International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
1 RADHA KRISHNA BALUSU, SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING, VELLORE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY VELLORE (TN.), INDIA.
2 MEENALOCHANI GANDHAM, SCHOOL OF COMPUTER SCIENCE AND ENGINEERING, VELLORE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY VELLORE (TN.), INDIA.
3 LAVU.SIRIAMMULU, SCHOOL OF ELECTRONICS AND COMMUNICATION ENGINEERING, VELLORE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY VELLORE (TN.), INDIA. ***
ABSTRACT: E-Governmentsystemsleveragethelatest in information and communication technology to help residents and companies get what they need from the government more easily and quickly, with the goal of fostering more participation in and confidence in our democratic system. Supporting and simplifying governance for all stakeholders (government, people, and enterprises) is a primary goal of e-governance initiatives.Using ICTs,these threegroupsmay belinked together and their procedures and activities bolstered. To rephrase, e-governance promotes and facilitates effective government via the use of technological methods. Certificates of all kinds, including those attesting to a person's birth, income, death, or membership ina particular community,may beused on the several websites that make up this endeavour. The citizen's request is sent to the relevant authority for processing. A user's certificate may be issued to them when they have been properly notified. This has the potential toshortentheamountoftimespentinlinefor obtaining necessary government certifications. In addition, government actions should be announced on the official website. The government benefits because it has the potential to give better service in a shorter amount of time, hence improving the efficacy and efficiency of government. Government services may be mademoreeasilyavailable,andtransactioncostscanbe reduced.
Although AI has been around for a while in many theoretical forms and complex systems, it is only with the advent of more powerful computers and vast stores of data that AI has been able to produce really impressiveoutcomesinagrowingnumberofapplication areas. Computer vision [1], practical diagnostics [2], natural language analysis [3], deep reinforcement [4], and numerous other fields have all benefited greatly fromAI.Whatwemeanby"artificialintelligence"(AI)is the development of software capable of learning and improvinguponitsownperformanceinwaysthatmimic human intellect. An intelligent autonomous system that can do tasks such as driving a vehicle, playing a game,
and carrying out a wide variety of complex activities is whatwe mean when wetalk aboutartificial intelligence (AI), not robotics. Artificial intelligence (AI) is at the crossroads of several other disciplines, such as Machine Learning [5], Deep Learning [6], Natural Languages Processing[3],ContextAwareness[7]andDataSecurity and Privacy [8]. The connections and overlaps between several AI-related disciplines are shown in Figure 1. Machine learning (ML) is the process by which a computer programme or other data processing device learnsfromexamplesofpastbehaviourtogeneratenew, morecomplexbehavioursandtomakebetterjudgments when presented with novel data or circumstances. Training a computational model is what makes ML algorithmspossible;itinvolvesexposinganalgorithmto a huge dataset (such as citizens' demographics) so that thealgorithmmaymakepredictionsabouttheprogram's future behaviour (e.g., employment rates). Supervised learning is a method of teaching a system new skills by observing its performance on an existing dataset. Deep Learning is a branch of machine learning that has evolved as a solution to the problems that plagued previous ML algorithms. Definition: Deep learning is the process of transforming raw data (such as a medical picture) into a target value (such as a diagnosis) by minimisingalossfunctionusinganoptimizationmethod (suchasstochasticgradientdescent)[9].Theterm"deep learning" refers to the fact that these algorithms, which take their cue from the neural networks inside the human brain, are constructed with a significant number of hierarchy artificial neurons that map the uncooked input data (implanted just at input nodes) to the expectedoutcome(generatedattheoutputnodes)thrua large amount of layers (recognised as hidden layers). The real act of mapping is carried out by the concealed layers, and consists of a sequence of elementary yet nonlinear arithmetic computations (i.e., a dot product followedbya nonlinearprocess).Oneofdeeplearning's greatest strengths is that it doesn't call for any special "feature engineering." Although machine learning has improved state-of-the-art outcomes in a number of areas,itisclearthatthereareanumberofdifficultiesin adapting deep learning for use in e-government applications[10]. Inthefirstplace,it's becomingharder
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
tolocate professionalsofthistechnology,particularlyin developing nations, who can create effective and trustworthy AI applications in light of recent and quick advancements in the machine learning sector. Second, a new set if development issues have been brought about bytheprojectcycleofAIprojects,especiallythoseusing deep learning. In particular, whereas conventional softwaredevelopmentisconcernedwithsatisfyingalist of functional and non-functional objectives, deep learning development is concerned with maximising a single measure over a wide range of factors in an inefficient, ad hoc fashion. Third, robust regulations and controls on data privacy and security are necessary for incorporating AI and deep learning technologies into egovernment services. Trust between citizens and governments, openness, and other technical issues in establishing and implementing safe systems are still obstacles to the adoption of specific standards for privacy and data security. E-government is the process of delivering and upgrading government services to individualsandcompaniesviatheuseoftheInternetand otherelectronicmeansinanefforttoincreaseefficiency and save costs. It is particularly true for developing nations that e-government plays a crucial role in promotingtheeconomicsofthegovernment,population, and industry. It allows for more efficient, transparent, andcost-effectiveinteractionsbetween governmentand people (G2C), government and corporations (G2B), and inter-agency and relationships (G2G) [11]-[14]. It also enables B2B transactions and tasks and brings consumers closer to businesses (B2C). The long-term objectiveofe-governmentistoimprovetheeffectiveness and efficiency of government services while cutting costs.Even more so,therearea number of benefitsthat maybefosteredbyadoptinge-governmentapplications, such as, but not limited to: By making it simpler to find recent news and alerts, e-government apps and media channelsmayincreasethegovernment'sopennessonits policy and current initiatives. Access to government services and information using open and simple technology may significantly increase individuals' faith in their government. • Citizen involvement: egovernment apps may facilitate citizen involvement in judgement and survey administration, so better reflecting people' perspectives and encouraging their active engagement in shaping their future. There is a positive impact on the environment thanks to the elimination of job postings and the reduced need for energy to power and operate government buildings and processing units that are made possible by the use of egovernment services. However, there are still many obstacles to overcome when rolling out e-government apps, such as the ones listed below. • Trust: individuals' trustingovernment,thequalityofinternetservices,and individual beliefs all have a role in how much they trust thesetypesofservices(e.g.,therestillalargenumberof citizens who prefer to handle paper applications rather
than web services). • Skill gaps: delivering high-quality online services calls on the recruitment of specialists in fields ranging from web development to data privacy and security. There is a lack of accessibility to the web and its services in many developing nations. • Security: cutting-edge security protocols are essential for protecting citizens' personal information and egovernment apps. Recent years have seen a rise in the useofe-governmentservicesacrossseveralnations[15]. Although many studies have been done to improve egovernment services, only a handful [16–19] discuss how to automate such services using the latest AI and deeplearningtechnologies.Therefore,itisstillcrucialto use cutting-edge AI methods and algorithms to solve problems and meet requirements in the realm of egovernment. To enhance e-government systems & their interactions with people, we offer a unique paradigm in thisstudythatmakesuseofcurrentbreakthroughsinAI. To start, we suggest a framework for applying AI in the administrationofe-governmentsystems,makingitmore efficient and less labor-intensive. Second, we create and proposeanumberofdeeplearningmodelswhosegoalis to automate e-government services for Arabic-speaking nations. These services include the identification of hand-written numbers and letters as well as sentiment analysis.
Image identification using deep residual learning. This work was written by K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun. Training neural networks with more depth is more challenging. To facilitate the training of nets far deeper than those previously used, we provide a residual learning approach. As an alternative to learning unreferenced functions, we deliberately reformulate the layerssuchthattheylearn residual functionsinrelation to the layer inputs. Here, we provide a large body of empirical data demonstrating that these networks are simpler to optimise and benefit greatly from deeper learning. We test residual networks with up to 152 layers in depth on the ImageNet dataset, which is 8x more than VGG nets [40] but still lower in complexity. Error on the Top - ranked test set is reduced to 3.57% when these residual nets are combined into an ensemble.Atthe2015ILSVRCclassificationcompetition, this result came out on top. CIFAR-10 analyses at 100 and 1000 layers are also shown. When it comes to recognising images, several different visual recognition tasksplaceheavyemphasisontherepresentationdepth. We gain a relative improvement of 28% on the COCO objectidentificationdataset,andthisisattributableonly to the depth of our representations. We earned first place in the ImageNet detection, Contest localization, COCO detection, and COCO segmentation tasks in the ILSVRC and COCO 2015 competitions1 because to the useofdeepresidualnetsinoursubmissions.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Forvoxel-wisedetectionofcerebralmicrohaemorrhage, a seven-layer deep neural network built on sparse auto encoder was developed. S.-H. Wang, H. Chen, X.-X. Hou, Y.-D. Zhang, and Y.-D. Zhang are the authors. In this study, we scanned participants using susceptibility weighted imaging to identify voxels inside the brain affected by cerebral microbleed (CMB). The discrepancy indataqualitybetweenCMBvoxelsandothervoxelsled us to use under sampling as a means of resolving the accuracy conundrum. We created a 7-layer DNN with 1 input, 4 sparse auto encoder, 1 softmax, and 1 output layers. Our simulations indicated that the approach was 95.13 percent sensitive, 93.3 percent specific, and 94.2 percent accurate. Compared to three other methods considered to be cutting-edge, this one produces superiorresults.
Applying deep recurrent neural networks to the task of video-to-language translation S. Venugopalan, H. Xu, J. Donahue, M. Rohrbach, R. Mooney, and K. Saenko authored the work. Artificial intelligence has been working on a solution to the grounding issue for visual symbols for quite some time. Recent advancements in machinelearningforhumanlanguageanchoringinstatic picturessuggestthatwearegettingclosertothisaim.In this study, we suggest employing a single deep network with the both recurrent and convolutional structure to do direct video-to-sentence translation. Few datasets of described videos exist, and the majority of available algorithmshaveonlybeentestedon"play"domainswith limited vocabularies. Our approach can generate sentence-level descriptions of open-domain films with bigvocabulariesbytransferringinformationfrom1.2M+ photos with class labels or 100,000+ images with captions. We evaluate our method in comparison to current efforts by looking at measures such language creation, accuracy in subject, verb, or object prediction, andhumanassessment.
A deep neural network with a tree search algorithm for Go mastery I. Antonoglou, V. Panneershelvam, M. Lanctot,S.Dieleman,D.Grewe,J.Nham,N.Kalchbrenner, I. Sutskever, T. Lillicrap, M. Leach, K. Kavukcuoglu, T. Graepel,andD.Hassabisaretheauthors.Othernameson the list include A. Huang, C. J. Maddison, Due to the vastness of the search space and the complexity of judgingboardsituationsandactions,theancientgameof Go has long been considered the most difficult of the retro titles for artificial intelligence. Here, we provide a novelmethodforplayingGoonacomputer,onethatuse "value networks" to assess board situations and "policy networks" to choose moves. These deep networks of neuronsaretaughttosolveproblemsbyarevolutionary mix of supervised learning via human expert games and supervised learning from games involving self-play. The neural nets play Go at the same level as the best Monte Carlo tree - based systems, which mimic thousands of
randommatchesofselfplaywithoutusinganylookahead search. We also provide an innovative search technique that integrates Monte Carlo simulation using value or policy networks. With this search technique, our software AlphaGo beat the humans European Go champion5gamesto0and99.8%ofotherGosystems.A computer programme has now won a full-sized game of Go against a human professional player, something that was expected to be at least a decade distant until this moment.
In recent years, several nations have begun using egovernmentservicesacrossawiderangeofgovernment institutions and standalone software programmes. The useofcurrentbreakthroughsinAIandmachinelearning inside the automating of e-government services is the subject of just a small number of the many research aimed at improving existing e-government offerings. Therefore, the application of cutting-edge AI methods and algorithms to e-government issues remains a pressingneed.However,therearestillmanyobstaclesto overcome when rolling out e-government apps, such as the ones listed below. When it comes to internet services, citizens' faith in the government, the quality of the services themselves, and their own personal beliefs all play significant roles in determining whether or not people will use them (e.g., there still a large number of citizens who prefer to handle paper applications rather than web services). Expertise gaps: delivering highqualityonlineservicescallsforassemblingafullteamof specialistsversedineverythingfromwebdesigntodata protection. A number of developing nations still have serioustroubleconnectingtothewebandusingitsmany services. For the safety of citizens and their personal information, e-government apps must use cutting-edge securityprotocols.
This study details a proposal for using Convolution NeuralNetworks,akindofDeepLearning algorithm, to automate government functions (CNN). New government programmes may be announced to the public and discussed in online forums, where citizens can provide constructive feedback that the government canusetoinformpolicychoices.Weneedsoftwarewith the cognitive abilities of humans in order to automaticallyidentifypublicopinionregardingschemes, andthisincludestheabilitytodeterminewhetherornot the sentiments expressed in online comments are good or negative. The author proposes developing a CNN model that can function like human brains in order to automatetheidentificationofopinions.Wecangenerate a CNN model for any service and programme it to make decisions automatically, eliminating the need for human
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
intervention. The author has previously described the notion of implementing various models in order to recommend this method; one model can detect or identifyhumanhand-writtendigits,whileanothermodel may detect sentiment from text phrases that can be offered by human concerning government plans. We've included a model that can read emotions in people's faces as part of our extension model. Oftentimes, a person's expressions convey their feelings more accurately than their actual words. As a result, our expandedworkcanreademotionsfrompeople'sfacesin photos.
First, we'll generate a deep learning model for recognising hand-written digits. This model will be a CNN-based hand-written model that will recognise a pictureofadigitandpredictitsname.ACNNmodelmay be created with only two picture types: train images (whichincludeallconceivableformsofdigitshumancan write in all possible ways) and test images (Using test images train model will be tested whether its giving better prediction accuracy). CNN will construct the trainingmodelbyanalysingallofthedatainthetraining set.Wewillfirstextractcharacteristicsfromthetraining photos that will be used to construct the model. Additionally, we shall extract features from the test pictureandusethetrainedmodeltocategoriesitduring thetestingphase.
Usingthismodule,wecancreateadeeplearning model for detecting sentiment in both written text and visual media. In order to create a text-based sentiment model, we will employ everypositiveand negative term in the English language. The photographs of people's expressions, both neutral and emotional, will beutilized to build a sentiment analysis system based on face analysis. The train model is applied to every incoming textorpicturetodetermineitsemotionaltone.
In the third and final section, "Upload Test Image and Identify Digit," we'll use a train model to uploadatextimageandthenrecognizeadigit.
Fourth, you may share your thoughts on public policy by utilizing the module "Write Your Comment AboutGovernmentPolicies."Thecollecteduserfeedback willbestoredintheappforfurtheranalysis.
The fifth module, "See Sentiment from Opinions," allows the user to view all user opinions and the corresponding feelings recognized by the CNN model.
A user may indicate his or her level of satisfaction with a certain government policy by uploadingaphotoshowinghisorherfacialexpression.
Usingthismodule,usersmaysubmitaphotoof theirfaceandhaveitanalyzedtodeterminetheir emotionalstate.
CNN:
This study details a proposal for using Convolution Neural Networks, a kind of Deep Learning algorithm, to automate government functions (CNN). New government programmes may be announced to the public and discussed in online forums, where citizens can provide constructive feedback that the government canusetoinformpolicychoices.Weneedsoftwarewith the cognitive abilities of humans in order to automaticallyidentifypublicopinionregardingschemes, andthisincludestheabilitytodeterminewhetherornot the sentiments expressed in online comments are good ornegative.
The author proposes developing a CNN model that can function like human brains in order to automate the identificationofopinions.WecanconstructaCNNmodel for any service and programme it to make decisions automatically, eliminating the need for human intervention. The author has previously described the notion of implementing various models in order to recommend this method; one model can detect or identifyhumanhand-writtendigits,whileanothermodel may detect sentiment from text phrases that can be offered by human concerning government plans. We've included a model that can read emotions in people's faces as part of our extension model. Oftentimes, a person's expressions convey their feelings more accurately than their actual words. As a result, our expandedworkcanreademotionsfrompeople'sfacesin photos.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
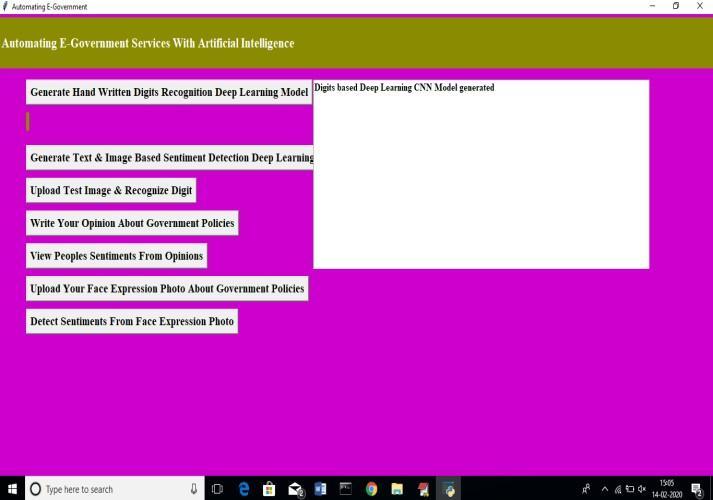
Home Page:
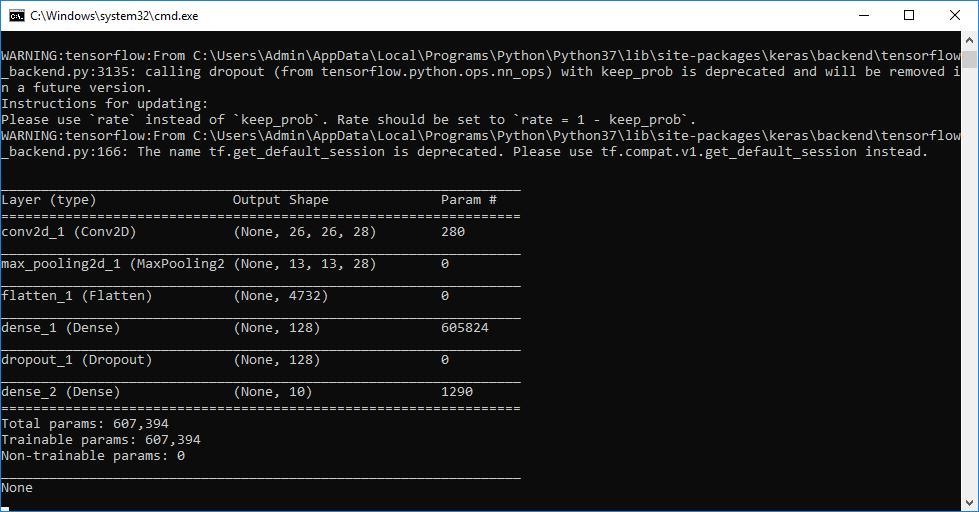
TocreateaCNNdigitsrecognitionmodel,usetheaforementionedpageanditsbuttonlabelled"GenerateHandWriteDigit growthRecognitionDeepLearningModel."
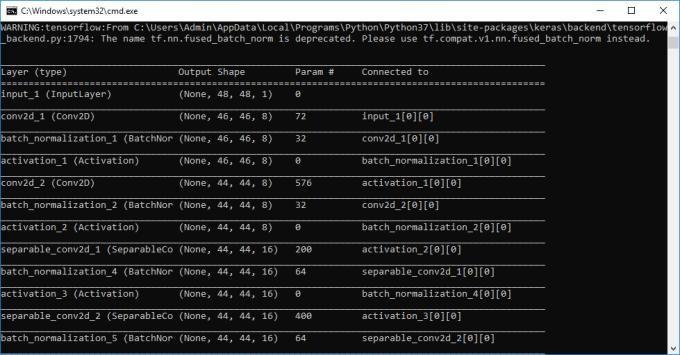
Theupperwindowdisplaysthecreatedmodelinnumericalform,whiletheblackconsoletotherightdisplaysinformation abouteachoftheCNNlayersthatmadeupthemodel.
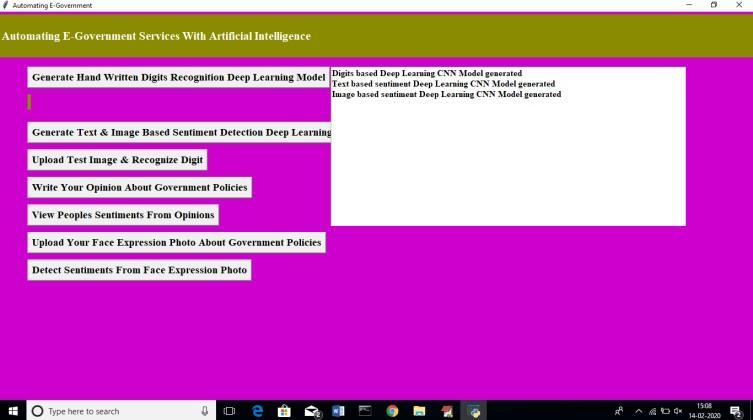
Conv2d, as shown in the screenshot above, indicates that a convolution or CNN has been used to construct the layer of imagefeatures.Thislayer'sfeaturesweregeneratedusinganimagesizeof26by26,whereassubsequentlayersused13 by 13, and so on. Now you can construct a CNN for text and picture based sentiment detection by clicking the "Generate Text&PictureBasedEmotionDetectionDeepLearningModel"button.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
There isa CNN model that usesbothtextandimages,asseenontheprevious screen. Detailsmay be foundon the blank screen.
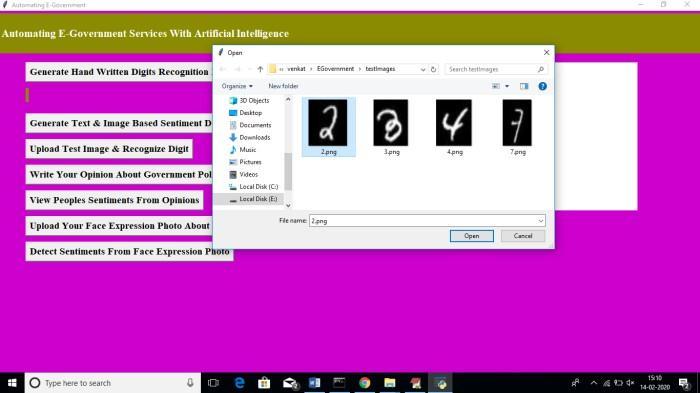
Nowyoumaysubmitphotographsofdigitsandlearntheirnamesbyclickingthe"UploadTestPicture&RecognizeDigit" button.Thetestmagesfoldercontainsallthedigitpictures.
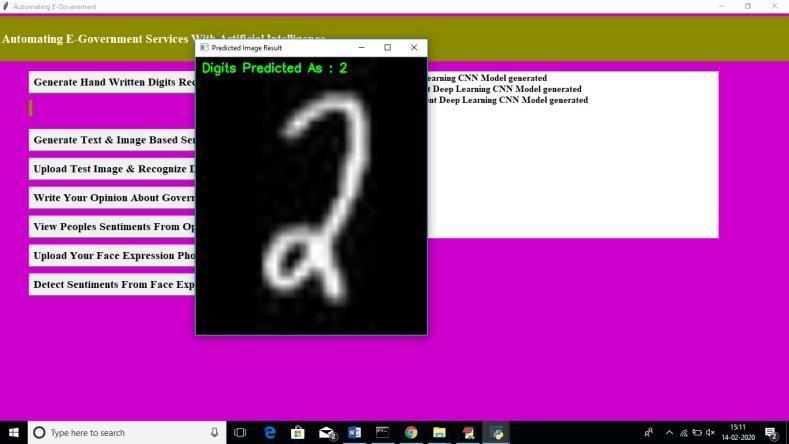
Above,I'muploadingapicturethatcontainsthenumber2,andbelow,youcanseetheresultsofthedetection.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Above,thepredicteddigitsreadasfollows:2.Toshareyourthoughtsoncurrentgovernmentpolicy,clickthetablabelled "WriteYourOpinionOnGovernmentPolicies."
Opinionscanonlybepostedwhenapersonhasfirstenteredtheirusernameintheboxprovidedabove,andthenclicked "OK."
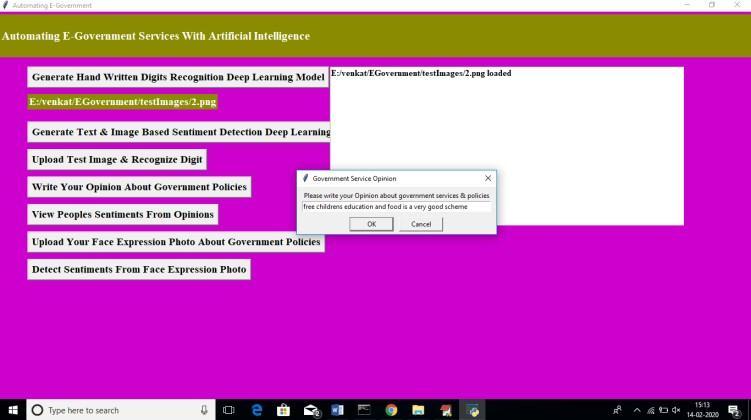
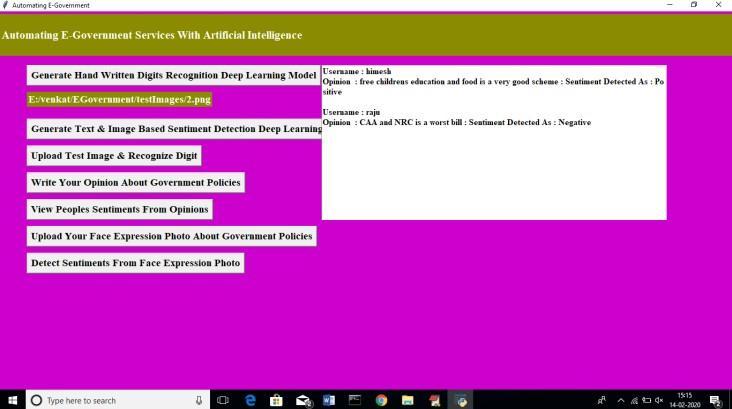
My opinion on some scheme is shown in the above screen, and the software attempts to determine if my comment is favourable or bad based on the wording I used. To read comments made by previous users, choose the option to "View People'sSentimentsFromOpinions."
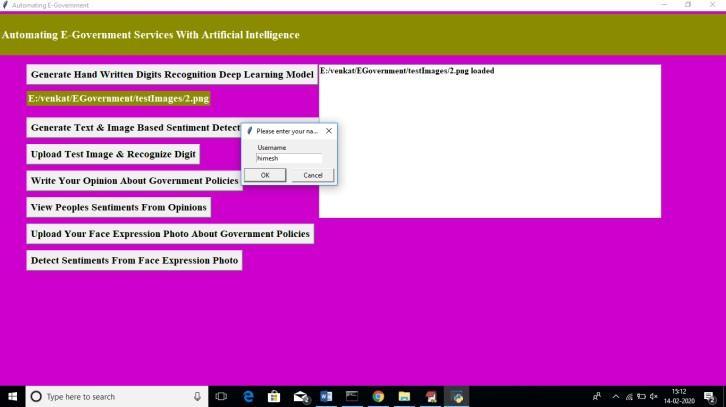
The views of all users are shown in the text space above the screen; the first opinion has a positive sentiment analysis, indicatingthattheuserispleasedwiththeproposedsolution,whilethesecondopinionhasanegativesentimentanalysis, indicatingthattheuserisdissatisfied.Usersmayalsoindicatetheirmoodbyuploadingaphotoofthemselvesdisplayinga pleasedorfuriouslook.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
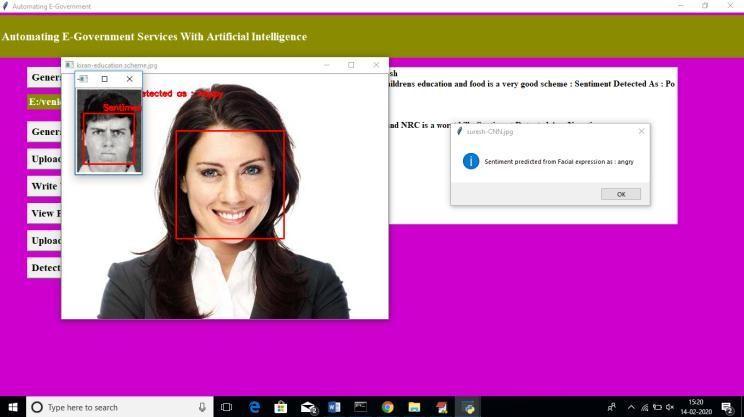
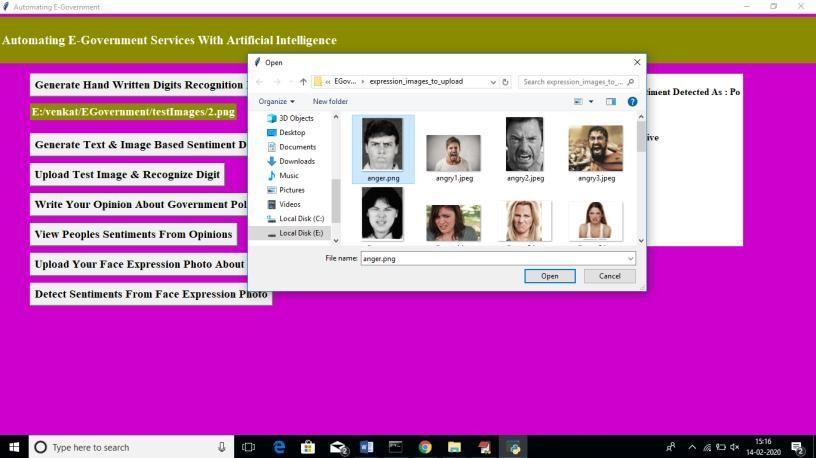
Ontheabovepage,Iamattemptingtosubmitapictureofanangryexpressionbeforebeingpromptedtoprovidemyuser name and the name of the referral programme. furthermore, unlimited people may share their photos. Proceed to the Detecttabandclickit.
Click
The emotions associated with each facial expression in thefollowingphotographhavebeenlabelled.Theresults of the survey of public opinion are also shown in the dialogue box. Any amount of comments or photographs of faces may be entered to analyse their emotional contentinthesameway.
As artificial intelligence (AI) and deep learning (DL) continue to grow, we may expect to see more government agencies using these tools to enhance their own operations and offerings to the public. However, thereisalonglistofproblemsthatpreventswidespread useofthesetechnologies,suchasadearthofspecialists, computingresources,trust,andinterpretabilityofAI.
In this article, we provide an overview of AI and egovernment, explore the global landscape of egovernment indexes, and conclude by outlining our recommendations for improving the condition of egovernment with a focus on the Gulf States. To better oversee thewhole e-governmentlifecycle,we presented
a methodology for managing government information resources. In response, we suggested a suite of deep learning methods that can streamline and automate a variety of online government functions. Then, we presentedasophisticatedinfrastructurefortheresearch anddeploymentofAIine-government.
Overall, this paper aims to increase e-trustworthiness, government's openness, and efficiency by introducing new frameworks and platforms for incorporating cutting-edge AI approaches into government systems andservices.
Plans are in the works to examine and improve the protocol for policy change in the future, as opposed totheprocessreformitself. Differentgovernmentshave adopted and defined this strategy in an effort to assist the governing style that would boost public confidence, create a more trustworthy and transparent system conducive to democracy, and ultimately lead to more effectivegovernance.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET)

e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
[1] K. He, X. Zhang, S. Ren, and J. Sun, ‘‘Deep residual learning for image recognition,’’ in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput.Vis.PatternRecognit.,Jun.2016,pp.770–778.
[2] Y.-D. Zhang, Y. Zhang, X.-X.Hou, H. Chen, and S.-H. Wang, ‘‘Sevenlayer deep neural network based on sparse autoencoder for voxelwise detection of cerebral microbleed,’’ Multimedia Tools Appl., vol. 77, no. 9, pp. 10521–10538,May2018.
[3] S.Venugopalan,H.Xu,J.Donahue,M.Rohrbach,R. Mooney, and K. Saenko, ‘‘Translating videos to natural languageusingdeeprecurrentneuralnetworks,’’2014, arXiv:1412.4729.[Online].
Available:https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.4729
[4] D.Silver,A.Huang,C.J.Maddison,A.Guez,L.Sifre, G. van den Driessche, J. Schrittwieser, I.Antonoglou, V. Panneershelvam, M. Lanctot, S. Dieleman, D. Grewe, J. Nham, N. Kalchbrenner, I.Sutskever, T. Lillicrap, M. Leach, K. Kavukcuoglu, T. Graepel, and D. Hassabis, ‘‘Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search,’’ Nature, vol. 529, no. 7587, pp. 484–489,2016.
[5] C. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning.NewYork,NY,USA:Springer,2006.
[6] Y.LeCun,Y.Bengio,andG.Hinton,‘‘Deeplearning,’’ Nature,vol.521,no.7553,pp.436–444,2015.
[7] G. D. Abowd, A. K. Dey, P. J. Brown, N. Davies, M. Smith, and P. Steggles, ‘‘Towards a better understanding of context and context-awareness,’’ in Proc. Int. Symp. Handheld Ubiquitous Comput.Berlin, Germany:Springer,1999,pp.304–307.
[8] C.Dwork,‘‘Differentialprivacy,’’inEncyclopediaof Cryptography and Security, H. C. A. van Tilborg and S. Jajodia,Eds.Boston,MA,USA:Springer,2011.
[9] L. Bottou, ‘‘Large-scale machine learning with stochasticgradientdescent,’’inProc.COMPSTAT,2010, pp.177–186.