International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Abstract - Named entity recognition(NER) isadifficulttask that has conventionally needed enormous amount of knowledge in the form of lexicons and feature engineering to achieve good performance. In the past, Named Entity Recognition systems were able to achieve great success in performing well with the cost of humankind engineering in designing domain-specific features and rules.Inthispaper,we propose a recurrent neural network architecturebasedonthe variant of RNN called LSTM with four layers to perform the task of named entity recognition. The proposed model hasfive steps; dataset collection, data preprocessing, sequential data extraction, building the model, fittingthemodelandanalyzing results. This model will classify the texts by understanding the meaning of them or context of sentences using the bidirectional LSTM without the need to remove stop words. With the proposed modelanaccuracyof96.89% wasachieved.
Key Words: NER, LSTM, Keras, RNN, Tenserflow
NamedEntityRecognitionisconsideredasoneofthefirst andkeystepsintheNaturalLanguageProcessingpipeline,it isalsoataskininformationextractionthatlookstoidentify and categories named entities mentioned in input textual content into some predefined categories such as organizations, locations, time expressions, quantities, monetaryvalues,medicalcodes, percentages,personnames etc.Inrecentyears,thewidespreadandproliferateduseof socialmediaandothermediacateringtoallkindsofpeople has resulted in increased unstructured cyber data and NamedEntityRecognitionisconsideredtobetheinstigating step to convert this unstructured format of data into structured format which is of use to lot of different applications. To understand NER formally, assume a sequenceoftokens, sequence=<w1, w2, w3........wn>.Thetask ofperformingNamedEntityRecognitionistooutputalistof tuples [1], <Is, Ie, ti,>, where each one of them is a named entitythatismentionedins.Here, Is and Ie areintherange representedby[1,N],whichrepresentsthestartindexand endindexofthementionednamedentity. ti isanentitytype fromthepredefinedsetofcategories.
Thisconceptisdiscussedindetailinthefollowingsection.
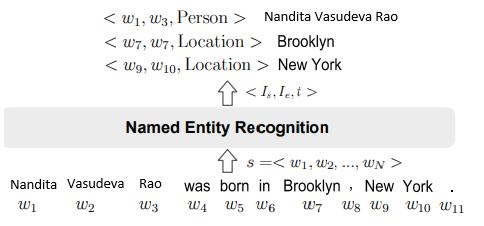
Fig-1: TheconceptofNamedEntityRecognition
Figure 1 shown above presents an example of the task of namedentityrecognition.HeretheNERsystemisfedwitha sequentialarrangementofwordsthatformsasentence.The firsttokenisidentifiedasanamedentityandthatentityisa person. Hence, the tag associated with the first token is ‘person’.Similarlythesecondandthirdtokenswhenfedto theNERsystemwillberecognizedasperson(‘person’isthe entity).Thenexttokeninthesequenceis‘was’,whichisnota namedentity.ThenextnamedentityrecognizedbytheNER systemwouldbe‘Brooklyn’whichisoftheentitytype‘GeoLocation’.
Intheconventionaldomainofinformationextraction,twoof the innovations resulted in notable enhancements. First, wordembeddingsareconsideredandusedtopresentevery token by a vector of low dimensions, which provides the frequencies of the adjacent tokens that are co-occurring. Whenitisjuxtaposedwiththebag-of-wordsapproachi.e.the basis of the general methods, word embeddings do seize semanticsimilaritieswiththetokensthatcannotbeclearly figuredoutfromtheirsurface.Theideabehindillustrating wordsisthatthecompanythosewordskeepisanancient definitioninlinguistics.Itssuddenpopularityisduetothe fact that the embeddings of the words are automatically tunedsuchthattoolsofinformationextractionleveragethe bestoutofit.Second,ithasbeenshownthattheutilizationof neural networks, which has the tendency of automatically learning features of non-linear combinations, results in enhancedidentificationthantheutilizationofCRFs,which have the tendency to only learn features of linear combinations[5]. Deep neural networks, specifically, long short-termmemorynetworks(LSTMs),havetheabilitytodo this task very effectively and efficiently [5]. The proposed method uses the LSTM to find internal features in the sequencesofwordseliminatingthenecessityofusingstop wordsforthepurpose.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: Section II Literature review, Section III presents the proposed architecture,andIVandVexplaintheexperimentalsettings, results, and discussion. Finally, Section VI discusses the conclusion.
JingLetal.[1]proposedasurveyonusageofdeeplearningin NER, in which they have provided a review on existing techniques of deep learning for the task of NER including discussionaboutNERresourceswithoff-the-shelfNERtools andNERcorpora.Theyalsoprovidesurveysontechniquesof deep learning that are most recently used in new NER problemsettingsandapplications.
Yanyao S et al. [2] proposed the CNN-CNN-LSTM model comprising the convolutional character, a long short term memory(LSTM)tagdecoderandwordencoders.Theauthors alsocarriedoutincrementalactivelearning[2],duringthe trainingprocess,andwereabletoachievegoodperformance results.
YWuetal.[3]contrastedthreevaryingNER methods;the traditional CRF-based NER approach, a DNN-based NER method that utilizes a arbitrarily initialized matrix of embedded words; and an DNN-based NER method that makesuseoftamatrixofembeddedwordsderivedfromthe unlabelledcorpus.All three approaches were trained with the training set and their functioning on the test set was documented.
Asim G et al. [4] suggesteda successful implementationof Deep Bidirectional Long Short Term Memory (DB-LSTM) whichachieveda93.69%F1score,consideredtobeagood resultforthetaskofNamedEntityRecognitioninTurkish.
MaryamH et al. [5]proposed a model whichshows thata purely generic model corresponding to statistical word embeddings [called long short-term memory networkconditionalrandomfield(LSTM-CRF)]anddeeplearningand theirproposedmodeloutperformedconventionalNERtools thatareentity-specific,andbyagreatmargin.
M.AliFauzietal.[6]proposedanapproachtoperformthe task of named entity recognition using a recurrent neural network,knownasLongShort-TermMemory.Thenetwork proposedistrainedtoperformtwopassesoneachsequence input, outputting its decisions on the second pass. For performingdisambiguationinthesecondpass,thenecessary informationisacquiredinthefirststep.Forthesecondpass, thenetworkistrainedtooutputavectorrepresentationof therelevantoutputtags.
P. V. Q. de Castro et al. [7] proposed a Deep Learning architecturebasedonBi-LSTMwithCRFandthisarchitecture wasevaluatedbyperformingthealteringofhyperparameters
for Portuguese corpora. The output achieved high performanceusingtheoptimalvalues,enhancingtheoutputs achievedforPortugueselanguagetoupto5pointsintheF1 score.
Chuanhai d et al. [8] proposed a bidirectional LSTM-CRF neuralnetworkthatutilizesbothradical-levelandcharacterlevelrepresentations.Bycomparingtheoutputsofdifferent variations of LSTM blocks, the authors found the perfectly suitableLSTMblockforCNER.Theyevaluatedtheirsystem onthethirdSIGHANBakeoffMSRAdatasetforasimplified CNERtaskandachievedaF1scoreof90.95%.
Arya R et al. [9] proposed a review on the learning approachesthathavebeenusedforNERintherecentpast and also focusing on how they evolved from the linear learning approaches of the past. They also present the progressofrelatedtaskseg.Entitylinking,sequencetagging etc.wherevertheprocesseshavealsoenhancedNERoutputs.
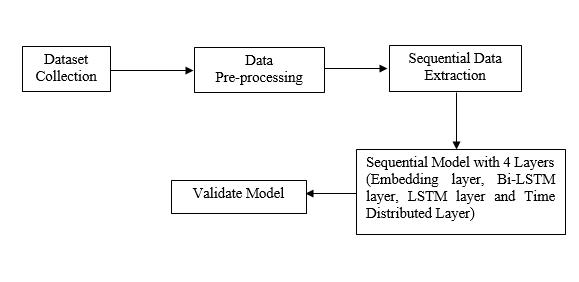
Figure 2 shows the architecture of our proposed system whichperformsthetaskofNamedEntityRecognition.The proposedarchitecturecomprisesfivekeystepsi.edataset collection, data preprocessing, sequential data extraction, buildingmodel,fittingandanalyzingmodel.Thesestepsare discussedindetailinthefollowingsections.
The implementation of the proposed model begins by loading the dataset. The dataset used for this model is availablepubliclyonkaggle.Thedatasetcontainssentences, and these sentences are tokenized and saved into a field calledwords,finally,thetagcorrespondingtoeachtokenis presentinthefieldcalledtag.
Theproposedmodelrequiresustotrainaneuralnetwork for the task of NER. So we need to perform some modificationsinthecollecteddataandprepareitinsucha way that it can easily fit into a neutral network. The modificationstodata aredoneinthisstep whichincludes
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
extractionofmappingsthatarerequiredtotraintheneural network.Wewillobtainthewordandtagmappingsandwe createtwonewfieldsinthedatasetwhichwillcontainallthe mappings.
The algorithm to extract mappings is represented in the figure3shownabove.
In this step, we will transform the columns in the dataset intosequentialarrays.Wehavetoalsoconvertthenewtag columncreatedinthepreviousstepintoonehotencoding which is leveraged by the model to recognize the named entities.
Neuralnetworkmodelshavethetendencytoworkonlywith graphicalstructure.Hence,,wefirstoutlinethestructureof the network and set the dimensions of input and output withrespecttoeachlayer.RNNsarecapableofworkingwell with varying combinations of input and output. We have used the RNN many-to-many architecture to perform this task. The goal is to output a tag for any given word consumedatalltimesteps.Intheproposedneuralnetwork, wearefunctioningwithprimarilythreelayers;embedding, bi-LSTMandLSTMlayersandthelasttimeDistributedlayer isusedforoutputproduction.
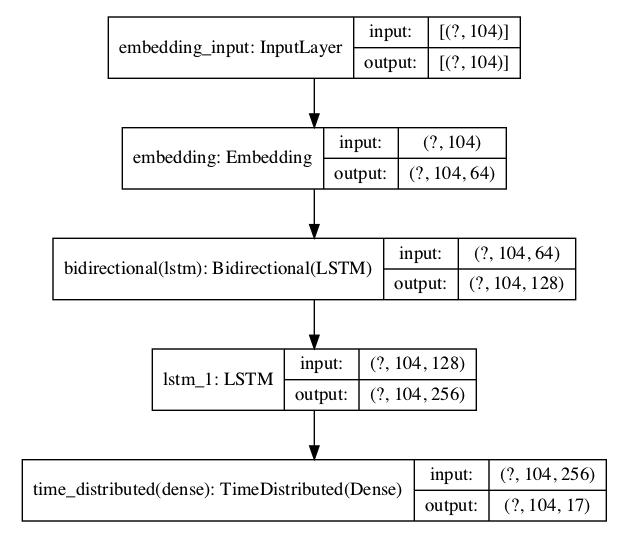
The architecture as mentioned before has four layers and these layers have specific input and output dimensions which depending on the dataset vacillates. In accordance withthedatasetcollectedinthisresearch,wehavesetthe inputandoutputdimensions.
The architecture/model with the four layers and its associatedinputandoutputdimensionsaspresentedinthe Figure4shownabove.
These layers are explained in detail in the subsequent sections.
The embedding layer:We definetheinputtobe themaximumlengthofthelongestsequence.Once the proposed network is trained, this particular layerwilltransformeachandeverytokenintoandimensionalvector.Forthisproposedarchitecture, wehavedefinedthen-dimensionas64.

Bidirectional LSTM: Bidirectional LSTM layer takestheoutputfromthepreviousembeddinglayer (104, 64).This layer has two outputs, one is the forward output and another backward output. Theseoutputsareintegratedbeforepassingittothe nextlayerbyconcatenationofthetwooutputs.Due to this integration, the number of outputs at this layeraredoubled.Inourmodel,itbecomes128.
LSTM Layer: An LSTM network is a RNN that consists ofLSTMcell blocksinsteadof thetypical RNNlayers.Thislayerhasanoutputdimensionof 256(TwicethedimensionsoftheBi-LSTMlayer).
TimeDistributed Layer:TheTimeDistributeDense layers provide completely-connected functioning acrosseachoutputovereachtime-step.Ifthislayer isnotused,itwouldresultinone-soleoutput.This layertakestheoutputdimensionfromtheprevious LSTM layer and outputs the maximum sentence lengthandmaximumtags.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
The model was validated by analyzing accuracy obtained whentestingdataisprovidedtotheensemblemodel.20%of thedataprovidedfortrainingthemodelwasreserved for testingthemodel.
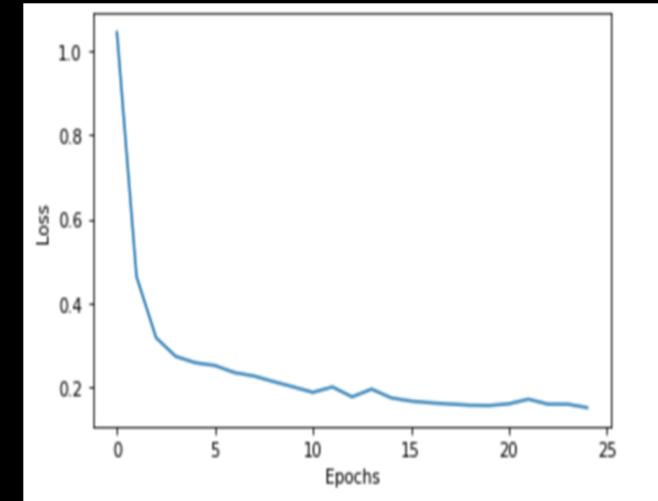
Theproposedmodelwastestedbyreservingapartofthe trainingdataforthepurposeandthenumberofepochsused was 25 and the batch size being 1000. The graph in the Figure 5 shows the model accuracy and loss across the epochs:
As described in this paper, we have proposed a Bi-LSTM based Neural Network for the task of Named Entity Recognition.Theresultsshowthatthemodelprovidesahigh performancewithanoverallaccuracyof96.89%bytheend oftheimplementation.ThetaskofNERisdifficultbecause, thoughthetokenizationofasequenceoftokenswillreveal itscomponents,understandingtheunderlyingcontextcan be difficult. Hence, we have proposed a model based on LSTM,whichcaneffectivelyunderstandtheinternalfeatures andassociationsbetweenthetokensandprovidealeverage forrecognizingnamed entities.Tosummarize,our results show that an Bi-Lstm based RNN enhances substantially uponcurrentNamedEntityRecognitionapproaches.
Thescopeforenhancementovertheproposedmodelcould betochangethemodelhyperparameterslikethenumberof epochs,embeddingdimensionsetc.
[1] J.Li,A.Sun,J.HanandC.Li,"ASurveyonDeepLearning forNamedEntityRecognition,"inIEEETransactionson KnowledgeandDataEngineering,vol.34,no.1,pp.5070, 1 Jan. 2022, doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2020.2981314.M. Young, The Technical Writer’s Handbook. Mill Valley, CA:UniversityScience,1989.
Fig-5: Resultsachievedwithproposedmodel. Itwasobservedthattheproposedneuralnetworkachieved anaccuracyof91%withthelossbeingat1.2164forthefirst epoch and by the last epoch, the network achieved an accuracyof96.97%withthelossbeingreducedto0.0916 which shows that the proposed model proved a high performance. The table 1 below presents the outputs achievedinthefirst,twelfthandthelastepoch:
Table 1: Outputsfortheproposedmodelw.r.tto intermediateepochs.
Epoch Loss Accuracy% 1 1.2164 91.00 12 0.1817 96.79 25 0.0916 96.97
Thistableshowsthatourmodelhasgraduallyenhancedin recognizingthenamedentitiesovertime
[2] Shen, Yanyao & Yun, Hyokun & Lipton, Zachary & Kronrod, Yakov & Anandkumar, Animashree. (2018). DeepActiveLearningforNamedEntityRecognition.K. Elissa,“Titleofpaperifknown,”unpublished.
[3] WuY,JiangM,LeiJ,XuH.NamedEntityRecognitionin ChineseClinicalTextUsingDeepNeuralNetwork.Stud Health Technol Inform. 2015;216:624-8. PMID: 26262126;PMCID:PMC4624324.
[4] A. Güneş and A. C. TantuĞ, "Turkish named entity recognition with deep learning," 2018 26th Signal Processing and Communications Applications Conference (SIU), 2018, pp. 1-4, doi: 10.1109/SIU.2018.8404500.
[5] MaryamHabibi,LeonWeber,MarianaNeves,DavidLuis Wiegandt, Ulf Leser, Deep learning with word embeddings improves biomedical named entity recognition,Bioinformatics,Volume33,Issue14,15July 2017, Pages i37–i48, https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btx228.
[6] Hammerton,James.(2003).NamedEntityRecognition withLongShort-TermMemory.ProceedingsofCoNLL2003.4.10.3115/1119176.1119202.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[7] QuintadeCastro,P.V.,FélixFelipedaSilva,N.,daSilva Soares,A.(2018).PortugueseNamedEntityRecognition UsingLSTM-CRF.In:,etal.ComputationalProcessingof thePortugueseLanguage.PROPOR2018.LectureNotes in Computer Science(), vol 11122. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-99722-3_9
[8] Dong, C., Zhang, J., Zong, C., Hattori, M., Di, H. (2016). Character-BasedLSTM-CRFwithRadical-LevelFeatures forChineseNamedEntityRecognition.In:Lin,CY.,Xue, N.,Zhao,D.,Huang,X.,Feng,Y.(eds)NaturalLanguage Understanding and Intelligent Applications. ICCPOL NLPCC20162016.LectureNotesinComputerScience(), vol 10102. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-50496-4_20.
[9] Roy,Aryan.“RecentTrendsinNamedEntityRecognition (NER).”ArXivabs/2101.11420(2021):n.pag.
NVSahanaiscurrentlyworkingas an associate software engineer in Bosch Global Software Technologies, Electronic City, Bengaluru,Karnataka,India Sheis a graduate from Bangalore InstituteofTechnology,Bengaluru, Karnataka,India

Dr.BhanushreeK.J.Professorat the Department of Computer Science&Engineering,Bangalore Institute of Technology, Visveswaraya Technological University, Karnataka, India Completed PhD in Computer Engineering from VTU University in2022.Publishedseveralpapers in international journals and conferences Research areas include Image Processing, Face RecognitionandMachineLearning
