Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022
www.irjet.net

p-ISSN:2395-0072

Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022
www.irjet.net

p-ISSN:2395-0072
Abstract:
In India, agriculture accounted for 18% of the GDP with about 42% of the workforce. The people involved in agriculture are high in percentage but their contribution to the economy is different. In today's world, people are getting more and more digitized. As a result, most people have smartphones and internet access. In rural areas people including farmers, shopkeepers and others are using these technologies to make their life easier. By keeping technological evolution, we have developed the farmer assistant to guide farmers and improve their productivity and profits. We have developed a model that will give the profit of selling at a particular time, and location and also guide the farmers on which crop to take in which area, and weather by using the soil quality parameters. It provides all the facilities needed for farmers in one place. Farmers can use this web assistant with basic smartphone use knowledge.
Key Words: technology, profit, farmer, cost, retailers, MachineLearning.
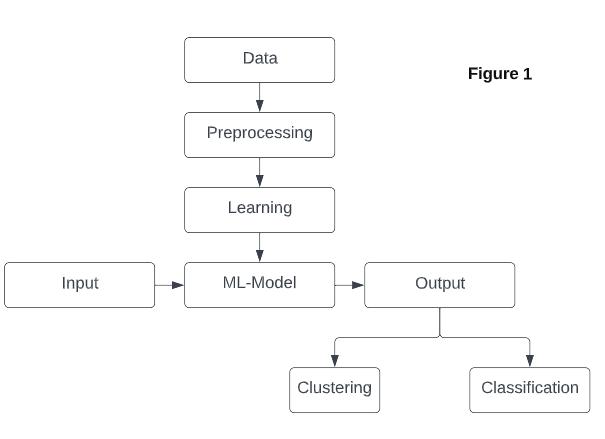
In today's world, huge data are present in various sections, including agriculture. In 2022 the Indian government announced the scheme; every licensed shop is getting the status of a governmental shop. There will be many facilities like soil testing and guidance. But they are limited in number and everyone can’t take the benefits from them. So we came up with the idea of a farm assistant website. By using modern technology like machine learning, we have the ability to provide those services online. Machine learning (ML) helps us predict results from huge amounts of present data.Figure1representsthemachinelearningalgorithm working, it pre-processes data and develops the ML model, whose output is to divide the soil according to similarityandpredictwhichcropwillbesuitableinsuch typeofsoil.
Fig-1:MLworking
To develop a Farming Assistance Web Service
application.Whichconsists ofaloginandregistrationEAuthentication System with OTP, so there will be no password-based vulnerabilities in the system. It helps farmers ensure greater profitability through direct farmer-to-dealer. It will have functionality like farmers can post complaints, may post their ads and notifications, farmers are notified of these notifications
via SMS whenever new ads are published, prediction of sellingproductsindifferentstatesorlocationsforprofit, using naïve based algorithm, real-time payment by UPI as well as a credit card. Finally, we are going to host an applicationonthegoogleengine.
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022
There are a huge amount of data available on farming, and to make a decision from that datawehavedifferentmachine-learningtechniques.For example Decision Tree, Gaussian Naive Bayes, Support VectorMachine (SVM),LogisticRegression,andRandom Forest.
The system recommends the crop based on soil fertility. The system is based on the XGBoost algorithm. XGBoost,whichstandsforExtremeGradientBoosting,is a scalable, distributed gradient-boosted decision tree (GBDT) machine learning library. It provides a parallel treeboostingandistheleadingmachine-learninglibrary forregression,classification,andrankingproblems.
There are lots of systems based on other methods we have studied in the literature survey. VrushaliBhuyarusesclassificationtechniquestopredict soil fertility by the decision tree method, naive Bayes, and random forest. They found out decision tree is the besttechniqueforclassification.DRameshusesMultiple Linear Regression for predicting rice yield. Sandesh Ramesh, Department of Information Science and Engineering Nitte Meenakshi Institute of Technology, uses regression and neural networks for crop yield prediction.
S.S.Bhaskarmadeastudyofsoilclassificationof JRip,naïvebayes,andJ48.TheyfoundJ48tobethebest method.Theyalsousedregressiontechniqueslikelinear regression and least square Median. They found least median squares regression produces better results for predictionthantheclassicallinearregressiontechnique. Jay Gholap uses the J48 algorithm for predicting soil fertility class. Also for performance tuning of the J48 algorithm, he uses attribute selection and boosting techniques. Suman cluster the data using the K-means Clustering on the soil dataset then the linear regression isappliedtoclassifytheclusters.
Fatih Bal and Fatih Kayaalp's “Review, of machine learning and deep learning models in agriculture” the identification of the plant species have been realized with ML and DL Methods depending on classification algorithms in smart agriculture applications based on artificial intelligence 126 citrus images obtained in different sizes and under various lighting conditions were trained with ML algorithms and a study was carriedouttodeterminethegreenfruit.
“Machine Learning Applications for Precision Agriculture: A Comprehensive Review” by Abhinav Sharma, Arpit Jain, Prateek Gupta, (Student Member, IEEE),andVinayChowdarydevelopthemanualspraying
www.irjet.net

p-ISSN:2395-0072
methodforpesticidesledtoimproperusageofresources and harms the environment. AI and IoT-enabled precisionagricultureremovetherandomnessandassist new-age farmers to optimize every step of the farming process.
Gaitán provided a systematic study of the impact of extremeweatherevents,suchashailevents,coldwaves, and heat waves, and their impact on agricultural practices. The author reported floods, droughts, frost, hail, heatwaves, and pest outbreaks are impacted by climaticconditions.
Acar employed an extreme learning machine (ELM) based regression model for the prediction of soil surface humidity. The author selected two terrains having areas 4 KM2 and 16 KM2 located on the Dicle university campus for experimental analysis. The realtime field data was extracted using polarimetric Radarsat-2 data, which was pre-processed using the SNAP toolbox [18] and features were added with the help of local measurements by separating the field into square grids. Once the pre-processing and feature extraction is done the data is passed to ELM based regression model to predict the soil surface humidity. The algorithm was tested with 5 different kernel functionsandthepredictionwasvalidatedusingaleaveone-outcross-validationtechnique.
Y. Mekonnen developed a power-efficient WSN using an Arduino microcontroller and ZigBee module to monitor and control essential parameters that affect crop growth such as soil and weather conditions in Florida, USA. Pise and Upadhye [164] explored Naive Bayes and SVM ML techniques for grading harvested mangoesbasedontheircolor,size,features,quality,and maturity. Grading fruits increases the profit of the agriculture and food industries. A mango image dataset comprising three different colors red, green, and yellow is created and used for training and testing the ML algorithm. The proposed approach presents limited scopeasitcandetectdefectsinaparticularsurfacearea which can be overcome by creating a dataset of rotationalviewimages.
Gradient Boosting is a boosting algorithm, in which each predictor corrects its predecessor’s error. XGBoost isanimplementationofGradientBoosteddecisiontrees. Inthisalgorithm,decisiontreesarecreatedinsequential form.WeightsplayanessentialroleinXGBoost.Weights are assigned to all the independent variables which are then fed into the decision tree which predicts results. Thesignificanceofvariablespredictedwrongbythetree is increased and these variables are then fed to the second decision tree. These individual classifiers/predictorsthenensembletogiveastrongand
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

more precise model. It can work on regression, classification, ranking, and user-defined prediction problems.
“To develop a Farming Assistance Website that will help farmers in ensuring high profitability by predictingsuitablecropsaccordingtosoilfertility.”
In Maharashtra, people say “Farmers know how to yield crops but don’t know how to sell”. This one-line statement hardly damaged the economic condition of farmers.Toaddressthisproblemwearedevelopingthis system, which will help farmers to get maximum profit. It has functionality that predicts where to sell, by calculating the selling price, and transport costs of a particularcity.
The system uses ML technologies to provide suitable solutionstofarmers.WehaveusedtheJ48Decisiontree Classifier to predict soil fertility and predict which crop will be suitable in such conditions. Also, suggest fertilizerstogetnutrientsthatarelost.
There are a number of ways in machine learning by which I can find out the fertility of the soil
buttheaccuracy,spacecomplexity,andtimecomplexity are different for different models. The models are XG Boost, Decision Tree, Logistic regression, Random Forest,etc.
For efficient working of our proposed model and after learning from the given literature survey XG Boost Technique in machine learning works very fine as comparedtoothersupervisedlearningtechniques.
Theworkingalgorithmisasfollows:
● Step 1: Make an Initial Prediction and Calculate Residuals
● Step2:BuildanXGBoostTree
● Step3:PrunetheTree
● Step4:CalculatetheOutputValuesofLeaves
● Step5:MakeNewPredictions
● Step 6: Calculate Residuals Using the New Predictions
● Step7:RepeatSteps2–6
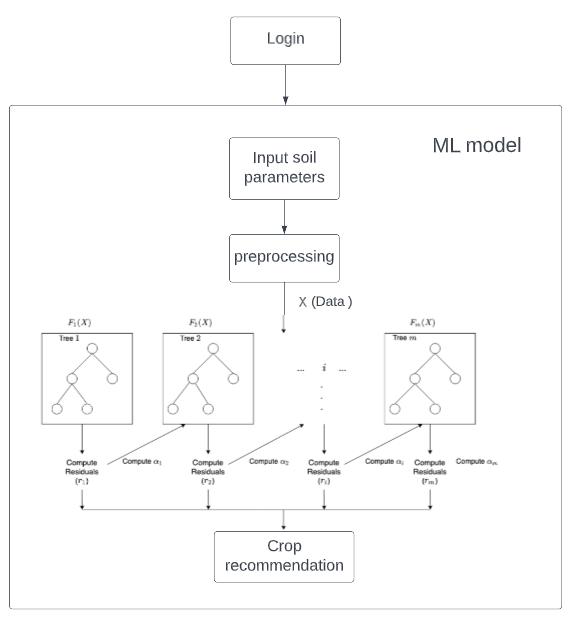
3.4 Proposed System Architecture
Theproposedsystemworkflow:
Fig -2: Workflow
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

Theaboveblockdiagramshowsustheworking of the ML model. The user has to login into the system and after that, he is able to see the system's functionalities. It takes soil parameters as input which includes nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), potassium (K), temperature, humidity, ph, and rainfall. Then XGBoost model gives us the crop that should be taken in such a condition. XGBoost work on boosting mechanism where theattemptstobuildastrongclassifierfromthenumber ofweakclassifiers.
Apartfromthemachinelearningpart,thereare lots of functionality provided in the system. Those are providingthemostprofitableplacetosellfarmproducts, farmerscanadvertisetheirfarmproducts,onlineselling between farmers and retailers, and secure payment gatewayfortransactions.
The proposed system has the best combination of machine learning functionality and other functionality. ByusingtheXGBoostMLmodel,theMLmodelprovided the crop recommendation with 99.31% accuracy whereas by comparing with other ML models it has maximum accuracy. The system has a UI that is easy to understandforfarmers.
[1].E.Acar,M.S.Ozerdem,andB.B.Ustundag,‘‘Machine learning based regression model for prediction of soil surface humidity over moderately vegetated fields,’’ in Proc. 8th Int. Conf. Agro-Geoinformat. (AgroGeoinformat.),Istanbul,Turkey,Jul.2019,pp.1–4
[2] . C. F. Gaitán, ‘‘Machine learning applications for agricultural impacts under extreme events,’’ in Climate Extremes and Their Implications for Impact and Risk Assessment. Amsterdam, The Netherlands: Elsevier, 2020,pp.119–138.
[3]. Y.Mekonnen,S.Namuduri,L.Burton,A.Sarwat,and S. Bhansali, ‘‘Review Machine learning techniques in wireless sensor network based precision agriculture,’’ J. Electrochem. Soc., vol. 167, no. 3, Jan. 2020, Art. no. 037522.
[4]. Mohamed Hamdy Eldefrawy, Khaled Alghathbar, Muhammad Khurram Khan, "OTP-Based Two-Factor Authentication Center of Excellence in Information Assurance (CoEIA), King Saud University, Saudi Arabia, Information Systems Department, College of Computer andInformationSciences.
[5] A. Menaga and Vasantha Shanmugam, "Smart SustainableAgricultureUsingMachineLearningandAI", VELS university May 2022, From: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/360444088
[6 ]. Azizatun Nurhayati, Arif Wahyu Widada , Irham , Esti Anantasari , Laksmi Y. Devi , Subejo ,Paper on “ Response to "Rektanigama": A Website Based Farming Record Application ”, Volume 04, Maret 2020 ISSN: 2581-1339.
[7]. Jude Immaculate H*, Evanzalin Ebenanjar P, Sivaranjani K, and Sebastian Terence J, “Applications of Machine Learning Algorithms in Agriculture ”, Volume 82,pagenumber:9312,November2019.
[8]. Azeem Ayaz Mirani, Muhammad Suleman Memon, Rozina Chohan, Asif Ali Wagan, Mumtaz Qabulio, “Machine Learning In Agriculture ”, INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC & TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH, Volume10,Issue05,May2021.
[9]. Tej Bahadur Shahi, Cheng-Yuan Xu, Arjun Neupane and William Guo, “Machine learning methods for precision agriculture with UAV imagery ”, Electronic ResearchArchive,September2022.
[10]. Faith Bal and Faith Kayaalp,” Review of machine learning and deep learning models in agriculture ”, International Advanced Researches and Engineering Journal,Volume05,Issue02,pages:309-323,2021.
[11]. Majwega Jackson, Ggaliwango Marvin, Amitabha Chakrabarty, “ Robust Ensemble Machine Learning For PrecisionAgriculture ”,IEEE2022.
[12].O.B.FalanaandO.I.Durodola,“MultimodalRemote Sensing and Machine Learning for Precision Agriculture ”,Articleno.JERR.92508ISSN:2582-2926
[13].Md. Tahmid Shakoor, Karishma Rahman, Sumaiya Nasrin Rayta, Amitabha Chakrabarty, “ Agricultural ProductionOutputPredictionUsingSupervisedMachine LearningTechniques”,IEEE2017.
[14]. Suman, Bharat Bhushan Naib “Soil Classification and Fertilizer Recommendation using WEKA” IJCSMS International Journal of Computer Science & ManagementStudies,Vol.13,Issue05,July2013
[15]. publication at: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/363923756
[16] Jay Gholap “ Performance Tuning of J48 Algorithm for Soil Fertility” 2012. Asian Journal of Computer Science and Information Technology 2: 8(2012) 251–252
[17]. Saran Condran, Micheal BEWONG, MD ZAHIDUL ISLAM, LANCELOT MAPHOSA, AND LIHONG ZHENG,” Machine Learning in Precision Agriculture: A Survey on Trends, Applications, and Evaluations Over Two Decades”,Volume10,IEEE 2022.
Volume: 09 Issue: 09 | Sep 2022 www.irjet.net
[18]. ABHINAV SHARMA, ARPIT JAIN, PRATEEK GUPTA, AndVINAYCHOWDARY,”MachineLearningApplications for Precision Agriculture: A Comprehensive Review” IEEE2021.
[19]. https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/xgboost/ [20].Crop YieldPrediction UsingRegressionandNeural Networks by Sandesh Ramesh, Anirudh Hebbar, Varun Yadav, Thulasiram Gunta, Balachandra A Department of Information Science and Engineering Nitte Meenakshi InstituteofTechnologyBangalore-56006
[21]. https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/xg boost-HowItWorks.html
[22] S.S.Baskar L.Arockiam S.Charles “Applying Data Mining Techniques on Soil Fertility Prediction” International Journal of Computer Applications Technology and Research Volume 2–Issue 6, 660-662, 2013


[23] D. Pise and G. D. Upadhye, ‘‘Grading of harvested mangoes quality and maturity based on machine learning techniques,’’ in Proc. Int. Conf. Smart City Emerg. Technol. (ICSCET), Mumbai, India, Jan. 2018,DOI:10.1109/ICSCET.2018.8537342
p-ISSN:2395-0072
Harshal S. Ushire B Tech Dept. of InformationTechnology-VJTI,Mumbai



Prof.PramilaM.Chawan,isworkingas an Associate Professor in the Computer Engineering Department of VJTI, Mumbai. She has done her B.E. (Computer Engineering) and M.E. (Computer Engineering) from VJTI College of Engineering, Mumbai University. She has 28 years of teaching experience and has guided 85+ M. Tech. projects and 130+ B. Tech. projects. She has published 143 papers in International Journals and 20 papers in National/International Conferences/ Symposiums. She hasworkedasanOrganizingCommittee member for25 International Conferencesand5ICTE/MHRD-sponsored Workshops/ STTPs/ FDPs.She has participated in 16 National/International Conferences. Worked as ConsultingEditoron–JEECER,JETR,JETMS,Technology Today,JAM&AEREngg.Today,TheTech.WorldEditor –Journals of ADR Reviewer -IJEF, Inters science She has worked as NBA Coordinator of the Computer Engineering Department of VJTI for 5 years. She had written a proposal under TEQIP-I in June 2004 for ‘Creating Central Computing Facility at VJTI’. Rs. Eight Crore was sanctioned by the World Bank under TEQIP-I on this proposal. Central Computing Facility was set up at VJTI through this fund which has played a key role in improvingtheteaching-learningprocessatVJTI.warded by SIESRP with Innovative & Dedicated Educationalist Award Specialization: Computer Engineering & I.T. in 2020 AD Scientific Index Ranking (World Scientist and University Ranking 2022) – 2nd Rank- Best Scientist, VJTI Computer Science domain 1138th Rank- Best Scientist,ComputerScience,India
