International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Associate
Professor,Department
***
Abstract - The health of the entire population is impacted by diabetes, a chronic illness that continues to be a major global concern. It is a metabolic illness that causes high blood sugar levels and numerous other issues, including heart and nerve issues, stroke, renal failure, and many others. Over the years, numerous researchers have made an effort to develop an accurate diabetes prediction model. But because there aren't enough relevant data sets andpredictionstrategies, this field still has a lot of unresolved research problems, which forces academics to apply ML-based techniques. In this study, machine learning algorithms have been utilized to diagnose people with diabetes so that we can better care for them. The prediction of diabetic illness patients is taken into consideration. The diabetic disease patient’s dataset includes diverse attributes like glucose levels, insulin levels, etc. The dataset in this study is initially examined using established machine learning techniques like decision trees, KNN, and random forests. Decision Tree accuracy was 83.11%, Random Forest accuracy was 88.42%, K-NN accuracy was 60.2%, and SVM (Linear) accuracy was 74.45%. The accuracy of the Decision Tree technique is enhanced from 83.62%to 89.5% by using the Pearson Correlation, while the accuracy of the K-NN approach is increased from 60.2% to 60.8%. In this study, the existing algorithm is improved, and we increase accuracy by about 74% in comparison to the accuracy attained by the original KNN algorithm, which was 60.8%.
Key Words: Machine Learning, Diabetic Retinopathy, component, Decision Tree, KNN, Pearson correlation, Random Forest
Diabetesisaconditioninwhichthereisinsufficientinsulin, which impairs blood sugar metabolism and causes blood sugarlevelstokeeprising.Patientswithdiabetesareunable to efficiently convert the eaten carbohydrates into the glucosesugarneededtofueldailyactivities.Asaresult,the blood sugar level gradually rises. Consequently, glucose doesn'treachallofthebody'scellsandinsteadstaysinthe bloodstream[1].
Diabetes is a metabolic condition that develops when the pancreas fails to produce the required quantity of insulin over an extended period of time. According to WHO, the premature mortality rate from diabetes increased by 5% between2000and2016.From2000to2010,thepremature
ofComputer
Engineering Dr. D. Y. Patil Institute of Technology, Pimpri, Pune-18death rate due to diabetes fell or was limited in affluent nations,butratesrosefrom2010to2016.Incontrast,rates roseoverthewholeperiodindevelopingcountries.In2014, 8.5% of individuals and senior citizens aged 18 and older haddiabetes.However,upuntil2016,1.6milliondeathsor incapacitiesweredirectlyattributabletodiabetes.From108 million in 1980 to 422 million in 2014, the number of diabeticpatientsincreased. People overtheage of 18,the prevalence of diabetes increased globally from 4.70% in 1980to8.50%in2014.(WHOofficialsite)[2].
To identify these fatal diseases, a sophisticated ML-based diagnosticsystemisneeded.Patientswithdiabetescanbe successfullydiagnosedatanearlystageusinganML-based expert decision system. For the purpose of predicting diabetes,researchersusedavarietyofdifferentdatasets.An adequatedatasetwiththerequiredfeaturesfortrainingand validationisrequiredforML-basedframeworks.Theability oftheMLmodeltopredictoutcomesproperlyisincreased bychoosingpertinentandrelevantcharacteristicsfromthe dataset. The dataset utilized in the suggested system was assembled by the hospital in Sylhet, Bangladesh and is availableinthe(UniversityofCaliforniaIrvine)UCIMachine Learningrepository[3].
The technologiesofmachinelearninganddeeplearningare directly related to solving problems in the real world. Machine learning uses classification algorithms to help in diabetes prediction. The various classification methods enableustodistinguishthecrucialcharacteristicsthatare morestronglyassociatedwiththepredictionofdiabetes.We employed a Convolution neural network from a Deep Learning algorithm for the prediction of diabetic retinopathy.Byclassifyingqualities,weareeffectivelyable todistinguishbetweendependentandnon-dependenttraits inpatients,allowingustodeterminewhichtraitcontributes to diabetes and which does not. An correct diagnosis is necessary because the number of diabetic patients is growingdaybydayovertime.Inrecentyears,diabeteshas becomeoneofthetopcausesofdeathindevelopingnations. Both the government and private citizens are funding researcheffortstofindacurefortheseriousdisease.Finding thebestclassificationsystemforDiabetespredictioniswhat drivesustodothis.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
This section reviews the most recent research in the field, providesinsightsintotheproblems,andlooksforgapsinthe methodsthatarecurrentlyused.Theliteratureinthisarea focuses on the use of machine learning's classification algorithminthehealthcareindustrytodesignandcreatean effective learning healthcare system for better diabetes diagnosis. Our source for the pertinent data is a literature review.
An adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system (ANFIS) and principal component analysis were used to describe an intelligent method for improving the accuracy of diabetes diagnosis(PCA).Tobemore specific,thePCAtechniqueis utilized to minimize the number of characteristics in the diabeticdataset.TheANFISclassificationapproachiscrucial for the early detection of diabetes [4]. Reduced attributes providethefoundationoftheANFISclassificationmodel[5].
DiseasePrognosisanalyzeddatausingtheK-meanalgorithm and machine learning. K-mean algorithm is the proposed system's foundation for both structured and unstructured data.A0.95accuracylevelwasattained.[6]ThePimaIndians DiabetesDatabase,whichiscompiledfromdatacollectedby theNationalInstituteofDiabetesandDigestiveandKidney Diseases,isthedatasetusedfordiabetesdiseaseprediction utilizing machine learning on big data in healthcare. The inputdatasetisinitiallypreprocessedintherecommended approach using the WEKA tool. The Naive Bayes, Support VectorMachine,RandomForest,andSimpleCARTalgorithms for machine learning are employed. The SVM's accuracy, 0.7913, is the highest [7]. Pima Indians Diabetes Database (PIDD), a dataset supplied from the UCI machine learning repository, is used for the prediction of diabetes using classification algorithms. Decision Tree, SVM, and Naive Bayes are the algorithms that are employed. The accuracy that Naive Bayes provides is the highest, at 0.7630. In the future,morediseasesmaybepredictedordetectedusingthe developed system and the machine learning classification algorithms[8].Thispaper[9]makesuseofthePimaIndians DiabetesDataSet.TheupdatedJ48classifierisusedtoboost thedataminingprocess'accuracyrate.Thissectionanalyses theeffectivenessofseveralclassifiersontheinputdataset. Alsopresentedisthesuggestedsystemthathelpstoenhance diabetesprediction.TheJ-48classifierswerecreatedusing the data mining application WEKA as a MATLAB API. J48, Decision Tree, Naive Bayes, Multiclass Classifier, Random Tree, Random Forest, and Multilayer Perception are the algorithms that are employed. The proposed algorithm's accuracyvalueis0.9987.Moredatasetswillsoonbeusedto verifythesuggestedalgorithm.[10]AnEffectiveRule-based DiabetesClassificationUsingID3,C4.5,andCARTEnsembles. ThedatasetsutilizedaretheBioStatDiabetesDatasetandthe Pima Indian Diabetes Dataset (PIDD) (BDD). Information gain, gain ratio, and gin index are utilized as foundation classifiersin the proposedwork tocreateseveral decision
trees with changing splitting criteria. These distinct classifiers are then blended via a variety of ensemble techniques. Experimental findings indicate that, when compared to alternative decision tree classifiers, the suggestedmethodologyhasachievedthehighestaccuracy. Similar ensemble techniques can be used in the future on datasets related to other diseases as breast cancer, heart disease,andliverillness.[11]Areviewofcurrentliterature reveals that there has been a significant amount of study doneonthediagnosisofdiabetes.However,thePimaIndian Diabetes Dataset has been used for the majority of the research(PIDD).
Thissectionanalysestheeffectivenessofseveralclassifiers on the input dataset. Also presented the suggestedsystem thathelpstoenhancediabetesprediction.
We are motivated to examine the effectiveness of various machinelearningalgorithmsinthepredictionofthediabetic condition since effective decision-making by medical professionalsisessential.Afterpreprocessingthedataset,the suggested system discussed the various classifiers. Standardizationandtheeliminationofmissingvalueswere thepreprocessingproceduresapplied.
The15krecordsinthediabetesdataset,whichwas acquiredfromKaggle,havethefollowingattributes:
NumberoftimesPregnant
PlasmaGlucoseConcentration
SkinfoldThickness
DiastolicBloodPressure
2-hourSerumInsulin
BodyMassIndex
DiabetesPedigreeFunction
Age(inYears)
Itcontainsapedigreecomponentthatprovidesinformation aboutthefamily'shistoryofdiabetes.Thedatasethaslabels onit.Label0indicatessomeonewhoisnotdiabetic,whereas Label 1 indicates a diabetic. Since the dataset is labeled, supervised learning was employed to train the model. We used30%ofthedatasetfortestingpurposesand70%ofthe datasetfortrainingpurposesforourmodel.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The proposed system, which employs a machine learning technique,usedthefollowingsteps:
Steps: 1. Initializationoftheclassifier.
2. Traintheclassifier:Allclassifiersinscikit-learnuses afit(X,Y)methodtofitthemodel(training)forthegiven traindataXandtrainlabelY. 3. Predictthetarget:Givenanon-labelobservationX, predict(X)returnsthepredictedlabelY 4. Evaluatetheclassifiermodel. The suggested system is implemented using the Deep Learningmethodologyinthemannerdescribedbelow:
Implementation:
7. Testing
The process ofconvertingraw data intoa comprehensible format is known as data preparation. Real-world data is frequently lacking in specific behaviors or patterns, inconsistent, incomplete, and likely to contain several inaccuracies.Suchproblemsaresolvedviadatapreparation. Rawdataareprocessedbeforebeingfurtherprocessed.Here areafewpreprocessingtechniques:
• Standardization:Astandardizationapproachisusedto modifythedatasetsothatithasastandarddeviationofone in order to increase the accuracy of the Machine Learning Algorithmsdatasetduringpreprocessing.
• Replacing Missing Values:Ifacolumn'smissingvalues arenumerical,theycanberemoved.Theaverageofallthe variable'scaseswasusedtoreplacethem.
Theprocessofselectingfeaturesthatcontributethemostto ourpredictionvariableorourintendedoutputisknownas featureselection.
The following methods for feature selection have been employed:
Pearson correlation:Wecandeterminetherelationship between two quantities with the use of a coefficient. It provides us with a measurement of how strongly two variables are associated. The Pearson's Correlation Coefficient'svaluerangesfrom0to1.1denotesastronglink between them, while 0 denotes no association. We are comparing the attributes inour dataset to the results. The characteristics of glucose, insulin, BMI, and the number of pregnanciesarecloselyrelatedtotheoutcome.
Feature Selection Using Random Forest:Sincerandom forest uses decision trees to categorize test data, it can be used for feature selection as well. In this method, the importance of each attribute is determined by taking into considerationthedecisiontree'spriority,whichtruncatesthe dataset.
Recursive feature eliminationforfeatureselection:In thismethod,theaccuracyischeckedbyselectinganumberof attributes in advance. The attributes that provide the best accuracyaredeterminedbyaddingeachattributeoneata time, checking accuracy recursively, and looking at all possiblecombinationsofaddingattributes.
Forprediction,thefollowingalgorithmhasbeenapplied: DecisionTree:Forclassificationtaskswherethedatasetis partitioned into smaller subsets, decision trees are a supervised learning technique. An related decision tree is createdalongwiththedataset'ssplit.Thedecisionnodesand leafnodesarepresentinthefinishedtree.Theclassification orjudgmentvalueisrepresentedbytheleafnode,andthe predictornodeisrepresentedbytherootnode.
1. Pickthebestattribute.Thebestattributeistheone thatseparatesthedataset.
2. Asktherelevantquestion.
3. Followtheanswerpath.
4. Gotostep1untilyouarriveatyouranswer.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
RandomForest:Duringtraining,numerousdecisiontreesare generatedusingtheRandomForestalgorithm,andtheoutput isaclassthatrepresentstheaverageofalltheclasses.Over fitting of the dataset by the decision tree is overcome by RandomForest.
:
1.Randomlyselect“k”featuresfromtotal“m” features
2.Amongthe“k”features,calculatethenode“d” usingthebestsplitpoint
3.Splitthenodeintodaughternodesusingthebest split4.
4.Repeatthe1to3stepsuntil“l”numberofnodes hasbeenreached
5.Buildforestbyrepeatingsteps1to4for“n” numberoftimestocreatean“n”numberoftrees.
K-NearestNeighbor:Thek-nearestneighboralgorithmisone used for supervised classification. The number of nearest neighborsisshownaboveas"k".This methodgeneratesa collectionofnamedpointsandappliesthoselabelstoanew point. The neighbor that is closest to the new point is designatedasitslabel.
ALGORITHMSTEPS:1. Determineparameterk=nearestneighbor
2.Calculatethedistancebetweenthequeryinstanceand allthetrainingsamples.
3.Sortthedistanceanddeterminenearestneighbors basedon k-thminimumdistance.
4. Collectthegroupsofnearestneighbors.
SupportVectorMachine:Thediscriminativeclassifierknown asthesupportvectormachine,orSVMforshort,isusedfor classification tasks. Finding the hyper plane in an Ndimensionalspace,whereNisthenumberoffeatures,and usingthathyperplanetoclearlyclassifythecharacteristics,is the basic objective of SVM. Any shape, such as a line or a curve, can be the hyper plane. SVM algorithms including linear, polynomial, and radial basis function SVM are employed.
Linear case: We should now consider the case of two classes’ problem with N training samples. Each sample is described by a Support Vector (SV) Xi composed by the different“band”withndimensions.Thelabelofasampleis Yi.Fora twoclasses’case,weconsiderthelabel -1forthe first class and +1 for the other. The SVM classifier consists in definingthefunction:(f(x)=sign((ω,X)+b))
whichfindstheoptimumseparatinghyperplane,whereωis normaltothehyperplane, andb / ωis the perpendicular distancefromhyper-planetotheorigin.
Non-Linear case:Ifthecaseisnonlinearasthefirstsolution istomakeasoftmarginthatisparticularlyadaptedtonoise data.ThesecondsolutionthatistheparticularityofSVMisto use a kernel. The kernel is a function that simulates the projectionoftheinitialdatainfeaturespacewithahigher dimension θ : KnH. In this new space the data are considered as linearly separable. To apply this, the dot product(xi,xj))isreplacedbythefunction:K(x,xi)=(φ(x), φ(xi))Thenthenewfunctiontoclassifythedataare:f(x)= sign(Σβi.αi.K(x,xi)NSi=1+b).Kernelsarecommonlyused: Thepolynomialkernel:K(x,xi)=((x.xi)+1)p.Thesigmoid kernel:K(x,xi)=tanh((x.xi)+1).
Maximum class predictions performed on a test data are applied to that class, which is chosen as the class for the testingdatabasedonpredictionsmadebyotheralgorithms on test data. KNN, Decision Tree, and Random Forest algorithms are employed in that voting process. This is a combination of these three algorithms since one of the algorithmsthatincorrectlypredictedthetestdatacouldbe correctlypredictedbyanotheralgorithm.
Themoreaccurateversionwoulddefineafunctionbasedon theaccuracyofthesealgorithmstotaketheimportanceofthe vote intoaccount,meaningthat rather thanassuming that each vote is equally important, the vote with the highest accuracy should be given priority by defining a suitable function.However,thebasisforthissuggestedmethodisthe equityofthevotescastbythreealgorithms.Fig.1depictsthe suggestedalgorithm'sabstract.
We are motivated to examine the effectiveness of various machine learning algorithms in the prediction of Diabetes sinceeffectivemedicalprofessionalsneedtomakedecisions.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
After preprocessing the dataset, we implemented various classifiersinthesuggestedsystem.Here,normalizationand the elimination of missing values were utilized as preprocessingapproaches.
We can determine the link between two quantities using Pearson's correlation coefficient. It provides us with a measurementofhowstronglytwovariablesareassociated. ThePearsonCorrelationCoefficient'svaluerangesfrom-1to +1.1denotesastronglinkbetweenthem,while0denotesno association.Wearecomparingtheattributesinourdatasetto theresults.Thecharacteristicsofglucose,insulin,BMI,and thenumberofpregnanciesarecloselyrelatedtotheoutcome.
TheaccuraciesachievedbyapplyingthealgorithmsDecision Tree,RandomForest,K-NN,SVM(Linear),SVM(Radial),SVMRFE(Recursive Feature Elimination) on the preprocessed diabetic dataset are 83.62%, 93.31%, 60.2%, 74.45%, 64.93%,74.45%respectivelyshowninthefigure2.
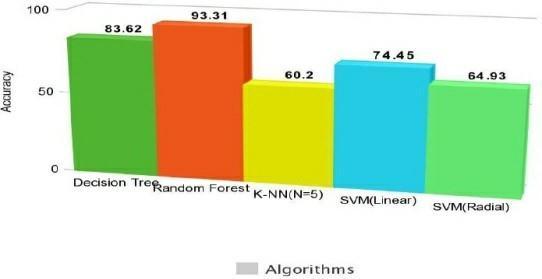
TheaccuracyratesforthemethodsDecisionTree,Random Forest, K-NN, and SVM (Linear) after applying Pearson Correlationtothediabetesdatasetare,respectively,89.5%, 92.64%,60.8%,and74.02%.
from83.62%to89.5%.AfterusingthePearsonCorrelation, the accuracy gained in the case of K- NN increased from 60.2% to 60.8%. The updated (proposed) algorithm's accuracy is estimated to be 74%. The proposed algorithm achievesanaccuracyof88%.
TheuseofMLtechniqueisthoughttobebeneficialindisease diagnosis. The patients benefit from early diagnosis and treatment. In this article, a few existing machine learning (ML) classification models for the accurate prediction of diabeticpatientshavebeendiscussed.Ontheclassification issue,anexpressionofcorrectnesshasbeenfound.Inthis study,diabetesdiseasehasbeenpredictedusingclassifier machinelearning techniques such Decision Tree, Random Forest,K-NN,andSVM(LinearandRadial).Incomparisonto the other algorithms, the Random forest performs better overallatpredictingdiabeticillness.
[1] T.M.Alama,M.A.Iqbala,Y.Alietal.,“AModelforEarly Prediction of Diabetes,”Informatics in Medicine Unlocked,vol.16,ArticleID100204,2019.
[2] Srivastava, Rashmi, and Rajendra Kumar Dwivedi. "A SurveyonDiabetesMellitus PredictionusingMachine Learning Algorithms."ICT Systems and Sustainability. Springer,Singapore,2022.473-480.
[3] A. Frank and A. Asuncion, UCI Machine Learning Repository,Oct.2010.
[4] K. Dwivedi, “Analysis of decision tree for diabetes prediction,”International Journal of Engineering and TechnicalResearch,vol.9,2019.
[5] K.PolatandS.Güneş,“Anexpertsystemapproachbased on principal component analysis and adaptive neurofuzzy inference system to diagnosis of diabetes disease,”Digital Signal Processing, vol. 17, no. 4, pp. 702–710,2007.
[6] Akash C. Jamgade, Prof. S. D. Zade, Disease Prediction UsingMachineLearning,IRJET,2019
[7] AymanMir,SudhirN.Dhage,DiabetesDiseasePrediction usingMachineLearningonBigDataofHealthcare,IEEE ,2018
Fig -2 : Histogramdepictingtheaccuracyofseveral algorithms
The accuracy rates obtained using the methods Decision Tree,RandomForest,K-NN,andSVM(Linear)onthediabetes dataset are 83.11%, 88.42%, 60.2%, and 74.45%, respectively. Random Forest has the maximum accuracy (93.31%), which is obtained. After using the Pearson Correlation, the accuracy ofthe Decision Tree is improved
[8] Deepti Sisodia ,Dilip Singh Sisodia, Prediction of DiabetesusingClassificationAlgorithms,ICCIDS,2018
[9] .GaganjotKaur,AmitChhabra,Improved J48 ClassificationAlgorithmforthePredictionofDiabetes, IJCA,2014
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

[10] Saba Bashir,Usman Qamar, Farhan Hassan Khan, M.YounusJaved,AnEfficientRule-basedClassificationof Diabetes Using ID3, C4.5 and CART Ensembles, IEEE, 2014
[11] Supaporn Phetarvut, Nantiya Watthayu, Nantawon, Suwonnaroop, Factors Predicting Diabetes SelfmanagementBehavioramongPatientswithDiabetes MellitusType2,JournalofNursingScience,2011.
Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072 © 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page392