International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Ar. Devanshu Yadav1 , Associate Prof. Ar. Varsha Khetrapal Kumar2
1Devanshu Yadav, M.Plan(Urban Planning), Sushant University, Gurugram, Haryana, India
2 Professor Varsha Khetrapal, School of Art & Architecture, Sushant University, Gurugram, Haryana, India ***
Abstract - Along with the building, many other industries apply sustainable development ideas. Highway infrastructure development and operation will make a significant contribution tothegoalofsustainable development.According to previous research, the majority of conventional roadways are not sustainable in numerous respects. Highways have significant challenges, including their deteriorating state, traffic, energy availability, and a lack ofmoneyforupkeepand capacity expansion to meet rising demand. But at the same time, they use a tremendous amount of natural resources and energy, produce trash, and emit gases that contribute to warming and climate change. Sustainable design, building, operation, and maintenance thus tookprecedenceatthistime.
The main question is how to provide innovative and high serviceability roads all by preserving the environment. Additionally, it is pointed out how the traditional highway construction process can be improved by incorporating the basic guidelines of sustainable development.
In this, I review various types of highway projects. in which we see what what types of problems or hazards they face in their projects.
Key Words: Sustainable construction and design, Green HighwayPolicy,Greenhighway
Asustainablehighwayisasystemofroadswhichlimitstheir impactontheenvironmenttoaminimumthroughdifferent sustainablepractices.Thegoalistomaximizethelifetimeof a highway while restricting its emissions. With the knowledge that roads are one component of the transportationinfrastructureandthattransportationisone means of addressing human needs, sustainability in highwaysshouldbeaddressed.Thecreationofasustainable highway should priorities access (rather than simply mobility),transportingpeopleandcommodities(ratherthan just cars), and giving people a variety of transportation options, such as safe and comfortable paths for walking, bicycling,andpublictransportation.Highwaysustainability must be approached with the understanding that transportationisnecessarytomeethumanneedsandthat roads are a key component of the transportation infrastructure.Thecreationofsustainablehighwaysshould focus on achieving access (rather than just mobility), transportingpeopleandgoods(ratherthanjustvehicles), andprovidingpeoplewithtransportationoptions,suchas
safeandcomfortableroadsforwalking,cycling,andpublic transportation,inadditiontohandlingenvironmentaland naturalresourcerequirements[1]
1. Reviewingafewcasestudiescanhelpuspinpoint the issues that cause Indian roads to deteriorate and fall apart more quickly than those in other countries.
2. To evaluate a document, recognize a new development,anddiscoverissuesinareportorfile.
3. Manyexpertsviewthephrase"sustainableroads" as paradoxical given the massive material consumption and negative effects on the environment caused by the building of new motorways and the usage of existing ones by automobiles.Thesocialandeconomicbenefitsthat ourroadwaysgive,suchasaccess,mobility,andthe economic advantages of transporting people and commodities,mustalsobetakenintoaccountwhen carefully considering the triple bottom line principles.Inthatcase,roadsareaveryimportant component of our infrastructure and unquestionably a required component of our society'sinfrastructure.
Thispaperdescribesaportionofalargerstudythatsought to:-
1. Define social sustainability for highway construction.
2. Identify the key factors contributing to social sustainability.
3. Evaluate the significance of the identified factors andthelikelihoodthattheywillbeimplementedin highwayprojects.
4. Assesstheagreementamongexpertsregardingthe significanceoftheidentifiedfactors.
5. Provide performance measures for the identified factors.
Inordertoimproveeffortstowardapplyingsustainability andavoidnonapplicableelementsinotherexistingsystems,
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
which involve non-existing conditions in the nature of highway construction projects, this research set out to establish an extensive rating system specifically for sustainablehighwaysinIndia[2]
Many experts view the phrase "sustainable roads" as paradoxical given the massive material consumption and negativeeffectsontheenvironmentcausedbythebuilding of new motorways and the usage of existing ones by automobiles. The social and economic benefits that our roadwaysgive,suchasaccess,mobility,andtheeconomic advantagesoftransportingpeopleandcommodities,must also be taken into account when carefully considering the triplebottomlineprinciples(profit,people,andtheplanet). Inthatcase,roadsareaveryimportantcomponentofour infrastructureandunquestionablyarequiredcomponentof oursociety'sinfrastructure[3].
Thephrase"smarthighway"hasnumerousdefinitions,but themostbasiconeisthatitreferstoavarietyoftechnology thathavebeenintegratedintoroadways.Inamoreprofound sense,itisacomprehensivevisionforfuturetransportation systemsthat examinescreativesuggestionsfor effectively usingthepotentialpresentedbyemergingtechnology.So,a smart roadway integrates physical infrastructures with software and data, as wemight say. Accordingly, the road itself may serve as a venue for improvements. A smart highway will make it possible to incorporate technology, suchaslinkeddevicesandtheInternetofThings(IoT),onto existing transportation routes in order to improve transportation efficiency, pedestrian and vehicle safety, cleanenergyusage,andsustainability[4]
Gettingbacktotheglobalscene,accordingtoINDRA'sITS Industry Report 2019, smart road technologies are a growingindustrywithawiderangeofmarketopportunities. Accordingtotheanalysis,thismarketwilldevelopatarate of7%annuallyoverthenextfewyears,withaforecastfor 2022 that this market will be worth more than 2 billion euros annually in Europe. This study seeks to provide an overviewofthesmartapproachtoroadengineeringinthis inventive and dynamic environment by putting forth a thoroughbutnotexhaustiveassessmentofthemostrecent advancesinsmartroadimprovements.
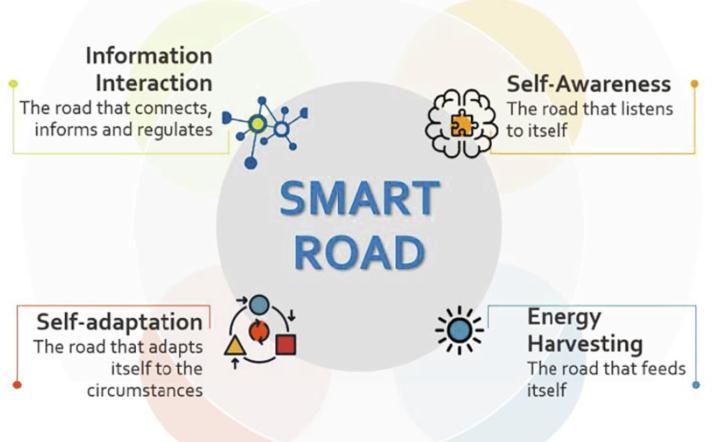 Source:AndreaPompigna⇑,RaffaeleMauro
Source:AndreaPompigna⇑,RaffaeleMauro
KeyfeaturesforSmartRoad.
Smartroadsaddressfourfundamentalissues:
Self-awareness,orthecapacitytoautomaticallyandinrealtimemonitorroadconditions,includingtrafficstatus
Information Interaction, or the capacity to link intelligent devices for monitoring roads and vehicles, as well as to connectsensornetworksanddatabaseswithinanintelligent communicationsystem
Self-Adaptation, or the capacity to automatically adapt to changingroadconditions.energyharvesting,orthecapacity toextractrenewableenergyfromsubgrade,pavements,and otherinfrastructuresanddeliverittootherthingslikethe entiresmartroadsystem.
The environmental implications, interdependence of the transportation components, government or public organisationmanagedregulation,andcapitalintensityofthe highwayinfrastructure.
The Chinese government continued to invest in roadway developmentin2013.Thesignificanceofthe"OneBelt,One Road" has been apparent as a result of China attaching considerableattentiontoinfrastructure'sstrongeconomic andenvironmentaleffects[5]
Highway infrastructure needs to meet a number of requirements, including those for construction tools, funding, building techniques, and the kinds of designers, builders,andowners[5]
33.43billionmetrictonnesoffreightweremovedbyroadin China in 2015, accounting for 76% of total freight movement; 40.79 percent of this was transported by highway.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Ontheotherside,thereisagrowingunderstandingthatthe growth of highway projects has an influence on the environment, including soil wasting, noise pollution, landscape,biodiversity,andecosystems.
Sitepreparation,earthmoving,materialtrucking,pavingof roadwaysurfaces,buildingofstructures,andtheapplication ofarchitecturalcoatingsareallstepsinthedevelopmentofa highway project. Prior to site preparation, some projects mightalsocallforthedemolitionofbuildings.Inadditionto noise,theseactivitieshavethepotentialtoemitgreenhouse gases,airpollutants,suchasCO2,CO,NOx,HC,SO2,andPM, aswellasnoise.[3]
According to Demich (2009), it is preferable to begin building the highway in a sustainable fashion to minimise any negative effects while maintaining the need for new highwayconstructionandroadimprovements.
Any transportation system must have highway transportationasakeycomponent.Currently,theeconomy andsocietyarecentredaround roadsand vehicles..Every projectisdifferent,whichisakeyidea inhighwaydesign. Everyhighwayprojecthasspecificvariablesthatdesigners musttakeintoaccount,suchasthesettingandcharacterof the place, community values, needs, and possibilities for highwayusers.Asustainablehighwayisonethataddresses bothenvironmentalandhumanneedswhilealsotakinginto accountefficienttrafficandsafetyconcerns.Inordertomeet fundamental functional criteria including access, capacity, level of service, safety, and travel time, routesare chosen, alignmentsaredesigned,andcrossingsareplacedprimarily basedonengineeringconsiderations[5].
The goal of these infrastructure-focused solutions is to deliver the highest quality service at the most affordable price. The combination of functional requirements while improvingtheconstructed,natural,andsocialsurroundings is the essence of a sustainable roadway. According to ecological economists, a highway project can be planned, developed,built,andoperatedinsuchawaythat,whenthe environmentisconsideredasawhole,itshowsanetbenefit. The concept of sustainable roadways may initially seem contradictory,butitactuallyoffersachancewhosetimehas come,accordingtoHalKiss-off.
Thedevelopmentofamoresustainableapproachtohighway constructionleads-
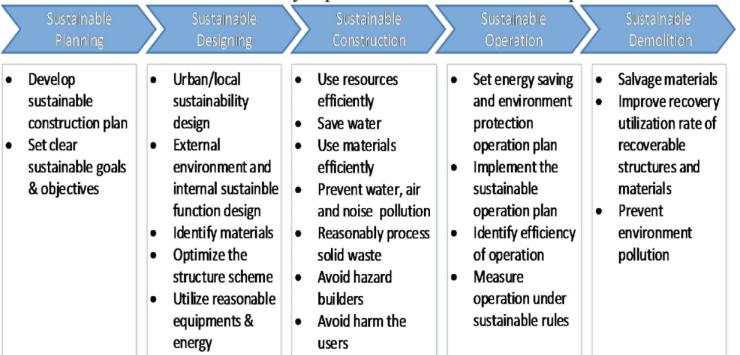 Source:ZhangJunjie, ShaunLund
Source:ZhangJunjie, ShaunLund
Theroadwayhasnegativeeffectson theenvironmentand society while also being crucial for economic growth and quality of life. However, while developing a long-term strategy,asustainablehighwayshouldnotonlybebuiltto fulfil present development needs, but also provide some room for future social and economic growth. Eventually, assistinputtingthe"OneBelt,OneRoad"policyintoaction.
Thetrade-offsthatarepartofeveryengineeringchoicein general,andthedesignofhighwaysinparticular,arewhat tietheaspectsofsustainabledevelopment together.Basic conceptslikeminimisingtheuseofnon-renewableenergy and natural resources, minimising adverse environmental effects,developingsustainabletechnologies,evaluatingthe economic effects of road projects, and balancing the costs andbenefitsofvariousoptionsaretoolsthatcanbeusedto implementsustainabilityinhighwayconstruction.Inorder to create a more sustainable road project, it is the responsibility of the highway engineer to incorporate science,technology,experience,andcreativityintohighway building[6]
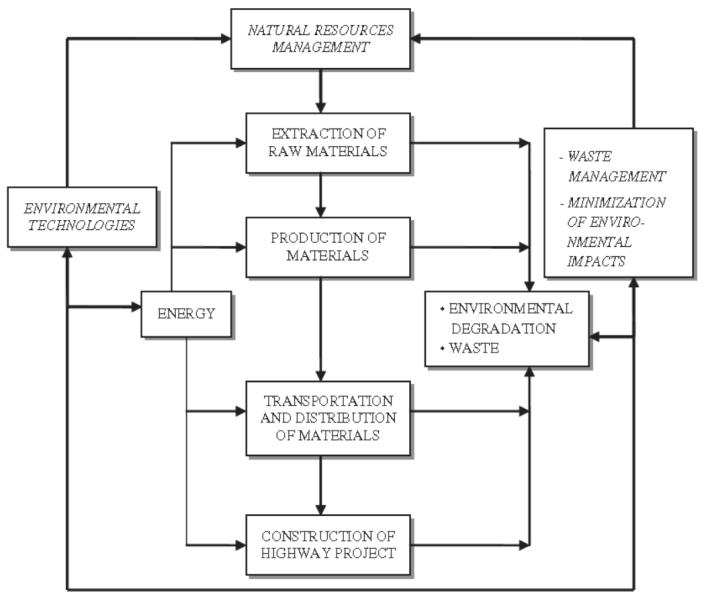
•Sustainable management of natural resources: The consumptionandexploitationofvastquantitiesofaggregate and asphalt materials is a characteristic of highway engineering. It would be ideal to use industrial byproduct materialsinplaceofnaturalsoils,aggregates,andcements. Utilizing waste and byproducts is an application of re-use andrecyclingtechniquesthathasa numberofobservable benefits,includingadecreaseintheamountofunnecessary materials that need to be disposed of, the preservation of natural resources for materials, a decrease in energy consumption, and a decrease in environmental pollution. Recyclingrequiresacomprehensivestrategy.
To establish research priorities and technical standards, government and business must collaborate. Government must establish guidelines for incorporating recycling into national culture. Industry must create its own marketing strategies, investin recycling,organise itself,comprehend societalissues,andseekoutmarketsforitsgoods.Eachof thesepartnershascertainrequirementsandstandardsfor evaluation and measurement. Sometimes, this leads to conflicting goals. It is necessary to develop standardised language,examinations,andcutting-edgetechnologies.Itis necessarytobuildandimprovechannelsforbroadcasting andcommunication.
• New environmentally friendly technologies: Since technology is one of the most essential ways that humans
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
interact with our environment, it is vitally crucial for sustainable development. Sustainable technologies offer workable answers for achieving economic growth and human fulfilment while preserving the environment. By lowering risk, increasing cost effectiveness, expanding process efficiency, and developing processes, products, or services that are ecologically friendly or benign while benefitinghumans,thesetechnologieshelptocontributeto, support,orpromotesustainabledevelopment.Utilizingnew equipmentorcapitalinvestments,aswellasthecreationof innovativeproductionmethodsandprocedures,areallways to bring about technological progress. This shift typically takes work; it typically calls for incentives to use environmentalpoliciestobecreatedthroughresearchand development.
Highway Policy in 2015 [8]. This policy encourages the creation of environmentally appropriate national route corridorsthroughoutthenationwiththehelpoffarmers,the nonprofit sector, and governmental organisations like the Forest Department. This paper reviews design and constructionmethodsforgreenmotorwayswhiletakinginto accountIndiancityperspectives.Thetransformationofthe conventionalhighwayintoagreenhighwaywillbeginwith the design approach and continue with the needed modifications throughout the phases of construction and maintenance.UnderstandingtheGreenhighwaypractisesto be adhered to throughout the method of design, construction,andmaintenanceofthehighwayiscontinually helpful before the formation ofcommoncharacteristics of Green highway technology. We also need to keep in mind thattheGreenHighwayinitiativeisavoluntarysocialgroup made up of the route's environmental and ecological department's government representatives, other involved departments,socialinstitutions,privatecontractors,labour unions, and parties involved in carrying out the Green Highway'ssocialobjectives[9]
Benefits to society, the environment, the economy, and human health are connected to the Green Highway. The advantages of green infrastructure are particularly highlightedinurbanandsuburbanresidentialareaswhere greenspace[10]
Greeninfrastructureembracesfollowingbenefits:
Alongwithbuilding,manyotherindustriesapplysustainable development ideas. Highway infrastructure development andoperationwillmakeasignificantcontributiontothegoal ofsustainabledevelopment.Accordingtopreviousresearch, themajorityofconventionalroadwaysarenotsustainablein numerous respects [7]. Highways have significant challenges,includingtheirdeterioratingstate,traffic,energy availability, and a lack of money for upkeep and capacity expansiontomeetrisingdemand.Butatthesametime,they useatremendousnumberofnaturalresourcesandenergy, producetrash,and emit gasesthatcontribute to warming andclimatechange.Sustainabledesign,building,operation, andmaintenanceconsequentlytookprecedenceatthistime. SincegreenhighwaytechnologywascreatedintheUnited Statesin2002,itisbeingpromotedhereeventhoughGreen Highway Partnership is deemed to as public non-public engagement. The Indian government created the Green
i. Social advantages: The highway has a significant effect on local businesses. A road will bring a business into the community, creating jobs and generating income for the government. Because therewillbelessmaterialsinthelandfill,thehouses therewillbedemolished,whichwilllowercostsfor residents in the neighbourhoods surrounding the landfill.Thequalityoflifeintheareawillrisewhen noiseandpollutionfromroadwaysaredecreased. Thesocietymaybenefitfromavarietyofbenefits, including reduced water use, the utilisation of recycledmaterials,protectionoflife,reducedlevels ofcontaminantsinsurfacerunoff,improvedstream andrecreationalwaterquality,etc.
ii. Green infrastructure solutions boost storm water infiltration rates, which reduces the amount of runoff that enters sewer systems and eventually endsupatlakes,rivers,andstreams.Thisresultsin reducedanddelayedstormwaterrunoffvolumes.
iii. Fastergroundwaterrecharge:Greeninfrastructure technologies' natural infiltration capabilities will hastentherateatwhichwellwatertablesrecharge. Increased well water recharge could increase the
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
availabilityofdrinkingwaterforbothprivateand publicusage.
iv. Green highway solutions soak runoff near to its sourceandmakeiteasiertopreventcontaminants from being carried to nearby surface waters. iv) Reducing storm water waste. Plants and bacteria will naturally filter and degrade a number of commonwastesfoundinstormwateroncerunoff hasfilteredintosoil.
v. Greeninfrastructuremakesiteasiertoincorporate treesandvegetationintourbanlandscapes,which improvesair quality.Thismayresultinbetter air quality.Throughleafuptakeandcontactremoval, trees and other vegetation remove bound toxins fromtheair.Treesandplantscanevencooltheair andlowerworkertemperaturesiftheyarewidely growninareasthatarecovered.dependentreaction thatcausesgaspollutionatgroundlevel.
vi. Recreationalspaces&wildlifehabitat:Greenways, parks, urban forests, wetlands, and vegetated swalesareallexamplesofgreeninfrastructurethat improve access to outdoor spaces & wildlife surroundings.
vii. Improvedhumanhealth:Greeneryandvegetation willbegoodforpeople'shealth.
viii. Increaseinlandvalue:Landclosertothehighway will be worth more due to clean and green infrastructure.[7]
One of the most cost-effective and widely used forms of transportationforbothfreightandpassengersisregardedas being road travel. India has a vast 4,24-million-kilometer roadnetwork,whichisthesecondlargestintheworld[1]. The main road system of the nation is operated by the 70,934kmlongNationalHighways.Calculationsshowthat more than 70% of the nation's freight and 85% of its passenger traffic are transported by roadways. Only approximately two percent of all roads are highways or expressways;theremainderaremotorways,majordistrict roads, district roads, rural and alternative roads that are consideredlowtrafficroads[2]
Transportation experts must incorporate green ideas into the processes of transportation designing, designing, building, and operating as a result of growing public awareness of climate change. Although the concept of a "green highway" is relatively new, the use of the relevant technologieshasbeenencouragedforsometime.Although greenroadsmightnotinitiallyresembletraditionalones,a drivercandetectsubtledifferencesuponcloserinspection.
Ontheshoulder,morefloraisgrowing,andmoretreesare being planted for ridding and life-buffering purposes. A
green highway is defined by five broad topics, including conservation and system management, water shed driven robustwatermanagement,lifecycleenergyandemissions reduction,recyclesuseandrenewableenergy,andoverall social group edges. In towns, highways become more aesthetically pleasing, and in rural areas routes become a morenaturalpartofthesetting.
1)Monitoringplantationexpansionandputtingtechniques into practise to increase the quantitative relationship betweenplantationsandsurvival.
2) Close observation of construction-related noise and air quality.
3)Thecommonvehiclesoperatingontheroute,suchasS.T. buses,trucks,multi-axlevehicles,etc.,willbeevaluatedfor theirlifemaintenance,fuelconsumptions,traveldistances (in kilometers), and other factors in order to estimate the GHGemissionbyinstallationasawholeandmethodologyto reduce the same and reduce the connected carbon footprints. Property transportation aims to protect the environment and conserve natural resources while considering societal needs and the cost-benefit ratio. To reducetheemissionofGHGandotherharmfulfilthygases that affect the environment, efforts must be made in conjunctionwiththetransportationsector.
4)Monitoringandreducingtrafficaccidents.
ItwilltakesometimeforIndiatoadoptthistechnologyand fullyimplementitthroughoutthenationalhighwaysystem spreadacrossthecountrywhereveritispossibletodoso based onGreenHighwayPolicybecause greenhighway is notanewconceptintheworld,butitsutilizationhasonly beenwidelyconsideredinIndiafromthelastfewyears.[5]
Ahighwayprojectthat isa successwill incorporatesocial well-being,economicviability,andenvironmentalintegrity. Thiswillhelptheregionthrive
Highway engineers must support and participate in interdisciplinary teams with other professionals, such as ecologists, economists, and sociologists, in order to successfullyhandletheissuesandchallengesofsustainable development. Road authorities are responsible to the community for more than just constructing roads. By incorporating the greatest environmental management practicesintoroadplanningandconstruction,sustainable highwaysaremadeareality.
Road construction is only one of the responsibilities that roadagencieshavetothecommunity.Byimplementingbest
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
practicesinenvironmentalmanagementduringtheplanning and construction of roadways, sustainable highways are madeareality.
Sustainability has grown to be a significant issue for the highwayandconstructionindustries.Itmadereferenceto thestrategy'sgreensupportanddirection.
Iwouldliketoexpressmyhonestanddeepestappreciation to Prof. Varsha Khetrapal, whohaveconstantlyguidedme, helpedmestructuremypaperandwitheverydifficultywith theirutmostprofessionalism.

Iwouldliketothankthemforalwayshavingtheattitudeand thesubstanceofagenius:theycontinuallyandconvincingly conveyed a spirit of adventure regarding this paper and excitementregardingteaching.Withouttheirguidanceand persistenthelp,thispaperwouldnothavebeenpossible.
[1] ministry of road transport and highway, “Green Highways,”2020.
[2] S.S.PatelandM.T.Student,“STUDYONHIGHWAY FAILUREANDITSMAINTENANCE,” Int. J. Creat. Res. Thoughts,pp.262–266,2018.
[3] Z. Junjie and S. Lund, “The Development ofSustainableHighwayInfrastructureintheStrategy ofOneBeltandOneroad,” First Int. Symp. Bus. Coop. Dev. South-East South Asia under B&R Initiat., pp. 172–175,2016.
[4] A.PompignaandR.Mauro,“EngineeringScienceand Technology,anInternationalJournalSmartroads :A stateoftheartofhighwaysinnovationsintheSmart Age,” Eng. Sci. Technol. an Int. J.,vol.25,p.100986, 2022,doi:10.1016/j.jestch.2021.04.005.
[5] F. Kehagia, “THE IMPLEMENTATION OF SUSTAINABILITYINHIGHWAYPROJECTS,”vol.4,no. 1,pp.61–69,2009,doi:10.2495/SDP-V4-N1-61-69.
[6] C K Rudresh, “green-roads-for-healthyenvironment.pdf.”
[7] D.Patel,“Design&constructionofGreenHighwayin India considering the Sustainable International Conferenceon,‘GREENHIGHWAYCONSTRUCTION –ASustainableApproach’Design&constructionof GreenHighwayinIndiaconsideringtheSustainable Development,”no.August,2022.
[8] A.H.IbrahimandM.A.Shaker,“Sustainabilityindex forhighwayconstructionprojects,” Alexandria Eng. J., vol. 58, no. 4, pp. 1399–1411, 2019, doi:

10.1016/j.aej.2019.11.011.
[9] O. Ademila and A. I. Olayinka, “Geotechnical investigation of pavement failure ; causes and inherent solutions for sustainable highway construction in Sub-Saharan Africa,” pp. 103–114, 2020,doi:10.17794/rgn.2020.4.9.
[10] TKMCE,“Green-highway,”2017.
MyselfAr.DevanshuYadav,ispursuing masters in Urban planning, Sushant University,Gurugram.
Prof. Varsha Khetrapal, Architect and EnvironmentalPlannerfromSPA,New Delhi.Herareaofresearchisonstreet planning and designing and its evaluation.Shehasalmost2decadesof experienceinthefieldofarchitecture andplanning,includingacademicsand industry.Shehaspublishedarticlesin variousjournalsandconferences.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page992
