International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
1M. tech Student, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, VJTI, Maharashtra, India 2 HoD, Dept. of Electrical Engineering, VJTI, Maharashtra, India 3 HoD, Diploma, VJTI, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - This study proposes a deep convolutional neural network (DCNN)-based technique for eye state identification (closed or open) utilizing the MRL datasets. goal, pre-trained CNN architectures on INCEPTION were first trained on datasets, which included open and closedeye states, before being evaluated and their performance quantified. For this study we are using inception v3 architecture. Simultaneously, the DCNN architecture suggested on the MRL datasets has been shown to be an appropriate andeffective approach for eye state recognition based on the results compared to earlier research. Through expanding to the literature on eye state identification, this approachmay help with the creationofHMIsystems.
Key Words: Human–machine interaction, Deep learning, Deep convolutional neural network, Transfer learning, Inception
Theconditionoftheeyeisamongthefacialcharacteristics used to determine whether an eye is open or closed. It is also a critical requirement for correctly depicting a person's physiological condition. Despite the fact that eye conditioncanbeexpressedinawiderangeofways,itcan be broadly split into two categories: open and closed. It has a lot of promise in fields like sleep recognition, facial emotion identification, runtime recognition, and ocular tiredness assessment. Furthermore, eye state is a useful tool for developing HMIs and is extensively used in computervisionsystems.Manypeoplearepronetovisual problems such as dry eye caused by computer use as a result of the recent technological advancements and the fact that computers are now a part of our daily lives. Computer vision syndromes (CVS) are a group of symptoms that are caused by people's inability to modify their eye condition (e.g., blinking) while concentrating at digital screens for a prolonged period of time. For this function, eye state identification is critical in identifying a person's blink condition when they are facing a screen. Having a small number of blinks on a digital display has both positive and negative ramifications. While the positive effects of blinking are linked with focus distraction and perception on displays, the negative impacts are associated with human health and are
alarmingsincetheyequatetoanincreaseinthenumberof personsinfectedwithCVS.Inthefieldofcomputervision, eye state identificationhas become highly important. It contributes significantly to the improvement of humancomputer interface technology by enabling precise eye stateandblinkrecognition.Furthermore,therehasbeena boom inawarenessin eyestateresearchsince identifying eyestateraisesawarenessinmanydisciplines.
Driverwearinesscanalsobedeterminedbythecondition of one's eyes. A number of methods are used to identify driver weariness, along with the observation of regulated equipment, physiological indications, and behaviors. Monitoring programmable devices is a non-invasive strategy with poor dependability because to the strong dependency on driver abilities and road quality. Controllable device screening requires the driver to connect data measuring devices to his body, making it nearly difficult to see these physiological indications. In behavioral and computer vision measurements, ocular features such as the degree of eye movement and the frequency of blinks are employed to identify weariness. Driver sleepiness is one of the most common causes of catastrophic vehicle accidents (insomnia, fatigue, inattention,andsoon).Identifyingdriversleepinessmight be a key aspect of future autonomous cars. Tiredness in driversmaybedetectedusingavarietyofapproachesand classified into three types: physiological, vehicle-based, andbehavioral.
Physiological measuresincludeelectrocardiograms(ECG), electroencephalograms (EEG), and electrooculograms (EOG) collected via responsive electrodes or electronic devices worn bythe driver. Physiological measures, while ontheother hand,are rarelyusedsincetheyobstruct the driver. Monitoring the vehicle’s-controlled machinery (steeringwheel,lanemonitoring,andbrakingregulations) relies heavily on the driver's talents and road circumstances. This is another low-accuracy non-invasive sleepiness detection approach. Because behavioral views focusonthepersoninsteadoftheresource,theyaremuch more reliable than physiological and tool-based approaches. They rely on computer vision systems to detectwearinessbyanalyzingthedriver'sbehavior,facial expression, eye state, and blink condition using video-
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
recorded visual signals. Because of their lack of invasiveness and focus on the driver, behavioral approaches have lately gained appeal. Recent advances in fields such as face and eye identification and tracking, machine learning feature extraction, and deep learning have resulted in significant gain in eye state recognition. Nonetheless, because eye state recognition involves so many properties, it is continually changing on a daily basis.Earlyeyestaterecognitionresearchconcentratedon three circumstances: feature-based, motion-based, and appearance-based. In feature-based approaches, geometric features and gray-level patterns are utilized. Movement-based techniques are focused on the characteristics of eyelid movement. The tissue componentsoftheeyeareexamined.inapproachesbased on physical appearance The outcomes of studiesimply thatview-basedtacticsoutperformotherstrategies.
However,environmental factorsplayanimportant role in effectively diagnosing the eye problem.Various both internal and external components, such as illumination, light angle, head position, and image quality, can have a significant influence on the look and shape of the eyes, making exact quantification of the eye condition difficult. Because the actual world is loud and new circumstances are unexpectedly uncontrolled. In recent papers on eye state identification, machine learning methods such as AdaBoostand support vector machine (SVM) were proposedtoimprovetheefficiencyofrecognitionsystems in unexpected (uncertain) circumstances. However, human techniques for feature extraction must be utilized inadditiontomachinelearningapproachestorecoverthe features. Moreover, because hand-crafted feature extractionmethodologiesdemandasubstantialamountof compute, the resulting systems are not only sluggish, but alsorequireasignificantamountofskillandexperience.
Dong et al. [8] used Random Forest, Random Ferns, and Random Trees. And SVM algorithms for categorizing feature sets provided by different feature extraction methods for ocular state definition. They stated that the histogram-oriented gradient (HOG) was less affected by the noise effect for classification purposes, and their technique had a success rate of up to 93%. Pauly and sankarused low-resolution eye pictures to identify blinking. Sankar [9] used a variety of features (mean intensity, Fisherfaces, and HOG feature) as well as classifiers like SVM and artificial neural network (ANN). The features learned by the HOG outperformed all other methods in the study when utilized with the SVM classifier, based on the comparative results of the five distinctmethodsemployedintheresearch.Zhaoetal.[10] introduced a deep integrated neural network that relied on eyeareaclassificationbasedonactionableintelligence. They tried many configurations by varying the training typesinthisintegratedneuralnetworkandclaimedthatit
produces the best results, allowing them to enhance the capacity to categories in tiny datasets by integrating transferlearningwithdataaugmentation.
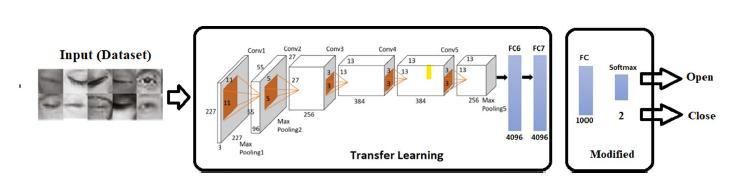
Deep learning technique advancement, as well as recent advances in artificial intelligence, has encouraged the creation of new approaches and concepts in picture classification. Because of CNN's excellent performance in image classification, one of the sub-branches of machine learning has had a significant impact in so many imagebasedtechnologies.Asaresult,insteadofthehand-crafted feature extraction methodologies used in previous research, the use of deep learning-based, specifically transfer learning-based techniques in eye state recognitionhasemergedasanintriguingcapacityinterms ofbothaccuracyandefficiency.
Transferlearningisamethodoflearning.respondingwith minordifferencesacrossdatasetsbyusingtheinformation gained by a neural network from one job to the next additional task for independent learning The network architecture is very essential in efficiency and speed of a deepnetworkforpictureclassificationInthisresearch,we investigate the various architecture approaches and modifications presented in the GoogLeNet and inception networks. These versions are evaluated in terms of computing efficiency and the network characteristics and performances are compared using the ImageNet 2012 dataset, as well as a critical assessment of inception networks. To achieve this, global average pooling and dropout were utilized. Avoid overfitting. This resulted in an error in. lowered by 0.6% when compared to the scenario when the final layer was removed used as a completely linked layer The use of average pooling The inception layer is then followed by a 1X1 convolution. Inception-v4 displays a strong effect to that offered by Inception-ResNetvariations'shortcutconnectivity Architecture Top 5 Error
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Several models were created using the GoogLeNet and ResNetdesigns,someadvancementsinthesemodelswere implemented, such as batch normalization [8], Smoothing of labels, inclusion of average pooling layers in the inception and reduction layers, as well as improved training Approaches were employed. All of these performances Models were evaluated using the ILSVRC 2012 classification. As seen in the table, the dataset has a top 5% error. The table displays the performance of GoogLeNetaswellastheperformanceofmomentum,RMS prop, and label in Inception-v2 smoothing. Application of these systems in conjunction with the use of Inception-v2 performed better after factoring. by 26.49% as compared to the GoogLeNet model Further, batch normalization of theauxiliaryclassifierinthenetworkInception-v2,i.e.The Inception-v3 network was supplied. 5.6% greater productivity. Inception-ResNet-v1 as well as InceptionResNet-v2 was built to increase performance without deterioration in the deep layer design, which resulted in anevenlowererrorrate.
Using an eye state dataset, a DCNN-based approach is used. Was intended for automated identification of eye condition(open/closed).or(closed)inthisstudy.

1. Resizing the image of close eyes and open eyes data for the CNN model divide data in training dataandtestdata.

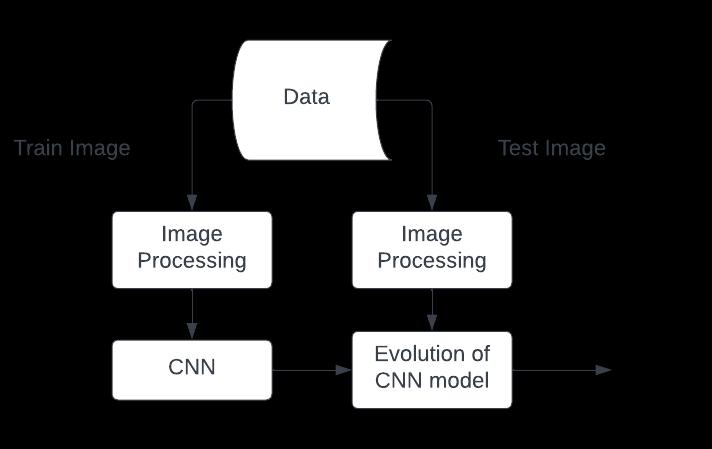
2. Train the data for the pre train CNN model for eyesstatedatatoadjustinghyperparameter
3. Measuring the performance of CNN model to evaluatingaccuracyforreservedTestedata
4. Comparing both the model for eye state recognition
ThephotoswerecollectedfromtheMRLdatasetandwere shotintypicallightingandbrightnesscircumstances;thus, theywerecomparabletoreal-worldscenarios.Thedataset was obtained under tough circumstances caused by individual variances and other environmental conditions suchaslight,blur,anddarkness,allofwhichareknownin the actual world. This dataset was used to identify eye statusordistinguishbetweenopenandclosedeyes.Based ontwocriteria,thedatasetwascategorizedintotwoparts (trainingandtesting)(openandclosed-eyeimages).
This dataset's open and closed eye photos are lowresolution, 24 *24 pixels in size, and are also openly available.Inthisdatasettotal84,898imagesavailable. we collected the data of 37 different persons (33 men and 4 women). t this moment, the dataset contains the images captured by three different sensors (Intel RealSense RS 300sensorwith640x480resolution,IDSImagingsensor with1280x1024resolution,andAptinasensorwith752x 480resolution). Thedataset issuitable fortestingseveral features or trainable classifiers. In order to simplify the comparison of algorithms, the images are divided into several categories, which also make them suitable for trainingandtestingclassifiers.
Fig 1 –FlowchartofMethod
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
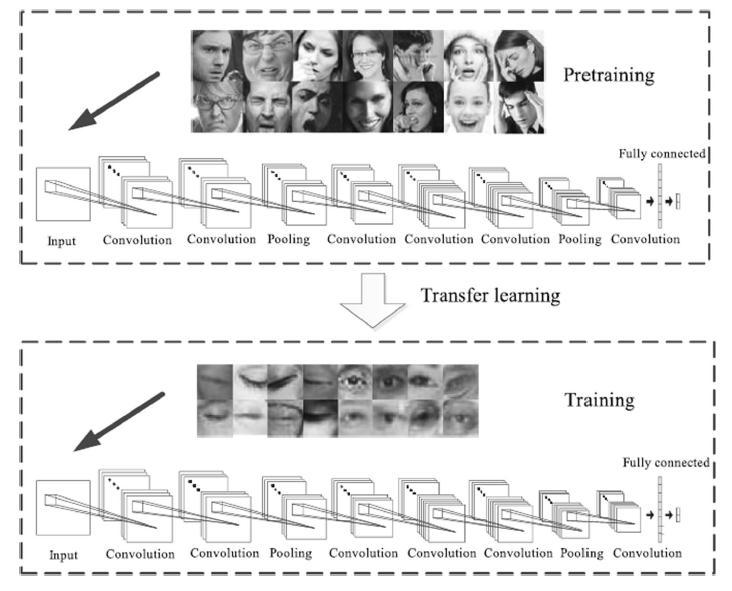
The image processing component depicted in Fig. 1 enables the pictures in the dataset to be created in line with the entry into the training of pre-trained CNN architectures. These architectures' input layer sizes were used to determine resizing. The training and test pictures in the eye state dataset were downsized for GoogleNet, ResNet18 [35], MobileNetv2 and ShuffleNet (224 224), AlexNet (227 227), and DarkNet19 (256 256) according to the input parameters of the pretrained CNN architectures . The prepared dataset of ocular states was readyAsa resultofthis approach; theproduced eyestate datasetwasreadyforthetrainingandtestingphases.This procedurewasappliedtotwodatasetsbasedontheinput ofeachtrainedCNNmodel.
CNNs are designed to continue functioning with pictures, which sets them apart from other methods. As a consequence, a 2D or 3D picture is automatically evaluatedforCNNinput.Anotherdistinguishingfeatureof CNNisthatitheavilyreliesonconvolutionalprocesses,as demonstrated by the "convolutional" abbreviation in its name.AsimpleCNNstructureconsistsofthreelayers:the convolution layer, the pooling layer, and the fully linked layer.Followingtheconvolutionlayer,subsamplinglayers such as normalization, activation, and pooling are used. stratum of evolution square number grids makes up the convolutionlayer(kernels).
These cores use convolution with the layer's data to construct and maintain the feature map. In other words, thekernelprocessesthelayer'sinputfromlefttorightand bottom to top while extracting the feature map. The mathematical formulation of the convolution process, the convolutionofacontinuousfunctionxandw(x∗w)(a),is definedinalldimensionsbythefollowingequation:
(x∗w)(a)=∫x(t)w(a t)da
In this case, is for any n≥1. Furthermore, the higher dimensional form replaces integral. In practice, however, the parameter t is expected to be discrete; hence discrete convolutionisdefinedasshowninthefollowingequation:
(x∗w)(a)=∑ax(t)w(t−a)
wherexistheinput,wisthekernel,andtheoutputisthe featuremapwhenagoesoverallvaluesintheinputspace. The pooling layer is primarily used after the convolution layer.Thislayer'sprimarygoalisto minimizepicturesize by merging certain portions of the image into a single value, and it also shows the image's features. Another approachusedaftertheconvolutionlayeristheactivation function. By training the non-linear predictions bounds, this variable is used to include non-linearity into deep learningmodels.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Fig – 4 ImageProcessing
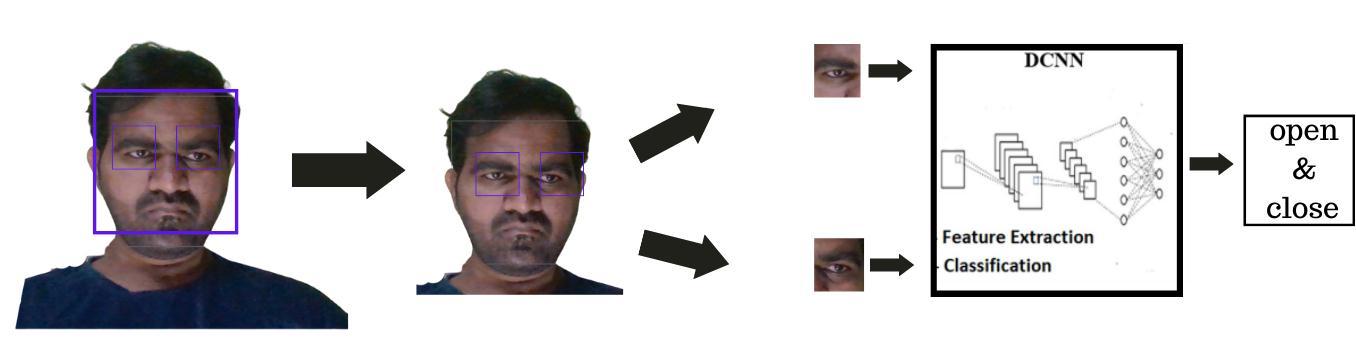
The problem of eye identification detection, which is addressed in this paper, is expected to meet real-world circumstances with varying degrees of difficulty. As a result, in addition to putting the proposed technique throughitspacesontheMRLdatasets,Ithasalsobeenput through its paces in a real - world situation. A flowchart was built in order for the suggested approach to classify the eye condition on the video. In addition, a film from a real-world event was used to show the efficacy of the suggested DCNN. The detection method retrieved the person's eye area from this video, and the acquired right and left eye regions were categorized in DCNN. In this video, DCNN trained on datasets was validated individually, and the most reliable eye state detection methodwasidentifiedbycomparingtheresults.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Eyeconditionrecognitionhasawiderangeofapplications, rangingfromHMIsystemstomonitoringdrivertiredness, dry eye, and computer vision syndrome caused by prolonged use of digital screens. Identification of eye status,eithersensitivelyonoroff,canpavethewayforthe developmentofaplethoraoftechnologyinthisfield.Many real-world events necessitate the identification of eye states. As a result, the proposed approach was put to the test by using a video from a realistic scenario. In this article, an eye state identification approach based on DCNN was demonstrated using the MRLdatasets. In this modelweuse10epochandgot94%accuracy,1.4lossand validation loss are 1.8 and validation accuracy is 92%. In theconfusionmatricescreatedasaresultofthesetests,it was seen that the proposed method trained with MRL showedthebestperformanceInthisdatasetweareusing 82,000imagesitsincludelowlightimageaswellasimage of eyes with the glass so its give the good accuracy. The suggested approach also has been evaluated in a realworld setting, and the findings demonstrate that it performs well even under adverse conditions. For the futurestudieswecanaddsomemoreimagesorcombining anotherdataandtrainthemodelforgoodaccuracy
[1] M.V.SowmyaLaxshmi,P.U,L.ChandanaandS.N,"An Enhanced Driver Drowsiness Detection System using Transfer Learning," 2021 5th International Conference on Electronics, Communication and Aerospace Technology (ICECA), 2021, pp. 1671-1678, doi:10.1109/ICECA52323.2021.9676050.
[2] Qaisar Abbas, “HybridFatigue: A Real-time Driver Drowsiness Detection using Hybrid Features and Transfer Learning” International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications (IJACSA), 11(1), 2020.
[3] Y. Xie, K. Chen, and Y. L. Murphey, “Real-time and Robust Driver Yawning Detection with Deep Neural Networks,”Proceedingsofthe2018IEEESymposium Series on Computational Intelligence, SSCI 2018, pp. 532–538,2019
[4] Eyosiyas Tadesse, Weihua Sheng, Meiqin Liu,(2014) “Driver Drowsiness Detection through HMM based Dynamic Modeling.” 2014 IEEE International Conference on Robotics Automation (ICRA) Hong KongConventionandExhibitionCenter
[5] Giri, Santosh Joshi, Basanta. (2019). “TRANSFER LEARNING BASED IMAGE VISUALIZATION USING CNN”.Vol.11.41-49.10.5121/ijaia.2019.11404.
[6] Bakheet S, Al-Hamadi A. “A Framework for Instantaneous Driver Drowsiness Detection Based on Improved HOG Features and Naïve Bayesian Classification.”BrainSciences.2021;11(2):240
[7] Chirra, Venkata & Reddy, U. Srinivasulu & Kolli, Venkata Krishna Kolli. (2021). “Virtual facial expressionrecognitionusingdeepCNNwithensemble learning.” Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Computing. 12. 10.1007/s12652-02002866-3.
[8] Dong, Y., Zhang, Y., Yue, J., Hu, Z.: Comparison of random forest, random ferns and support vector machine for eye state classification. Multimed. ToolsAppl. 75(19),11763–11783(2016)
[9] Pauly,L.,Sankar,D.:Non-intrusiveeyeblinkdetection fromlowresolutionimagesusingHOG-SVMclassifier. Int.J.ImageGraph.SignalProcess. 8(10),11(2016)
[10] Zhao,L.,Wang,Z.,Zhang,G.,Qi,Y.,Wang,X.:Eyestate recognitionbasedondeepintegratedneuralnetwork andtransferlearning.Multimed.ToolsAppl. 77(15), 19415–19438(2018)
Jigar Sapkale received the B. E degree in Electronics and communicationEngineeringfrom Gujarat Technological University, in 2020.He is currently pursuing theM.TechdegreeinElectronics and Telecommunication from Veermata Jijabai Technological InstituteMumbai,India.

Surendra Bhosale received B.E ElectricalfromShivajiUniversity, Kolhapur, Maharashtra and M.E. Degree in Electrical from the University of Mumbai, Maharashtra. Currently, He has Ph.D. Degree in Electrical Engineering from the University of Mumbai, India.. His teaching and research areas include Wireless Communications and Routing algorithms, Applications of Machine Learning and Deep Learningalgorithms.
