International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
1Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sanskar College of Engineering & Technology, Ghaziabad U.P, India
2Assistant Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Sanskar College of Engineering & Technology, Ghaziabad U.P, India ***
Abstract - Productionof cementincementindustries causes hazardous impact over environment by emitting harmful gases like carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, Sulphur dioxide & nitrogen oxide in environment. Therefore replacement of this material is an essential aspect to be worked out for preparing green concrete. Concretepreparedwithindustrialwastessuchasmarble dust, fly ash, ground granulated blast furnace slag and steel slag etc. can enhance the durability of reinforced concrete structures and reduce consumption of natural resourcesandenvironmentpollution.Thereplacementof cement with Marble Dust Powder (MDP) provides a durable modification in compressive strength, making themcompatibleforthemanufacturingofconcrete.The replacement of materials offers cost reduction, energy savings and protection of environment. Marble dust is usedasareplacementoffineaggregatesinmanyliterature worksbutthisinvestigationdiscovers thefeasibilityofthe substitution of marble waste for cement to achieve economy and environment friendly concrete. Water reducing admixtures (WRAs) also known as super plasticizers are most commonly used admixtures worldwide. Water reducing admixture, as its name suggests, reduces the water required to attain a given slump. Inthepresentinvestigationoptimumpercentage ofreplacementofcementwithmarbledustinconjunction withsuperplasticizersforM20gradeofconcretehasbeen evaluated. Parameters selected for investigation are compressivestrengthafter7and28daysandworkability.
Key Words: Marble Dust, Super Plasticizer, Ordinary Portland Cement, Workability, Compressive Strength & Admixture
Cement is widely used in concrete for infrastructure development.TheOrdinaryPortlandCement(OPC)isone of the major ingredients used for the preparation of concrete and has no substitute in the civil construction industry. Unfortunately, production of cement leads to emissionoflargeamountsofcarbon-dioxidegasintothe atmosphere,amajorcontributorforgreenhouseeffectand theglobalwarming,henceitismandatoryeithertoquest for another material or partly replace it by some other material. Higher concrete substance of High Strength Concretealtogetherinfluencesthequalityatthesolidified
state because of shrinkage and more noteworthy assessment of warmth of hydration. Higher concrete substanceofHighStrengthConcretealtogetherinfluences thequalityatthesolidifiedstatebecauseofshrinkageand morenoteworthyassessmentofwarmthofhydration.The expenseofdevelopmentmoreovergetsheightenedfurther more leaving the waste materials to the environment straightforwardly can bring about natural issue. Henceforththereuseofwastematerialhasbeenreferred.
Theadvancementofconcretetechnologycandecreasethe applicationofnaturalresourcesandenergysourcesand lessen the charge of pollutants on the environment. Natural resources have become costlier. Natural stone processing plants produces large amount of stone dust withavitalimpactoverenvironmentandhumans.Theuse of the alternative materials provides reduction in cost, energysavings,superiorproducts,andlesserhazardsin the environment. Stone blocks are altered into smaller blocksinordertogivethem thedesiredshapeandsize. During the altering process of marbles, original marble massislostby25%intheformofdust.Annually,250-400 tons of Stone wastes are generated on site. The marble cuttingplantsareemittingthepowderinanynearbypitor vacantspaces,neartheirunitalthoughnotifiedareashave been marked for disposing leading to serious environmentalanddustpollutionandcoveringvastarea ofland
Thisprojectdescribesthefeasibilityofusingthemarble sludgedustinconcreteproductionaspartialreplacement of cement The compressive Strength of concrete was measuredfor7and28days.
These are the materials which delivers very high workabilitywitharemarkabledecreaseinwatercontent (at least 20%). These can be added to concrete mix to producehighslumpflowingconcrete.Theeffectofsuper plasticizerslastsonlyfor30to60minutes,dependingon compositionanddosageandisfollowedbyrapidlossin workability.Oneoftheimportantfactorsthatgovernthe issue water–cement ratio during the manufacture of
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
concrete,lowerwater-cementratioleadstolesscapillary pores and also lower permeability and enhanced durability. Although Super plasticizer are essential to produce a truly high performance concrete (HPC) characterisedbylowwater-cementratioandworkability level without high cement content. Concrete are being producedwithw/cratioofrange0.25-0.20,enablesthe productionofhighlydurablehighperformanceconcrete. The workability also increases with an increase in the maximum size of aggregate. But smaller size aggregate provideslargersurfaceareaforbondingwiththemortar matrix, which increases the compressive strength. For concretewithhigherw/cratiouseoflargersizeaggregate isbeneficial.Highrangesuperplasticizerwasusedinall the concrete mixes to achieve good workability. Super plasticizersareaddedtoreducethewaterrequirementby 15to20%withoutaffectingtheworkabilityleadingtoa highstrengthanddenseconcrete.Toachievetheuniform workability,theadmixturedosagewasadjustedwithout changingtheunitwatercontent.Thisensuredtheidentical W/C ratio for a particular cementious content and the effectofpozzolanicmaterialreplacementcandirectlybe studiedonthevariouspropertiesofconcrete.
From composition point of view, there are four major categoriesofsuperplasticizersnamely-
• Sulphonated melamine formaldehyde condensate (SMF),
• 6Sulphonated naphthalene formaldehyde condensate(SNF),
• Modifiedlignosulphonates(MLS)
• Polycarboxylate(PCE)basedsuperplasticizers
The basic mechanisms of water reduction are through dispersionofcementparticlesbyelectrostaticrepulsion and/or steric hindrance. Fine particles such as cement grains have a tendency to flocculate when mixed with water.Whentheyflocculate,acertainamountofwateris often trapped inside agglomerates. Water reducing admixtures are used to deflocculate and to free the trappedwater.
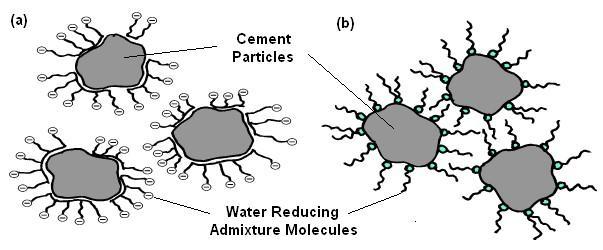
Toinvestigatetheinfluenceofpartialreplacementof cement with marble dust, along with addition of waterreducingadmixturei.e.superplasticizer.
Tocheckmechanicalpropertieslikeslumpvalueand compressive strength of concrete prepared by partialreplacementofcementandadditionofsuper plasticizerandtocompareitwiththecorresponding propertiesofconventionalM20concrete.
Tofindoutoptimumpercentageofreplacementof marbledustalongwithadditionofsuperplasticizer after which the modified concrete will show degradationinitscompressivestrength.
Fromtheliteraturesurveyitisobservedthatsubstantial amountofworkhasbeencarriedoutbyfewresearcherson assessment of Previous study over marble dust& super plasticizershasbeendiscussedunderthischapter.Many experimental studies have been carried out over the behaviour and properties of concrete influenced by additionofmarbledustandsuperplasticizers.Henceitis veryimportanttostudyanddiscusspreviousinvestigation asthesestudiesprovidedirection&scopeforfuturestudy &evolutionofmaterialsinconstructionindustries.
Marble powder possessing cementious properties are being used as replacement of cement in production of concrete .It has been varied at different percentage for replacement of cement in different grades of concrete .Sincemarblepowderistreatedaswasteproductproduced duringsawingandcuttingofmarblesinindustries,itcan resultineconomicalconcreteproductionascementisthe costliermaterialusedandalsoproductionofcementleads toenvironmentpollution.
Superplasticizersarethechemicaladmixtureaddedduring mixingofconcrete.Thefunctionofthesuperplasticizersis toimparthighworkabilityandstrengthtotheconcreteby reducingw/cratio.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Table 1 PropertiesofOPC53
Properties Result
Fineness 7% Specificgravity 3.15 Standardconsistency 31.5 Initialsettingtime 35min Finalsettingtime 270min
Table 2 Propertiesoffineaggregates
Properties Result
Specificgravity 2.62 Waterabsorption 1% Bulkdensity 1680 Finenessmodulus 3 Typeofsand Narmadariversand
Table 3 Propertiesofcoarseaggregates Properties Result Specificgravity 2.86 Waterabsorption 0.81% Impact value 13.56% Los Angeles abrasion value 22.04%
appearance, and has great demand. Chemically marble consists of calcite, dolomite or serpentine minerals. Quartz, muscovite, tremolite, actinolite, micro line, talc, garnet, osterite and biotite are some of the major impurities whereas SiO2, limonite, Fe2O3,manganese, 3H2O and FeS2 (pyrite) are some of the chemical impurities associated with marble.Alargequantityof marblepowderisgenerated duringthealteringprocess resultinginthemassofmarblewastewhichis20%oftotal marblequarriedhasreachedashighasmillionsoftons. Emitting these waste materials directly to the environmentcancauseenvironmentalproblems.
Other than deflocculation of cement grains, phenomena thattakeplaceduetosuperplasticizersinconcreteare:
• Inducedelectrostaticrepulsionsbetweenparticles
• Dispersions of cement grains & consequent releaseofwatertrappedwithincementflocks
• Reductioninsurfacetensionofwater
• Formationoflubricationfilmbetweenparticles
• Changeinmorphologyofhydrationproducts
• Inducingsterichindrancethatpreventsparticleto particlecontact.
SuperplasticizerusedinthisinvestigationisSikament® 3070NS.ItisadarkbrownliquidsolutionapprovedbyIS 9103-1999,ASTMC494,IS2645.Itschemicalbaseconsists of Modified Naphthalene Formaldehyde Sulphonate ,havingRelativeDensity~1.15kg/lat25°C&pHValue≥6.
Marble is a metamorphic rock formed from the transformation of a pure limestone. Marble used for construction and decoration is durable, has a noble

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Following test were conducted for investigation of propertiesofconcrete: Compressivestrengthtest,Slumpconetestforworkability Collectionofrawwater Preparationoffreshconcrete Castingofspecimen Curingofspecimen Testingofspecimen Resultanalysis&discussion
Figure3FLOWCHARTOFMETHODOLOGY
Table 5 MIXPROPORTIONS(perm3ofconcrete)
Mix (%) Replace
Cement Kg/m3
FA Kg/m3
CA Kg/m3
Water Kg/m3
Following Nomenclature was adopted for testing of different types of mixes prepared by replacement of cementby5%,10%,15%,&20%ofmarbledustbyweight ofcement&doping1.5%ofsuperplasticizerbyweightof cement.
Table 6 TYPESOFMIXES
Type Of Mix
%OFMARBLEDUST SUPER PLASTICIZERS (%byweightof cement)
CC 0%(CONVENTIONAL CONCRETE) 0%
MD1 5%MARBLEDUST 1.5%
MD2 10%MARBLEDUST 1.5%
MD3 15%MARBLEDUST 1.5%
MD4 20%MARBLEDUST 1.5%
Marble Dust Kg/m3
SP lit/m3
0% 373.38 609.6 220.8 68.02 0 0 5% 354.71 609.6 1220.8 168.02 18.669 6.44 10% 336.04 609.6 1220.8 168.02 37.338 6.44 15% 317.373 609.6 1220.8 168.02 56.007 6.44 20% 298.70 609.6 1220.8 168.02 74.676 6.44
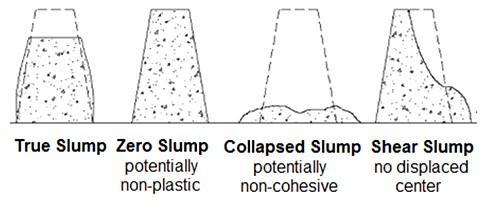
This test is conducted to determine the workability of concrete. Its apparatus consists of a cone of 10cm top diameter, 20 cm bottom diameter, & 30 cm height as showninfig.3-16.Ithastwohandlesforliftingpurpose. Concrete to betestedforits workability isplacedinthe cone.Slumpthusformedgenerallyhaseitherofthethree slump pattern specified as shown in fig.3-15. An even slumpistermedastrueslump,ifonehalfoftheconcrete cone slides down it is called shear slump & if entire concreteconeslidesdownitistermedascollapseslump.
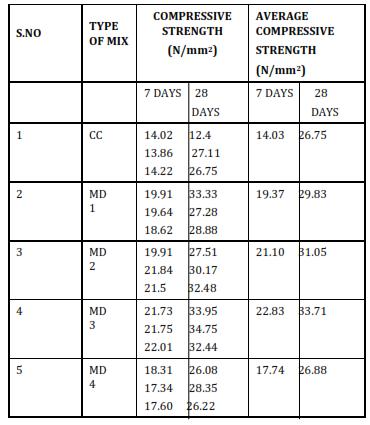
TABLE 7 COMPRESSIVE STRENGTH OF DIFFERENT MIXES
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Suitability of other waste materials in conjunction with super plasticizers for replacement of cement can be experimentallydeterminedinfuture.Otherpropertiesof concretecanalsobeidentifiedbyreplacingofcementwith waste marble dust in conjunction with different super plasticizers in same or other various proportions. More economical and environment friendly concrete can be produced by using waste material as replacement of cementinotherdifferentpercentage
1. Ahmad,Saeed,AttaullahShah,andKarametAli.2004. “EffectofWaterReducing ConcreteAdmixtureson thePropertiesofConcrete.” 29thConferenceonOUR WORLDIN CONCRETE&STRUCTURES 117–24. Retrieved (http://cipremier.com/100029013\nwww.cipremier .com).
2. Anwar, Abdullah, Sabih Ahmad, Syed Mohd, Ashraf Husain,andSyedAqeelAhmad.2015.“Replacement Of Cement By Marble Dust And Ceramic Waste In Concrete For Sustainable Development.” 2(6):496–503.
3. BalenduSirsant&S.P.Mishra.2015.“Comparative and Quantative Analysis of Variation Pattern in Concrete Mixes Due to Use of Admixtures.” International Journal of Civil, Structural, Environmental and Infrastructure Engineering ResearchandDevelopment (IJCSEIERD) 5(2):17–24. Retrieved(http://www.tjprc.org/viewarchives.php?y ear=2015_26_2&id=11&jtype=2&page=2).
Fromtheaboveresultsoftheexperimentalinvestigation usefulness of marble powder & super plasticizer as constructionmaterialwasinvestigated.Variousconcrete cubes have been casted using these materials to investigatecompressivestrength.Slumpvalueswerealso examined.
The above results shows that replacement of 15 % of cement with waste marble powder and doping of super plasticizerat1.5%ofweightofcementshowsmaximum compressivestrengthinthe experimentascomparedto 5%,10%&20%replacementofcement.
Whereas; Slump values shows linear increment with increase in percentage replacement of cement. At 15 % replacement, a slump of 130 mm was obtained, which commitstoobtainaconcretewithenhancedworkability.
4. Bansal,ErR.S.2015.“PartialReplacementofCement With Waste Marble Powder With M25 Grade.” 3(2):202–5.
5. Biswal, K. C. and Suresh Chandra Sadangi. 2010. “Effect of Superplasticizer and Silica Fume on Properties of Concrete.” Cement and Concrete Research 01(01):94–96.
6. CVaidevi.2013.“ENgineeringStudyonMarbleDust asPartialReplacementofCementinConcrete.” Indian Journalofengineering 4(9):9–11.
7. Dubey, Rahul and Pardeep Kumar. 2012. “Effect of SuperplasticizerDosagesonCompressiveStrengthof Self Compacting Concrete.” International Journal of CivilandStructuralEngineering 3(2):360–66.
8. Gurumoorthy, N. 2014. “Of Cement in Concrete.” 3(3):740–43.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
9. Karthikeyan, M., S. Shijina, P. Velu, and A. Sibi Chakkaravarthy. 1982. “Comparative Study of M20 GRADE of Concrete Casted Using OPC & PPC with PartialReplacementofCementbyMarbleDust.”
10. Latha, G., A. Suchith Reddy, and K. Mounika. 2015. “ExperimentalInvestigationonStrengthPowderas CementitiousMaterial.”12691–98.
11. Mohamadien,Hassana.2012.“TheEffectofMarble PowderandSilicaFumeasPartial Replacementfor CementonMortar.”3(2):418–28.
12. ProfVeenaandProfGulfamPathan.2014.“Feasibility andNeedofUseofWasteMarblePowderinConcrete Production.”2014:23–26.
13. Rai Roshan, Roshan k. 2015. “Influence of Marble Dust as Partial Replacement of Cement in Normal CuringConcrete.”2(4):1142–47.
14. SahuC&GuptaMK.1979.“EffectofSuperplasticizer on Properties of Fresh and Hardened Concrete.” TransportationResearchRecord 8(720):1–7.
15. Shilpa Jain, Prof. Anubhav Rai, Prof. Yogesh Bajpai. 2014. “Comparative Study of M40 Concrete with MarbleDustand.”4(11):355–58
16. .Shirule, P. a., a. Rahman, and R. D. Gupta. 2012. “Partial Replacement of Cement With Marble.” International Journal of Advanced Engineering ResearchandStudies,IJAERS (30):0–2.
17. Tamrakar,Roshan. 2013. “Experimental Studieson Property of Concrete due to Different Ingredient BasedSuperPlasticizer.”2(5):1036–40.
18. IS 516 (1959): "Methods of test of strength of concrete".
19. IS 2386 (1953) PART I,II&III: "Methods of test of aggregateforcocnrete".
20. IS12269(1987):"Specificationof53gradeordinary portlandcement".