International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Design of Optimized Vedic Multiplier
Christina T.J 1 , Dr. Kiran V21MTECH 1st year, Dept. of ECE, RV college of Engineering, Karnataka, India
2Associate Professor, Dept. of ECE, RV college of Engineering, Karnataka, India ***
Abstract - Multiplicationisanessentialoperationinmost arithmetic applications, and multipliers form one of the most important elements in any digital signal processor. Speed and area efficient multipliers are crucial in DSP applications. The speed of digital circuits must be increased and the area must be decreased. In this paper, an UrdhvaTiryakbhyam algorithm based 8 X 8 and 16 X 16 Vedic multiplier using carry save adder, which has optimized speed and area is designed. The proposed algorithm was developed in Verilog HDL, and its implementation was carried out using Xilinx Vivado. The suggested multiplication technique is then illustrated to show its usefulness. This Vedic multiplication circuit has turned out tobeeffectiveintermsofspeedandarea.
Key Words: Carry Save Adder, Urdhva Tiryakbhyam Sutra,VedicMultiplier,VedicMathematics
1. INTRODUCTION
Multipliers are one of the most common elements in digital circuit designs, since they are fast, reliable, and efficient components. There are varieties of multipliers presentanddependingonthetypeofapplication,specific architectureisselectedtosuittherequirements.
Multipliers generally determine the performance of an algorithm, because multipliers are usually placed in the critical delay path of the algorithm. Different algorithms are available for use, each with a unique set advantages andtrade-offsinvariousparameterslikespeed,power,or area. Since digital multipliers play a crucial role in DSP, researchonthemhasalwaysbeenactive.
1.1 Vedic Multiplication
The proposed multiplier architecture is developed on the basis of Vedic multiplication Sutra. Vedic sutras are used ineventhetraditionalwaytomultiplytwointegersinthe decimal system. This paper uses Vedic multiplication sutras,whichareappliedtothebinarynumbersystem.
1.2 Urdhva Tiryakbhyam Sutra
The multiplier proposed is developed on the basis of ancient Indian Vedic Mathematics algorithm Urdhva Tiryakbhyam (UT). The UT Sutra facilitates the simultaneous generation of partial productsandthesums
associated with them. The algorithm can be generalizable tonxnbitnumbers.
1.3 Algorithm for 8 X 8 Bit Multiplication using UT
Considertwo8-bitnumbersareMandN
where,CP=CrossProductandF=CarryOverflow
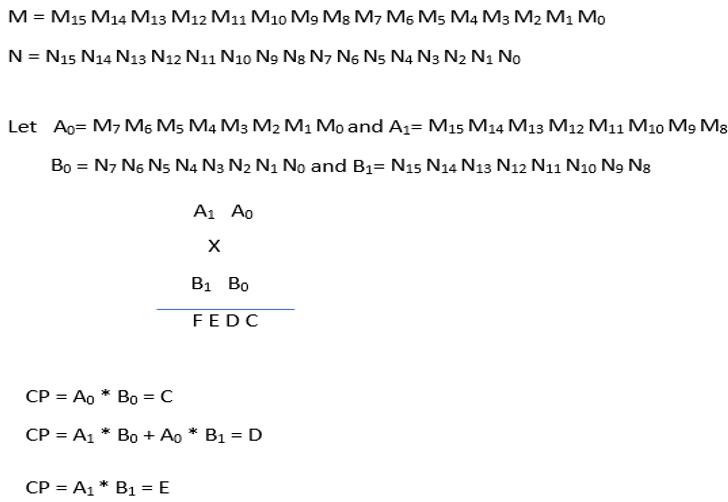

1.4 Algorithm for 16 X 16 Bit Multiplication using UT
Considertwo16-bitnumbersareMandN
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
2. METHODOLOGY
The8X8,16X16multipliersaredevelopedandtestedfor functionality using the proposed Vedic multiplier algorithm. High-speed arithmetic can be computed effectively using Vedic mathematical methods. The UT sutra demonstrates that it is a practical method for achieving fast multiplication operations. Due to the parallel computation of partial products when the UT sutraisused,themultiplierunit'slatencyisdecreased.
The carry-save adder is used in this case to calculate the partial products of multiplication. This enables architectures that quickly calculate the partial products using a tree of carry-save adders. The final multiplication resultisthenobtainedbyaddingthefinalsetofcarrybits tothefinalpartialproductsusingone"normal"adder.For this final stage, it is typical to employ a very quick carrylookahead or carry-select adder to achieve the best performance.
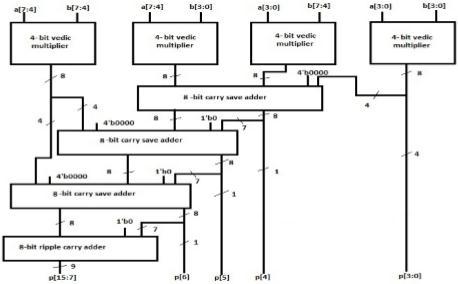
2.1 8 X 8 Vedic Multiplier
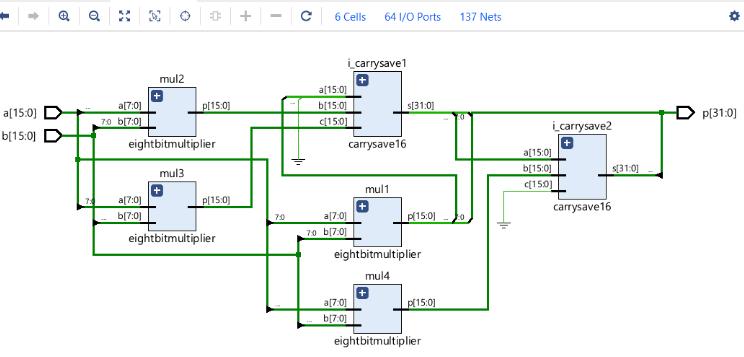
Fig.1showstheexisting8X8architecture.Forproposed8 X 8 Vedic multiplier presented in paper, architecture is developed as in Fig 2. The proposed method is realized using four 4 X 4 multiplier and adder blocks. Carry save addersareutilizedtoincreaseoverall speedandoptimize the area. In the Fig.2, a 16-bit output is generated by multiplying two 8-bit inputs. The adder blocks utilized in the design will not add a lot of latency because they are employed in carry save arrangements. This design has a larger than average transistor count. However, the improved performance is a compensation for the hardware complexity. As can be observed, CSA block inputs have zero padding. This is to ensure that all inputs totheCSAstagehaveuniformbitlengths.
Fig -1:Existing8X8
MultiplierArchitecture
a[7:4]
4bitMultiplier 4bitMultiplier 4bitMultiplier 4bitMultiplier
8 8 8 8
4 4 8
8bitCSA 8bitCSA
b[3:0] a[3:0] b[7:4] a[7:4] b[3:0] a[3:0] b[7:4] 4
Fig -2: Proposed8X8MultiplierArchitecture
FullAdder FullAdder FullAdder FullAdder
FullAdder
FullAdder
FullAdder FullAdder FullAdder HA
Fig -3: 8-bitCSA 2.2
16 X 16 Vedic Multiplier
a[7] b[7] c[7] s[4]...s[6] s[7]
a[0] a[3] b[2] a[2] b[1] a[1] b[0] b[3] c[0] c[3] c[2] c[1] s[0] s[1] s[2] s[3] s[8] c[9]
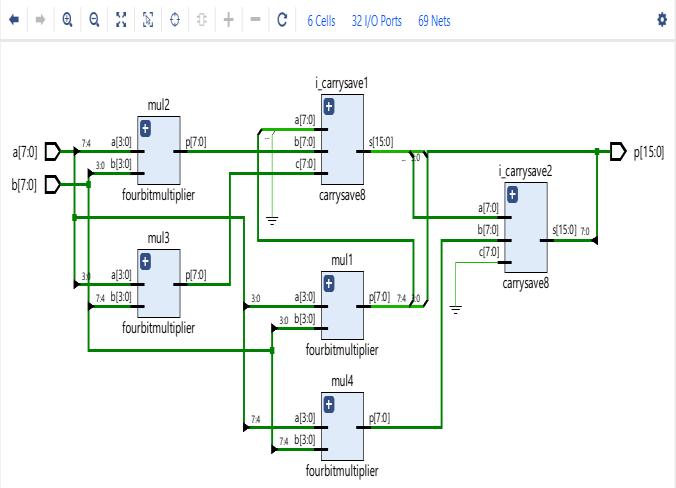
Initially a 2-bit Vedic multiplier is designed, then progressivemultiplierstagesaredesignedtoobtainthe16 X 16 multiplier design. Following that, 8 X 8-bit Vedic multipliers and 16 X 16- bit Vedic multipliers were built utilizingthe4-bitmultiplierasbasicblock.
8bitMultiplier 8bitMultiplier 8bitMultiplier 8bitMultiplier
16 16 16
16bitCSA
b[15:8] a[15:8] 8 16
8 16
b[7:0] a[7:0] b[15:8] a[15:8] b[7:0] a[7:0] 8
16bitCSA
Fig -4: Proposed16X16MultiplierArchitecture
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
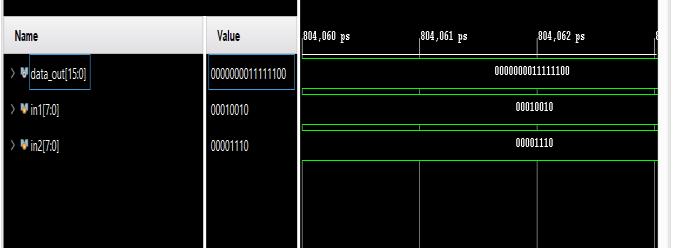
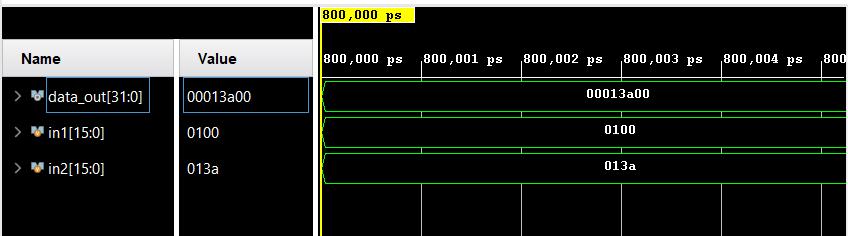
3. RESULTS
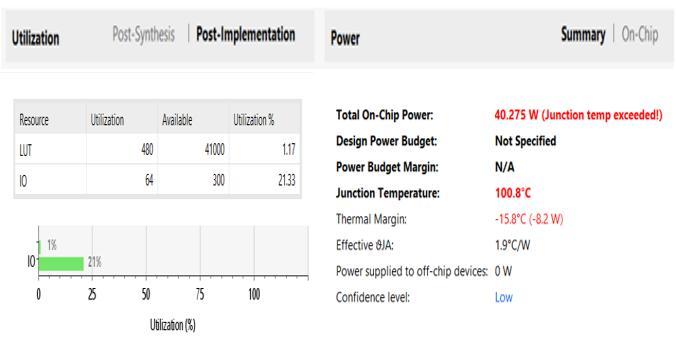
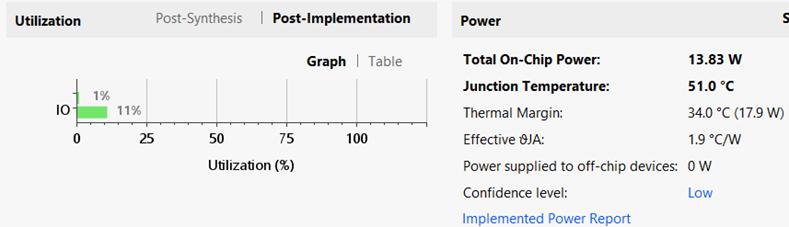
Fig.6showstheRTLschematicoftheproposed8 X8- bit VedicMultipliercircuitandFig.9showstheRTLschematic of proposed 16 X 16 Vedic Multiplier. As mentioned earlier, we see that the proposed system uses Carry Save adders. Fig.7 and Fig. 10 shows the output simulation waveforms. For both the circuits, resource utilization is shown in Fig.8 and Fig. 11. The design is implemented in XilinxVivadousingVerilogHDL.
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
3.3 Device Utilization Summary
Table 1 shows the summary of device utilization of the implemented8x8and16x16VedicMultipliers.
Table-1:SummaryofUtilization
Logicutilization 8X8Vedic Multiplier 16X16Vedic Multiplier
Numberof Slices 33 143
Numberof LUT’s 109 480 Numberof bondedIOB’s 32 64
TimeDelay(ns) 11.743 14.055
3.4 Comparison between other multipliers and Proposed Vedic Multiplier (8 x 8)
Time delay and area, as shown in Table 2, are two important multiplier parameters that were improved for the8X8multiplierasshownfromtheresults,illustrating the advantage of Vedic multipliers over other multipliers.
Table-2:Comparisonbetweenconventionalmultipliers andProposed8x8VedicMultiplier
Multiplier Area(inLUT) Delay(inns) Booth Multiplier 216 25.860 ArrayMultiplier 130 23.106 Wallace Multiplier 145 16.678
ProposedVedic Multiplier 109 11.743
3.5 Comparison between other multipliers and Proposed Vedic Multiplier (16 x 16)
The time delay and area for a 16 X 16 multiplier is compared and contrasted using different multipliers in Table3.
Table-3:Comparisonbetweenconventionalmultipliers andProposed16x16VedicMultiplier
Multiplier Area(inLUT) Delay(inns) Booth Multiplier 632 37.041 ArrayMultiplier 505 61.241 Wallace Multiplier 590 36.7 ProposedVedic Multiplier 480 14.055
Performance of various 8X8 and 16X16 multipliers is compared,considering parameters likedelayand number ofLUT's.Incomparison to theconventional multipliers, it isfoundthattheproposed Vedicmultiplier'scomputation speed is relatively faster. The delay is found to be lesser (11.743 for 8 X 8 multiplier and 14.055 for 16 X 16 multiplier). Additionally, there are lesser LUTs in the proposed design. As a result, the suggested Vedic multiplieruseslesserarea.
4. CONCLUSION
Using the Urdhva Tiryakbhyam sutra and the Carry Save Adder, the design of the 8 X 8 and 16 X 16 Vedic multipliersisexplored inthispaper. Xilinx Vivadoisused to simulate and synthesize the proposed multiplier. Performance is compared with existing multipliers includingWallacetree,Array,andBoothmultipliers.When compared, the results suggest that the proposed Vedic multiplier using the Urdhva Tiryakbhyam sutra with CSA gives better speed. It can be concluded that the proposed Vedicmultipliercanbeutilizedtooptimizespeedandarea andismoreefficientthantraditionalmultipliers.
REFERENCES
[1]Y. B. Prasad, G. Chokkakula, P. S. Reddy and N. R. Samhitha, "Design of low power and high speed modified carry select adder for 16 bit Vedic Multiplier," International Conference on Information Communication and Embedded Systems (ICICES2014), 2014, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/ICICES.2014.7034180.
[2]G. C. Ram, Y. R. Lakshmanna, D. S. Rani and K. B. Sindhuri, "Area efficient modified vedic multiplier," 2016 InternationalConferenceonCircuit,PowerandComputing Technologies (ICCPCT), 2016, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/ICCPCT.2016.7530294.
[3] N.H.Sastry,J.B.S.BharadwajandG.S.Jeevith,"Design and Implementation of 8-Bit Vedic Multiplier in 18nm FinFET Technology," 2021 International Conference on Recent Trends on Electronics, Information,
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056
Volume: 09 Issue: 10 | Oct 2022 www.irjet.net p-ISSN:2395-0072
Communication & Technology (RTEICT), 2021, pp. 251256,doi:10.1109/RTEICT52294.2021.9573681.
[4]Satish,DevaneandB.RatnaRaju.“AHighSpeed16*16 Multiplier Based On Urdhva Tiryakbhyam Sutra.” International Journal of Science Engineering and Advance Technology,IJSEAT,Vol1,Issue5,October–2013
[5]A.V,S.S,S.SandS.L,"SpeedandPowerEfficientVedic Multiplier using Adders with MUX," 2021 Innovations in Power and Advanced Computing Technologies (i-PACT), 2021,pp.1-5,doi:10.1109/i-PACT52855.2021.9696992.
[6]D.K.KaharandH.Mehta,"Highspeedvedicmultiplier used vedic mathematics," 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (ICICCS), 2017,pp.356-359,doi:10.1109/ICCONS.2017.8250742.
[7]M. A. Sayyad and D. N. Kyatanavar, "Optimization for Addition of Partial Product in Vedic Multiplier," 2017 International Conference on Computing, Communication, Control and Automation (ICCUBEA), 2017, pp. 1-4, doi: 10.1109/ICCUBEA.2017.8463787.
[8]E. Masurkar and P. Dakhole, "Implementation of optimized vedic multiplier using CMOS technology," 2016 International Conference on Communication and Signal Processing (ICCSP), 2016, pp. 0840-0844, doi: 10.1109/ICCSP.2016.7754264.
[9]G. R. Gokhale and S. R. Gokhale, "Design of area and delay efficient Vedic multiplier using Carry Select Adder," 2015 International Conference on Information Processing (ICIP), 2015, pp. 295-300, doi: 10.1109/INFOP.2015.7489396.
[10] V. Meghana, Sandhya S, Aparna R and C. Gururaj, "High speed multiplier implementation based on Vedic Mathematics," 2015 International Conference on Smart Sensors and Systems (IC-SSS), 2015, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/SMARTSENS.2015.7873593.
© 2022, IRJET | Impact Factor value: 7.529 | ISO 9001:2008 Certified Journal | Page841

