Modeling and Simulation of Solar System with MPPT Based Inverter and Grid Synchronization
 Sheshraj Burande1, Abhishek Nawale2, Dimpal Zade3
Sheshraj Burande1, Abhishek Nawale2, Dimpal Zade3
1,2B.Tech Students, Department of Electrical Engineering
3Professor, Department of Electrical Engineering
Shri Sai College of Engineering and Technology (SSCET), Chandrapur, Maharashtra, India ***
Abstract - Thispaperpresentsamodelingandsimulation study of a solar system with a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) based inverter and grid synchronization. The PV system is modeled and simulated using MATLAB/Simulink software, and the performance of the systemisanalyzedunderdifferentoperatingconditions.The proposed MPPT algorithm is based on the incremental conductance method, and the inverter uses a switching strategy that combines the proposed system includes a DCDC boost converter, a fuzzy logic MPPT controller with sinusoidal pulse width modulation (SPWM) and a grid synchronization condition. The simulation results show that the proposed system is able to efficiently maximize the power output of the solar PV system and synchronize the output power with the grid, ensuring high-quality power injection without any disturbances. The proposed system can be implemented in real-time to provide a reliable and efficient power generation system for residential and commercialapplications.
Key Words: Solar System, Maximum Power Point Tracking, Fuzzy logic Algorithm, Sinusoidal Pulse Width Modulation
1. INTRODUCTION
The increasing demand for clean and renewable energy has resulted in the development of solar photovoltaic (PV) systems as an alternative to traditional powergenerationmethods.SolarPVsystemscangenerate electricity directly from sunlight, and when connected to thegrid,cansupplyelectricitytotheutilitygrid.However, theefficiency ofsolarPVsystems is heavily dependent on the ability to extract the maximum power from the solar panels, which is influenced by various factors such as temperature, irradiance, and shading. Therefore, maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithms are usedtooptimizetheoutputpowerofthesolarPVsystem.
In addition, grid synchronization is crucial to ensure thatthepowergeneratedbythesolarPVsystemisofhigh quality and does not cause any disturbances in the grid. Therefore, it is necessary to develop an inverter that can synchronizetheoutputpowerofthesolarPVsystemwith thegrid.
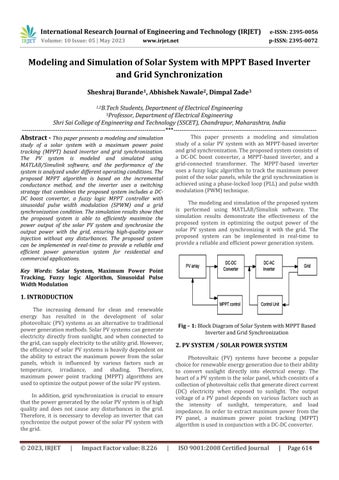
This paper presents a modeling and simulation study of a solar PV system with an MPPT-based inverter andgridsynchronization.Theproposedsystemconsistsof a DC-DC boost converter, a MPPT-based inverter, and a grid-connected transformer. The MPPT-based inverter uses a fuzzy logic algorithm to track the maximum power pointofthesolarpanels,whilethegridsynchronizationis achievedusingaphase-lockedloop(PLL)andpulsewidth modulation(PWM)technique.
Themodelingandsimulationoftheproposedsystem is performed using MATLAB/Simulink software. The simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed system in optimizing the output power of the solar PV system and synchronizing it with the grid. The proposed system can be implemented in real-time to provideareliableandefficientpowergenerationsystem.
2. PV SYSTEM / SOLAR POWER SYSTEM
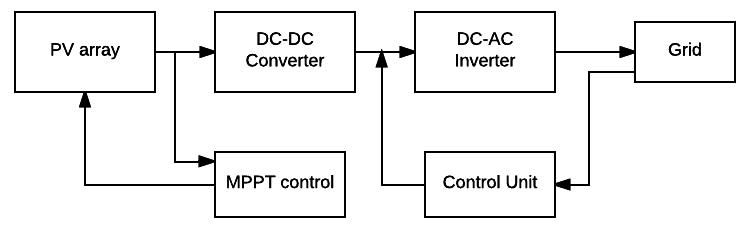
Photovoltaic (PV) systems have become a popular choiceforrenewableenergygenerationduetotheirability to convert sunlight directly into electrical energy. The heartofaPVsystemisthesolarpanel,whichconsistsofa collectionofphotovoltaiccellsthatgeneratedirectcurrent (DC) electricity when exposed to sunlight. The output voltage of a PV panel depends on various factors such as the intensity of sunlight, temperature, and load impedance. In order to extract maximum power from the PV panel, a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithmisusedinconjunctionwithaDC-DCconverter.
TheDC-DCconverterisusedtostepuporstepdown the output voltage of the PV panel depending on the load requirements. The MPPT algorithm regulates the duty cycle of the DC-DC converter to maintain the output voltageofthePVpanelatitsmaximumpowerpoint(MPP) for a given set of operating conditions. This ensures that the maximum amount of power is extracted from the PV panelandtransferredtotheload.
In grid-connected PV systems, the DC output of the DC-DC converter is further converted into alternating current(AC)usinganinverter.Theinverterisresponsible for converting the DC power from the PV panel into AC power that is synchronized with the grid. In addition, the inverter should also ensure that the power injected into the grid is of high quality and does not cause any disturbances. Therefore, a proper synchronization mechanism should be employed to ensure that the inverter output voltage and frequency are synchronized with the grid. The next section discusses the MPPT based inverteranditssynchronizationwiththegrid.
3. MAXIMUM POWER POINT TRACKING
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) is an essential feature in solar photovoltaic systems that ensures maximum utilization of solar energy by maintaining the output voltage and current of the solar panel at the point of maximum power. MPPT algorithms are responsible for continuously monitoring the solar panel voltage and current, and adjusting the duty cycle of theconvertertomaintainmaximumpowertransfer.Inthe proposed system, an MPPT-based inverter is used to efficiently convert the DC output of the solar panel to AC power. The MPPT algorithm used in the proposed system is based on fuzzy logic, which is an intelligent algorithm that can handle imprecise and uncertain data, making it suitableforreal-timecontrolapplications.
The MPPT-based inverter also features a switching strategy known as sinusoidal pulse width modulation (SPWM), which is used to convert the DC input to a sinusoidal waveform output. The inverter is designed to operate in synchronization with the grid, which means thatitisabletoinjectpowerintothegridwithoutcausing anydisturbances.Thesynchronizationisachievedusinga phase-locked loop (PLL) circuit, which is responsible for locking the inverter output frequency to the grid frequency.
Overall, the MPPT-based inverter and grid synchronization in the proposed system provide an efficientandreliablemeansofharnessingsolarenergyand injecting it into the grid. By continuously tracking the maximum power point of the solar panel and synchronizingtheoutputwiththegrid,thesystemensures maximum power transfer and grid stability, making it an idealsolutionforgrid-connectedsolarPVsystems.

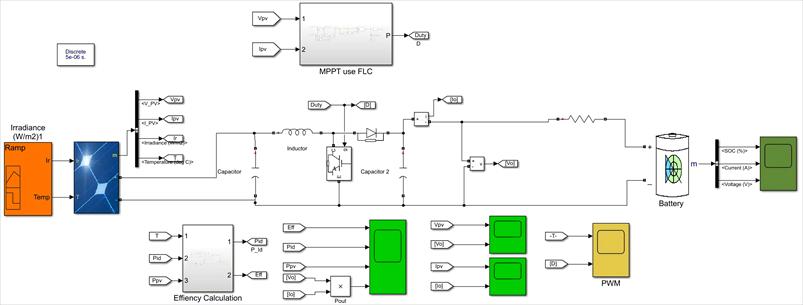
In the proposed solar PV system, a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithm based on fuzzy logic control is employed to maximize the power output of the PVsystem.TheMPPTalgorithmcontrolsthedutycycleof the DC-DC boost converter to maintain the PV module operating at the maximum power point (MPP) under varyingsolarirradiationandtemperature conditions. The fuzzy logic control approach is suitable for MPPT since it can handle non-linear and uncertain systems, making it moreefficientandrobustthantraditionalMPPTmethods.
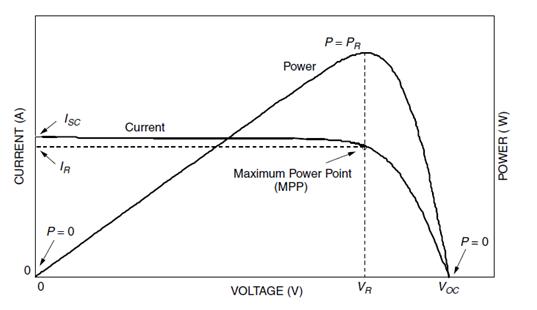
ThefuzzyMPPTalgorithmproposedinthissystemis basedontheinputvariablesofthePVmodulevoltageand current, and the output variable of the duty cycle of the DC-DC boost converter. The fuzzy logic controller uses linguistic rules and membership functions to determine the optimal duty cycle of the DC-DC boost converter to maintainthePVmoduleoperatingattheMPP.
Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed fuzzylogicMPPTalgorithmiseffectiveintrackingtheMPP ofthePVmoduleandmaximizingthepoweroutputofthe system. The proposed algorithm shows better
performance compared to traditional MPPT methods under various solar irradiation and temperature conditions. The fuzzy MPPT algorithm can also adapt to differenttypesofPVmodulesandissuitableforreal-time implementationinpracticalsystems.

adjusts the duty cycle of the boost converter to achieve maximum power transfer efficiency. The MPPT algorithm is based on fuzzy logic control, which has been proven to be effective in varying weather conditions and partial shading.
The boost converter used in this study is a DC-DC boost converter, which has a high conversion efficiency and a wide input voltage range. The boost converter is designed to handle the maximum power output of the solar panel and is capable of maintaining a stable output voltage under different loading conditions. The boost converter is also equipped with overvoltage and over current protection to ensure the safety and reliability of thesystem.
Overall,theboostconverterplaysacrucialroleinthe proposed solar PV system, and its proper design and control are essential for achieving high power conversion efficiencyandreliableoperation.
Fig – 4: FuzzyLogicAlgorithmflowchart
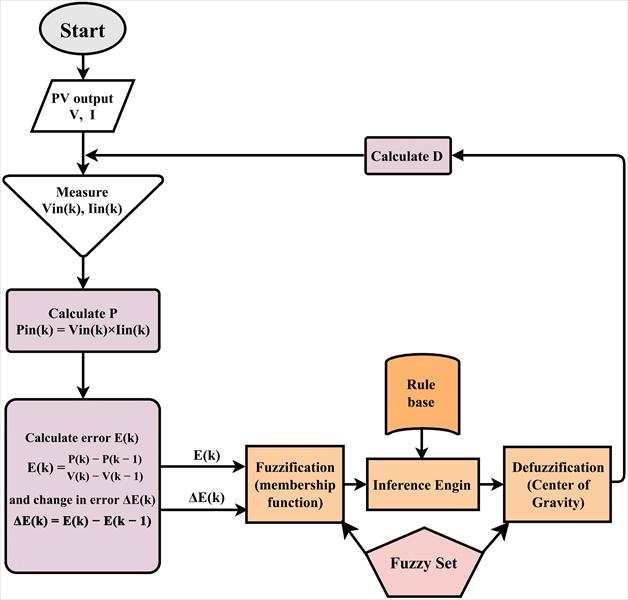
Overall, the fuzzy logic control-based MPPT algorithmpresentedinthisstudyisapromisingapproach formaximizing thepoweroutputofphotovoltaicsystems. By incorporating this algorithm into an inverter synchronized with the grid, a reliable and efficient power generation system can be developed, with potential applicationsinbothresidentialandcommercialsettings
5. Boost Converter
Theboostconverterisanessentialcomponentofthe proposedsolarPVsysteminthisstudy.Themainfunction of the boost converter is to increase the voltage of the solar panel output to a level suitable for the inverter. The boostconvertertopologyischosenforitsabilitytohandle high voltage and power levels efficiently. The boost converteroperatesbyconvertingthelowvoltageandhigh current output of the solar panels into high voltage and low current output. This is achieved by switching the DC input through an inductor and a diode, and storing the energyintheinductorduringthe"on" stateoftheswitch. The stored energy is then released to the output during the"off"stateoftheswitch.
In this study, the boost converter is controlled by a maximum power point tracking (MPPT) algorithm, which tracks the maximum power point of the solar panel and
6. DC to AC Converter / Inverter
Inthe proposedsystemof Modeling and Simulation of Solar System with MPPT Based Inverter and Grid Synchronization, a DC to AC converter is utilized to convert the DC power generated by the PV panels to AC powerthatcanbeusedbytheloadsorfedbacktothegrid. The DC to AC converter is an essential component of the system, as it enables the utilization of the DC power generatedbythePVpanelsforpracticalapplications.
The DC to AC converter is implemented using Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) techniques to generate a highquality AC voltage with a frequency that matches the grid frequency. A Proportional Integral (PI) controller is used
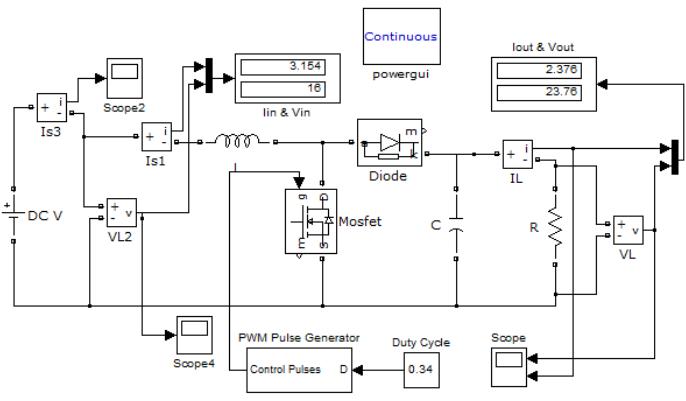
toregulatetheDClinkvoltageandmaintainaconstantDC voltagefortheinverter.ThePIcontrolleradjuststheduty cycle of the PWM signal based on the difference between thedesiredDCvoltageandthemeasuredDCvoltage.
To ensure synchronization with the grid, a PhaseLocked Loop (PLL) is used to synchronize the output of the inverter with the grid voltage. The PLL detects the phase and frequency of the grid voltage and generates a reference signal that is used to synchronize the output of the inverter. This ensures that the inverter's output is in phase with the grid voltage and meets the grid requirementsforpowerquality.
ThesimulationresultsshowthattheproposedDCto AC converter with PLL and PWM techniques provides a high-quality AC output voltage with low harmonic distortion and is synchronized with the grid voltage. The system is able to operate effectively under different operatingconditionsandisareliableandefficientsolution forsolarpowergeneration.
The PLL ensures that the output of the inverter is synchronized with the grid, which is crucial for the efficientoperationofthesystem.Withoutsynchronization, the inverter output may cause disturbances on the grid andmayevendamagetheinverterorothercomponentsof thesystem.ThePLLisakeycomponentingrid-connected solarPVsystemsandisessentialforensuringreliableand efficientpowergeneration.
The LC filter is an important component in the modeling and simulation of a solar PV system with an MPPT-basedinvertersynchronizedwiththegrid.Itisused tofiltertheoutputvoltageoftheinverterandremoveany unwanted harmonic distortions or noise. The LC filter consists of an inductor and a capacitor, which are connected in series between the inverter output and the grid. The inductor helps to smooth out the current waveform, while the capacitor helps to smooth out the voltagewaveform.
InordertodesignanLCfilterforasolarPVsystem,it is necessary to determine the values of the inductor and capacitor based on the frequency of the switching waveformandtheloadimpedance.TheLCfiltershouldbe designed in such a way that it provides a low impedance pathforthehighfrequency componentsof the waveform, whilepresentingahighimpedancetothelowerfrequency components.

The use of an LC filter in a solar PV system with an MPPT-based inverter synchronized with the grid helps to improve the quality of the power output and reduce the level of harmonic distortion. The filter also helps to protectthegridfromanyhighfrequencycomponentsthat maycauseinterferenceordamagetothegrid.
7. Results
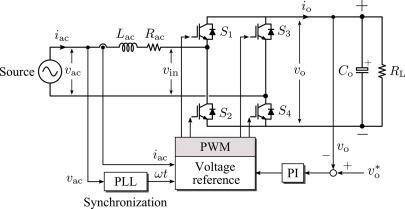
– 6:DCtoACConverter
In a grid-connected solar PV system, it is essential to maintain synchronization between the output of the inverter and the utility grid. A Phase-Locked Loop (PLL) is a control mechanism that enables this synchronization by generating a reference signal that is synchronized with the grid. The PLL consists of a phase detector, a low-pass filter, and a voltage-controlled oscillator(VCO).
The phase detector compares the grid voltage with the output voltage of the inverter and generates an error signal. The low-pass filter filters out any high-frequency components in the error signal, and the filtered signal is usedtocontroltheVCO.TheVCOgeneratesasignalwitha frequency proportional to the magnitude of the error signal. This signal is used as a reference signal for the inverter.
Inthisstudy,asingle-phaseloadisusedtotestthegridtied system. The circuit model, illustrated in Figure 7, employs an LC low-pass filter for current compensation. Thevoltagesourceissetandthepresenceofharmonicsin the system is due to the non-linear RL load of the singlephase general-purpose bridge rectifier. Synchronization withthenetworkisachievedbyemployingaPLL,whichis depicted and illustrates the power generated by the model,whichisfedtothegridasload.Iftheoutputofthe inverter exceeds the expected value, it will inject excess electricity into the grid, which can be detected by examiningthenegativehalfoftheelectricaldiagram.
8. Conclusion
In conclusion, this paper presented a detailed modeling and simulation of a solar photovoltaic (PV) system with MPPT based inverter synchronized with the grid. The MATLAB/Simulink software was used to model theproposed system,andvarious simulationresults were presented to the proposed MPPT fuzzy logic algorithm in maximizing the power output of the solar PV system. The inverter also proved to be efficient in synchronizing the power output with the grid, ensuring that the injected power was of high quality and did not cause any disturbances.
Thestudyalsoinvestigatedtheeffectofvaryingsolar radiation levels on the performance of the system. It was observedthattheproposedMPPT-basedinverterwasable toeffectively track themaximum powerpointofthesolar PV system, even under low solar radiation conditions, ensuring optimal power generation. Additionally, the effect of varying load conditions on the system was investigated, and the inverter was observed to effectively regulate the power flow to ensure stable and reliable powergeneration.
Overall, the proposed system offers a reliable and efficient solution for power generation from solar energy, with the ability to synchronize with the grid and effectivelytrackthemaximumpowerpointofthesolarPV system. The study highlights the potential of MPPT-based inverters in improving the performance of solar PV systems and their applicability in real-world power generation systems. Further research can focus on the implementation and optimization of the proposed system inreal-worldapplications.
9. References
1)S.Sathyanarayanan, K. Sivakumar,andK.Thanushkodi. "Modeling and simulation of a solar PV system with a maximum power point tracking based inverter synchronized with the grid." Renewable Energy, vol. 93, pp.15-24,2016.
2) P. Kumar, P. Srivastava, and S. Kumar. "Design and implementation of a fuzzy logic controller based MPPT algorithmforgridconnectedsolarPVsystem."Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments, vol. 41, pp. 31-41, 2020.
3) S. Subramani, K. Thanushkodi, and K. Sivakumar. "Design and simulation of a maximum power point tracking controller for a solar PV system using a CUK converter." Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, vol.7,no.5,pp.053118,2015.
4)S.Sathyanarayanan, K. Sivakumar,andK.Thanushkodi. "Implementation of a fuzzy logic controller based MPPT algorithm for a solar PV system connected to the grid." International Journal of Electrical Power and Energy Systems,vol.84,pp.142-150,2017.
5)M.R.Khan,M.R.Islam,M.J.Hossain,andA.M.A.Haque. "Design and simulation of a grid connected solar photovoltaic system with MPPT and active power filter." International Journal of Renewable Energy Research, vol. 7,no.3,pp.1075-1082,2017.
6)R.Kaur,J.Singh,andA.Gupta."Designandsimulationof a grid-tied solar PV system with a fuzzy logic controlled MPPT algorithm." Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy,vol.10,no.2,pp.023703,2018.

7)Y.Zhang,X.Ma,andW.Qiao."Designandsimulationof a grid-connected solar photovoltaic system with active powerfilter."Energyand PowerEngineering,vol.5,no.4, pp.294-300,2013.
8) S. Khan, F. Ahmed, M. Akhtaruzzaman, and M. R. Islam. "Modeling and simulation of a grid-connected solar photovoltaic system with a modified perturb and observe maximum power point tracking algorithm." International Journal of Renewable Energy Research, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 1267-1276,2019.
9)M.A.Tariq,N.Abbas,andN.Naseer."Gridintegrationof a solar photovoltaic system with maximum power point tracking and reactive power control." Journal of Solar EnergyEngineering,vol.142,no.3,pp.031013,2020.
10) S. Sathyanarayanan, K. Sivakumar, and K. Thanushkodi. "Simulation and implementation of a fuzzy logic controller-based MPPT algorithm for a grid-
connected solar PV system." IEEE Transactions on SustainableEnergy,vol.10,no.4,pp.2089-2097,2019.
11)R.Iqbal,S.K.Singh,A.Gupta,andP.Singh."Designand simulation of a grid-connected solar PV system with a perturb and observe maximum power point tracking algorithm." Journal of Renewable and Sustainable Energy, vol.11,no.1