Designing a Generative AI QnA solution with Proprietary Enterprise Business Knowledge using Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG)
Suvoraj BiswasSolutions Architect, Ameriprise Financial, Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA ***

Abstract - Large Language Models from OpenAI’s ChatGPT or Google’s BARD have the capability to generate human-like responses in natural language. This capability can be used to design solutions to solve many enterprise business use cases. In this prototype solution we are trying to design an Enterprise content search solution using Generative AI. This QnA (Question and Answering) framework would be designed based on OpenAI’s APIs on top of the private business knowledge for internal stakeholders of an organization. This solution would try to leverage the summarization and embeddings generation capabilities of OpenAI’s API as well as Vector Database as part of the private knowledge repository in the solution. In the prototype solution we will measure the cost of the Q&A system based on OpenAI's offerings with different types of LLM models for a fixed knowledge dataset.
Key Words: Generative AI, LLM, Embeddings, Vector Database, Pinecone, Langchain, Open AI, GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer), Machine Learning, Solution Architecture, Enterprise AI Knowledge framework, RetrievalAugmentedGeneration(RAG)framework.
1. INTRODUCTION
Content is an integral part for any Enterprise. The contents or business knowledge are useful for internal stakeholders who consume this knowledge about a process or workflowandcompletea specific workstream. Considerthefollowingproblemstatementsandusecases:
a) Airline industry- It uses various internal and external applications for managing bookings/reservationsorpassengersdataorfleet schedules. An internal employee like a booking agent has to have good business knowledge to serve the external customers. The agent spends a huge time figuring out the correct workflow by referringtotheproprietaryenterpriseknowledge articles.
b) Financial organizations- They have built a huge knowledge and research repository based on the market research done by their analystsover time but finding the correct step or referring to the correct research is a huge pain when the informationisinacasestudyformat.
The traditional Enterprise search system depends on the regular full text search or partial text search and lists downtheknowledgesourcesorarticlesbasedontheexact word matching. This sometimes pulls the incorrect sourcesofinformationortoomuchinformation.
OurproposedGenerativeAIbasedsolutionwouldhelpthe enterprise stakeholders to correctly point out the exact response or steps/process flows out of the tons of knowledge articles. The solution outlined below would also use the Large Language Model’s summarization capabilityto provide exactresponsesso thatusers do not needtobrowsethroughtheknowledgesourcestoidentify theinformationtheyarelookingfor.Theprocessiscalled Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) wheretheLLM modelisusedtogeneratehumanreadableresponseinthe natural language while setting the context or boundary withintheEnterprisebusinessknowledgesothattheLLM modeldoesn’thallucinateorgenerateincorrectresponse.
That would definitely help the enterprise to save tons of business hours with a high customer satisfaction rate. In the following sections we will cover some important concepts of AI which are the basic building blocks of our proposedsolution.
1.1 Introduction to Embeddings
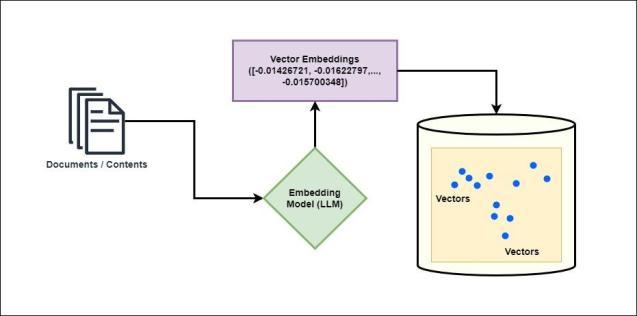
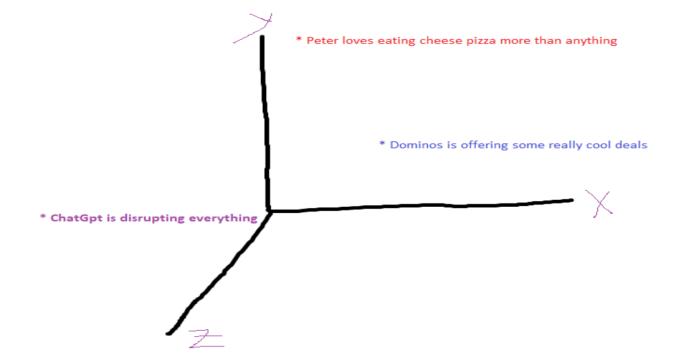
Embedding is one of the major building blocks in our solution. Embeddings refer to the mathematical representation of a piece of text or words or graphic contents such as images or media contents (video/audio) in such a way that it becomes easier to find the closeness or relatedness of those data. E.g. consider the following threesentences-
a) Peter loves eating cheese pizza more than anything
b) ChatGpt is disrupting everything
c) Dominos is offering some really cool deals
For a human it is very easy to figure out that the two sentences (a) and (b) have some closeness since both are connected with pizza, however the 2nd sentence (b) has no relatedness with the rest of the sentences. If these above three sentences are plotted against a three dimensionalgraphitwouldprobablylooklikebelow:
In the machine world embeddings work similarly. It generatesacomplexmathematicalmodeltorepresentthe above lines by generating an “N” number of dimensions. This mathematical representation is called a “Vector”. In theGenerativeAIlandscapeEmbeddings(Vectors)playan important role. Large Language Models like ChatGpt have the capabilities to generate Embeddings of the input contentandatthesametimecanpreservethemeaningsof the supplied data. The LLM model called "textembedding-ada-002" can generate embeddings having 1536 dimensions.
1.2 Introduction to Vector Database
As we can see the complex multi dimensional representation of the data in the machine learning world can not be stored in the traditional relational database or noSql database. The traditional columnar or scalar databases lack the capabilities to store the vector data type and scale accordingly. Information retrieval in the vector database works differently than the traditional database, where it tries to output content which exactly matches with the input query whereas in the vector databaseitusesalgorithmlike Kth nearest neighbor (KNN) or Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) to find data having shortest distance and return the similar results.
Vector databases add more functionality to an LLM basedapplicationlikesemanticretrievalofdataoradding a memory by remembering the context of the interaction. Inourproposedsolution,thevectordatabaseisplayingan integralrole.
1.3 An Overview of Prompt Engineering
In the AI world Prompt Engineering refers to the designing of a short piece of text or phrase based on certain principles that can be passed to the Large Language Model to effectively generate the contents as output. The prompt engineering is one of the important building blocks as if this is not properly constructed then LLMmodelslikeChatGptcanhallucinatemeaningiteither generates an illogical meaningless content or out of context responses. So it is always a best practice to validate the input texts we pass to the LLM model’s API based on the defined principles of Prompt Engineering. Based on the intent or purpose of the input phrases the model can exhibit capabilities like summarizing a large pooloftextsorcontentorinferringorclarifyingthetopics or transforming the input texts or expanding the input text.
1.4 Overview of the OpenAI LLM models
OpenAI has offerings from a diverse set of Large Language Models having varying degree of capabilities andlimitationofinputtokens.ForexampleGPT4andGPT 3.5 are capable of understanding the natural language as input and based on the intent or requirements can generate responses in natural language. The DALL-E model is pre-trained to generate or produce graphical images based on the input or prompt engineering in natural language. The Embeddings model “textembedding-ada-002” can produce embeddings of the supplied input texts which help to find the relatedness between two different phrases or sentences. Following table summarizes the various models and their basic functionalities.
OpenAI’s Large Language Models
Moderation Thismodelisfinetunedtodetectunsanitized content
Whisper Itcangeneratetextfromaudio.
Embeddings Itcangenerateembeddings(mathematical representation)oftexts
DALL-E Itcangenerateimagesbasedonnatural languageinput.

GPT-3.5 LLMmodelthatunderstandsnatural languageandgeneratesthesame.
GPT-4 LLMmodelsthatcanunderstandnatural languageandcangeneratethesame.An improvedversionoverGPT-3.5
2. DESIGNING THE LLM SOLUTIONS
InourproposedsolutionwetriedtoutilizetheAIorLLM workflowsasmuchaspossibletodesignoneoftherobust and scalable Generative AI based solutions. In the traditional Question & Answer based product the system works by matching either exact data from the article or doing partial or full text search and listing the article results.Sometimesthisworksbestbutmostofthetime it missestheintentofthequestionbeingaskedbyusersand listsonlyresultsbasedonjustwordmatching. Sometimes this frustrates the end users as they still need to go through the entire article to figure out what they are looking for and sometimes the results lack listing it correctly.
OurGenerativeAIsolutiontriestousethepowerofVector database based on the Embeddings data model and not onlylists thetoplists ofcontentbutitutilizestheOpenAI summarizing capability to assist the user with the point content or instructions that they are looking for. The entiresolutionconsistsoftwoworkflows-Pre-Processing oringestionofthedataandRetrievalFramework
2.1 Pre-Processing (Ingestion pipeline)
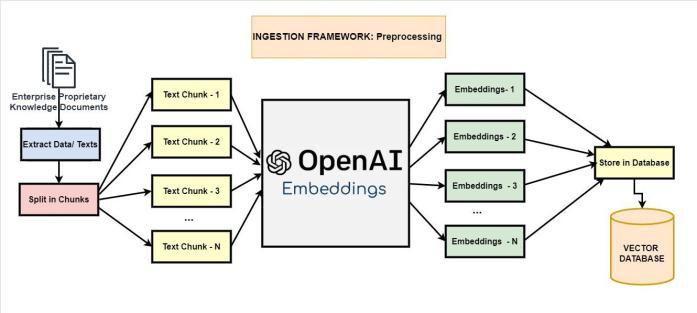
In the pre-processing stage, we designed the Ingestion framework which is the backend component. This is responsibletoingesttheEnterpriseknowledgerepository byscanningthesourcesofarticlesandthenbreakingthem into chunks of tokens or smaller meaningful segments. This strategy is called the chunking strategy. Based on the article source and the way they are formatted, the engineering team needs to determine the chunking strategysothatthearticlesourcecanbeeasilyingestedto buildanLLMknowledgerepository.
Based on the chunking strategy, the tokens are looped through by the framework and for each token block it is senttotheEmbeddingsAPIoftheEmbeddingsLLM(textembedding-ada-002) to generate the corresponding Embeddings of the input tokens. While sending the token blockstotheLLMmodeltheframeworkneedstoconsider the token limitation that is enforced by OpenAI. So this process using this framework shouldn’t be realtime and should be considered as the Day 1 activity or preprocessingactivity.
Following information flow diagram shows that the input knowledgearticlesareextractedfromtheHTMLsourceor document sources like PDF / Word docs / CSVs. This extracted content is split into multiple chunks based on the chunking strategy defined by the content team or the businessteam.E.g.Wecanconsiderthechunkingstrategy as sentences consisting of 10 or more words (fixed size chunking) or phrases based on logical groups (content aware chunking). If the input articles are enterprise articlesthenfixedsizechunkingperformsbest.Howeverif input content are research based articles then content
aware chunking would work best to identify the exact logicalsegments.
Also we need to use the stop words elimination strategy toremoveanyunwantedstopwordstomakeeachchunka meaningful & insightful text chunk. As you know that the stop words refer to the common words or text character or symbol that generally doesn’t carry much meanings of itsown butin ournatural languageit eitherconnectstwo phrases or multiple words to form paragraphs or sentences(exampleofstop wordsare - he,him, they, has, have,that,which,in,out,be,;,.).Weneedtoeliminatethe stop words from the text chunks which the solution is generating so that we can stay within the limit of the tokens input to the LLM and make the solution cost effective.
The text chunks are sent to the Embeddings API (/embeddings) of OpenAI to generate the embeddings vector. The Vector Embeddings are stored in the Vector databasealongsidethemetadatainformationofthesource articlewhichcanbereferencedifneeded.
Id
Table -2: AsampleDBtablestructureisasfollows:
Sample Data Model
AutogeneratedId(type:number)
embeddings_content Embeddingsdata(fieldtype: vector)
article_name
article_link
create_date
Itstoresthearticlename(type: text)
URLoftheHTMLarticle
Recordcreationdatetime

2.2 SERVE / Retrieval Framework
Once we have the pre-processing work completed by ingesting the enterprise knowledge content, we will have the Vector database available for consumption by other components.

The Serve framework is where the end users would be able to query against the AI based knowledge repository we built during the pre-processing stage. The high level designstepsaregivenbelow-
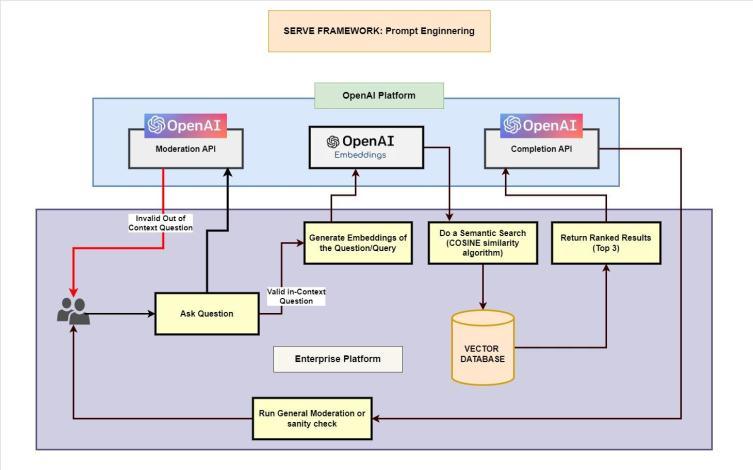
a) User asked a question, which is sent to OpenAI’s moderationAPI(/moderations)tovalidateifthis is a valid and meaningful question and doesn’t haveanysensitiveorinvalidwordings.
b) If the question is invalid then the user is alerted immediatelyandnoresponsesaregenerated.
c) If the question passes the moderation strategy then this is a meaningful and valid in-context question.
d) This valid question is then posted to OpenAI's embeddingsAPIwhichconvertsitintoa seriesof VectorEmbeddingsforfurtherprocessing.
e) This question phrase of Embeddings data is used to query the knowledge repository (Vector Database) that is curated during the preprocessingstage.
f) In the vector database the similarity search is performed to list the top similar results based on ranking using algorithms such as cosine similarity.
g) This result is then sent to OpenAI’s completion API(/v1/completions)whichsummarizesintoa
natural language pattern for the user to understand easily. The metadata (article url or references) are also preserved alongside the summarization.
The result from the OpenAI’s completion API is also validated with a general moderation action. Thiswayweensuretheanswerscomingfromthe internet data trained foundation model do not haveanymixedinvaliddatafromoutside.Though we put the guard rails when we invoked the completion API while passing the top results as a context.
Thevalidresponseisthensentbacktotheuser.
3. TECHNOLOGY STACK
The recommended technology stack for both the frameworks are given below. Since this Generative AI landscape is evolving fast so we may expect more new tools and technologies will be available to solve various potentia;lusecasesandsometoolswouldberetired.
a) Development Framework: Langchain is one of themostpopularpythonframeworksforbuilding LLMbasedapps.BoththeingestionandtheServe componentsarebuiltwithLangchain.
b) Vector Database: As a OnPremise solution the recommendationistousethe pgvector extension for PostGres database. Postgres with pgvector extensionisavailableasadockercontainer.
c) UI framework: Streamlit or Chainlit are the popular python framework which can be used to glue the UI/UX side. However, ReactJs or AngularJs can also be used to build interactive UI components.
4. RESULTS
We created a prototype project with the basic minimum python components to see the performance. The prototype minimum viable product can be enhanced with more advanced python modules to make it more feature rich.BasedontheLangchainAIframework,theprototype solution also integrated with in-memory open source ChromaVectordatabaseforstoringtheEmbeddings.
WemeasuredtheperformanceoftheOpenAIEmbeddings generation based on the supplied document having 200 words. The performance metrics have been compared withwhatisavailableinthemarketfromfreeopensource libraries.
We also captured the performance of the various LLM modelsavailablefromOpenAIforafixedsizeprompt.The resultsaregivenbelow.
4.1 QnA code
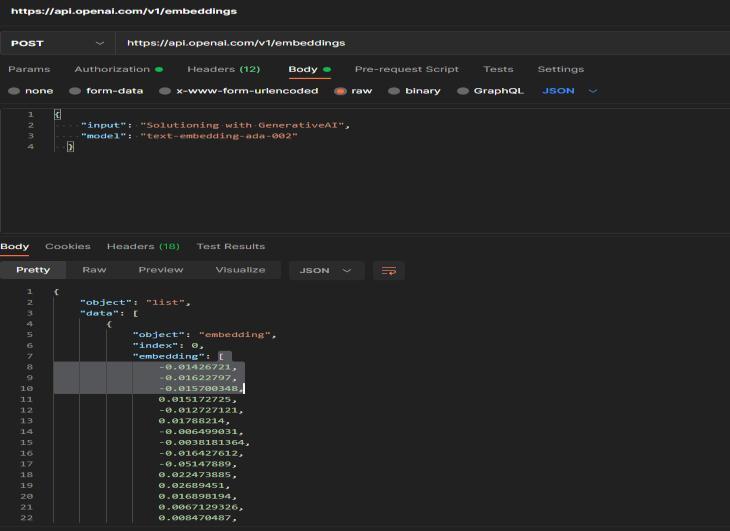
In our prototype solution we used python code to demonstratetheingestionprocesseswesolutionedabove. We used the Langchain framework and Pinecone vector database to store the embeddings generated by the OpenAI’s default LLM model “text-embedding-ada-002”. The ingestion code is the basic code block but this can be extended to scan and load PDF, html, csv, excel data sources. We also integrated a retrieval component to demonstrate how we can query the vector database to retrieve most similar data and then send it to the LLM model to summarize and produce response in natural language.
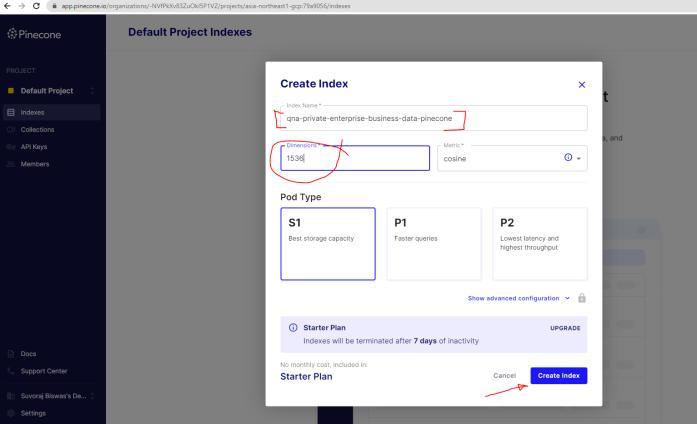
Step 1: Create an Vector index data store in Pinecone SAAS database having dimension size of 1536 and supportingcosinemetricforretrieval
Step 2: Following python modules should be installed first.
pip langchain
pip pinecone
Step 2: Run the QnA python code snippet shared below whichdemonstrateshowthetext data isvectorized using OpenAI’s api and stored in the Pinecone database created inStep1.
Also similar documents are retrieved based on the given queriesandpassedthecontexttoLLMtogeneratehuman readableanswersinnaturallanguage.
import langchain, pinecone
from langchain.llms import OpenAI from langchain.vectorstores import Pinecone from langchain.document_loaders import DirectoryLoader from langchain.embeddings.openai import OpenAIEmbeddings from langchain.chains.question_answering import load_qa_chain from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
directory_path = 'data'
PINECONE_ENV = "<pinecone env>"
PINECONE_API_KEY = "<pinecone apikey>"
PINECONE_INDEX_NAME = "qna-privateenterprise-business-data-pinecone"

OPEMAI_API_KEY = "<openai apikey>"
# Set up Pinecone client pinecone.init(api_key=PINECONE_API_KEY, environment=PINECONE_ENV) index = pinecone.Index(PINECONE_INDEX_NAME) print("******** Pinecone initialized. Index status ********\n") print(str(index.describe_index_stats())) print("********************************** *****************\n")
# Load the source documents (e.g. frequently asked Q/A for ecommerce site) def load_documents(directory_path):
print("\nSTEP 1:: Scanning directory & loading all the documents ")
loader = DirectoryLoader(directory_path)
documents = loader.load()
print("Found ecommerce FAQ sample ... loading the document for chunking\n")
return documents
# split or chunk the texts based on fixed chunk size (1000) def split_docs(documents, chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=20):
print("\nSTEP 2:: Started Chunking the document ")
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter(chunk_size =chunk_size, chunk_overlap=chunk_overlap)
chunks = text_splitter.split_documents(documents)
print("***** Total Number of documents chunked:: " + str(len(chunks)) + "\n")
return chunks
# Generate Embeddings using OpenAI's Embeddings model and store into Pinecone database def generate_embeddings():
print("\nSTEP 3:: Initializing OpenAI Embeddings model for converting docs into vectors")
embeddings = OpenAIEmbeddings(openai_api_key=OPEMAI_AP I_KEY, model="text-embedding-ada-002") return embeddings
index = Pinecone.from documents(chunks, embeddings, index_name=PINECONE_INDEX_NAME) return index
# Retrieve similar documents from Pinecone def get_similiar_docs(query, k=1): similar_docs = index.similarity_search(query, k=k) return similar docs
def get_answer(query):

model_name = "text-davinci-003"
llm = OpenAI(model_name=model_name, temperature=0, openai_api_key=OPEMAI_API_KEY) chain = load_qa_chain(llm, chain_type="stuff")
similar_docs = get_similiar_docs(query) answer = chain.run(input_documents=similar_docs, question=query)
return query + " \nAnswer:: " + answer + "\n\n"
print("\n****** Starting Enterprise data ingestion to load FAQ articles into Pinecone vector db******") loaded_docs = load_documents(directory_path) chunks = split_docs(loaded_docs)
embeddings = generate_embeddings() index = store_embeddings_in_pinecone(embeddings) print("*************** Ingestion completed ***************\n")
print("********************************** *****************\n")
def store_embeddings_in_pinecone(embeddings):
print("\nSTEP 4:: Store the embeddings into the Pinecone vector db ")
print("\n****** Starting Retrieval using OpenAI and context from Pinecone vectordb ******\n")
query1 = "How to cancel my order ?"
print("Question 1:: " + get_answer(query1))
query2 = "Do you have any loyalty program ?"
print("Question 2:: " + get_answer(query2))
query3 = "How do I reset my password ?"
print("Question 3:: " + get_answer(query3))
query4 = "Can I return a product purchased using store credit?"
print("Question 4:: " + get_answer(query4))
query5 = "What to do if a wrong item is received ?"
print("Question 5:: " + get_answer(query5))
Code execution results and pinecone index dashboard fromWindowsterminal.
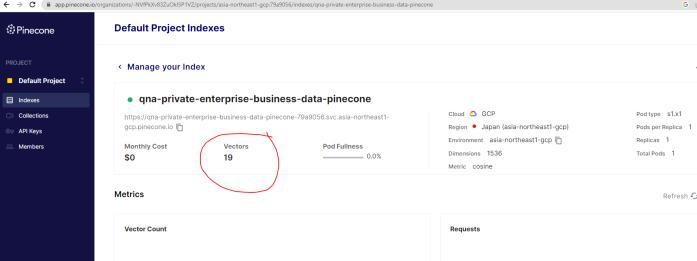
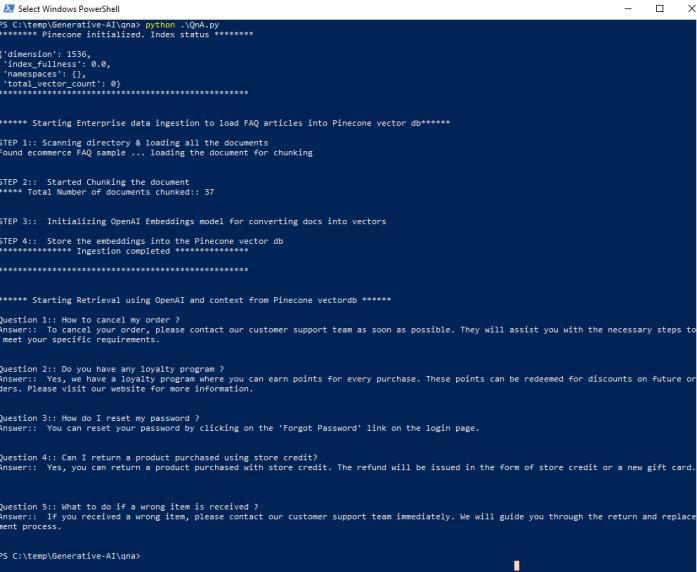
5. CONCLUSION
In this article we demonstrated how we can leverage the Retrieval Augmented Generation technique to provide a context to the Large Language Model to generate human understandable responses in natural language which can beusedasanEnterpriseIntelligentQnAsystemthatcould help the internal as well as external stakeholders to perform AI based search to find answers out of the huge knowledgebase.Wealsodemonstratedhowtheenterprise knowledge articles are ingested as Vectorized format into Vector database (Pinecone) which could be used to find similar answers out of huge data using cosine algorithm andthenusetheOpenAI’scompletionAPItogeneratethe meaningful answer. A sample python code is used to demonstrate the flow which can be enhanced more with addedfeaturesandcatertotherequiredusecase.

REFERENCES
[1] OpenAI API reference documentation and sample requests/response model for completion & embeddings api: https://platform.openai.com/docs/api-reference
[2] AWS paper on the Retrieval Augmented Generation (RAG) strategy for enterprises: using context with LLM https://docs.aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/latest/dg/j umpstart-foundation-models-customize-rag.html
[3] Source code for the QnA python code in Github repository: https://github.com/suvorajb/EnterpriseQnA-demo/tree/main
[4] Pinecone Vector database documentation on Langchain: https://python.langchain.com/docs/modules/data_co nnection/vectorstores/integrations/pinecone
[5] Langchain documentation on Question answering over documents: https://python.langchain.com/docs/use_cases/questi on_answering/
BIOGRAPHIES
Suvoraj Biswas has almost 19+ years of IT Work Experience in solutioning and building enterprise business critical applications in the field of IoT, Generative AI, Cloud Migration and Enterprise Architecture. He is working as a Solution Architect in a leading Financial Organization. based out of Minneapolis.


