International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
One of the leading causes of death in people is cancer. There has been a lot of research into using image processing, classification, and techniques to identify and diagnosecancer.Buttheillnesscontinuestorankamong the deadliest. As a result, one of the reasons to treat cancer is not just its early detection. In the proposed method, cancer cells are identified using image processing, artificial neural network techniques, area measurement, and cell clump detection. Using the suggested method, we can automatically identify cancerous characteristics in any CT image, mammography image, or biopsy sample. There were numerous proposed algorithms, but they lacked flexibilityandhadunevenlevelsofaccuracy.Thesystem pre-processes the input images using a variety of methods, including grey scaling, binarization, inversion, and flood fill operation, before applying the proposed algorithm.Ifthe suggested approachcansuccessfully be used for automatically detecting cancer cells in a novel way and fine-tuned with a feedback system, it will open upnewdimensionsinthedetectionofcancercellsinthe fieldofmedicalsciences.
Keywords: Image Preprocessing, Image segmentation, ResNet50.
The obstreperous division of abnormal cells is referred to as cancer. Tumors can be produced by the spread of cancerous cells through the lymphatic or circulatorysystems.Butit'simportanttorememberthat not all tumors are malignant. Both benign (not cancerous) and malignant tumors are possible (cancerous). Over a hundred different forms of cancer have been identified, and each type has numerous Sub types with unique variations. The early stages of cancer detection are particularly difficult due to the enormous variation. Inthevastmajorityofcases,thecausesofcancerarestill poorly understood. Consequently, cancer treatment becomesconsiderablymoredifficult.
Additionally, due to the disease's extreme complexity, scientists, physicians, and engineers from
aroundtheworldareconductingresearchinthesubject of cancer in an effort to better understand the disease and, in the process, discover permanent treatments for each form of cancer. Even though the process is drawn out and challenging, having greater knowledge can help doctors treat cancer patients more successfully. This inspired us to consider how cancer is discovered and to use technology to hasten the process. Researchers studying cancer might save a tone of time and improve the effectiveness of their work if they can use image processing to automatically identify cancer cells. This is because the human error component will be completely eliminated.Enormousamountsoftimeandalsoimprove the effectiveness of the research, as the possibility of humanerrorwillbeeliminatedentirely.
Kumarsuggestedabrand-newmethodfordetecting malignancy that makes use of clinically preferred aspects. This approach is based on the K mean cluster and segmentation premise. Cell segmentation, feature extraction, and classification for the enhancement approach are a few of the processes in this procedure. The original image was divided into parts using the imagesegmentationconceptofimageprocessing.During thefeatureextractionprocess,thesegmentedimagesare used to extract the features. When KNN and SVM-based classifiers are used as the last step in a classification process, the results are shown for both a wide range of photosandtheimageswiththeselectedfeatureset.[1]
Jain proposed a novel preprocessing technique to detect lung cancer. In this study, we applied a special noise reduction method to lessen the noise difference betweentheinputandoutputphotos.[2]
Ramin suggested an image analysis method for locating cancer cells and counting the number of cancerouscellsinthesourcephotos.Raminprovidedan image analysis method for the identification of cancer cellsand quantificationofthenumberofmalignantcells in the source images. The four essential steps in this approach are preprocessing, categorization, bound regions, and cell counting. During preprocessing, noise detection for the original image was eliminated.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Following the original image's classification using the KNN method, it will group into the same cluster value. Onthebasisoftheoutputfromthesecondstage,wethen count the common cells in the third step. The bound nucleus separation process uses the local thresholding technique.Regardingerrorratioandstandarddeviation, theresultsaregood.[3]
Using the transform Technique, Thilagavathi introduced a novel technique for counting red blood cells. Red blood cell estimation uses this approach. The five phases of this method are presented. Feature extraction, segmentation, image collection, preprocessing, and counting. Apply the basic XOR operation to two binary images after determining the lower and upper threshold values for segmentation, preprocessing with the saturation image, and segmentation. One of the most popular ways to identify cancer is often through digital mammography. Many different solutions were presented in response to the multiple categorization problems for the digital mammography image. Many features are retrieved in this employing different standard procedures and fundamental notation. The tumour in this area is calculated using the MLE technique. One of the simplest ways to diagnose breast cancer is by misreading a mammogram.Bydoingthis,wecanlocateandrefinethe image's edges. Finally, determine the size of the tissues and distribution in a picture without segmenting it. Additionally, cancer cells now have a quick and delicate location thanks to nanotechnology. The contaminated cells in a human body can be identified and eliminated usingnanotechnology.[4]
Mello suggested two techniques for finding cancercellsinsideahumanbody.Thesetwoapproaches aredifferentiatedbytheiruseofcolour.TheRGBcolour formatoftheinputimageisconvertedtotheHSLcolour model in this. To the binarization, the HSL colour model is employed. The edges of the binarization image are filteredtomakethemmorerounded.[5]
Since this work is intended for all type of cancer cell detection the dataset on cancer is available in www.kagglecom
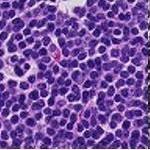
IMAGE SELECTION PREPROCESSI NG CELL COUNTING FEATURE EXTRACTION SEGMENTATI ON
DATA SET OF IMGAES
MODEL TRAINING (RESNET50)
PREDICTI ON








OUTPUT
To obtain more accurate results, the input image must go through a number of steps. These steps consist of
Image acquisition:
The cancer cell image considered hr for this work is Which is a microscopic image which is of size (90x90) Since thisistoosmall for processing itneeds resizingof theimage.
Fig2:Inputcancercellimage(size90x90)
Using the RGB to Gray () function and the Luminosity Method, which states that 3-dimensional colour has three different wavelengths and their own contribution, we must take the average according to their own contribution and is given by the following equation, the original input cancer image is converted into a grayscale image to reduce the noise level of the imageandforfurthersegmentation.
Grayscale=0.299R+0.587g+0.114B.
Otsu's thresholding method, which is based on classification,seeksthethresholdthatreducesintraclass variance, which is determined by the weighted sum of variances for the two classes. The linear discriminant criteria used by Otsu's thresholding method presume thatapicturesimplyconsistsofobjects(foregroundand background),withtheheterogeneityanddiversityofthe backdrop being disregarded. To try to reduce the overlapping oftheclassdistributions, Otsu's established thethreshold.
Fig5:Cannybasedimage


J=imclose(I,SE)standard closing function, which uses the structuring element SE to perform morphological closing on the canny-based image. The morphological close operation is a dilation followed by an erosion, with both operations utilising the same structuringelement

The technique of segmenting an image involves breaking it up into several region, to detect objects or otherimportantdetailsindigital image.Therearemany edge detector in DIP Robert edge detector, Prewitt edge detector, sobel edge detector, canny edge detector and logedgedetectorshereinthisworkcannyedgedetector, is used for cancer cell detection since Canny edge detectorisbestforvisualappearance.
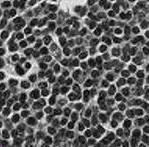
Canny edge detection is composed of five steps which areasfollows.


Fig6:Closingimage
Inversion: Inversion is necessary in the work carried here since the counting operation is performs only on the for ground pixels, performing inversion which make easyforcellcountingjustbyInvertingtheclosing
Fig7:Invertedimage
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Feature extraction:
Feature extraction attempts to reduce the number of features in a dataset by generating new ones from existing ones (and then discarding the original features).This new, smaller set of features should then summarize the majority of the information in the originalcollectionoffeatures.
Cell Counting:
To detect the boundary lines of the original image or cells, we use a clever edge detection algorithm thatfindsalloftheoriginalimage'sedgepixels.Weused the closing operation after identifying the edge pixels of theoriginalimage.
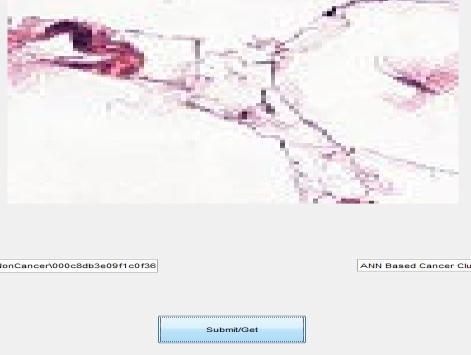
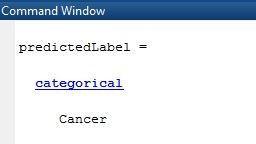
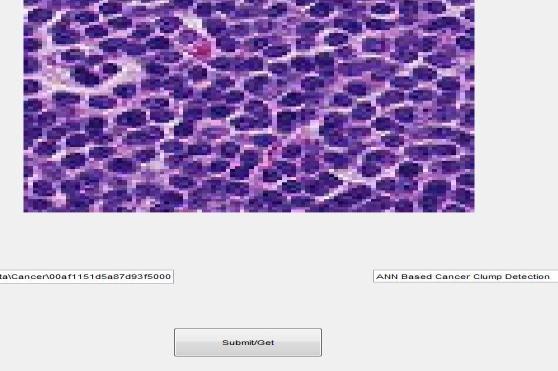
Here in this work after cell counting the image is giving as trainingimageforResNet-50.The1st layerofResNet-50isused for the prediction, if the cells in the image is cancerous then that image is labeled as cancer and other is non cancer. The imagedatastorecontainsimagesofvarioussizes,butthe networkrequiresimageswithdimensionsof224by224 by3.Useanenhancedimagedatastoretoautomatically resize the training images. Provide instructions for performing additional augmentation operations on the training images, such as randomly flipping them along the vertical axis, translating them up to 30 pixels, and scalingthemupto10% bothhorizontallyandvertically. Data augmentation is used to keep the network from overfittingandtoretaintheprecisecharacteristicsofthe trainingimages.
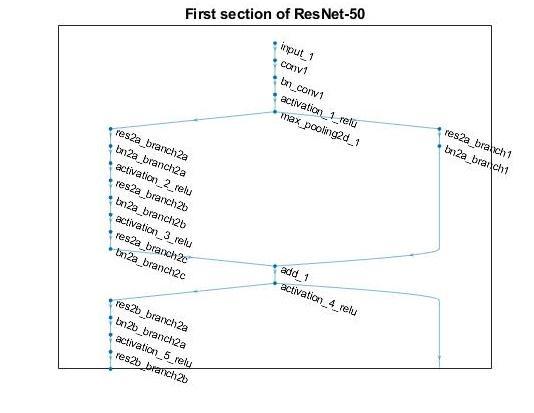
Model training using ResNet-50: ResNet-50isaconvolutionneuralnetworkwith 50 layers. A pretrained version of the network that has been trained on over a million photos is available in the Image Net database. The pertained network can classify photos into 1000 different object categories, such as animals,akeyboard,amouse,andapencil.
The confusion matrix is used to evaluate the performance of classification models for a specific set of testdata.Itcanonlybedeterminedoncethetruevalues of the test data are known. To assess the efficacy of a classificationmodel,aNxNmatrixknownasaconfusion matrix is used, where N is the total number of target classes. Here if the predicted value is logic 1 then it is cancerandifthepredictedvalueislogic0thenitisnon cancer.
Fig11:Confusionmatrix






Fig9:WorkingofResNet-50
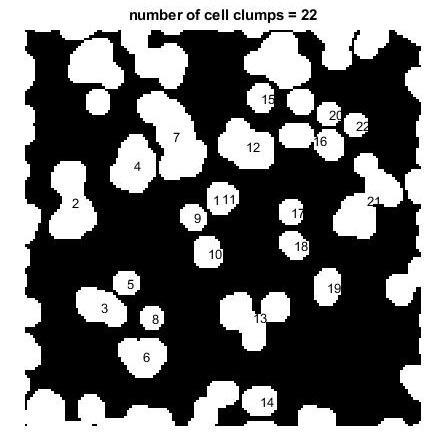
In this project work main concern is to detect the cancer clumps in a microscopic image and further classifyingthoseimagesbasedonthecellcounting.Here
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
by selecting the one of the cancer cells images which undergocertaindigitalimageprocessingtechniquesthat help us to detect the clumps in the cancer cell image by usingmachinelearningalgorithmweareabletoclassify clumps and to which class the image belongs to, here mainly considering two classes cancerous and noncancerous. This model proves to work for all the cancer cellimages.
segmentation, feature extraction and training later the detected clumps in a cancer image are trained using ResNet50 algorithm to classify the cancer cells into two different classes weather it is cancer or non-cancer. In this work different cancer cell images were tested and proved successfully. This project helps us to save the patientsbydetectingatearlystage.
1. http://lymphomapictures.org/p/37/non-hodgkinlymphoma/picture-37 *2+ Kumar R., “Detection and Classification Using Clinically Significant and Biologically Interpretable Features” Proc of Journal of Medical Engineering,Volume 2015 (2015), Article ID 457906,14pages.
2. Rammin M., M., “Counting Number of Cells in Images using Genetic Algorithm,” 12th International Conference on Hybrid Intelligent Systems,Dec.2017.pp.185-190.
3. Thillagavathi K., “Automatic Red Blood Cell Counting in images UsingHough Transform,” Proc. of 2016 IEEE Conference on Information and Communication Technology, Apr. 2016, pp. 267271.
Fig12:cancercellprediction
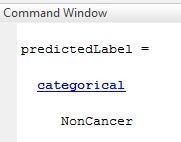
Image13:noncancercellprediction
In medicine early cancer cell detection is considered as one of the challenging tasks for the doctors. The proposed work effectively detects the number of clumps at the early stage by using different image processing techniques like preprocessing,
4. Meello, , Marco A.,“Imaage sedments for artificial andautomaticprocessforidentifyingcancerlumps Eggs,” 30th Annual International Aug. 2016. pp. 3103-3106.
5. Ammon, G.(2012, April 9). Image Segmentation for images using Digital Signal Processing. Retrieved from:
6. A history of medical imaging (2017). Retrieved from: PPT R. Boyyle and R. Vision: A First Course,On Image Processing Blackwell Scientific Publications,2012,page.32-34.
7. E. Davies e Vision: Theory, Algorithms and Practicalitiesusing Image processing and Image segmentation,AcademicPress,2011,Chap.3.
8. Gonzalaez, R.C and Wooods, R Digital Image Processing,AddisonWesley,20142,pp414–428