ASSET MAPPING FOR DECENTRILIZED PLANNING BY DESIGNING THE BYPASS ROAD USING QGIS.
Mr. Nihalahmad Riyaj Faras1 , Dr.V.T. Gaikwad2 .1Under Graduate student, Department of Civil Engineering, Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology Budhgaon, Sangli, Maharashtra, India

2 Associate Professor, Programme Head, Department of Civil Engineering, Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology Budhgaon, Sangli, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract: Designing a new road bypass alignment has become a crucial part of transportation planning and traffic management inorder to reduce accidents, boost designspeed, cut travel distances, and save fuel. This project is a case study of a comprehensive design process for a new road bypass routing that considers a number of factors, including the terrain, land use, and environmental consequences. A densely populated region of Budhgaon and Kavalapur with an inefficient and accident-prone road network serves as the study area for this investigation. Geographic information system (GIS) data, survey data, and satellite imagery are all used to design the proposed road bypass alignment. The alignment is improved to cut down on travel time, lessen the number of abrupt turns, and increase the road's design speed, by reducing the number of intersections, removing blind curves, and providing appropriate sight distance The 5.820 km long proposed road bypass alignment is designed to improve design speed, shorten travel distances, conserve fuel, and reduction in accidents. The estimated 12% cut in travel distance will result in significant fuel savings. The new road bypass alignment is also intended to improve the local environment by lowering carbon emissions and noise pollution. Overall, this study provides an essential framework for creating a new roadbypass alignment that can help lower accident rates, shorten travel times and conserve fuel. Along with this, Asset Mapping is to be done on this proposed road bypass alignment for public utilities and estimated cost of bypass road is found out
Key Words: Geographic Information Systems.
1. INTRODUCTION:
Decentralisedplanningisanapproachofplanninginwhich alllocalorganisationsandinstitutionswilladopt,implement, andmonitortheplanwithouttheassistanceofacentralised organisation. The Decentralizedplanning is the planning whichisadoptedatdifferentlevels.UsingQ-GISsoftwarefor decentralisedplanningisaneffectiveapproachformaking decisions andallocating resourcesthat makesthemost of contemporary geospatial technologies. Q-GIS is a free and open-sourcesoftwarewhichallowsitsusersforgeographic data creation, analysing, and visualising geospatial data. Making decisions about land use, natural resource
management,disasterresponse,andothercrucialtopicsmay be done collaboratively using Q-GIS to analyse data, build and update maps, and make data-driven decisions, along with this it is commonly used for the designing the road alignmentandformappingtheassets
Decentralized planning using Q-GIS software offers an exciting opportunity to promote more effective and equitabledecision-makingandtocreatesustainablesystems thatcanadapttothechangingneedsofcommunitiesover time. To have a proper decentralized planning it is very important to have good and safe means of connectivity to cities, towns and villages. If there is inappropriate connectivity to towns/cities/villages, the decentralized planning tends to fail. At the present if we focus on State Highway 75 of Maharashtra (SH75) it has a curtail importancetodecentralizedplanning.
1.1 PROBLEM STATEMENT:
The region of Budhgaon-Kavalapur area is densely populated these days, these densely populated region is connectedbythestretchof6.200km(Kilometers)ofroad whichisMaharashtraStateHighway75.Alongthisexisting roadtherearenumberofAssetslocatedsuchasIndustries, Institutions,Banks,Hospitalsetc.thisAssetscontributesthe hugeamountoftraffictothisexistingroadduetowhichthe Trafficproblemsoccurswhichultimatelyleadstonumberof accidents in this region. In the region of BudhgaonKavalapurarea,roadsideencroachmenthasbeenincreased, while which contains some of the Historic and Religious monuments, so due to these there is no scope for road widening.
The existing stretch of 6.200 km road contains the numbersofblindcurve,someofthemaretrulysharpwhich hastheangleof90degree,soitbecomesdifficultfordriver of vehicle to pass the curve. For passing the curve one vehiclehastostopandlettheothervehicletopassanddue tothisTrafficproblemmayarises.So,thereisneedtodeal withthisReal-lifeproblemofBudhgaon-Kavalapurarea
1.2 Objectives:
Todesignsafeandefficientroadalignmentby usingQGISsoftware.
ToreduceAccidentsonroad
ToBypasstheheavytraffic.
Offerbettertransportationfacilities.
To locate necessary assets along proposed alignment.
ToenhancetheconnectivityofexistingSH75.
1.3 Existing Road (Maharashtra State Highway 75) connectivity & Importance:
Sangli-Tasgaon-Vita-Mayani Road (SH75)
ThishighwaystartfromSangli,runstowardsthenorth-east up to Kakadwadi and then towards the north up to the districtborder.AfterpassingMiraj,TasgaonandKhanapur talukasitentersSataradistrict.
This road route has opened for traffic the rich and fertile agricultural tracts in the district. It traverses through the entirelengthandbreadthofthedistrict.Italsoservesasa linkbetweenMadhavnagarRailwayStationandSangli.
Ittouchesthefollowingplacesinitsstretch:
(1)Madhavnagar. (2)Budhgaon.
(3)Kavalapur. (4)Kakadwadi.
(5)Tasgaon. (6)Shirgaon.
(7)Borgaon. (8)Limb.
(9)Alte. (10)Karve.
(11)Vita. (12)Gardi.
(13)Nagewadi. (14)Mahuli.
Goingfromsouthtonorth,thefollowingroadseithercrossit ortakeofffromit.
Place of junctionName of road
Kakadwadi: (1)Kakadwadi-Miraj
(M D R)(MajorDistrictRoad).
(2)Kakadwadi-Kuchi(M.D.R)
Tasgaon: (1)Karad-Tasgaon(M.D.R).
(2)Tasgaon-Islampur(M.D.R.).
(3)Tasgaon-Kundalpur-Kerewadi (M.D.R.).
(4)Tasgaon-Khanapur(M.D.R.).
Shirgaon: Shirgaon-Dhamani Khurd (O. D. R.) (OtherDistrictRoad).
Vita: (1) Guhagar-Chiplun-Karad-JathBijapur(S.H.)(StateHighway).
(2)Vita-Kherada-Pusesavali(M.D.R.).
(3)Islampur-Kundal-Vita(M.D.R.).
Abovetheroadscontributesthetrafficonthishighway.
1.4 Importance of Highway for economic development of the Sangli District:
Maharashtra is a western state of India, which has the Sangli district. The district's economy is based mostly on agriculture,withmorethanhalfofthepeopleworkinginthe agriculturalsectorandmostofthemhastheagricultureas primeoccupation.Fromtheothercrops,theregioniswellknown for the cultivation of grapes, sugar cane, and turmeric.Thedistrict'smostsignificantcropisgrapes,andit is also the greatest grower of grapes in Maharashtra. The grape cultivation is concentrated in the Tasgaon and Khanapur talukas of the district. Sangli district produces high-quality grapes, particularly the Thompson seedless variety,whichisinhighdemandbothinthedomesticand international markets. Grapes are mainly grown for table consumption,butthedistrictalsoproduceswineandraisins.
Sugar cane is another important crop in Sangli district.Thedistricthasalargenumberofsugarfactories, whichprocessthesugarcaneintosugarandmolasses.Sugar caneisgrownintheKaradandWalwatalukasofthedistrict. Turmeric is another important crop in Sangli district, particularly in the Jath and Atpadi talukas. The district produceshigh-qualityturmericthatishighlysoughtforon both the domestic and international markets. Other crops grown in the district include wheat, jowar, bajra, and legumes. Another significant crop farmed in the area is pomegranates. Pomegranates are primarily farmed in the district's north, particularly in the talukas of Atpadi and Kavathemahankal.Grapes,sugarcane,andturmericarethe three most prominent agricultural products in the Sangli area.Thedistrict'sagriculturaloutputmakesasubstantial contribution to the regional economy, creating jobs and encouraging the expansion of the economy. For cities and villagestodevelopandtogrow,theremustbeeffectiveroad connectivity. For economic development and expansion, roads provide a means of transit for people, products, services,andagricultural sectors,whichisveryimportant foreconomicdevelopmentofSanglidistrict.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW:

Prof. S.V. Sabale and Piyush S. Hokarne, et al (2021) [1]
Presented paper aims on the application of GIS (GeographicalInformationSystem)anditsusageoftheopensourcesoftwareinvariousfield.Thisuser-friendlysoftware whichisQuantumGeographicInformationSystems(QGIS)is most popular, leading and user-friendly open-source GIS
software. It is very easy to use, extensible, and has a constantly growing community and user base. More and morePrivateusersandorganizationschooseQGISastheir mainstreamGISsoftware.
Prof. A.K. Patil and M.Y. Patil, et al (2019) [2]
Carryoutthe case study of roadaccidents on TasgaonSangliroadwhichmainlycausedduetoCarelessnessandlack ofawarenessofdriver,consistofnumbersofsteepcurves along with this there are a lot of pot holes present on this roadi.e.,theconditionofroadisterrible.Thiscasestudyalso givesdataofaccidentcausedonthisroad.Accordingtothis casestudyintheyear2016therearetotal803numbersof accidentsoccuronthisroad,inwhich376causedtodeath and791gotseriouslyinjured.
Joseph Rei Mark (2019) [3]
SummarizesthedesigningofroadalignmentusingtheGIS forsafeandconvenienttrafficoperations.Thispaperhelpsin designingtheroadalignmentaspereconomic,environment, socialconsiderationsusingtheGIStool.Italsofocusesonthe classification of roads in Philippines and problem of road alignmentwhichisanalyzedusingGIS.
Pallavi Sonsale and Mayur Chaudhary, et al (2021) [4]

Had outlined the process for creating GIS-based asset mapping,utilityinfrastructuremapping,consumermapping, and topographic mapping and final analysis are all done together. Initial work on this project is done for MIDC's MillenniumBusinessParkinMahape.Thispaperprovidesan important information regarding the various types of MappingincludingtheAssetMappingusingtheGIS.
3. METHODOLOGY:
3.1 Software study and Data collection:
In this phase the software named as Q-GIS is thoroughlystudiedandneedfuldatasuchasDEM (DigitalElevationModel)fileistoobtainedfromthe BhuvanGovernmentofIndiawebsite
3.2 Asset Mapping along the existing Road:
In this phase the present status of Assets such as Industries,Institutionsetc.alongtheexistingroad whichcontributesitsuser’straffictothis existing roadistobefoundout.Itisdeterminedbycarrying out a physical survey in the study area and collectingtheinformationfromtheassetsandthen MappingtheAssetsbyusingtheQ-GISsoftware.
3.3 Survey of Study Area:
ItincludesvarioustypesofSurveyssuchas
3.3.1 Traffic Survey:
InthissurveytheTrafficCapacityratio and Traffic Analysis of Study Area is done at peak hours and non-peak hours.FromthisSurveyitisconcluded that the existing road has Traffic Volume Capacity Ratio is more than 0.7andthusthisroadfallsunderthe Sub- Arterial Road. But at present it cannot sustain the present Traffic volume, so this Sub- Arterial Road is need to be widened which is not possible at current scenario of encroachment and religious monuments. So, there is need to DesigntheBypassRoad.
3.3.2 Curve Study Survey:
In this Survey the Curves which are present on the existing road are critically examined and studied and theirdegreeofbendistofoundout.On theseexistingroadstherearetotal12 numbers of curve out of which 4 are theCompoundcurve,5aretheSimple curve,1isReversecurveand2arethe 90degreessharpcurve.So,fromthis Curve study it is concluded that at given study Area of BudhgaonKavalapur the Existing Road contain the sharp curves which ultimately leadstoAccidentssothereisneedto designandconstructtheBypassRoad.
3.4 Designing the Bypass Road: 3.4.1 Fixing the Alignment:
In this phase the proposed Bypass Roadalignmentisfixed.Duringfixing theproposedBypassRoadalignment various points are taken into consideration some of them are follows:
Ecofriendly: The proposed Bypass Road alignment should be passed from such area, such that there shouldbenocuttingoftreesandthus thisalignmentshouldbeecofriendly.
Easy and Straight: The proposed Bypass Road alignment should be easy and straight with No sharp curves.
Cost: The alignment should be selected in such a way that it minimizesthecostofconstruction,so thattheproposedalignmentshould beeconomicalintermsofcost.

Traffic Divergence: The proposed alignmentshouldbeselectedinsuch a way that it diverts the traffic flow from existing road and provides an efficient and safe route for transportation.
3.4.2 Preparation of Drawings:
Inthisphasethedetailed Design and DrawingsofproposedBypassRoadare prepared.
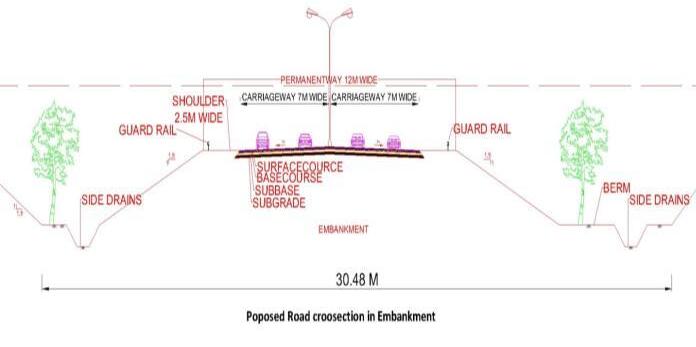
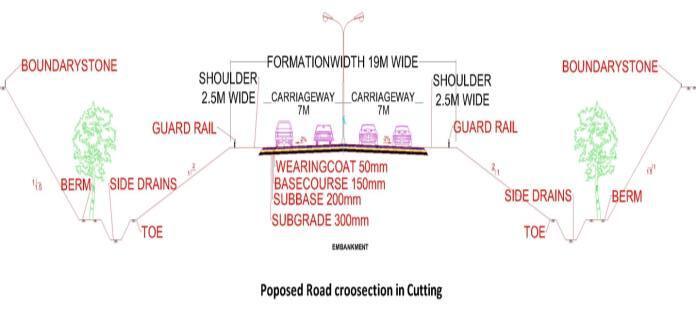
Design Characteristics of New proposed Bypass Road:
Road type:SH75(Statehighway75)Bypass Road,Flexiblepavementroad,DoubleLane Two-waytraffic.
Roadway width: 30m(meter)
Carriage way width: 14m(7meachlane).
Formation width: 19m
Side slopes: Inembankment1in2,InCutting1 in1.5
Shoulders: 2.5mwide
Other: Unlined side drains, Berms, Boundary stones,Streetlightandguardrails
3.4.3 Cost Analysis:
Inthisphasetheoverallprojectreport i.e., DPR (Detailed Project Report) which includes the all the items of workandtheirdetailedQuantitiesand thecostofindividualquantitiesofitem of work which is required for the constructionoftheseBypassRoadisto be found out. It includes the Quantifying the item of work such as finding the quantity of Cutting and filling (Embankment) and different itemsofwork,thenabstractingtoget thefinalcostofproposedBypassRoad.
6
Basecourse
Providing,laying,spreadingandcompactingst oneaggregatesofspecificsizestowaterbound macadamspecificationincludingspreadingin uniformthickness,handpackingtopropergra deandcamber,applyingandbroomingrequisi tetypeofscreening/bindingMaterialstofillup theintersticesofcoarseaggregate,wateringan dcompactingwithvibratoryrollertotherequir eddensity.ByMechanicalMeansGradingI(UsingScreeningTypeB(11.2mm)
SurfaceDressing-Providingandlayingsurfacedressingaswearin gcourseinsinglecoatusingcrushedstoneaggr egatesofspecifiedsizeonalayerofbituminous binderlaidonpreparedsurfaceandrollingwit h8-10tonnesmoothwheeledsteelroller.-c)10mmnominalchipplingsize(bitumen9.0kg /10Sq.M--Bitumenofspecifiedgrade(VG30bulkbitumenratesareconsideredto arriveatrates) 13
ProvidingstackingfilingmurumforW.B.M. Roadasperdirectionofengineerincharge includingalltaxes,transportation etc.completed
Cuttinggroundforrequireddepthand areaasperthedrawing,designincluding alltaxes,transportationetc.
0cm.breakingclods,dressingtotherequiredli nes,curves,gradesandsection,wateringandc ompactingtonotlessthan97%ofstandardpro ctordensityforaleadof300m.to500m.inclusiv e,fromthesiteofexcavationtothesiteofdepos itionasdirected.
Providing,laying,spreadingandcompactingst oneaggregatesofspecificsizestowaterbound macadamspecificationincludingspreadingin uniformthickness,handpackingtopropergra deandcamber,applyingandbroomingrequisi tetypeofscreening/bindingMaterialstofillup theintersticesofcoarseaggregate,wateringan dcompactingwithvibratoryrollertotherequir eddensity.ByMechanicalMeansGradingI(UsingScreeningTypeB(11.2mm) Aggregate)
6
Sr. No DescriptionofItems Qty. Rate per unit Unit AmountinRS. Remark 1 RoadSurveyUsingQGISSoftware 5.82 3050 Km 17751 2 ReconnaisanceSurveyofRoadalignmentinplain countryincludingtakingthreedimensionsof apexes,verificationoftypeoflandetc.alongwith thealignmentetc.complete(WithChaining). 5.82 2011 Km 11704.02 SSR2021-22 SrNo.9,Item No.1.09 3 Clearinggrassandremovalofrubbishuptoa
thearea. 177394 4 Sq.m 709574.4 SSR2021-22 SrNo.85,Ite mNo.2.07 4 Transferingandtakingoutdesignoncoordinates

ofbaselineongroundusingnailsforexsisting roadsurfacesandsurveypegsfornewalignment includingtakingoutcoordinatesforhorizontal curvesatrequiredintervalof50metersetc. complete.(Extralinesuchasrightofwaymedian edgestotoelinenotincluded).
Cuttingdownbranchesoftrees,bushesetc. stackingthematerialneatlyasdirected(For MotarableRoad)
5 5.82 7648 Km 44511.36 SSR2021-22 SrNo.21,Ite mNo.1.21
RoadEarthwork Excavationforroadwayinearth,soilofallsorts, sand,gravelorsoftmurumincludingdressing sectiontotherrequiredgrade,camberandside slopesandconveyingtheexcavatedmaterials withallliftsuptoaleadof50m.andspreadingfor embankmentorstackingasdirected.
53218 359 cu.m 19105290.7 SSR2021-22 SrNo.99,Ite mNo.2.26 AbstractSheet NameofProject:BypassRoad (L=5.82km) 5
8
7
SubBasecourse
Providing,laying,spreadingandcompactingstonea ggregatesofspecificsizestowaterboundmacadams pecificationincludingspreadinginuniformthickness ,handpackingtopropergradeandcamber,applyinga ndbroomingrequisitetypeofscreening/bindingMat erialstofilluptheintersticesofcoarseaggregate,wat
BaseCourse
Providing,laying,spreadingandcompactingstonea ggregatesofspecificsizestowaterboundmacadams pecificationincludingspreadinginuniformthickness ,handpackingtopropergradeandcamber,applyinga ndbroomingrequisitetypeofscreening/bindingMat erialstofilluptheintersticesofcoarseaggregate,wat
SurfaceDressing
4. RESULTS:
9
Providingandlayingsurfacedressingaswearingcour seinsinglecoatusingcrushedstoneaggregatesofspe cifiedsizeonalayerofbituminousbinderlaidonprepa redsurfaceandrollingwith8-10tonnesmooth wheeledsteelroller.-d)6mmnominalchipplingsize(bitumen7.50kg/10S q.M--Bitumenofspecifiedgrade(VG30bulkbitumenratesareconsideredtoarriveat rates)
10
Excavationforcatch/sidewatergutterinallsortsofso ilstothespecifiedsectionincludingstackingtheexcav atedstuffinaregularbundanddisposingof unsuitableorexcessstuffasdirectedallsortsof
11 ProvidingandfixingKMmetrestonesasperI.R.C. standardincludingfixinginstandardsize______bloc kincludingcuring,paintingletteringetc. complete. Fixing1:2:4ordinarykm.stonesin
ProvidingandfixingMandatory/Regulatorysignboa rdsincircularshapeof______mmdiamadeoutof___ _mmaluminumsheetbondedwithwhiteretroreflec tivesheetingofClassB M25gradeconcreteblockofsize60cmX60cmX75cm includingtransportationetc;complete.ClassB(Type IVHighintensitymicro-prismaticgradesheetingHIP)shallhave7yearswrittenwarrantyfromtheman ufacturerandauthoriseddistributor/convertorissu edforfieldperformanceincludingthescreenprinted areasandcut-outsheetingandcutoutdurabletransparentoverlayfilmandthiswarrant ycertificateinoriginalshouldbesubmittedtotheEngi neerinchargebythecontractor/suppl600mmdia madeoutof3mmaluminumcomposite
PaintingLine,Dashes,ArrowsetconRoadsintwocoa tsonnewworkwithreadymixedroadmarkingpaintc onfirmingtoI.S.164onBituminoussurfaceincluding cleaningthesurfaceofalldirt,dustandotherforeign matter,demarcationatsiteandtrafficcontrol (Over/Upto10cmwide)(MORTH-803)New Surface
Costing of Bypass Road Project
Totalcostofroadconstruction: Rs.
12,88,01,538/-
ContingencyCharges(5%): Rs.64,40,076/-

Overheadcharges(8%):Rs.1,03,04,123/-
Watercharges(8%): Rs.1,03,04,123/-
GRAND TOTAL COST OF CONSTRUCTION OF BYPASS ROAD: Rs. 15,58,49,860/-
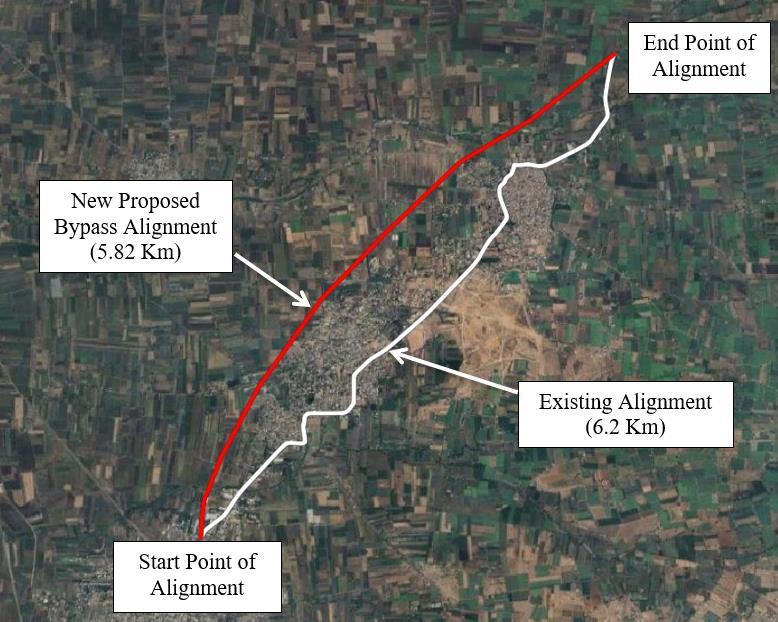
Thispaper,focusesondesigningtheDoubleLaneTwo-way Traffic Bypass Road, having the length of 5.820 km which startsfromthepoint[PashchimMaharashtraPatraDepot, Sangli]N16053.648’E074035.344’andendstopoint[Near KavalapurBridge,Sangli]N16056.042’E074037.246’,which hastheestimatedcostof Rs. 15,58,49,860/- forthe 5.820 km (Excluding Land Acquisition Cost) whichwillbe Rs. 2,67,78,326/- Rs. per kilometer.
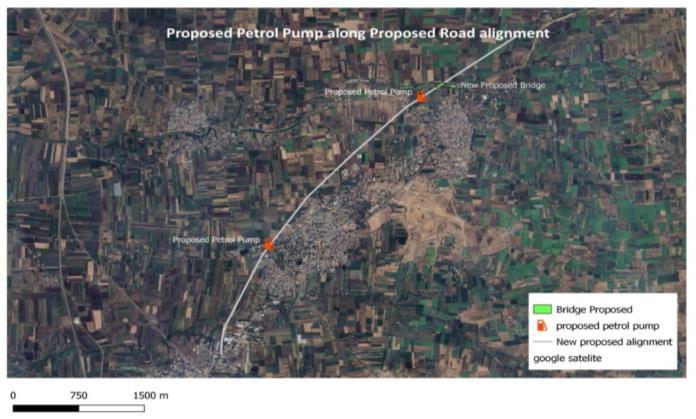
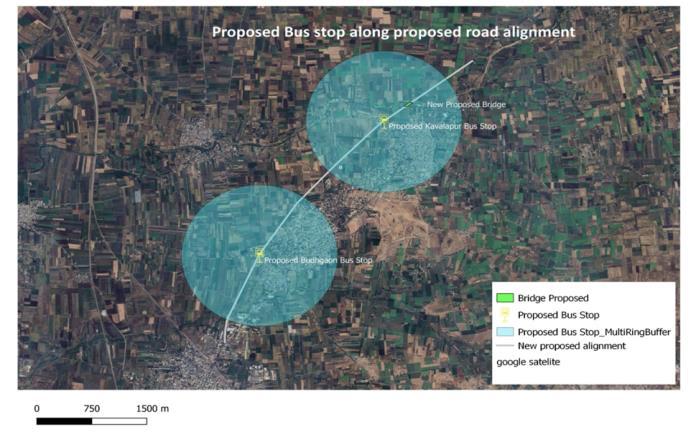
Also,for better publicutilitiespurposes,Asset Mapping is donealong the proposedBypassRoadalignment with the AssetssuchasBusstops,Fuelstations,foreffectiveuseof this utility on this proposed Bypass Road. This Assets are providedwiththeBUFFERZONE(blueshadedareainfigure 6) this buffer zone will serve the area covered under the zone and thus Decentralized Planning can be done in effective manner for this proposed Bypass Road. So, this BypassRoadwillsolvetheReal-Lifeproblemconcernedwith Budhgaon-Kavalapurarea.
5. CONCLUSION:
TheseCasestudyincludesdesigningtheDoubleLanetwoway traffic Bypass Road which starts from start point [Pashchim Maharashtra Patra Depot, Sangli] N16053.648’ E074035.344’ up to end point [Near Kavalapur Bridge] N16056.042’E074037.246’Alongtheexistingstatehighway 75. This Bypass route will divert the heavy traffic from existing road alignment .The existing stretch of SH 75 highway having the length of 6.200 KM which passes through Kavalapur – Budhgaon villages, which makes the roadalignmentmoretediousforthepassengersbecauseit consistsofnumberofsteepcurves,encroachmentalongthe road alignment which obstruct the eye view of passenger and thus reduces the visibility and road widening is not possible due to present of prime assets such as religious monument,publicassetsetc.
Sothisbypassroadofhavingthestretchof5.8KMwhich eliminatethesteepcurvesandthereducesthecomplication forwideningoftheroadsoduetothistraveltimewillget reduceandthusultimatelysavethefuelconsumptionand providebettervisibilityandresultingreductioninaccident andalongwiththisbypassroadalignment,AssetMappingis tobedone for publicutility purposejust byprovidingthe Busstops,Gasstationsandotherpublicutilitywhereveris needed along the stretch of these bypass road. The future scope of this Bypass Road can be utilized in the fields of Trade,Tourism,Governance,Education,Agriculture,Facility managementetcwhichisveryimportanttoincreasetheGDP (GossDomesticProduct)ofSanglidistrict.
6. REFERENCES
[1] Prof.S.V.SabaleandPiyushS.Honkrne,etal,“Paperon Application of Q-GIS Software,” e-ISSN: 2395-0056 pISSN:2356-0072issueon5th May2021
[2] Prof.A.K.PatilandM.Y.Patil,etal,“AReviewonRoad SafetyandCausesofAccidentsonTasgaon-SangliRoad,” vol.06,08Aug.2019,e-ISSN:2395-0056,p-ISSN:23950072
[3] 2017JosephReiMarkCo,“ResearchpaperonPlanning ofNewRoadAlignmentusingGeographicInformation System (GIS)”, Date of issue December 2019, DOI: 10.13140/RG.2.2.15991.16806.

[4] PallaviSonsaleandMayurChaudhary,etal,“GISbased asset mapping, utilities infrastructure mapping, consumer mapping, topographic mapping & 3d modellinginanintegratedmanner”,e-ISSN:2395-0056 p-ISSN:2395-0072IssueMay2021
BIOGRAPHIES:
Mr. Nihalahmad Riyaj Faras. Undergraduate student, Department of Civil Engineering, Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology

Budhgaon, Sangli, Maharashtra, India.
Dr.V.T. Gaikwad.
He is Associate Professor, ProgrammeHeadatDepartmentof CivilEngineering,Padmabhooshan Vasantraodada Patil Institute of Technology Budhgaon, Sangli, Maharashtra, India. His Qualification is Ph.D. (Civil Engineering), M.E. Civil. He is the member of professional society ISTE(IndianSocietyforTechnical Education).

