International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Ashutosh1, Nikhil Bajpai2
1Student, Mechanical engineering, Bansal Institute of engineering and technology, Uttar Pradesh, INDIA.
2Assistant Professor Mechanical engineering, Bansal Institute of engineering and technology, Uttar Pradesh, INDIA. ***
In general we can say that prosthetic ankle are the artificial devices which are used as a body part on the place ofmissing body parts is there any person who faces the difficulty of losing a body part due to diseases or by major accident then the body part which is artificial manufactured is transplanted on that place which provide some comfort and freedom to work but they are not work as a natural body part they fulfill some primary needs of work which are essential .the selection of these types of devices is very difficult because it requires meet the characteristics which are present in natural path the material should have high quality and lightweight with high tensile strength it requires to bear the force acting on it some other properties which are considered as flexibility in durability fracture resistance and chemical resistance and it should be cost efficient this property is playing a major role in designing the artificial ankle for the prosthetics.
Key Words- Composite fiber, Light Weight, Strength, Material properties, Durability
Prostheticlimbareartificialdeviceswhichareusedinthe place of missing body parts the limb or ankle which are designedtomeettheperformancelevelofnaturalhuman limb and also provide comfort so that the weight of prostheticithasbeenalwaysaproblem,theapproximate weight is start from 2.5 kg - 4 kg or more as per the efficiency class and work of prosthetic the weight of prosthetic main cause excessive muscle work that will resultinhighenergylosswhichisfeelliketiredandless comfortableforhumansso thattherearesomematerial which are less density and sustain the load of the body parts. The foot is made with different types of structure whichisbiomechanicalstructureanditisworkwiththe combinationofsomepartslikemuscles,veinsandbones etc. The human ankle is made as like a c -channel shape whichisgoodforstructuralloadingandhighloadbearing capacity, when load applied the middle bones of ankle work as a linear spring which supports the force and increaseloadbearingcapacity.
In prosthetics there are many types of material present and currently in use which are fulfill the needs of prostheticsbutthosematerialarenotavailableatlowcost .therearestudyiscontinueonthematerialslikedifferent compositesfibers(Kevlar,glassfiberetc.).
1 K. M. Walke and P. S. Pandure [2]observes that the propertiesofthecarbonfiberandglassfibergoodstrength anddurabilitywhichisrequiredandthedensityofthese fibersislowascampertometals.
2. In Evaluation of High Strength Materials for Prostheses,[1]Theweightofprosthesishasalwaysbeena problem for prosthetic researchers. The weight of a prosthesis may cause excessive muscle work that will result in high energy consumption for amputees Prosthesesarenormallyexcessivelyheavy,whichtendsto increase residual limb trauma and energy expenditure withthelikelihoodoflesssuccessfulprostheticfunction.
3.G.VERESanalyses[4]thatthefootwithitsactiveand passive structures (muscles, bones, Apo neuroses and ligaments) represents a complex three dimensional system. In addition it is not only purely a mechanical system,asanengineerwouldprefer, Forthepurposeof theanalysesthefootisconsideredtobeasegmentedsolid coplanarbody,placedinthesagittalplaneofthefootand articulatingwiththecrusinthetalocruraljoint.Theforce actingononeorbothlegisanalyzed. Onconcludingthisin mystudy there are different typesof material laminates with fibers and develop a hybrid which is use as a prosthetic material which is light in weight and cost effective for humans and effects on design of ankle with thismaterials.
To find which metal has similar properties to use as a prosthetic material with cost efficient and easy to manufacturing.Tofindthelaminatedmaterialandthebase material,whichissuitableforlightweighthighstrength forstaticinfuture?
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
Thesebasematerialsaresandwichingb/wthelaminating fibersinalengthwithspecificthicknesswhichisrequired.
Stainless steel- ThesetypesofSteelusedformakinghigh strengthstructurewiththetoughnessandwithoutlosing itsductility,theyaremadebytheheattreatmentprocess whichincreaseitsstrength,thistypeofsteelsarehaving ultimatehightensilestrengthandtheyareclassifiedasa low carbon Steel in special class they are having less amountofcarbonpercentagetothehighstrengthofthis typeofsteelisnot generate fromthecarboncompound presentinmetalcompositionbuttheothercompoundor materialcompositioninthemetaltheyprovidegoodload bearingcapacityisforthesetypesofSteel.
Its strength is increased by cold rolled as much as 90% withoutcracking.
Steelprovidegoodresistanceoverchemicalcompounds, freefromcorrosion,itshowsgoodductility.
Aluminum -It has less density and less modulus of elasticityitselongationuptobreakis12to25%.Medium tensilestressandfracturetoughnessislowascompareto otheris22to35MPa.
Titanium- Titaniumandaluminumwhichhaslessdensity andfinetensilestrengthwhichisgreaterisusedasabase materialforthelaminatingmaterials.
Table1. Comparative study of some materials
Material Ultimatetensile strength(MPa) Modulasof elasticity (GPa)
Density (g/cm^3)
Stainless steel 586 193 7.75
Titanium 1070 96 4.62
Aluminum 310 71 2.77
Material properties of base materials1.2 Laminating fiber materials –
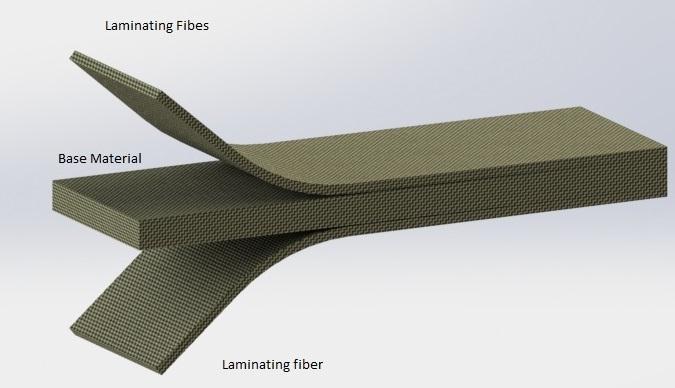
Carbon fiber- Carbonfiberisalightestmaterialusedasa prosthetics which have low density and the modulus of elasticity as compared to other materials used to make prosthetics they are laminated on the both side of base material with varying thickness as per the loading conditionsoruseinprosthetics.themixtureofcarbonand glass fiber exhibit great combination which provide the great strength and they have less tensile strength and havinghighstrengthtoweightratioandthepropertyof carbonfiberisincreasedwhenthelaminatedcarbonfiber is in continuous and straight fiber form and then the stiffnessisincreasedupto3timesoftheglassfibersothat if the each layer of carbon fiber is in forward and right orientation scheme then the each layer improve the mechanicalpropertyofmaterial.
Kevlar - It has very low density which shows that it is verylightinweightthantheothermateriallikeglassfiber orcarbonfiberitusedasalaminatingmaterialbecauseit isweakwhenaloneusedtomakeastructureunderhigh loadingcompressionbutitcanbear 5timesmoretension than compression loading but it also shows another property which is very important that is fracture resistancewhenhighfractureloadingisoccuritcanresist corrosionorotherchemicalreactionthehybridofKevlar andcarbonfiberisdevelopedbecausewhentheKevlaris mixedwithresinsitresistanddifficulttomanufactureso thatthehybridformmadewhichprovidetoovercomethis problemanditalsoimprovethelimitationsofKevlarfiber and improve some properties like stiffness talk and the impactofanyload.
Glass fiber- It has average compressive and tensile strengthascomparedtoothermateriallikeKevlarwhereit canbefoundindifferentqualityaspertherequirementof useranddifferentformsofglassfiberisalsoavailablecan highly absorb the tension but it is twice weaker in comparisonloadingitisveryflexibleinnatureandmore durablethanotherfiberitcannotregainitsshapeandsize
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
soitcannotprovidemomentuminstructure.Thehybridof glassfiberandcarbonfiberimprovethequalityaslikein carbonfiberandhybrid,doesthehybridofglassfiberand carbonfibergivesgoodratioofstrengthtowrightwhere strength is very high as compared to weight .the other propertiesarealsoenhanceswhichareimportantonthe basisofprostheticslikeweight,durability,flexibilityand thecostofcompositematerialwhichplaysamajorrolein makingprostheticschoosingthematerialforprosthetics.
Table2. Comparative study of above laminating fibers-
Material Ultimate tensile strength (MPa)
Modulas of elasticity (GPa)
Density g/cm^3 Elongation uptobreak
Carbon fiber 3790 300 2.25 1.5%
Kevlar 3600 86.9 1.44 2.4%
Glass fiber 4500 88.9 2.48 5.7%
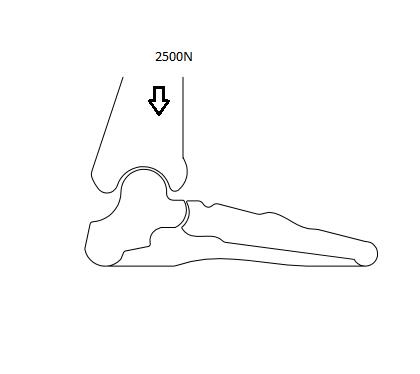
Thedesignsimpleprostheticanklewhichusedasasample or prototype for my analysis it has different layers for different materials and force acting on the structure is 2500 Newton. Which is the approximate weight of the humanbodyappliedonone anklewhenthewhole body weightisdependingononelegandthesteptimeis2sec?
Force distribution on ankle-
Softwareisusedansys18.2versionwhichusedtoanalyze thebehaviorofmechanicalstructureswhenforcesacting onthatstructure.Itismajorlyusedsoftwareforanalysisin industriesorresearchlabs.
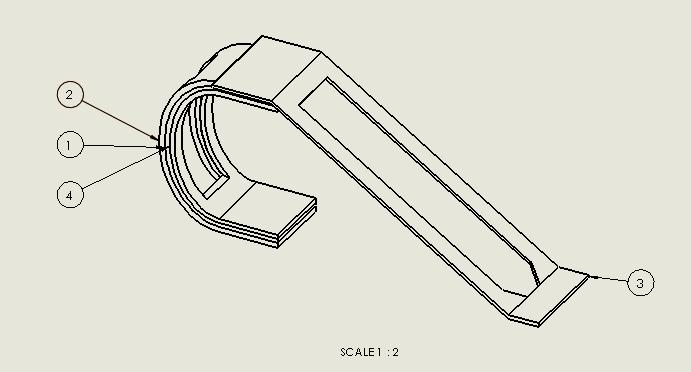
This is a simple design of an ankle which is use as a prototypefortesting.inwhichcontinuouslaminatingfiber isusedthicknessof1and3layeris.3cm,the2layeris .5cmthickand4layeris.4cmthick.Theyaresimpleadded on both side of first layer. 2 and 4 layer is of laminating material (fiber) like carbon fiber, glass fiber and Kevlar. The 1 and 3 layer is a base material like aluminum, titanium and stainless steel. The other accessories used whicharenecessaryformakeanankle.
Firstwecheckthedeformationon-2500loadinyaxiswith bottom side is fixed or act as ground. Then we check equivalentstressgeneratedinthebodywhichisbasedon von misses theory Equivalentstress(also called von Missesstress) is often used in design work because it allows any arbitrary three-dimensionalstressstate to representasasinglestressvalue.Equivalentstressispart of the maximumequivalentstressfailure theory used to predictyieldinginadesign.
Equivalent elastic strain is calculated by the addition of components ofelastic, plastic, thermal, and creepstrainsandthenequivalenttotalstrainiscalculated from totalstraincomponents. Weight is based on the density of materials. Strain energy is checked which is generated in the body. In ansys stress tool calculate differentquantitieslike:Equivalentstress(σe),Maximum tensilestress(σ 1), Maximum shearstress(τ MAX) This usesMohr'scircle:where-σ1andσ3=principalstresses., Mohr-CoulombstressThistheoryusesastresslimitbased ondifferentvaluesandequations.
Indesignoptimizationwecanreducethematerialwithour requirement which is of any type like Mass Reduction, Force variable and volume etc.it increases the life, durability and fulfill our requirements, by this we can reduce more weight and make better design for
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
professionaluse.Iftheorientationofsheet3isreversedin oppositedirectionthenallpropertiesareenhanceddueto supportofcurvebase.
TestandResult-Theresultisbasedonthemeanvalueof different values from different material in which the Titaniumhavinghighvalueresultinalllaminatingmaterial sothecomparisoninB/Wthecarbonfiberwithtitanium, KevlarwithTitaniumandglassfiberwithTitanium.
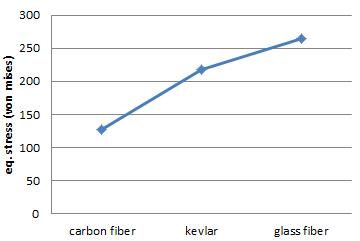
Chart-1: Eq.Stress(WonMisses)
Chart-2: Max.Deformation
Chart-4:FOS(Max.TensileStress)
Chart-5:Massinkg
On comparison in above charts deformation of carbon fiberwithTitaniumislessthantheothermaterialandall thefactorofsafetywhichcomesunderstressToolfactoris high.
In this study we observe that Carbon fiber shows high performance than the other materials laminating with differenttypesofbasematerialinwhichtitaniumshows highvalues,whicharenecessaryforprostheticanklelike tensile strength , density, and cost. It also improve the durabilityofcomposites andtheweightofoveralldesign is.45kgwithotheraccessoriesitbecomes.7kgandwecan reducethe weight asper the requirementforceisabout 1500maxthentheweightisoverallbodyis.5kgwhichis morecomfortableforhumans.Thecostofcarbonfiberis normalascomparetoKevlarwhichishighandavailability islow.Thisisthesimpleanalysisofcontinuouslaminating materialwithfiber.
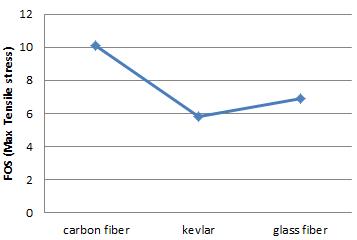
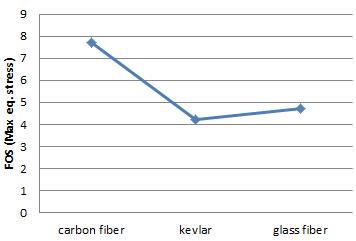
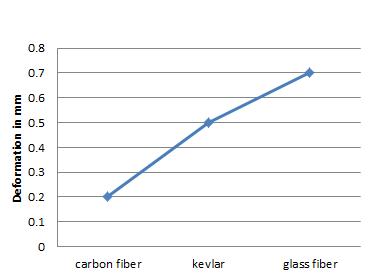
Chart-3:FOSMax.eq.Stress
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN: 2395-0072
2 Evaluation of High Strength Materials for Prostheses Virgil Faulkner, C.P.O. Martha Field, M.S.JohnW.Egan,M.S.NormanG.Gall,M.D.
1Mechanical Properties of Materials Used For Prosthetic Foot: A Review K. M. Walke, P. S. Pandure(DepartmentofMechanicalEngineering, M.E.S.CollegeofEngineering,S.P. Pune Unuversity,India)
Staros, A., "Materials and External Prostheses," Bull.Pros.Res.,10(8):77-91,1986.
Mooney,V.,"InnovationsinCareoftheAmputee," TextMed.,75:98-102,1975.
StrengtheningTechniquesofSteelStructure: An Overview .Md. Mofizul Islam*, RubieyatBinAli, Moushtakim Billah Department of Civil Engineering, Bangladesh University of Engineering & Technology, Dhaka - 1000, Bangladesh
3Graphic analysis of forces acting upon a simplified model of the foot G. VERES National College of Prosthetics, Sophies Mindes OrthopaedicHospital,Oslo
FromConventionalProstheticFeettoBionicFeet: A Review StudyRino Versluys, Anja Desomer, Gerlinde Lenaerts, Pieter Beyl, Michael Van DammeBramVanderborght,InnesVanderniepen, GeorgesVanderPerreandDirkLefeber.
HeatTreatingMaterialsPark,Ohio44073-0002:: 440.338.5151 :: www.asminternational.org :: MemberServiceCenter@asminternational.org
Published byASMInternational®::Data shown aretypical,nottobeusedforspecificationorfinal design
Maraging_steelhttps://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Maraging_steel
Datasheetsfrommatweb.com
Fatigue resistence of steels . bruce boardman, deereandcompany,technicalcenter.
Mechanical properties of boron and Kevlar -49 reinforced Thermosetting composites and econaomicimplications.ByKaiKinHerbertYeung and Kaminei Pitcheswara Rao. Department of biomedical and mechanical engineering. city universityofHongKong.
Effect of cyclic loading on the mechanical properties of steel. Author: Pierre Darry VERSAILLOT,Civ.Eng.Universitatea politehnica Timisoara,Romania
BetaTiAlloyswithYoung’smodulas.Instituteof Material Research ,Tohoku University.by Tomomichi Ozaki*,Hiroaki Matsumoto ,sadao WatanabeandShujiHanada.
EXPERIMENTAL STUDY OF DEFORMATION BEHAVIOR AND FATIGUE LIFE OF AISI 304 STAINLESS STEEL UNDER AN ASYMMETRIC CYCLICLOADING Yung-ChuanChiou*Journalof MarineScienceandTechnology,Vol.18,No.1,pp. 122-129(2010)
AcomperisionoffatiguebehaviorbetweenS355 and S690 steel.Abilio M>P> de jesus ,rui matos,Bruno F.C.Fontoura,Carlos Rebelo,Luis Simoes da Silva ,Milan Veljkovic.journal of constructionsteelresearch79(2012)140-150
Specification for Structural Steel Buildings, AllowableStressDesignandPlasticDesignJunel, 1989 with Commentary .AMERICAN INSTITUTE OFSTEELCONSTRUCTION,INC.OneEastWacker Drive,Suite3100Chicago,IL60601-2001.
Safety Data Sheet .by Midwest Tungueston Service.
2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page950
