International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
2
1M.Tech. (Highway Engineering), UVCE, Karnataka, India. Email-rakshitha773@gmail.com 2Professor, Civil Engineering Department, UVCE, Karnataka, India. Email-gsuvce@gmail.com ***
ABSREACT - Blackcotton soil deposits can be found throughout India. When exposed to changes in moisture content, blackcotton soils exhibit significant swelling and shrinkage, making them particularly challenging from an engineeringperspective.Toimprovethemechanicalbehaviour of soil and increase the dependability of construction, many different ground improvement techniques, such as soil stabilization and reinforcement are used. In this study, an effort was made to enhance the strength properties of blackcottonsoiltreated with TerrasilandZycobondinvarying dosages of 0.06%, 0.08%, 0.1%, and 0.12% by dry weight of soil with an optimal content of Waste Foundry Sand (30%) was used as stabilizers, and the behaviour of soil to various laboratory tests was examined. The test results demonstrate that blackcotton soil stabilized with 0.1% by dry weight of terrasil and zycobond yield significant strength in terms of maximum dry density, CBR, and UCC, as well as a reduction in the Freeswell index.
Key Words: Blackcottonsoil,WasteFoundrysoil,Terrasil andZycobond,CBR,UCS
Pavement requires high-quality materials with sufficient strength and durability qualities. The largest obstacle to providing a full road network in a developing nation like India is the lack of available funding to build roads using conventional methods; as a result, it is necessary to investigatefeasiblelow-costconstructionmethods.Oneway to address the rising demand for road construction is to employ locally accessible materials that have undergone appropriate treatment. The goal of developing innovative construction and soil stabilising methods is to reduce the thickness of the pavement on inferior subgrade. In these situations,naturalsoilsaretreatedwithvariouscompounds toenhancetheirengineeringqualities.Researchisunderway toseeifwastematerialcouldbeusedasapartialsubstitute in an effort to use refuse in huge quantities. By blending thewastematerialswiththesoil,itispotentialtoalterthe soilvariedqualitiesandimproveweaksoil.
Blackcottonsoilishighlyclayedsoilthatrangesincolour from grey to black. They contain a highly expanding clay
mineral called montmorillonite. It is quite sensitive to variationsinmoisture.ItcollectedfromGulbargadistrict.
Ferrous and non-ferrous metal casting both produce wastefoundrysandasaby-product.High-gradesilicaisused. It can be put to use in many of the same applications as manufactured or natural sand. Waste foundry sand from SaravanafoundriesinBangaloreisgatheredforexperiments.
Terrasil and Zycobond is a nanotechnology based product manufactured by Zydex industries Ltd. Terrasil is a water soluble,heatstableandrelativesoilmodifier.Italsoreduces water permeability and maintains breathability of the soil layer.Zycobondactsasabondingagent,itenhancesquality ofsoillayer,controlssoildisintegration,quickdryingofsoil layers,reducesundulationsandlowmaintenancecosts.Itis available inconcentratedliquid formand itis to be mixed with water in specified proportion before mixing with the soil.
TodeterminethepropertiesofBlackcottonsoil
Toaccesstheinfluenceofvaryingdosageofwaste foundrysand(10%,20%and30%bydryweightof soil)onstrengthcharacteristics.
Tofindoutoptimumdosageofwastefoundrysand toachievemaximumstrength.
Toaccesstheeffectofvaryingdosageofterrasiland zycobond(0.06%,0.08%,0.1%and0.12%bydry weightofsoil)onthestrengthproperties.
To find out the optimum dosage of terrasil and zycobond with addition of waste foundry sand to achievemaximumstrengthofsoil.
Researchers T. Raghavendra et al. (2018)(1) conducted a studywiththeaimofevaluatingthestrengthofstabilisedsoil duringacuringtime.Theytestedsoilwithvaryingchemical dosages for stabilisation. According to their test results, a nanochemical dosage of 1 kg/m2 has the strongest effect. Withanincreaseinnanochemicaldosage,thefreeswellindex falls.
The changein soil qualitiesof untreated soil is the study's mainfocus,accordingtoNandanA.Pateletal.(2015)(2).The
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
studyshowsthechangeinthicknessduetoreactivityofsoil treatedwith0.041%terrasilisabout25%smallerthanthe thickness obtained for blackcotton soil, despite the test results showing a marginal drop in Atterberg's limits, Permeability,andCBRincreased.Thebenefitassociatedwith 0.041%terrasilissustainablefromaneconomicstandpoint.
ThepurposeofAjayKumaretal.(2017)(3) istoinvestigate how blackcotton soil behaves both with and without stabilisation.Accordingtotheirfindings,theidealamountof terrasilisdiscoveredtobe0.07%weightofdrysoilandis moreeffectivewhenlimeisaddedatarateof2%.At0.07% of terrasil, the liquid limit, plastic limit, and differential freeswellindexstarttofallandthengraduallyincrease.
ThegoalofNandanA.Patel(2015)(4) istoexamineTerrasil and Zycobond impact the soil index proportion of untreatedsoil.Accordingtotheirtestresults,thesoil'sliquid limitimproved,theplasticlimitdropped,theFreeswellindex decreased, and the soaked CBR also improved. From an economicstandpoint,improvingsoilqualitieswiththeuseof terrasil(0.041%)andzycobond(0.020%)isfeasible.
Manali D. Patel et al (2020)(5)'s intent is to determine the foundry sand mix in order to ascertain the proportionate quantityaddedforgreaterstrength.Maximumdrydensity andoptimummoisturecontentbothrisewiththeadditionof WFS.Thetestresultsindicatethat20%ofthesoil'sweight shouldbetherecommendeddosageoffoundrysand.
Intheirstudy,KuldeepGrower(2019)(6),theyusedmarble dustandfoundrysandindosagesrangingfrom13%to22% tostabilisethesoil.Itisclearfromtheexperimentalresults thatfoundrysandstabilisessoilmoreeffectivelythanmarble dust.Becausefoundrysandhasahighsilicacontent,itcan betterbondwithsoilparticles,enhancingthesoil'sbearing ability.
Selvaraj A et al(2018)(7) .'s objective is to investigate how Blackcottonsoilbehavesbothwithandwithoutstabilisation. According to the test results, terrasil dose increases cause Atterbergelimitstodecrease.Withanincreaseindosage,the swelledindexalsodropped.Theoptimalcontentofterrasilis set at 1.0% by dry weight of soil for the soaking CBR, increasedmaximumdrydensityandsoil.
Inthisstudy,anefforthasbeenmadetoenhancethestrength properties of soil from black cotton that has been treated withNanochemicals.Threestepsmakeuptheexperimental process. On Blackcotton soil the following tests were performedinthefirststage:Wetsieveanalysis,Atterberg's limit test (LL and PL), Modified Proctor Compaction test, California Bearing Ratio test (CBR), and Unconfined Compression test. Blackcotton soil treated with Waste FoundrySandof10%,20%,and30%bydryweightofsoil, Freeswell Index Test, Modified Proctor Compaction Test,
California Bearing Ratio Test (CBR), and Unconfined CompressionTestwereconductedintheSecondStage.Based on strength characteristics, the stabilized samples were evaluated to determine the ideal dosage of waste foundry sand.InthirdstageBlackcottonsoiltreatedwithTerrasiland Zycobondof0.06%,0.08%,0.1%,and0.12%bydryweightof soilwiththeidealdoseof Wastefoundrysand,theFreeswell index test, Modified Proctor Compaction test, California BearingRatiotest(CBR)andUnconfinedCompressiontest were performed. Based on strength characteristics, the stabilisedsampleswereevaluatedtodeterminetheimpactof variedTerrasilandZycobonddosages.
The soil sample that passed through a 425 µm sieve was usedforthetest.Twosamples,eachweighing10gm,were thenobtainedandplacedinseparate100mlcylinders.Upto 100mlofdistilledwaterwasplacedinonecylinder,andup to 100 ml of kerosene oil was placed in the other. For 24 hours,thetwocylinderswereallowedtoreachequilibrium. Followingthat,theultimatevolumesofbothcontainerswere noted.Thelowestdosagewasdeterminedtobeideal.
Themaximumdrydensityand idealmoisturecontentofthe soilcombinationweredeterminedusingtheModifiedProctor CompactionTest,whichwascarriedoutinaccordancewith IS2720 Part-8 (reaffirmed 1995). Increases in MDD and decreasesinOMCarecausedbyanincreaseincompacting energyperunitvolume.IS heavycompactionisperformed.
TestswereconductedinaccordancewithIS2720(Part-16) (reaffirmed 1997), and samples were prepared in various arrangements. After being mixed with the ideal amount of water,sampleswerecompactedtoMDD.Heavycompaction hammers were used to compact the CBR samples. Further researchisbeingconsideredonfourdaysofsoakedCBRat 2.5mmpenetration.
TestcarriedoutinaccordancewithIS2720(part10)Static compactionwasusedtopreparecylindricaltestspecimens. Thesamplewastestedforvariouscuringperiods0,7,14,and 28 daysin order to examine the effect ofcuringstrength attributes.
Blackcotton soil Particle size distribution Gravel,% 0
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Sand,% 23.72 SiltandClay% 76.28
Atterberg’s limit
Liquidlimit,% 76.3 Plasticlimit,% 36 Plasticityindex,% 40.3
Maximumdrydensity,gm/cc 1.482
Optimummoisturecontent,% 28.0 California bearing ratio
UnsoakedCBR,% 5.58 SoakedCBR,% 1.397 Unconfinedcompressivestrength, kg/cm2 1.570
Table -2: ResultsofFreeswellindextest
Description Free swell index Free swell ratio
BCsoil+4%cement+ 10%WFS 61.90 1.619
BCsoil+4%cement+ 20%WFS 45.45 1.455
BCsoil+4%cement+ 30%WFS 36.36 1.364
Table -2: ResultsofModifiedcompactiontest
WFS MDD g/cc OMC % 10% 1.77 30.8 20% 1.83 25 30% 1.922 31
Fig.1 VariationinCompactioncurvesofBlackcottonsoil treatedwithpercentageof Wastefoundrysand
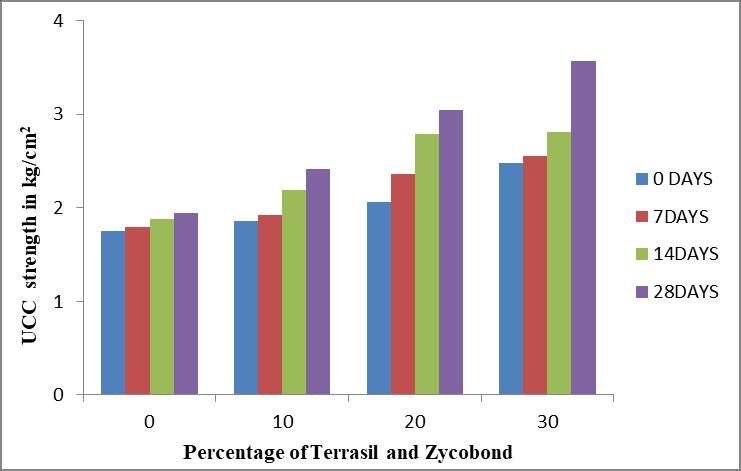
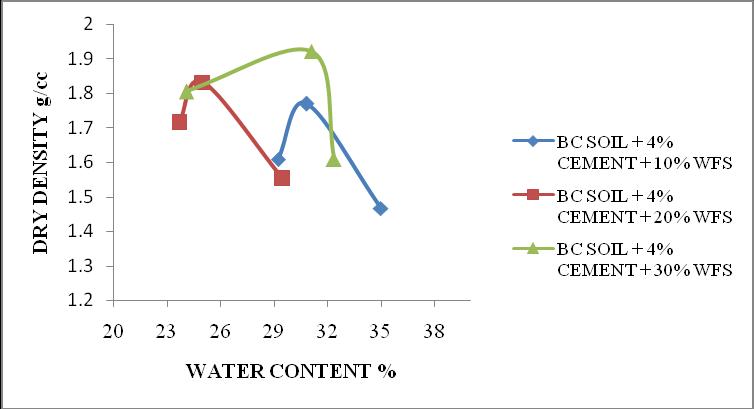
Table -3: ResultsofCBR
WFS Unsoaked CBR Soaked CBR 10 8.38 5.123 20 10.71 5.587 30 12.57 6.518
Table-4: ResultsofUCC WFS
Unconfined compressive strength, kg/cm2
0 days 7 days 14 days 28 days 0 1.748 1.79 1.879 1.95 10 1.864 1.92 2.193 2.417 20 2.066 2.365 2.79 3.05 30 2.479 2.55 2.811 3.567
Fig.2 VariationinUCCofBlackcottonsoiltreatedwith percentageofWFS
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1037

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
TREATED BLACKCOTTON SOIL
Table-5: ResultsofFreeswellindextest Description
FSI FSR
BCsoil+4%C+30%WFS+0.06%of T&Z 40 1.40
BCsoil+4%C+30%WFS+0.08%of T&Z 36.36 1.364
BCsoil+4%C+30%WFS+0.1%of T&Z 20 1.20
BCsoil+4%C+30%WFS+0.12%of T&Z 25 1.25
Table -6: ResultsofModifiedcompactiontest
Terrasil and Zycobond MDD g/cc OMC %
0.06% 1.78 17.5 0.08% 1.82 16.3 0.1% 1.84 16.2 0.12% 1.827 15.6
Terrasil & Zycobond
Table-8: ResultsofUCC
Unconfined compressive strength, kg/cm2
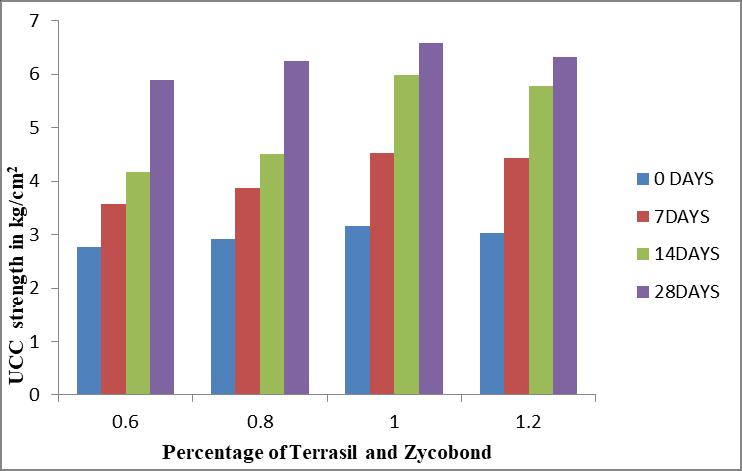
0 days 7 days 14 days 28 days 0 1.748 1.79 1.879 1.95 10 1.864 1.92 2.193 2.417 20 2.066 2.365 2.79 3.05 30 2.479 2.55 2.811 3.567
Fig.4 VariationinUCCofBlackcottonsoiltreatedwith TerrasilandZycobond
Fromtheresultsofinvestigationfollowingconclusionscan bedrawn
Freeswellindexdecreasesfrom40%to20%with increaseindosageofTerrasilandZycobondalong withoptimumcontentofWastefoundrysand.
Maximum Dry Density is achieved at 0.1% of terrasil and zycobond is 1.84g/cc and Optimum MoistureContentof16.2%.
Fig.3 VariationinCompactioncurvesofBlackcottonsoil treatedwithTerrasilandzycobond
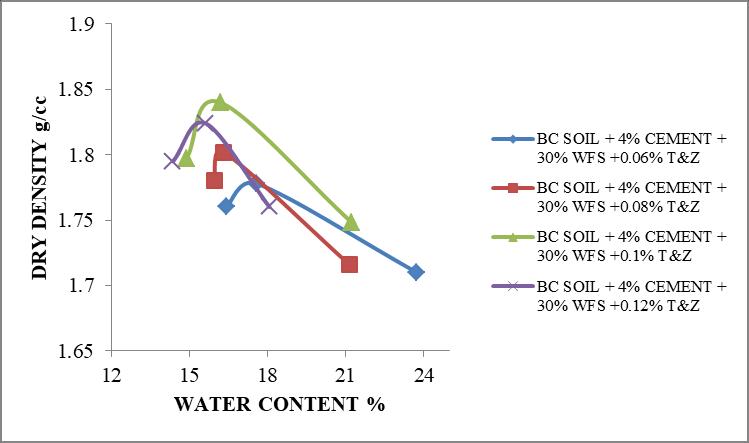
Table -7: ResultsofCBR
Terrasil & Zycobond Unsoaked CBR Soaked CBR
0.06% 10.709 6.989 0.08% 12.57 8.840 0.1 % 13.969 9.778 0.12% 13.50 8.850
HigherSoakedCBRandUCScanbeachievedwitha combination of 0.1% terrasil and zycobond with 30%wastefoundrysandand4%cement.
The Crust thickness of Stabilized blackcotton soil with Optimum content of terrasil and zycobond decreaseswhencomparetocrustthicknessofsilty soil.
Blackcotton soil stabilized with terrasil and zycobond(0.1%)withWastefoundrysandof30% and4%ofcementyieldsubstantialstrength.
Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page1038
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056 Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
[1] TRaghavendraetal(2018)“StabilizationofBlackcotton soilusingTerrasilandZycobond”NationalConference Proceeding NTSET ISSN: 2320-2882 National Conference On Trends In Science, Engineering & TechnologybyMatrusriEngineeringCollege&IJCRT.
[2] NandanA.Pateletal(2015)“Scientificallysurveyingthe usage of Terrasil chemical for soil stabilization” InternationalJournalofResearchinAdventTechnology, Vol.3,No.6,June2015E-ISSN:2321-9637.
[3] Ajay Kumar Pandagre and Rajesh Jain (2017) “ExperimentalstudyonindexpropertiesofBlackcotton soil stabilized with Terrasil” International Research JournalofEngineeringandTechnology(IRJET)e-ISSN: 2395-0056Volume:04Issue:01|Jan-2017.
[4] NandanA.Pateletal(2015)“Subgradesoilstabilization using Chemical additives” International Journal of Science,EngineeringandTechnologyResearch(IJSETR), Volume4,Issue10.
[5] Manali D. Patel et al (2020) “Stabilization of soil by Foundrysandwaste”InternationalResearchJournalof EngineeringandTechnology(IRJET)e-ISSN:2395-0056 Volume:07Issue:05.
[6] KuldeepGrowerandTriptiGoyal(2019)“Experimental studyofWastefoundrysandandMarbledustasasoil stabilizingmaterial”InternationalResearchJournalof EngineeringandTechnology(IRJET)e-ISSN:2395-0056 Volume:06Issue:06.
[7] SelvarajAetal(2018)“Laboratoryinvestigationofsoil stabilizationusingTerrasilwithCement”International Journal of Trendy Research in Engineering and Technology(IJTRET)Volume2Issue2(3).
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal |
