International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Abstract - Self-drivingcarshaveasignificantfuturesince they save time that can be utilised productively. Recently, severalaccidentswerecausedbyself-drivingautomobiles. Inthissuggestedstudy,aCNNmodeliscreatedtoforecast thesteeringangleforself-drivingcars,sincesteeringangle prediction is their core notion. The simulator is used to capture the CNN model's steering angle and road visuals. The trained model ran autonomously in the simulator, completing full laps with training loss of 10.74% and validationlossof11.89%.Thistaskisbetweenlevel1and level2vehicleautomation.Thesystemcanhelpbuildselfdriving cars. The system's technique may be deployed in actual cars and prototypes, enhancing self-driving vehicle safety.
Key Words: Self-driving, machinelearning, deep learning, objectdetection,classification
INTRODUCTION1.
This project's objective is to build a convolutional neural network (CNN) model that, if deployed, will make it possibleforasimulatedcartooperateindependently.This will be achieved by making precise predictions of the steering angle needed to safely operate the vehicle while driving.Specifically,neural networksandotherAI-related concepts are used. The dataset of human drivers will be usedtotrainthemachineatfirst.Throughthis,themodel mayacquiretheknowledge necessaryto correctlypredict the steering angle of the car or vehicle at any given time. Artificial intelligence might potentially enhance its prognostic capabilities by training and experience gained from both automated and manual driving. Someday this conceptmay berefinedtothepointwhereitmaybeused to preexisting highways. Connecting the model to the simulatorandthenpushingittoworkinautonomousmode constitutes the system's functionality. When determining the optimal steering angle, the CNN model takes the path into account. CNNs have powerful skills in the fields of learning and classifying a wide range of characteristics. When given a training dataset, it may develop or extract features that are exclusive to the data on its own. The photosofroadwaysandtheassociatedsteeringanglesare used to train the CNN model. Once the training phase concludes,themodelisre-establishedwiththeprogramme and the simulator for further use. The model will make projectionsabouttheangleofthevehicle'ssteeringwheel. The purpose of the work that is going to be done is to enhance the performance of autonomous cars that are
already on the market in terms of their level of safety. In today’sworldallareautomated,sothereisbigdemandfor automation in every field, even in the field of automobiles. There are several research going on automated vehicles Autonomous cars. Self-Driving Vehicles can move safely with little or no human input. 6 tiers of self-driving cars (0-5levels).
With current CNNs, it is possible to outperform humans on benchmark datasets, which has profoundly altered the landscape of image and pattern recognition. Most pattern recognition tasks were formerly accomplished using a combination of hand-crafted feature extraction and a classifier before the widespread use of CNNs. CNNs' main strength lies in the fact that they can learn features automatically from training instances, eliminating the need for humans to manually choose only sensible characteristics. CNNs excel in accuracy compared to a regular flattened neural network because they use the 2D structure of pictures to their advantage. Although CNNs with learnt features have been in use in the business sector for over twenty years, their popularity has skyrocketed in recent years as a result of two breakthroughs. The first is the availability of huge, labelled data sets for training and validation, such as the Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge (ILSVRC). Second, convolutional neural network (CNN) learning techniques have been adapted for use on massively parallel graphics processing units (GPUs), which significantly quickens the processes of both learning and inference. A CNN that can do more than just recognise patterns is described here. An whole processing pipeline necessary to control a vehicle is learned by the system. One sort of deep neural network architecture, the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is optimised for tasks like picture categorization. The first part of a CNN is called the input layer. Also included is an output layer, which is normally a one-dimensional group of neurons. In order to process images, CNN employs a series of convolution layers that areonly loosely coupled to one another. Additionally, they have down sampling layers, also known as pooling layers, whichhelp to lower the required number of neurons in the following layers of the network. Last but not least, in orderto link the pooling layer to the output layer, CNNs often useone or more completely linked layers. We can take little bites out of an image's visual elements using a method called convolution. In a convolution layer, each neuron is in charge of a tiny group of neurons in the layer above it.CNN works well for a variety of tasks including image
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
recognition,imageprocessing,imagesegmentation,video analysis, and natural language processing. Like a classic neural network, convolution is a linear process that multipliesaninputbyasetofweights.Sincethismethod takes in data in a two-dimensional array, the multiplicationoperationiscarriedoutbetweenthefilters or weights in that array. Networks for visual perception (CNNs)useawidevarietyoflayeredstructures.
Todevelopa model which can beusedinself driving vehicles.
Theprocessofdevisingaseriesofvariablestosolvethese challenges while effectively defining the data is known as "FeatureExtraction."
Here,imagesareinputintooneofthreedifferentmodelsor setups:
1. CNN
2. MLP(MULTILAYERPERCEPTRON)
3. MLPalongwithmanualfeatureextraction
Focused on basic level of implementation, i.e., intermediatebetweenlevel1and2automation.
Main aspect of the project is to maintain vehicle on theroad(steering).
A CNN model will be trained using gathered road visuals and steering angle data to enable autonomouslycontrolledvehiclenavigation.
To improve the security of autonomous cars while ontheroad.
Aliteraturereview,alsoknownasa narrativereview,isa sub-genre of review article as well as a type of academic paper that summarises the most recent findings, theories, andmethodsrelatedtoaspecificsubjectarea.Thistypeof review may also be referred to by its alternative name: narrative review. Literature reviews are considered secondary sources since they do not report on new or previously unpublished material. Research in practically every academic discipline begins with a study of the relevant body of prior work. Evaluation, exploration, and applicationare the three primaryapproaches to writing a reviewoftherelevantliterature.
Featuresareextractedfromrawdataandtransformedinto a set. The Feature Extraction process in machine learning takes the initial consistent data and creates the borrowed values, also called features, which are meant to be descriptive and non-redundant, thereby streamlining the subsequentlearningandobservedphases.
Reducing the resources required to define a massive data collection is a primary goal of feature extraction. The fundamental issue that arises from the complex sum of variablesduringanalyticalinquiryofintricatedata.Largescale analyses are notoriously memory and processingintensive since they use the classification algorithm to "overfill"thetrainingpatternwiththenewpattern'sdata.
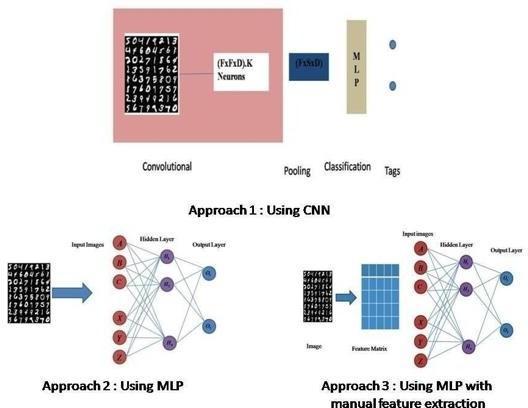
The three methods are summarised in Figure 1. For the survey, we logged all outcomes and tried to guess which method would turn out to be the most effective. The artificialneuralnetworkknownasamultilayerperceptron (MLP)isakindoffeedforwardnetwork(ANN).Nodesare organisedintoatleastthreedistinctlevelsinanMLP,with theinputlayerservingasthefoundationforthehiddenand output layers. Each node is a neuron with a nonlinear activation function, except for the input nodes. By way of training, MLP employs the supervised learning method of back propagation. In contrast to a linear perceptron, MLP hasbothseverallayersandnon-linearactivation.[1]
Figure 1: Surveycarriedonthreemethods.
To improve the efficacy of machine learning algorithms, featureextractioninvolvestransformingtrainingdataand establishing it with additional features. Using tools from Deep Learning, including Convolutional Neural Networks, this method can determine the effects of fully automated featureextractionanddistribution(CNN).[2]
We compared the performance of a Convolutional Neural Network equipped with automated feature extraction to that of a conventional Multi-Layer Perceptron using the wholepictureandatypicalFeatureExtractionmethod.Itis intended to provide a review of the modern make-up of Feature Extraction methods that has arisen over the last
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
several years. As the raising of application demand increases, a large study and analysis in the Feature Extractionplatformbecameveryactive.[3]
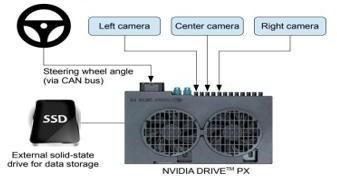
Data is collected by the unmanned vehicle's cameras, radars, and other sensors, and the vehicle's computer systempowerstheintelligentdrivinginstrumentnecessary for the vehicle to operate autonomously. The ability of an autonomous vehicle to correctly identify lanes is a crucial componentofitsoverallsafetyperformance.
Numerousstudiesarebeingconductedonvariouslaneline recognition techniques at present, with most falling into one of two categories: feature-based or model-based. For lane detection, you may employ techniques like boundary tracking, etc. It is still difficult to precisely recognise thelanelineinthegatheredlanelinepicturedue totheeffectsoflight,wear,vehicleshade,andtreeshadow.
Theapproachconsistsof3stages: Pre-Treatment ImageProcessing
Restoretotheoriginalperspective
Camera calibration and identifying the region of interest are two examples of the preparatory work performed before actual treatment begins. Edge detection, colour thresholding,obtaininglanelinepixelsbycombiningedge andcolourfiltering,slidingwindow,andpolynomialfitting are all examples of procedures used in image processing. Tests conducted on the Open CV platform confirm the algorithm's superior real-time and anti-interference performance, demonstrating its ability to accurately identifyboththedottedandsolidlanesandsoenablerealtimelinemarkinginsidevideofootage.Thistechniquemay be used in the safety-assistant driving system or the autonomousvehiclesystemtofurtherimprovetheamount ofcomputationandtheresilienceofthealgorithm.[4]
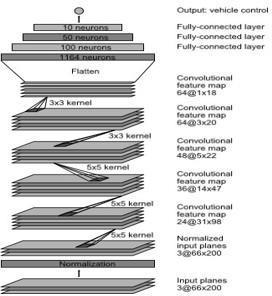
To do this, we trained a convolutional neural network (CNN) to convert the raw data from a single front-facing camera into directional inputs. This comprehensive strategy yielded impressive results. Using simply the human steering angle as a training input, the system automatically learns internal representations of the required processing processes, such as recognising valuable road elements. Because the internal components self-optimize to maximise overall system performance, ratherthantargetinghuman-selectedintermediatecriteria likelanedetection,thesystem'sperformancewillimprove. Figure2and3showstheblockdiagramandCNNnetwork used.[5]
Inordertofunctionsafely,self-drivingvehiclesneedtobe able to stick within their designated lanes. Even though autonomous vehicles have a plethora of sensors fitted, including radar, LiDAR, ultrasonic sensors, and infrared cameras, regular colour cameras are still crucial due to theirinexpensivecostandabilitytogleansubstantialdata.
One of the most critical responsibilities for a self-driving automobileisdeterminingtheappropriatevehiclecontrol input based on a camera's collected picture. In the conventional method, several aspects of the problem are treated independently, such as lane recognition, course planning,andcontrollogic.[6]
Image processing methods like colour enhancement, the Hough transform, edge detection, etc. are often used to identifythelanes.Afterdetectingthelanes,thenextstepis to use that information to inform the path planning and control logic. The success of this method is dependent on beingabletoproperlyextractandanalysevisualfeatures.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Here we describe an end-to-end learning solution to lane maintaining for autonomous vehicles, which uses frames fromthefrontcameratocalculatetheappropriatesteering angles.
The comma.ai dataset is used for both training and assessing the CNN model. This dataset includes both still imagesanddataonthedriver'ssteeringanglewhileonthe road.Basedontheresultsofthetests,itcanbeconcluded that the model can provide reasonably precise vehicle steering.[7]
The neural networks seen in animals' brains provide as inspiration for ANN. Without task-specific rules, these systems learn from examples. By analysing manually annotatedsamplesandusingtheresultstoidentifycatsin other photos, they may learn to recognise photographs includingcatsduringimagerecognition.Theyareunaware of the fact that felines have fur, tails, whiskers, and other felinecharacteristics.Characteristicsusedforidentification aregeneratedfromprocessedexamples.
Artificial neurons,or"neurons,"arethe buildingblocks of an ANN and are designed to function like their biological counterparts in the brain. Like biological synapses, each connectionhasthepotentialtorelayinformationtonearby neurons. An artificial neuron with the ability to send and receivesignals.
Theoutputofaneuronisanon-linearfunctionofitsinputs inANNimplementations,andthesignalofaconnectionisa real integer. Connecting edges. As a system learns, the weights of its neurons and edges adapt. The quality of a connectionmightbediminishedbyaddingmoreweightto a device. It's possible that neurons have a signalling threshold.Anatomically,neuronshaveseverallayers.Each layer may adjust its inputs in its own unique way. This process of sending and receiving signals from the input layertotheoutputlayermayberepeatedseveraltimes.
Deep learning neurons are layered. One layer's neurons only link to the two layers above and below. Input layer receivesoutsidedata.Outputisthelastlayer.Hiddenlayers exist between them. There are also single-layer and unlayered networks. Multiple connections are available between two levels. Each neuron in one layer may link to thenext.Agroupofneuronsinonelayermaylinktoasingle neuroninthenextlayer,loweringthelayer'sneuroncount. Feedforward networksareformedbyneuronswithsolely these connections. Recurrent networks link same- or previous-layerneurons.Fig.4demonstratesANNlayering.
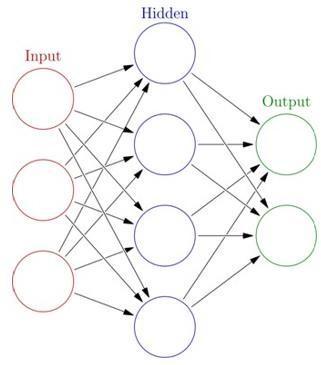
Inthefieldofmachinelearning,picturesareanalysedusing deep, feed-forward convolutional neural networks. Convolutional networks, like the visual cortex of animals, useatree-likepatternofconnections.Corticalneuronsonly respondtostimulithatfallinsidetheirownreceptivefield. It is possible to fill the visual area because the receptive fieldsofmanyneuronsoverlap.Bycontrast,CNNsneedless work before they can be used. This means the network picksupfiltersthatwerespecificallydesignedbyhumans. It's a significant plus because you don't need to rely on humanexpertiseandworkfromthepasttousethis.CNNs are used in NLP, recommender systems, and image/video recognition.
Input, output, and hidden layers are all components of convolutional neural networks. Convolutional layers convolved bymultiplication ordotproductareoftenused asthehiddenlayersinCNNs.Duetotheactivationfunction andfinalconvolution,theinputsandoutputsofthepooling, fullyconnected,andnormalising layers(togetherreferred to as "hidden layers") are hidden from view. Conventionally,layersarecalledconvolutions.It'sasliding dot product or cross-correlation. This influences how weightiscomputedatamatrixindexpoint.
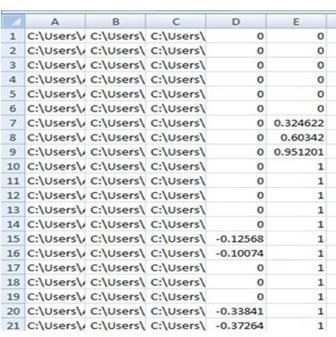
The dataset is collected through manual driving the car in the simulator. The images ofthe road and it’s respectivesteeringanglesarerecorded.
Thentheseare storedinthe formofdrivinglog,inthe formatofcsvfile.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056


Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
the core component in the application that is, the layers intheConvolutionalNeuralNetwork(CNN)model.
The procedure used, which is shown in Fig. 7, to extract thepictureand,byextension,tocategoriseit,isasfollows.
Images of the track and respective steering angle is recordedthroughmanualsimulation.

Figure 5: Datasetemployed
Figure 6: Drivinglog
The below figure shows the system architecture of the proposedsystem,
Figure 8: Databaseselection
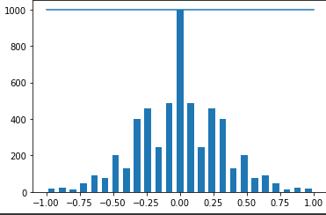
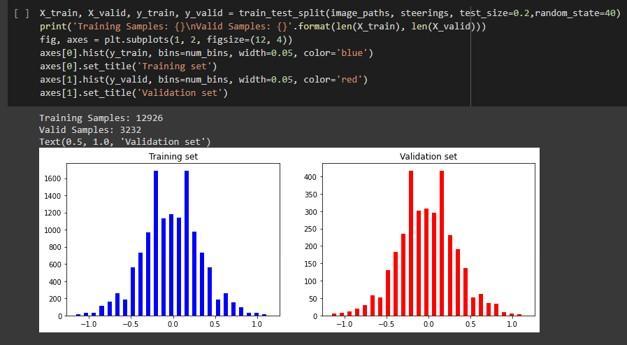
There should be balance in the data, i.e. there should be almostsamenumberofleftturnsandrightturns,elsethe modelgetsbiasedtowardsonesideofturning.
The system design includes the general framework and system architecture. The input goes through a series of stages before its class is predicted by the neural network model.Theseincludeimagefilteringandcontourdetection. The video capture input is later predicted based on its features.Systemarchitectureprovidesahigh-levelviewof
Since model is to defined and trained, that has to be testedtoknowabouterrorsinthemodelduringtraining. Hence the entire data is split into training and testing data.
2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

Images of the road and the steering angle at which they weretaken,capturedduringmanualdrivinginasimulator, willbeincludedinthedataset.ACNNmodelisconstructed after randomly preprocessing these photos. The constructed CNN model then has to be trained to provide accurate steering angle predictions. It is important to validate the model to see how well it predicts. This is achieved by splitting the dataset into a training set and a validationset.Validationofthemodelrequiresonly20%of the data. When the model is complete, it is tested in a simulatortoseewhetheritconsistentlyprovidesaccurate predictionsofthesteeringangle.
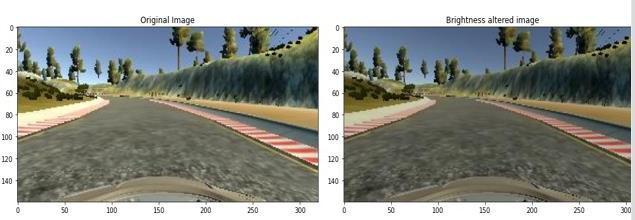
Figure 10: Datasplitting
3.3.4 Preprocessing Image
Preprocessing of images are required hence to make training of model efficient and model should have higher accuracy.
Figure 11: Pre-processingoftheimage.
3.3.5 Defining a model
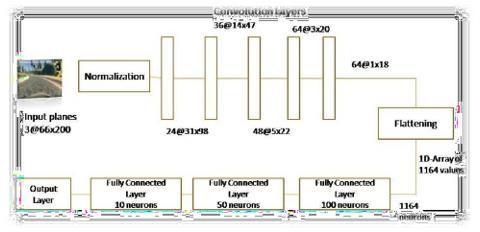
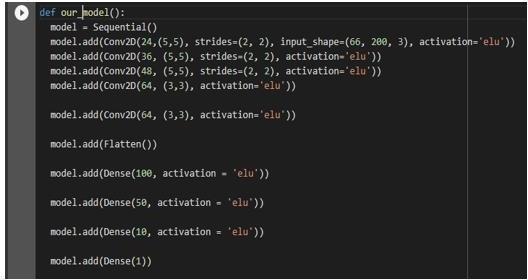
A Convolution neural network based sequential model is definedandistrained.
3.3.6 Connecting to the program
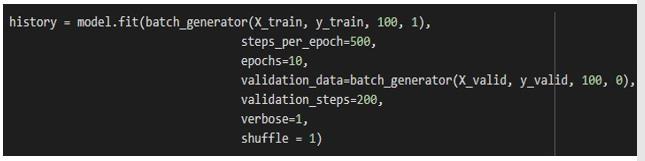
The trained model should loaded and connected to the simulationprogram.
3.3.7 Simulation Output
Modelisthenmadetoruninsimulatorintheautonomous mode.
Figure 13: Layersdesignedinthemodel.
The model is trained by employing the following parametersisasshowninthebelowfigure,
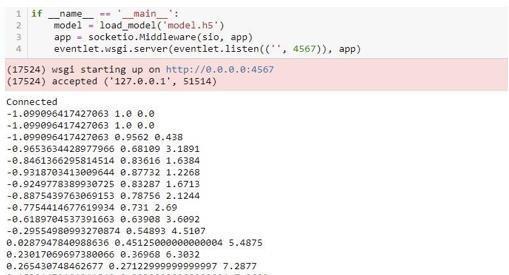
Figure 14: Modelparameters.
Thetrainedmodelisloadedbyusingtheh5fileformatand itisasshowninthebelowfigure,
Figure 15: Loadingthemodel.
Figure 12: System architecture for the proposed system
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
The below chart shows the activity planned for the implementationoftheproposedmodel.
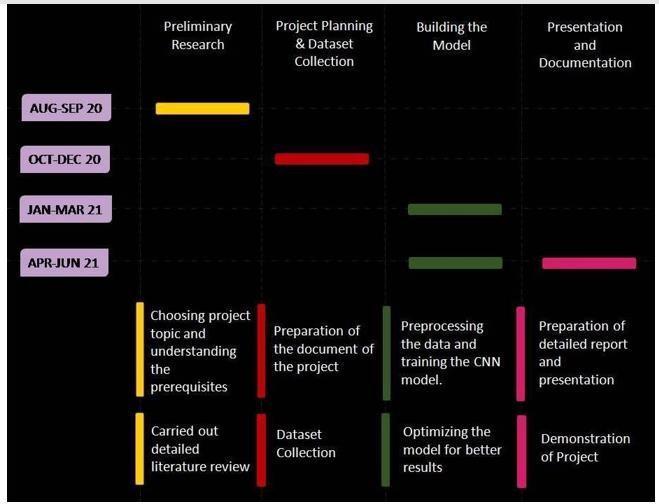
The trained final model is made to connect with the simulator and is made to run on autonomous mode. There are two different tracks, out of which one track is used for data collection and the other were not used for data collection, i.e. manual driving is done for first track andnotforsecondtrackduringdatacollection.Themodel willperform well in the first track as it was the used for data collection.Anefficientmodelshould runproperlyin second track also, which the proposed model done effectively with least errors. The model proposed completesfullroundofboththetracks.
Figure 16: Plannedchart.
Thissectionprovidesthedetailsofthescreenshotcaptured after the implementation and shows the performance analysis.
Theemployeddatasetisanimportantpartofanymodelis thedataset.Theaccuracyandtheprecisionofamodelcan bedeterminedbytherobustnessandthevarietyofdatain thedataset.Datawererecordedusingmanualdrivingofthe car in simulator. Around 8000-14000 images were collectedanditsrespectivesteeringangleisrecorded.The steering angle for the respective images were already stored in the csv file automatically as a driving log. Then randomly few images were preprocessed for bringing in the variety for the images and for the better accuracy for the modeltrained.

Thesummaryofthemodelisasshowninthebelowfigure whichgivestheinformationofthehiddenlayer.
Losses of the training and validation is provided below, LossiscalculatedperepochwhiletrainingtheCNNmodel itself. There are two types of losses, one is training loss and another one is validation loss. There are various problemswhenitcomestotrainingthemodel.Themodel should not be overfitted or underfitted, this can be evaluatedbythelossobtainedwhiletrainingthemodel.If validation loss is more than the training loss thenthe model is said to be overfitted and vice versa is underfitted. In these both the conditions modelcannot predictaccurately.
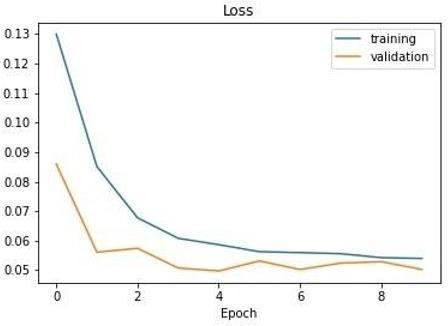
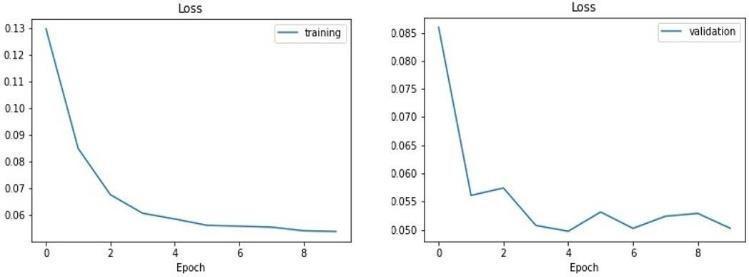
Figure 17: Modelsummary.
Ifboththelossesarealmostequalorifthegraphlinesare converging then the model does not have overfitting or underfitting problem and it is perfect for predicting the required output. The comparison of the losses per epoch is
Figure 18: Validationandtraininglosses. showninFigure.
Figure 19: Lossesofthemodel.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
TheproposedworkproposedaCNNmodelthatcanpredict thesteeringangleforthevehicleinthesimulatortomake itrunsafelyontheroadandindifferenttracksaswell.The proposedmodelhasatraininglossofaround10.74%and validation loss of around 11.89%. And the model could drive the vehicle in the simulator effectively on both the tracks,evenonthetrackonwhichitwasnottrained.This showsthemodelisaccurate enoughanditdidnotmakeany wrong predictions as well. Hence can say the model is accurate and efficient enough. The proposed work is of intermediate level between level 1 and level 2 of autonomousvehicle.UseofCNNmadeitstillmoreefficient, sinceCNN is best foranalyzingvisual data.Thisproposed work can be implemented in real life scenarios for selfdriving vehicles. This work will increase the efficiency of self-drivingvehiclesintermsofsafety.
The future work includes, Since the proposed work is of intermediate level between level 1 and level 2 of autonomous vehicle, there is a huge room for future development and self-driving vehicles has more future scopeaswell.Theadvancementoftheproposedworkcan be increased by adding other required features of selfdriving vehicles like braking system, detecting the traffic signals, object detection in all sides, automatic speed control and other controls as well making it a complete autonomoustoimplementinreallifeself-drivingvehicles.
[1] S. Dara and P. Tumma, "Feature Extraction By Using DeepLearning:ASurvey,"2018SecondInternational Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), Coimbatore, 2018, pp.1795-1801,doi:10.1109/ICECA.2018.8474912.
[2] CENwankpa,WIjomah,AGachagan,andS Marshall, “Activation Functions: Comparison of Trends in PracticeandResearchfor Deep Learning,”2018, doi: arXiv:1811.03378v1.
[3] Z. Wang, Y. Fan and H. Zhang, "Lane-line Detection Algorithm for Complex Road Based on OpenCV," 2019 IEEE 3rd Advanced Information Management, Communicates, Electronic and Automation Control Conference (IMCEC), Chongqing, China, 2019, pp.14041407,doi:10.1109/IMCEC46724.2019.89839 19.
[4] Bojarski, Mariusz & Del Testa, Davide &
Dworakowski, Daniel & Firner, Bernhard & Flepp, Beat&Goyal,Prasoon&D.Jackel,Lawrence&Monfort, Mathew & Muller, Urs& Zhang, Jiakai &Zhang,Xin & Zhao, Jake & Zieba, Karol. (2016). End to End LearningforSelf-DrivingCars.
[5] Z. Chen and X. Huang, "End-to-end learning forlane keeping of self-driving cars," 2017 IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium (IV), Los Angeles, CA, 2017, pp. 1856-1860,doi:10.1109/IVS.2017.7995975.
[6] Y.LeCun,B.Boser,J.S.Denker,D.Henderson,R.E. Howard, W. Hubbard, and L. D. Jackel. Backpropagation applied to handwritten zip code recognition. Neural Computation, 1(4):541–551, Winter1989.
[7] LIUC,WANGZQ.TheResearchonAdvertisingModelof Self-Driving Car Platform[C]//2017 IEEE 3rd Information Technology and Mechatronics EngineeringConference(ITOEC2017),2017.