International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Nalawade1, Sanjeevan Bapat2
1Final Year Student, Information Technology Department, Thadomal Shahani Engineering College, Bandra(W), Mumbai - 400050
2Final Year Student, Information Technology Department, Thadomal Shahani Engineering College, Bandra(W), Mumbai - 400050 ***
Abstract - Phishing is a sort of social engineering in which an attacker sends a fake communication in order to fool a person into disclosing sensitive information to the attacker or to install harmful software, such as ransomware, on the victim's infrastructure. It is critical to correctly classify phishing websites in order to detect and prevent phishing assaults. If a phishing assault has already happened, the classification of phishing websites can be used to establish recovery methods. Phishing website classification is a well-known engineering research topic. Machine Learning is commonly utilized in the identification of phishing websites because of its benefit of discovering essential traits froma dataset ofmultiple websites. The goal of this study is to address the problem of phishing website classification utilizing various classifiers, and ensemble learning. Ensemble learning approaches are used to enhance a classifier's performance. Extensive tests were conducted on the well-studied open access data collection "Phishing Testing Dataset" in this paper. Measures like f1score, accuracy, recall and precision have been employed to evaluate the various models. The suggested approach has a remarkable accuracy of 97% in classifying phishing websites, according to experimental data. The proposed model would be viable in helping cyber-security experts and also the general public recognizes phishing websites accurately.
Key Words: Phishing, Websites, Detect, MachineLearning, Classification, Ensemble
“Love Bug”, which is also known as, the first phishing email,isconsideredtobethereasonmanypeoplelearned aboutphishing.OnMay4,2000,severalpeoplefellvictim to the Love Bug. Beginning in the Philippines, mailboxes throughout the world were flooded with the message "ILOVEYOU." "Kindly check the attached LOVELETTER coming from me," the message body stated. Those who couldn't stop themselves from discovering their hidden crushdownloadedwhattheybelieved wasa harmless.txt
file, just to release a worm that harmed their local computer. The worm overwrote picture files and transmitted a clone of its own to all of the user's Outlook contacts. The history of phishing reveals that phishers' strategieshavestayedprettysimilar.Thegrowthofsocial media has been a significant change. Social networking sites are a virtual treasure trove of personal data that fraudsters may and do use to customize emails to individual recipients, a technique known as spear phishing.Thehighstakesandthelowresourcesneededto carry out an assault have made spear phishing the preferred method for thieves pursuing access to confidential information housed in the systems of major organizationsandenterprises.
Phishing is the practice of delivering deceptive messages or emails that seem to originate from a trustworthy source. Emails are the most common method of carrying out phishing attacks. The main purpose of the attacker is to embezzle sensitive details such as credit card information or login credentials or to install any kind of malwareonthepersonalcomputerofthevictim.Everyone should be aware of phishing attacks in order to stay safe fromsuchattacks.
A phishing domain is a website that looks and sounds similartoan official website.Theyarecreatedin order to deceivesomeoneintothinkingitisauthentic.
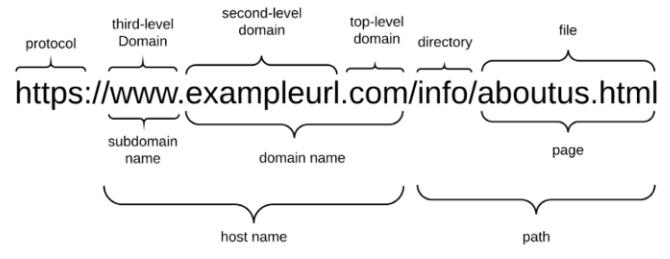
TheURL(UniformResourceLocator)isutilizedtolocate anyresourceontheWorldWideWeb(orWWW).
A hostname is made up of a domain name and a subdomain name. The phishing attacker has complete commandoverthenameofthesubdomainandroute.The attacker has the ability to register any domain name that hasnotpreviouslybeenregistered.Itcanonlybemodified once.Theuniqueelementofthewebsitemakesitdifficult for security guards to detect phishing websites. Once the fake domains have been identified, it is simple to thwart
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
the users from accessing them. The following diagram portraysthecriticalpartsofthestructureofaURL.
This section addresses several pieces of literature on phishing website categorization. For the identification of phishing websites, several machine-learning techniques havebeenused.
OthermethodsofPhishingattacks:
Cybersquatting (also known as domain squatting) is the practice of registering, trading in, or utilizing a website address with the goal of profiting on the goodwill of someone else'sbrand. Thecybersquatter mayoffertosell the domain at an exorbitant value to an individual or corporation that owns a trademark included within the name, or he or she may utilize it for fraudulent reasons suchasphishing.
Typosquatting,alsoknownasURLhijacking,dependson mistakesmadebyInternetuserswhenenteringa website linkintoaninternetbrowserorontypographicalmistakes that are difficult to catch when reading. URLs established using Typosquatting appear to be reputable domains. A user may input a wrong website URL or click a link that appearstobefromatrustworthydomain,leadingthemto analternatewebsitehostedbyaphisher.
Machine Learning (ML) is a form of AI (Artificial Intelligence) methodology, which uses numerous statistical, optimization, and probabilistic strategies to increaseperformancebasedonpastexperiencesandfresh data.AwiderangeofMLapproacheshasbeenusedwidely to identify any phishing websites and prevent their consequences.
Several ML methods are quite effective in the early identificationofphishingwebsites.UsingMLalgorithms,it is simple to discern between legitimate and counterfeit websites.Accurateclassificationwillhelp peopletodetect phishingwebsitesbeforetheirlocalsystemisattackedand the data is compromised. Additionally, classification is a complicated supervised optimization problem. For categorizing phishing domains, several classification approaches such as SVM, KNN, and Naive Bayes are employed.
In [1], the authors have applied two algorithms to determineifawebsite(URL)iscounterfeitorgenuine.The proposedsolutiontrainedthemodelusingRandomForest Classifier and Decision Tree Algorithm to classify the websites.The model recordedanaccuracy of 97% for the RandomForestAlgorithm.
The authors, in [2], recommended utilizing Machine Learningapproachestodetectphishingsites. Theauthors have employed the Random Forest Algorithm to classify phishingwebsites.
In [3], Rishikesh Mahajan and Irfan Siddavatam applied three Machine algorithms SVM, Decision Tree, and Random Forest algorithms on the phishing websites dataset. Among three machine learning algorithms, the RandomForestclassifierrecordedanaccuracyof97.14%.
[4] provided a detailed survey about the usage of ML methodologies for the identification and deterrence of phishingwebsites.Theauthorspresentaphishingwebsite detectionmodelinvolvingtheselectionofoptimalfeatures and neural networks. The fuzzy rough set hypothesis has been employed to identify the most impactful features from a set of databases. The four classification models usedtoclassifythewebsitesaretheKernelSupportVector Machine(SVM),theDecisionTreeClassifier,theK-Nearest Neighbor(K-NN),andtheRandomForestClassifier.
Using the Random Forest Classifier, the authors of [5] presentamethodologytodeterminephishingwebsitesby employing a URL identification technique. The dataset is gathered from Phishtank. The suggested technique is divided into three phases parsing, followed by heuristic dataclassification,andlastlyperformanceanalysis.Only8 of the 31 characteristics are evaluated for parsing. The randomforestapproachachieveda95%accuracylevel.
The c4.5 decision tree approach has been utilized in the paper [6] to demonstrate an efficient way to detect phishing sites. This approach collects webpage characteristics and generates the heuristic values. These heuristic values were sent into the c4.5-decision tree method,whichdeterminedifornotthetargetwebsitewas a genuine website or a phishing website. The dataset was gathered via sources like PhishTank and Google. This procedure was divided into two stages: pre-processing anddetection.Here,thefeaturesareretrievedonthebasis
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
oftherulesdefinedinthefirststagei.e.thepre-processing stage, and the attributes along with their values were input.
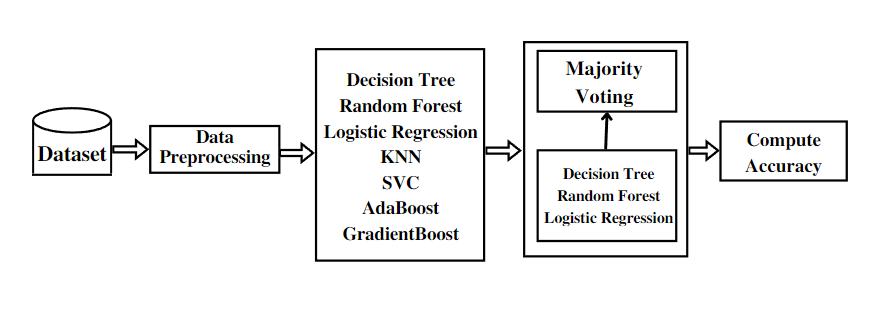
Phishing websites are identified in this study utilizing classifierssuchasRandomForest,DecisionTree,andKNN, and Ensemble Classifiers such as AdaBoost and GradientBoost. The Phishing Testing Dataset is used for the experimental analysis. A total of 8955 cases and 32 attributes areconsidered. The Phishing Testing Dataset is available at []. Hard and Soft Voting classifiers are also used with high-accuracy classifiers. Individual and ensembleclassifierswillbediscussedinthesubsections.
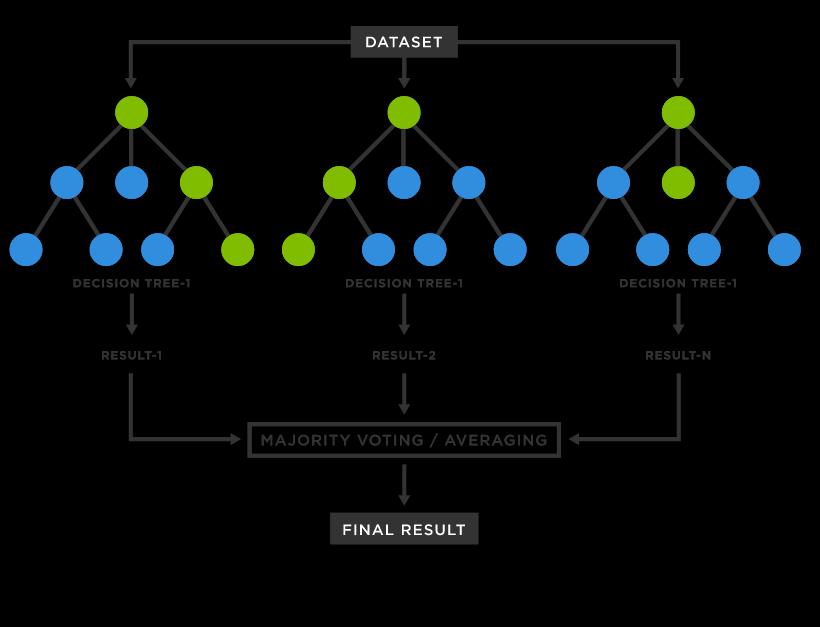
The forest with many decision trees is created by the random forest algorithm. High detection accuracy is providedbylargenumbersoftrees.Thebootstrapmethod is used to create trees. In characteristics of the bootstrap algorithm and samples of the dataset are chosen at random and replaced to create a single tree. The random forest algorithm’s randomly chosen features the best splitterforclassificationwillbeselected.
Amongallthesupervisedlearningtechniques,theK-NN (K-NearestNeighbor)isconsideredtobethesimplestone. By assuming a resemblance between the new case/data andexistingcases,thetechniqueplacesthenewdatapoint in the group that best fits the available classifications. On thebasisofsimilarity,inordertoclassifyanewdatapoint itstoresallofthe existingdata.Thus employingtheK-NN method,itispossibletopromptlyandreliablyclassifythe new data into a relevant class. K-NN is more commonly utilized for classification problems, although there are cases when it can be employed for regression issues as well. Since the K-NN algorithm is a non-parametric algorithm,itdoesnotrelyonanyunderlyingassumptions. The K-NN technique is also sometimes called a lazy learner method since it does not instantly learn from the training set; rather, it saves the dataset and applies a functiontoitwhenithastocategorizethedata.
Fig -2:RandomForest
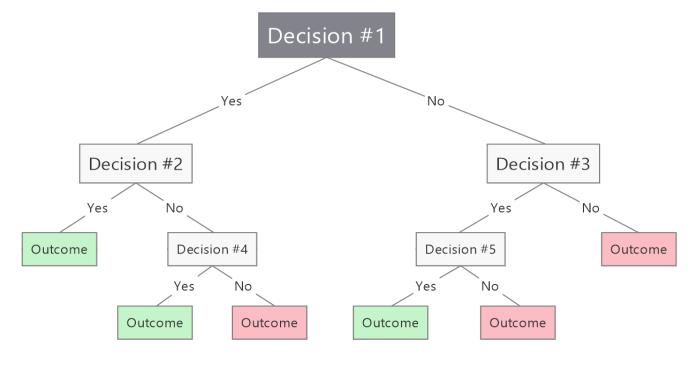
A decision tree's job starts by calculating values such as the Gini index or information gain to find out attributes that are available for classification, which becomes the tree's root. This process keeps on repeating until a leaf node is found. In a tree representation, a decision tree provides a training model that predicts a target value or class. Each leaf node is a result label value and every middlenodeissomeattributefromthedataset.
2022, IRJET
Impact Factor value: 7.529
A supervised machine learning technique called ensemblelearningemploysnumerouslearningalgorithms toproduceasingle,idealpredictivemodel.Toincreasethe model'scapacityforprediction,itincorporatesavarietyof supervised learners. Techniques for ensemble learning that are frequently employed include bagging, boosting, andstacking.Ensembleclassifierscategorizenewsamples using weights or majority voting and are built from a number of base (weak) classifiers. Different algorithms use base learners, often known as weak learners. As an illustration, consider the various base individual learners, such as K-NN, SVM, Bayesian, Decision Trees, etc. There arevarioustuningfactorsforbaselearners.Decisiontrees arethefundamentallearningalgorithm,thesameasinthe Random Forest ensemble. Weak learners are often referredtoasbaselearners.Weakstudentsfrequentlybut irregularly record with little accuracy. When learning the connectionsbetweeninput andoutput,itislacking. Weak
ISO 9001:2008
Journal | Page592
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
learners are combined in ensemble learning to achieve high accuracy. Based on the approach, the algorithm is chosen.
Adaptive boosting, often known as AdaBoost, is a commonly used boosting strategy that aims to turn multiple poor classifiers into one potent classifier. Only a single classifier is not often enough to predict the result with decent accuracy. By aggregating numerous weak classifiers and allowing each one to gradually learn from the incorrectly classified items of the others, a strong modelcanbecreated.
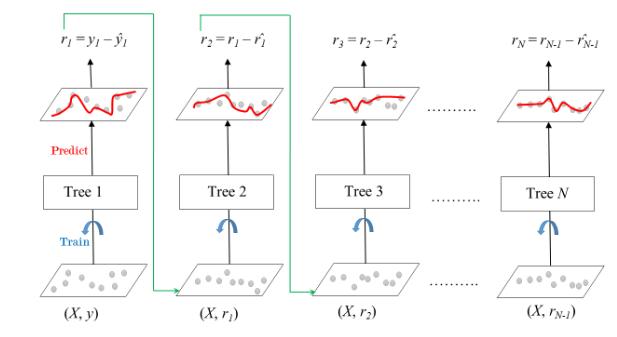
Considering a dataset with N points, or rows, in our dataset.
In gradient boosting, the error of the previous classificationisimprovedinthenextone.
In this case, n is the total number of classes in the dataset. The group of data points is x. y is our result variablewhichthedatawillbeclassifiedinto.Eachtupleis given a weight to prioritize some over others. When the assigned weights are high, those tuples ordata points are takenintoconsiderationforthenextpass.
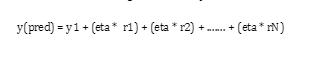
‘w’ which is the initial weighted sample will be the same forallthedatapoints:
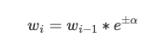
Totalerrorcanbecalculatedas:
Usingthiserrorweightscanbeupdated,
The two possible outcomes for an alpha, positive or negative,show:
When some data is correctly classified in that case the valueofalphabecomespositive.Sowedecreaseitsweight toreduceitspriority.
When the result is incorrect, the value of alpha becomes negative. Here we increase the weight so this particular tuplehasahighchanceofbeingselectedfortraining.
The ensemble consists of N trees. The matrix X and labels Y are first used as training parameters for the first Tree. The residual errors r1 are determined using the labeled classifications y1. Then, Tree2 is trained with the r1 and X from Tree1 , and so on. Using the predicted outcomes r1, the residual r2 is determined. This goes on untileverytreepresentisfullytrained.
This makes use of a critical parameter known as shrinkage.
A forecast from a tree in an ensemble is said to have shrunkwhenitismultipliedbyeta,whichhasvaluesfrom 0 to 1. This is referred to as shrinking. To reach a certain level of model performance, the estimator-to-eta ratio must be balanced; a decrease in the learning rate necessitatesanincreaseinthenumberofestimators.Now when every tree has been trained every prediction is possible.
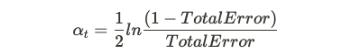
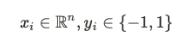
The efficiency of the ensemble classifier was assessed using a variety of evaluation metrics, including accuracy, recall, MCC, precision, and f-measure. These metrics are obtainedfromtheTable1representationoftheconfusion matrix. The terms "TN" and "FN" stand for "amount of genuine websites detected as genuine," "TP" stands for "amountofphishingwebsitesclassifiedwhichareactually phishing websites," and "FP" stands for "amount of genuine sites wrongly detected as phishing websites." Table2showstheaccuraciesofdifferentalgorithmsused.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 11 | Nov 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

phishing websites have been created, there are still many difficulties, such as accuracy. We put up a strategy for categorizing data from phishing websites to address this. Inordertocategorizethedatafromphishingwebsites,an ensemble model is built in this work utilizing a voting classifier. Voting Classifier has decent classification accuracy. A variety of indicators are employed to gauge the model's effectiveness. In order to categorize the data fromphishingwebsites,thesuggestedmodeliscontrasted with other methods already in use. These two heterogeneous classifiers were combined, and the result was an exceptional accuracy of 96.98%. The findings demonstratethattheproposedstrategiesaresuperiortoa single classifier from every angle. Users may successfully identify phishing websites with the suggested ensemble learningtechnique.
[1] Atharva Deshpande, Omkar Pedamkar, Nachiket Chaudhary,Dr.SwapnaBorde,2021,DetectionofPhishing Websites using Machine Learning, INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENGINEERING RESEARCH & TECHNOLOGY (IJERT)Volume10,Issue05(May2021),
[2] Dutta AK (2021) Detecting phishing websites using machine learning techniques. PLoS ONE 16(10): e0258361. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0258361
[3] Phishing website detection using machine learning algorithms - IJCA. (n.d.). Retrieved October 26, 2022, from https://www.ijcaonline.org/archives/volume181/number 23/mahajan-2018-ijca-918026.pdf
[4] M. Rastogi, A. Chhetri, D. K. Singh and G. Rajan V, "SurveyonDetectionandPreventionofPhishingWebsites using Machine Learning," 2021 International Conference on Advance Computing and Innovative Technologies in Engineering (ICACITE), 2021, pp. 78-82, doi: 10.1109/ICACITE51222.2021.9404714.
[5] S.Parekh,D.Parikh,S.Kotak,andP.S.Sankhe,“ANew Method for Detection of Phishing Websites: URL Detection,” in 2018 Second International Conference on Inventive Communication and Computational Technologies (ICICCT), 2018, vol. 0, no. Icicct, pp. 949–952.
[6] L. MacHado and J. Gadge, “Phishing Sites Detection Based on C4.5 Decision Tree Algorithm,” in 2017 International Conference on Computing, Communication, ControlandAutomation,ICCUBEA2017,2018,pp.1–5.