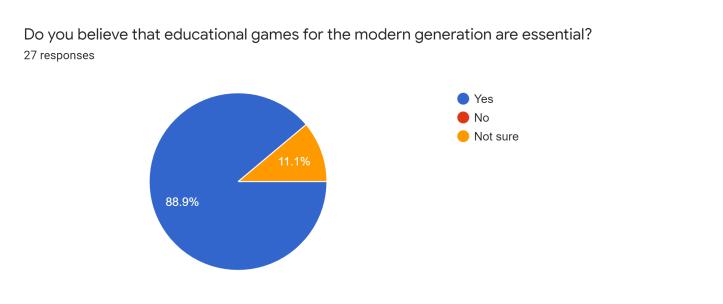
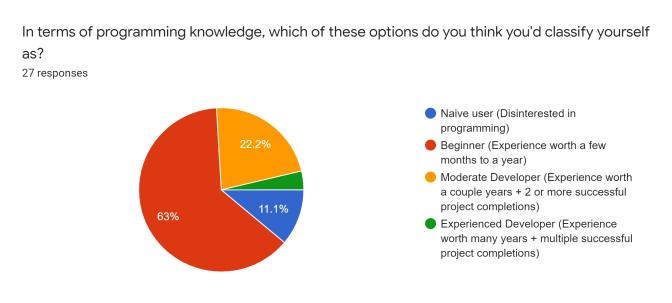
After reviewing the critical inferences along with the supportiveoutlooksdecipheredthroughtheevaluations,we developed a conceptual survey that helps understand the varietyofopinionsthatthetargetusersputforwardthrough theinvolvementofresourcefulquestionsentailingspecific categorizationinreferencetotheenticementandefficiency factors.Thefollowingarescreenshotsoftheresultsobtained fromamassivenumberofinterestedusers(112responses, specifically):
1)
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
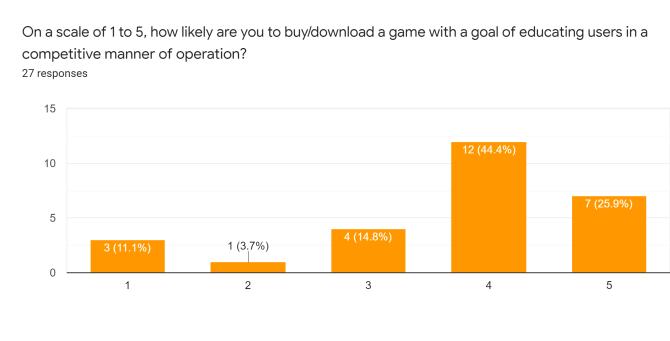
The survey formulated several differences amongst the varietyofsurveytakersasclearlyobservedintheprevious section.Asindicatedintheresponsesproducedovertime, theconcernedpublicopinionrowstowardstheideologyof incorporatingtheuseofeducationalgamestohelpbuilda community of technology-driven learners that could potentially develop newer concepts of perceptions into concerned topics of interest. Devising interactivity capabilitiesintothedevelopedproductcatchestheeyeofthe moderngenerationintermsoffulfillingtheneedofcognitive andhealthypsychologicaldevelopmentconcerns.Basingthe systeminavirtualfieldofavarietyofenthusiasticplayers turnedmoreheadsasopposedtosoloridingtheprogram.As a matter of the category of specific educational fields of interestthatcouldpotentiallybethemaintopicofinterest forthegames,thetechnicalfieldcaughtasignificantamount of attention as compared to the likes of other fields, showcasingasenseofinterestfromtheuserstowardsthe virtual world even further. As a result of the above inferences,wecouldconsiderthatonlineeducationalgames portray a high rate of curiosity and attention. The users would most definitely be open to trying out possible venturesintodevelopingeducationalgames.Itmightnotbe possible to push through this domain with high quality productsduetocostandbusinessconcerns.However,basic, and inexpensive resources, can be used to build diverse instructionalgamesforconcept-richtopicsthatstudentsfind challenging to learn. Students' motivation to learn and interpersonalskillscanbothbeimprovedinthisway.Future studentscanalsobenefitfromthegamescreated.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 12 | Dec 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[1] S. Tobias, J. D. Fletcher, D. Y. Dai, and A. P. Wind, ‘Review ofresearch on computer games’, Computer games and instruction, pp.127–222,2011.
[2] J. J.Vogel, D.S. Vogel,J. Cannon-Bowers, C. A.Bowers, K. Muse, and M. Wright, ‘Computer gaming and interactive simulations forlearning: A meta-analysis’, Journal of Educational ComputingResearch,vol.34,no. 3,pp.229–243,2006.
[3] J. Kirriemuir and A. McFarlane, ‘Literature review in games andlearning’,2004.
[4] K.SalenandE.Zimmerman,Rulesofplay:Gamedesign fundamentals.MITpress,2003.
[5] M.Prensky,‘Digitalnatives,digitalimmigrantsPart1’, Onthehorizon,vol.9,no.5,pp.1–6,2001.
[6] M. Zyda, ‘From visual simulation to virtual reality to games’,Computer,vol.38,no.9,pp.25–32,2005.
[7] T. Marsh,‘Seriousgamescontinuum: Betweengames forpurposeandexperientialenvironmentsforpurpose’, EntertainmentComputing,vol.2,no.2,pp.61–68,2011.
[8] R. T. Hays,‘Theeffectivenessofinstructionalgames: A literaturereviewanddiscussion’,DTICDocument,2005.
[9] S. Egenfeldt-Nielsen, ‘Overview of research on the educationaluseofvideogames’,Digitalkompetanse,vol. 1,no.3,pp.184–213,2006.
[10] F. Ke, ‘A qualitative meta-analysis of computer games as learningtools’, Handbook of research on effective electronic gaming ineducation,vol.1,pp.1–32,2009.
[11] J. V. Dempsey, K. Rasmussen, and B. Lucassen, ‘Instructional gaming’, Implications for instructional technology.’, presented at the Annual Meeting of the Association for Educational Communications and Technology,Nashville,TN,1996.
[12] S. Kim and M. Chang, ‘Computer games for the math achievement of diverse students’, Educational Technology&Society,vol.13,no.3,pp.224–232,2010.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page55
