International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Abstract - In the last few years, Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence are being used to upgrade our healthcare system and treat serious diseases. In today's world, diabetes is a major threat to our health and it is a major cause of death in the world. In this materialistic age, people are very busy in earning money so that they can fulfill their daily needs. But due to this busy lifestyle, they are not able to pay full attention to their health and for this reason the number of people suffering from various diseases is increasing continuously. As we know that the field of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is growing very fast and touching every aspect of our life. Machine Learning (ML) is a part of AI and it is possible that using machine learning techniques, we can create high-quality models with the help of which diabetes and its side effects can be predicted. In this paper we experimentally analyze the adoption of machine learning in diabetes care to examine how it can improve the accuracy of diagnosis and make life easier for patients and doctors.
Key Words:Diabetes,MachineLearning,RandomForest, MultilayerPerceptron,KNN
According to IDF Diabetes Atlas Tenth edition 2021 [1], approximately537millionpeopleworldwidearesuffering fromdiabetes.Itisbelievedthatby2030thisnumberwill increase to 643 million and 783 million by 2045. In our country, in the year 2021, the estimated number of diabetic patients in the age group of 20 to79 years was 74.2millionandby2025thisnumberislikelytoincrease to 124.8 million. Which means that, in 2021, one out of every 17 people in India suffers from diabetes and this numberisincreasingrapidly.Diabetesisachronicdisease, mainly due to the imbalance of our body's metabolism. When we eat carbohydrates, such substances become dextrose after digestion and they become glucose after being absorbed by the small intestine. Pancreas secretes insulin and in the body of a healthy person, glucose is converted into energy by insulin. People suffering from diabetes do not have enough insulin in their body or the insulin made by their body does not work completely. Therefore, the cells of the body do not absorb sugar and the amount of sugar in the blood increases. When level of glucose increase in the body, the metabolism of fats and proteins is disturbed and in this condition the chances of
destruction of the body's systems and organs increase. TherearethreetypesofdiabeteswhosenamesareType1, Type2andGestational.Type1diabetes,alsocalledinsulin dependent diabetes, begin due to the lack of complete production of insulin by the pancreas in the body. In this type of diabetes, patients need insulin to keep their disease under control and survive, and if they stop taking insulin,theycanbeatriskofdeath.Type2diabetesisalso called diabetes in older people. In this type of diabetes, insulinisproducedinsidethebody, butitsquantityisnot enough to meet the need of the body and the cells of the body are not able to use sugar as a source of energy. Due to this, the level of sugar in the body increases. During pregnancy, nutrients and water reach the unborn baby throughtheplacenta.Theplacentaalsoproducesavariety of hormones necessary for pregnancy, some of these hormones (estrogen, cortisol) inhibiting insulin. As the placenta grows, more of these hormones are produced, andtheriskofinsulinresistancealsoincreases.Normally, the pancreas makes extra insulin to overcome insulin resistance,butwheninsulinproductionbeginstodecrease compared to placental hormones, Gestational diabetes takesplace.
This paper is organized as follows: we have described in detail the work and literature related to our topic in section 2, we have described the proposed research and the machine learning algorithms used in this research in section 3, we discuss about implementation in section 4 anddiscussestheresultsfromtheperformedexperiments andfutureworkinsection5.
The main objective of literature review is to get information about the work done in our domain in the pastandonthebasisofthat,getanideaforourstudy.This increasesourknowledgerelatedtothatdomainandhelps us to improve our project further. In this section we will try to know about the research work done in Healthcare and their assessment using Machine Learning and Data Miningtechniquesinthepast.Minyechil,A.,&Rahul,J.[2] they studied various techniques of data mining and various machine learning algorithms were applied in different medical datasets. They found that single algorithm provided less accuracy than group of algorithms. They found that decision tree algorithm
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
providedhighaccuracy.Inthisstudy,theyusedWekaand javaastoolstopredictdiabetesdataset. KumariSonuand Archana Singh [3] proposed an intelligent and effective methodology for the automated detection of diabetes usingneuralnetworktechnique.A.IslamandN.Jahan[4], usedthePimaIndiandatasettostudyandpredicttherisk level of diabetes. They used many machine learning algorithms to classify the data and studied the outcome obtained from them. G Bansal and Singla [5] presented a hybrid method to detect diabetes. They selected the Pima Indian DiabetesDataset to dotheir study. They used nonlinear Support Vector Machine with partial least square method. Classifiers used for the model are the neural network, SVM, and DT. The accuracy rate of their method was 84.5%. Quan Zou et al [6] proposed a model for diabetes prediction using three different classifiers and thePIMAIndianDiabetesdataset[7].BoththeWEKAand MATLAB platforms were used for their study. Random Forest (RF) and Decision Tree (DT) were implemented in WEKAandNeuralNetworkwasimplementedinMATLAB. Amaximumaccuracyof80.84%wasachievedusingRF.
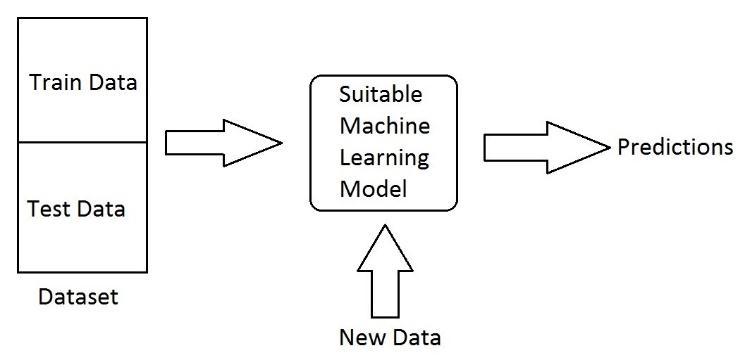
Machine Learning (ML) represents computer algorithms which can observe and analyze data on their own. That means, first of all we should collect data related to a particulardomain.Thenwehavetodevelopandalgorithm throughwhichwecanrepresenttherelationshipbetween various elements in the dataset. This algorithm is called machine learning model. This model works like brain for thecomputertounderstandingthedata. Wesplitthedata generally into two parts: the train data and the test data. Thetraindataisusedtoprovidetrainingthemodel.After the training, the model will be able to predict the future behaviorwithnewdata,calledtestdata.Thegoodpart of Machine Learning is that many models were already developed by Computer Scientists using different types of logic. These model can be used without the need of redevelopingthem.
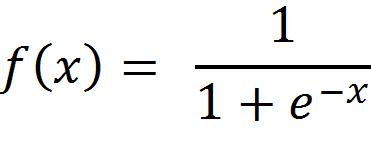
Random Forest is an algorithm that operates based on several DecisionTree (DT). Ituses multiple Decision Tree duringtrainingphaseandthefinalresultisdecidedbased on the decision given by majority of Decision Tree. RandomForestisgenerallyusedinclassificationproblems where we have to classify the digit written by a human being into the available 10 digits (0 to 9) or classify a patient into a diabetic or non-diabetic. The advantage of Random Forest is to reduce overfitting problem that generallyoccurinmanyMachineLearningmodels.
KNearestNeighbor(KNN)isanalgorithmthatclassifiesa newdatapointbasedonitsnearestneighbors.Agroupof neighborsareselected(thisisk value)andthedata point is classified under that class to which majority of neighbors belong. Here k represents the number of selectednearestneighbors.Choosingkvalueproperlywill give more accuracy. Choosing right value for is called parametertuning.
Multi-layer Perception is also known as MLP. These are fully connected dense layers, which transform any input dimension to the desired dimension. The multi-layer perceptron defines the most complex architecture of artificialneuralnetworks.Itislargelymadeupofmultiple layers of perceptron. Every node in the multi-layer perception uses a sigmoid function. The sigmoid function takes real values as input and converts this input to numbers between 0 and 1 with help of the sigmoid formula.Sigmoidfunctioniswrittenas:
For this study, I use three classification model of ML. Thesemodelsare:
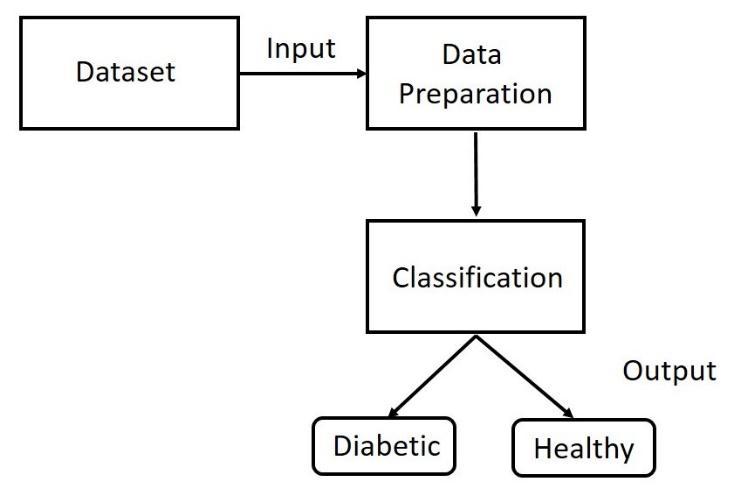
Thisdiabetespredictionsystemconsistsoftwomainsteps and both steps work together to achieve the desired
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
results. The first step of this system is data preparation andsecondstepistheclassification.
4 SkinThickness
5 Insulin
Fig - 3:Mainstagesofproposedsystem
In this study, Pima Indian Diabetes Dataset (PID) will be use. The Pima Indian Diabetes Dataset contains 768 instances. This dataset consists of one target variable (Outcome) and the 8 attributes: Pregnancies, OGTT (Oral Glucose Tolerance Test), Blood Pressure, Skin Thickness, Insulin, BMI (Body Mass Index), Age, Diabetes Pedigree Function. Each attribute is explained in Table 1. The manipulation of this dataset has been done in Jupyter Notebook with the help of Pandas library. First of all, loading the dataset with the pandas read_csv() method. Then use isnull().sum() method to check Null values in the dataset. Now check zero value in each column and after applying pandas library methods, we found 5 zero value in Glucose, 35 zero values in BloodPressure, 227 zerovalueinSkinThickness,374zerovaluesinInsulin,11 zero value in BMI. With the help replace() method of pandas, we will replace zero value with mean of that particular column. After completing data preprocessing, separate the dataset into training (70% of the data) and testdatasets(30%ofthedata).
S. No.
1 Pregnancies
2 Glucose
3 BloodPressure
Number of times pregnant
Plasma glucose concentration a 2 hours in an oral glucose tolerance test.
Diastolic blood pressure(mmHg)
Triceps skin fold thickness(mm)
2 – Hour serum insulin(muU/ml)
6 BMI Body Mass Index (kg/m^2)
7 DiabetesPedigreeFuction Diabetes pedigree function
8 Age Age(years)
9 Outcome Class variable (0 or 1),268of768are1, 500of768are0
Wecanuse train_test_split() forthis. Scikit-Learnlibrary provides fit() and predict() methods for performing training and prediction, respectively. Now import the particularClassifierclass,aninstanceofthethisparticular class was created and fit() and predict() methods were executed. After this, we again trained the machine using crossvalidationapproach Weconsidered5,10,15,20fold for training the machine. Now we will evaluate the performanceoftheseclassifiers.Forthis,findthevalue of TP(TruePositive),TN(TrueNegative),FP(FalsePositive) and FN (False Negative). Now calculate Accuracy, Sensitivity, Specificity, Precision, F1 score, Mean Squared Error (MSE) and Root Mean Squared Error (RMSE). Accuracy shows the number of correct predictions of all predictions. Sensitivity shows the number of correctly predicted patients with diabetes. Specificity shows the numberofcorrectpredictionsfornon-diabetics.Precision shows ratio of accurate positive observations. F1 score is used to measure the accuracy of a Machine Learning Model.TheMSEisameasureofhowcloseafittedlineisto data points and RMSE is just the square root of the mean squareerror.ThemodelwithhighestAccuracy,Sensitivity and Specificity is the best machine learning predictive model.
A confusion matrix is a table of data that summarizes the performance of a Machine Learning model. It helps to know wherethemodel is performing well andwhereit is failing. Generally, confusion matrix is created for the Classification models to know their performance on test data. For the two prediction classes of classifiers, the matrixisof2x2tableandfor3classes,itis3x3table.The confusion matrix is divided into two dimensions that are predicted values and actual values along with the total number of predictions. Basis structure of 2x2 confusion matrix:
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
TN(TrueNegative) FP(FalsePositive) FN(FalseNegative) TP(TruePositive)
TN (True Negative) = Model has given prediction No, and theactualvaluewasalsoNo.
TP(TruePositive)=ThemodelhaspredictedYes,andthe actualvaluewasalsoYes.
FN(FalseNegative)=ThemodelhaspredictedNo,butthe actualvaluewasYes.
FP(FalsePositive)=ThemodelhaspredictedYes,butthe actualvaluewasNo.
In this study, first we train the machine by splitting our dataset.
Totalrecords=768 Trainingdataset=70%of768=538 Testingdataset=30%of768=230
ConfusionMatrixforMulti-LayerPerceptron 121 37 27 45 ConfusionMatrixforRandomForest 140 18 31 41 ConfusionMatrixforRandomForest 122 36 30 42
With the help of these confusion matrix we calculate the accuracyofusedmodels.
AccuracyofMulti-LayerPerceptron=72.17%
Accuracy of Random Forest = 78.70%
AccuracyofKNN=71.30% Now we trained the model using cross validation method andchecktheaccuracyofthemodel.
Cross Validation
Measure - ment Matrix
MultiLayer Percept ron
Random Forest KNN
5
TPRate 0.753 0.763 0.677
TPRate 0.759 0.757 0.689 FPRate 0.295 0.305 0.378 Precision 0.758 0.754 0.687 ROCArea 0.808 0.821 0.653 Accuracy 75.91 % 75.65% 68.80% 10
FPRate 0.304 0.295 0.386 Precision 0.751 0.761 0.678 ROCArea 0.798 0.819 0.640 Accuracy 75.26% 76.30% 67.70%
TPRate 0.763 0.762 0.674 FPRate 0.297 0.294 0.386 Precision 0.760 0.760 0.676 ROCArea 0.809 0.824 0.638 Accuracy 76.30% 76.17% 67.44% 20
15
TPRate 0.733 0.753 0.682 FPRate 0.314 0.313 0.378 Precision 0.735 0.749 0.683 ROCArea 0.793 0.824 0.650 Accuracy 73.30% 75.26% 68.22%
In this study by applying three machine algorithms we developthree model.After comparingthese model onthe basis of different parameters, we can say that Random Forestmodelisthebestmodel.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
62.00 64.00 66.00 68.00 70.00 72.00 74.00 76.00 78.00 5
Fig - 4: PerformanceMeasurement
In this research paper, we have applied commonly used machine learning techniques and datasets to predict the diabetesdiseaseinapatient.Inthisstudy,wecheckedthe performance and accuracy of each of the algorithms used on the basis of various parameters and tried to find the bestalgorithmoutofthethree.Inthisstudy,wefoundthat out of the three algorithms used, Random Forest is the best compared to the other for the classification of diabetes dataset. The experimental results may aid in better clinical decision-making for early health care preventionandcontrolofdiabetes.
[1] IDF Diabetes Atlas Tenth edition 2021, https://idf.org/aboutdiabetes/what-is-diabetes/factsfigures.html
[2] Minyechil, A., & Rahul, J. (2017). Analysis and Prediction of Diabetes Diseases Using Machine LearningAlgorithm: EnsembleApproach.Volume:04, Issue 10. Retrieved from ww.irjet.net/archives/V4/i10/IRJET-V4I1077.pdf
[3] Kumari Sonu and Archana Singh, A data mining approach for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, 2013 7th International Conference on Intelligent Systems
and Control (ISCO), DOI: 10.1109/ISCO.2013.6481182, https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/6481182
[4] Aminu, I., & Nusrat, J. (2017). Prediction of Onset Diabetes Using Machine Learning Techniques. International Journal of Computer Applications, Volume 180 – No.5. pdfs.semanticscholar.org/2c3a/6609a76762e3d40bd d90d8c07fa714d611fa.pdf
[5] G. Bansal and M. Singla, “Ensembling of non-linear SVM models with partial least square for diabetes prediction,” Lecture Notes in Electrical Engineering, Vol. 569, pp. 731–739, 2020. https://assets.researchsquare.com/files/rs1572946/v1/3c5e9981-c99a-43ab-aac725a6d347cfa2.pdf?c=1650486875
[6] Q. Zou, K. Qu, Y. Luo, D. Yin, Y. Ju, and H. Tang, "Predictionofdiabetesmellituswithmachinelearning techniques," Frontiers in Genetics, Vol. 9, no. November,pp.1-10,2018.
[7] Pima Indians Diabetes Database, https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/uciml/pimaindians-diabetes-database
[8] John, George H., and Pat Langley. "Estimating continuous distributions in Bayesian classifiers." Proceedings of the Eleventh conference on Uncertainty in artificial intelligence. Morgan KaufmannPublishersInc.,1995.
[9] Kavakiotis, Ioannis, Olga Tsave, AthanasiosSalifoglou, NicosMaglaveras, IoannisVlahavas, and IoannaChouvarda."Machine learninganddata mining methods in diabetes research." Computational and structuralbiotechnologyjournal(2017).