Improved Fuzzy Logic Controller for a Global Mobile Telecommunication Network

Abstract - The inadequacy in call admission management is observed as one of the known limiting factors affecting the performance of the network, resulting in to increase in call drop rate, congestion, and high traffic intensity. The research work applied the mechanism of the Handoff Queue-based Call Admission Control scheme and FuzzyLogicartificial intelligencetodevelopanintelligentCall Admission Control for global mobile telecommunication networks. ThedevelopedintelligentCACmodelisatwo-phase fuzzy logic model. Phase one is the Fuzzy policer while Phase two is the Fuzzy Congestion Controller (FCC). The Fuzzy policer intelligently optimizes the delivery of calls and call drop with its fuzzification, inference engine, defuzzification analysis of queue capacity, call mean bit rate and call mean burst rate. These parameters enable it to estimate when new calls comply or violate the threshold at the Base Station. In the second phase of the developed system, the Fuzzy congestion controller optimizes the system resources by adjusting the handoff queue capacity for variations in the relative mobility of calls in the buffer and available free channels in the base station. The comparison of the system throughput of the proposed system, and existing congestion controlsystemsshowsthattheproposedsystemoutperformed the existing Call Admission Control models. It minimizes call drop rate probability and provides a significant reduction of cell loss due to congestion and buffer overflow under various network traffic variations.
Key Words: Call admission control, Handoff queue, Fuzzy congestion controller, Network traffic, Call drop rate, Cell loss
1.INTRODUCTION
The increase in the number of network subscribers in Nigeria had contributed to [1] continual network poor qualityofservicebecauseofthelackof adequatefacilities usedbythenetworkproviders. Also,“[2]observedthatthe proliferation of mobile devices such as mobile phones, smartphones, and tablets and advancement in wireless technologieshaveledtoanincreaseindemandforInternet servicessuchasvoiceoverInternetprotocol(VoIP),video streaming,internetsurfing,andonlinegaming,etc.byusers, anywhere and anytime”. “Due to the high influx of subscribers, the network performance of Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) systems began to deterioraterangingfrompoornetworkcoverage,constant
block/drop calls (Poor call initialization and Handover), call/network congestion, and poor internet services [1]”. “MobileNetworksarefacedwithlimitedwirelessresources withhighmobilityofusersduringcommunication,resulting inincreasedhandoffsbetweencalls[3]”.Thesefactorsresult in unsatisfactory network utility due to poor admission controlandinadequateresourcereservation.“Toreducethe high call drop rate, delay response and traffic congestion requireanefficientcalladmissionapproach[3]”.
Inaddition,themanagementofnetworkresourcesisamajor probleminthecellularcommunicationindustry.Aseriesof research reviews had been done on network congestion control, network resource management, an approach to minimizecalldroprateandoptimizednetworkresourcesfor a better quality of service. “The introduction of call admissioncontrolschemeprovidesadependableapproach toachieveoptimalresourcemanagementinlieuoflimited wireless resource availability. Call admission control algorithmsareimportantforwirelessnetworksnotonlyfor providing the expected Quality of Service (QoS) requirementstomobileusers,butalsotomaintainnetwork consistency and prevent congestion [3][4]”. However, the issue of uncertainties in network performance and variations that occurs at different intervals has been discussedinrecentstudiessuchas[3][1].Theattemptmade was promising, further approaches to efficiently address theseissueswillbeunveiledinthispaper.
Hence,thispaperprovidesanefficientcalladmissioncontrol mechanisms with Fuzzy logic an artificial intelligence methodandhandoffqueuemodeltoaddressthechallenges of network congestion and resource management. The expected outcome provides an improved algorithm to maximize user capacity, reduce traffic congestion and maintaingoodqualityofservice.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
[3]presented“efficientcalladmissioncontrolalgorithmfor mobility management in LTE networks”. “The work developedanintelligenttechniquetomanageandregulate the incoming calls and handoff calls in the Long-Term Evolution (LTE) networks using Fuzzy Logic based call admission control. The results of the system were used to compare with fuzzy and non-fuzzy techniques, using parameterssuchasdropcalls,averagelengthqueueandsize
of the queue to evaluate the drop call probability. The outcome shows a significant improvement in the network performanceresultinginlowcalldropprobability[3]”.[5] proposed“CallAdmissionControl(CAC)optimizationin5Gin downlink Single-Cell MISO System. The work provided a solution to the problems of CAC in 5G network for two categoriesofservicessuchasenhanced MobileBroadband (eMBB) and ultra-Reliable Low Latency Communications (URLLC)”.TheyusedSequentialConvexProgramming(SCP) tofindasuboptimalsolutiontotheproblem.[1]presented fuzzylogicimplementationforenhancedWCDMAnetwork using selected KPIs. In the work, empirical and analytic methods were used for the system analysis. Empirical analyseswereconductedontwodesignatednetworkswhich areMTNandAIRTELobservedwithhighnetworktrafficto evaluatetheirnetworkperformancesusingtheselectedKPIs [1].
TheSelectedKPIsincludeReceiveSignalLevel(RXLEV),Call Setup Success Rate (CSSR), Call Drop Rate (CDR) and Call CompletionSuccessRate(CCSR)[1]wasusedtoevaluatethe variousperformancecharacteristicsofthenetworksbased ontheQoS.TheresultsoftheempiricalanalysisoftheKPIs from the fieldwork measurements of five (5) geographical locations within Owerri, Nigeria, failed below Nigeria CommunicationCommission(NCC)threshold.Theyapplied fuzzy logic technique to the system after varying the congestionloadcharacteristicsforthedifferentgeographical locationsusingthefollowingparameters:meanbitrate,mean burstrate,networkstatisticsandretain-ability.Theirresult was promising. [6] proposed an “intelligent fuzzy logic system for network congestion control using Efficient Random Early Detection (FRERED) system”. The system improvedthefuzzy-Basedsysteminthe“FuzzyHybridERED algorithm,bydesigninganefficientcontrolmechanismthat eliminatesthecalldelayanddropschallengesinthenetwork. Theirtechniquesusedthequeuesize,averagequeuelength anddelayapproximationasinputvariablesincomputingthe packetdropprobability[6]”.Theirapproachproducedbetter resultsthantheexistingsystem.
[7] studied the “Performance Analysis of GSM network in Minna metropolis of Nigeria”, the work compared the performanceofvariousKPIsthatwereusedbyNCCforrating QoS.TheKPIsusedareCallSetupSuccessrate(CSSR),Call DropRate(CDR),SDCCH,TCHCongestionRate”.Theywereof the view that “KPIs that are used to measure Network Performance(N.P)canalsobeusedtomeasurethenetwork formultipleradioresourcemanagementfunctionssuchas pagingnetworkaccess,congestion,Calldrop,Handover,and powercontrol”[7]. AndthemostimportantoftheKPIsfrom operators’perspectiveincludes”BitErrorRate(BER),Frame Erasure Rate (FER), Bit Error Probability (BER), Received SignalLevel(Rx-Level),ReceivedSignalQuality(RxQual)and MeansOpinionScore(MOS).Thedrivingtestwasperformed usingTEMSInvestigationtools.Twodifferentmeasurement methodswereusedtocollectlogfilesfortheperformance
analysis. They are short calls, which was used to collect accessibility statistic, and long calls used to obtain retainabilitystatistic[7]”.“Thenetworkoperatorsevaluatedwere named W, X, Y, and Z. The results obtained were used to compareNCCKPIstargets.Fromtheresult,itwasshownthat operatorXhadthebestnetworkquality,followedbyWwhile YhadtheworstnetworkqualityfollowedbyZintheareaof study” [7]. The result also showed that Y had the bestplannednetworkrequiringminimalhandoverwhichmeans 100%handoversuccessrate.Theauthorsfurtherdidanindepthanalysisof"W"network,theproblemthataffectsthe siteswasidentifiedandoptimizationmeasuresrequiredto resolvetheproblemswererecommended.
Anotherattemptwasmadeintheworkof[8].Theauthors proposed“afuzzyapproachforcalladmissioncontrolinLTE networks. Their result was promising as it reduced the number of rejected calls and minimized very low call droppingprobabilityduringthebusiesthour[8]”.Buttheir mechanismdidnotconsiderhandoffcallsandconsiderable thresholdtoregulatequeuecapacityintheBaseStationfor new incoming calls for the handoff calls initialization and dropcalls.Theseresearchgapspointedoutwillbeenhanced withtheproposedmethodsinthiswork.
[9] in their work on “Quality ofservice assessment: a case study on performance benchmarking of cellular network operatorsinTurkey”.“TheyStudiedthebenchmarkingofthe cellularnetworkinAnkara,Turkey,bycomparingtheGSM andUMTSnetworkoperatorsA,B,andCtodeterminewhich networkrendersthebestnetworkperformanceinAnkara”. Thestudywascarriedoutusingsomeselected“KPIswhich include CSSR, Call Setup Time (CST), CDR, Speech Quality (SQ) Perceptual Evaluation of Speech Quality (PESQ) and ReceivedSignallevel(RxL).End-userperceptionofservice qualitywasintegratedintoQoSassessment.Theyconsidered the upper-level layer of the ETSI QoS structure which are accessibilityandretainability.Accessibilitywasmeasuredby thenumberofcallattempts(#CA)andsuccessfulcalls(#SC)” [9].

3.1 Summary of Literature Review
Theworkof[6]proposedanintelligentfuzzylogicsystemfor network congestion control using Efficient Random Early Detection(FRERED)system.Thoughtheirworkoutsmarts theexistingfuzzyhybridEREDsystem,theirmodelfailedto minimizecallsdroprateinthebufferwhichleadstonetwork congestion.Theapplicationofhandoffqueuemodelwould haveproducedbetterresults.Also,theworkof[1]presented “fuzzylogicimplementationforenhancedWCDMAnetwork using selected KPIs. In the work, empirical and analytic methodswereusedforthesystemanalysis[1]”Theirresult was promising but they did not consider variations of networkcongestioninthebufferandthelevelofitseffecton thesystem.Thoughtheyusedvariablessuchasnegativeand positiveofthe“networkstatistics”whichisnotsufficientto
determine congestion of call waiting for free cells to be initiated.
Therefore, the proposed system in this paper developed a hybrid model of handoff mechanism and queue model to produceanefficientmodeltoimprovethequalityofservice for global mobile telecommunication network using fuzzy logicartificialintelligence.
3. RESEARCH METHODOLOGY

This work adopted Object-Oriented Analysis and Design (OOAD)methodologyforthedevelopmentoftheproposed system. It developed an efficient Call Admission Control mechanism using the integration of Queuing and Handoff model with Fuzzy logic artificial intelligence model. The developedintelligentCACmodelisatwo-phasefuzzylogic model.
PhaseoneistheFuzzypolicerwhilePhasetwoistheFuzzy CongestionController(FCC).TheFuzzypolicerintelligently optimizes the delivery of calls and call drop with its fuzzification, inference engine, defuzzification analysis of queuecapacity,callmeanbitrateandcallmeanburstrate. These parameters enable it to estimate when new calls complyorviolatethethresholdattheBaseStation.
In the second phase of the developed system, the Fuzzy congestion controller optimizes the system resources by adjustingthehandoffqueuecapacityconcerningvariations in the relative mobility of calls in the buffer and available free channels in the base station. It outputs the queue capacitywhichisreceivedasinputtoFuzzypolicerthefirst phase of the developed system. The handoff queue model manages undelivered calls on the mobile station by using releasedcellsintheBasestations(BS)toconnectthecalls waiting for free channels. The mechanism of the Handoff queue depends on the threshold parameter specified to managethequeuecapacity.Hance,thedevelopedsystemhas an efficient mechanism of passing or dropping calls to stabilizes network Quality of Service (QoS) and control congestionuncertaintiesinthenetwork.
The architecture of the proposed fuzzy logic traffic controllerispresentedinfig1.


The components of the proposed system’sarchitecture areasfollow:
i. Fuzzy Congestion Controller: Fuzzy congestion controller(FCC)handlesthecallschanneledinthebufferto prevent network congestion in the Base state. Before the waitingcallsinthebufferareassignedtonewfreecells,the FCCmanagesthecallsinthebufferbytheirAvailableguard channel, Relative mobility to intelligently optimize the “Queuecapacity”inthebufferusingfuzzylogicmodel.The outputoftheprocessisusedtodirecttheFuzzypolicerthat
manages the call complies in the base station. This mechanismensuresthatthesystemiscongestionfree.
ii. HandoverMechanism:thedevelopedsystem uses handover method to manage the drop calls using the mechanism of Available Guard Channel, Relative Mobility, andQueueCapacityforthetransferofcellstodifferentand initializeitsconnections.
iii. CallArrivalDetector:Thecallarrivaldetectionisthe parameter that detects the call mean bit rate and the call mean burst rate. These parameters are input in the Fuzzy PolicertooptimizethecallcapacityintheBasestation.This ensuresthatallincomingcallsarecompliedwithordonot exceedthenumberofcallsthataresupposedtobedelivered. Thecallsthatarenotconnectedarequeuedupinthebuffer.
iv. Pass/DropSwitch:Thereasonfortheextensionisto providetheFuzzypolicer(FP)withmoreinformationthus helpingitinmakingmoreaccuratedecisionsonpassingor droppingcells.
v. FuzzyPolice:TheintelligencemechanismsofFuzzy PolicerintheBaseStationenhancedthemanagementofthe capacityofthequeuemodel.Itusedtheparameters:meanbit rate, mean burst rate, and queue capacity from the Fuzzy ControllertodeterminethecalldroprateattheBasestation. Thisimpliesthatifthequeuecapacityinthebasestationis exceededthesystemwilldropormovecallsinthebufferto preventcongestion.
Thefuzzypolicercontrolstheoverallnetworkofthesystem. Itefficientlymanagescalldeliverywithoutdroppingthecalls by channelingundelivered callstothe queue inthe buffer, awaiting a free channel to connect them. Also, it communicateswiththequeuecapacityoutputfromtheFuzzy controllerinthebufferforanefficientdecisiononwhetherto passordropnewincomingcallsintheBaseStation.
3.1 Activity Diagram of the proposed system
The Activity diagram of the proposed system is shown in Figure3.4
thefuzzypolicerwillthensignaltothepass/dropswitch.The proposed fuzzy traffic controller' aim is to simultaneously monitortheMeanrateandrejectburstswhilepreventingand relievingcongestion.
3.2 Algorithm
Step one: Arrival of calls from the users at the base station;
Steptwo:Callarrivaldetectorgeneratescallmeanbitrate andcallburstratefromcallusersrequestforfuzzypolicer’s analysis
Step three: Pass/drop switch pass calls based on the threshhold≤86dBorsendunadmittedcallstothebufferif threshhold≥86dB
Step four: Handover mechanism analyzes unadmitted callswithinthebufferWhiletheadmittedcallsaredelivered,
Stepfive:HandoverChannelAccumulationtakesdecision aboutassigningfreecelltodelivercallsif(threshold≤18)in thebufferotherwiseCallsaredropif(threshold≥18)
Step Six: Handover Initialization assigns free cell to waitingcallsinthebufferandinitializesitdelivery

StepSeven:HandoverChannelAccumulationdetermine and sends reports (Available Guard Channel and Relative MobilityofQueuelengths)ofthestateofthenetworkinthe buffer(queueregister)toFuzzyCongestionController.
Step Eight: Fuzzy Congestion Controller intelligently analyzesthestateofthenetworkinthebufferandoutputs conditionofthequeuecapacity,whichissenttoFuzzyPolicer forfurtheranalysis
Activitydiagram.
The activity diagram shows the system connectivity components.TheFuzzy Policer(FP)continuouslyevaluate thecompliance/violationlevelsofthequeuecapacityinthe Base Station. Thereby it sent the call drop rate and call completionsuccessratesvaluestothepass/dropswitch.The switchwouldeitherpassordropandcallcompletionsuccess ratesfractionsofthecellsinthememorybasedonthevalues ofthedroprate.
The cell arrival detector checks the mean bit rate and mean-burst length of the incoming traffic from an already connecteduser.Thetwo-parametermeasurementsserveas input to the fuzzy policer including the buffer state of network accepted from Fuzzy congestion controller that representsthecongestionstateofthenetworkbasedonthe inferenceenginedecisiononanalyzingthe“Numberofguide channels” and “Relative Mobility” of queue length in the buffer(queueregister).However,theoutputdecisionfrom
StepNine:FuzzyPolicerdeterminesthestateofcallburst rate,callmeanbitrateandqueuecapacity(Buffer)tocontrol congestion occurrence in the system by deciding call drop andpassinthebasestation.
StepTen:Determinesystemthroughput
StepEleven:GOTO:stepone
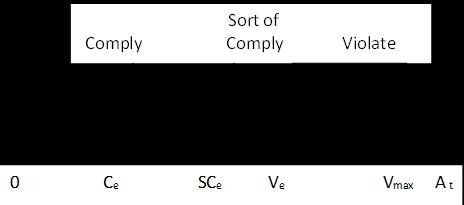
whereA1=CallMeanBitRate,A2=CallMeanBurstRate, CDP=CallDropProb,C=comply,SC=SortofComply,V= Violate,P=Pass,D=drop.
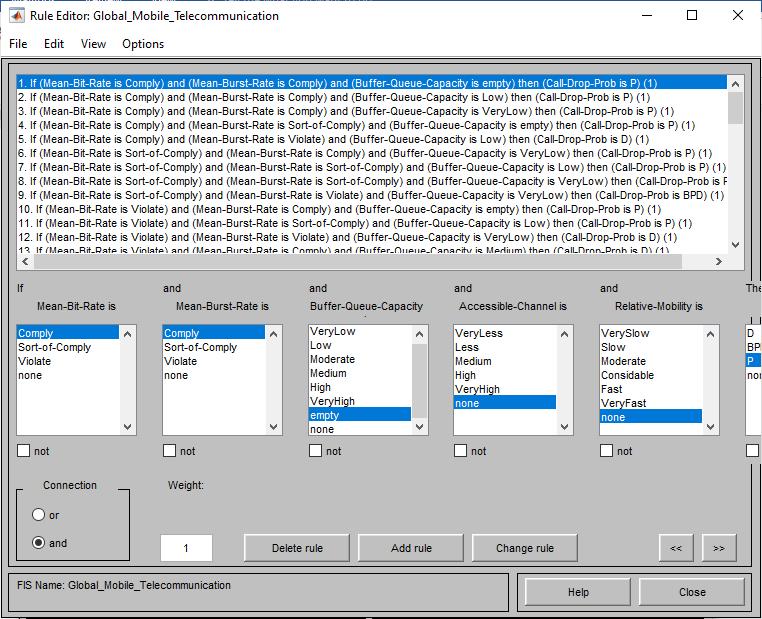
Table .1 presented the proposed twenty-six rules used to developedintelligentcalladmissioncontrolsystem.Therule baseisconstructedonthebasisofknowledgefromstudying variousliteraturesonCallAdmissioncontrolsystem.
TheTwenty-sixrulesarepresented”asfollows:
1.If (Mean-Bit-Rate is Comply) and (Mean-Burst-Rate is Comply) and (Buffer-Queue-Capacity is empty) then (Call-Drop-ProbisP).
2.If (Mean-Bit-Rate is Comply) and (Mean-Burst-Rate is Comply)and(Buffer-Queue-CapacityisLow)then(CallDrop-ProbisP)
3. If (Mean-Bit-Rate is Comply) and (Mean-Burst-Rate is Comply) and (Buffer-Queue-Capacity is VeryLow) then (Call-Drop-ProbisP)
4. If (Mean-Bit-Rate is Comply) and (Mean-Burst-Rate is Sort-of-Comply) and (Buffer-Queue-Capacity is empty) then(Call-Drop-ProbisP)
5. If (Mean-Bit-Rate is Comply) and (Mean-Burst-Rate is Violate)and(Buffer-Queue-CapacityisLow)then(CallDrop-ProbisD)
6. If (Mean-Bit-Rate is Sort-of-Comply) and (Mean-BurstRateisComply)and(Buffer-Queue-CapacityisVeryLow) then(Call-Drop-ProbisP)
7. If (Mean-Bit-Rate is Sort-of-Comply) and (Mean-BurstRate is Sort-of-Comply) and (Buffer-Queue-Capacity is Low)then(Call-Drop-ProbisP)
26.If(Accessible-ChannelisHigh)and(Relative-Mobilityis Fast)then(Queue-CapacityisMedium)
Table-2: Fuzzylogicrulesforcongestioncontrolinthe Buffer.
1 IfAccessibleChannelsisPreciselyLessandRelativeMobilityis Slow ThenQueueCapacityisHigh
2 If Accessible Channels is Less and Relative Mobility is Slow ThenQueueCapacityisMedium
3 IfAccessibleChannelsismediumandRelativeMobilityisSlow ThenQueueCapacityisModerate
4 If Accessible Channels is High and Relative Mobility is Slow ThenQueueCapacityisLow
5 If Accessible Channels is Very High and Relative Mobility is Slow ThenQueueCapacityisLow
6 IfAccessibleChannelsisVeryLessandRelativeMobilityisVery Slow ThenQueueCapacityisMedium

7 If Accessible Channels is Less and Relative Mobility is Very SlowThenQueueCapacityisLow
8 IfAccessibleChannelsisMediumandRelativeMobilityisVery SlowThenQueueCapacityisLow
9 If Accessible Channels is High and Relative Mobility is Very SlowThenQueueCapacityisVeryLow
10 If Accessible Channels is Very High and Relative Mobility is VerySlow ThenQueueCapacityisLow
11 If Accessible Channels is Very Less and Relative Mobility is Moderate ThenQueueCapacityisVeryHigh
12 IfAccessibleChannelsisLessandRelativeMobilityisModerate ThenQueueCapacityisMedium
13 If Accessible Channels is Medium and Relative Mobility is Moderate ThenQueueCapacityisMedium
14 If Accessible Channels is High and Relative Mobility is Moderate ThenQueueCapacityisLow
15 If Accessible Channels is Very High and Relative Mobility is Moderate ThenQueueCapacityisLow
16 If Accessible Channels is Very Less and Relative Mobility is Considerable ThenQueueCapacityisVeryHigh
17 If Accessible Channels is Less and Relative Mobility is Considerable ThenQueueCapacityisHigh
18 If Accessible Channels is Medium and Relative Mobility is Considerable ThenQueueCapacityisHigh
19 If Accessible Channels is High and Relative Mobility is Considerable ThenQueueCapacityisModerate
20 If Accessible Channels is Very High and Relative Mobility is Considerable ThenQueueCapacityisHigh
21 If Accessible Channels is Very Less and Relative Mobility is VeryFast ThenQueueCapacityisVeryHigh
22 If Accessible Channels is Less and Relative Mobility is Very Fast ThenQueueCapacityisVeryHigh
23 IfAccessibleChannelsisMediumandRelativeMobilityisVery Fast ThenQueueCapacityisHigh
24 If Accessible Channels is High and Relative Mobility is Very Fast ThenQueueCapacityisHigh
25 If Accessible Channels is Very High and Relative Mobility is VeryFast ThenQueueCapacityisMedium
26 If Accessible Channels is Very Less and Relative Mobility is Fast ThenQueueCapacityisVeryHigh
27 If Accessible Channels is Less and Relative Mobility is Fast ThenQueueCapacityisHigh
28 IfAccessibleChannelsisMediumandRelativeMobilityisFast ThenQueueCapacityisHigh
29 If Accessible Channels is High and Relative Mobility is Fast ThenQueueCapacityisMedium
30 If Accessible Channels Very is High and Relative Mobility is Fast ThenQueueCapacityisMedium
Theinput/outputspecificationsaredescribedinTable-3.
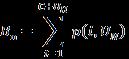
Table
Input/output specifications

3.3 Mathematical Models for Handoff Queueing
TheMathematicalmodelsfor“handoffqueueingforNew call blocking probability (Bn) and Blocking probability Bhandoffhandoverrequirement[10]”aregivenasfollow:
i. Newcallblockingprobability(Bn)
i. (1)
Where“C representsthelimitedamountofcodechannels accessible in the channel pool. Most cases each channel reserveswchannelswhollyformanagementofqueueissues.
UN representsQueuecapacityintheBasedStationN.
P(q) represents the steady state probability” (Ravi & Sanjiv,2012).
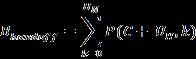
i. BlockingprobabilityBhandoff asgiveninequation (2)
WhereUHrepresentsQueueCapacityintheMobileStationH.
3.4 Member Functions
Thereareseveraltypesofmembershipfunctionssuchas triangular waveform, trapezoidal waveform, Gaussian waveform,bell-shapedwaveform,sigmoidalwaveformandScurvewaveform.Sincethisworkisareal-timeoperationthat involvessignificantdynamicvariationwithinashortperiod, triangular and trapezoidal waveform is utilized. The “proposedFuzzyCongestionController(FCC)alsousesthe max-min inference method for the inference engine and Tsukamoto'sDefuzzification.Themembershipfunctionsfor callmeanburstrateandmeanbitrateisshowninFig-3.
Low, Moderate, Medium, High, Very High”
Table-3 describes the congestion control mechanisms parametersanditslinguisticvariablesusedintheanalysisof theproposedsystem.
Fig-3:illustratesthemembershipfunctionsforcall meanburstrateandmeanbitrate
4. Results
TheMat-labinputdesignconsistsofcallmeanbitrate,Call meanburstrate,Relativemobility,AvailableFreeChannels, andBufferQueueCapacitytoimprovetheperformanceofthe existingsystem.TheoutputisCall DropProbabilitythatis optimized by the Fuzzy inference mechanism in asynchronous transfer mode to produce stability of the network.TheMATLABinput/outputsinterfaceisshownin Fig4.1
Fig-4:ThemembershipfunctionsforCalldroprate
“De, BPDe, Perepresentsthe drop rateimposedonthe cells.Dewouldbesetto0forthetotaldropofallcells,BPDe toavaluewithin[0,1]butcloserto1fordroppingafraction of the cells, and Pe is set to 1 for passing all cells. The FP decidesonthedropratec,accordingtothesetoflinguistic variables of parameters Al and A2, state of the network y generatedbytheFuzzyCongestionControl(FCC),andasetof built-infuzzycontrolrules”.
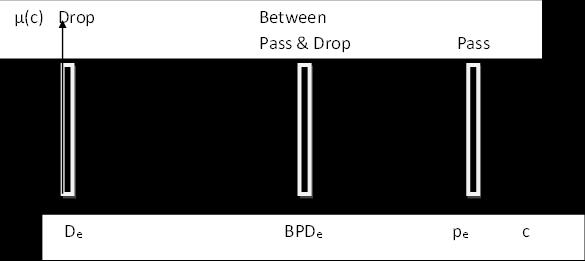
“Theoutputisthemembershipfunctionforthetermset T(c) which are Drop (D), between Pass & Drop (BPD) and Pass (P). Uncertainty in the network system may resultto dropcalls,callsbetweenpass&drop,andpassallcalls.The valueforDrop(D)callswillbesettozeroforthetotaldropof allcalls,andBPDsettoavaluewithin[0,1]butcloserto1for droppingafractionofcells,andpassingallcallssetto1”.The simulatedparametersarerepresentedinTable-4
Table-4:Simulatedparametersarerepresented
TheRulebasediagramisshowninFig-6.
InFig-6.theRulebasecontainstherulesproposedtocontrol congestionproblemsinthesystem.

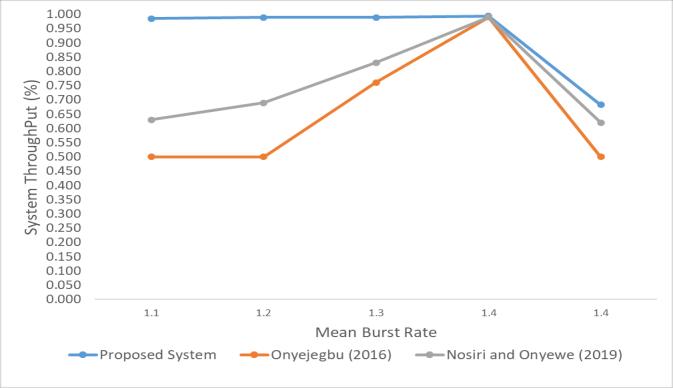
Thecomparisonofthesystemthroughputoftheproposed system,andexistingcongestioncontrolsystemsisshownin Fig-7.
4.1 Discussion
The proposed fuzzy policer and fuzzy congestion control weredevelopedusingMATLABR2018aversion.FromFig-7, the comparison of the rate of call delivery (system throughput)oftheproposedsystem,andexistingcongestion control systems shows that the proposed system outperformed[11]and[1]CallAdmissionControlmodels. These demonstrated that the proposed system minimized calldropratemorethantheexistingsystems,itprocessesa givenamountofcalldeliveryefficiently.
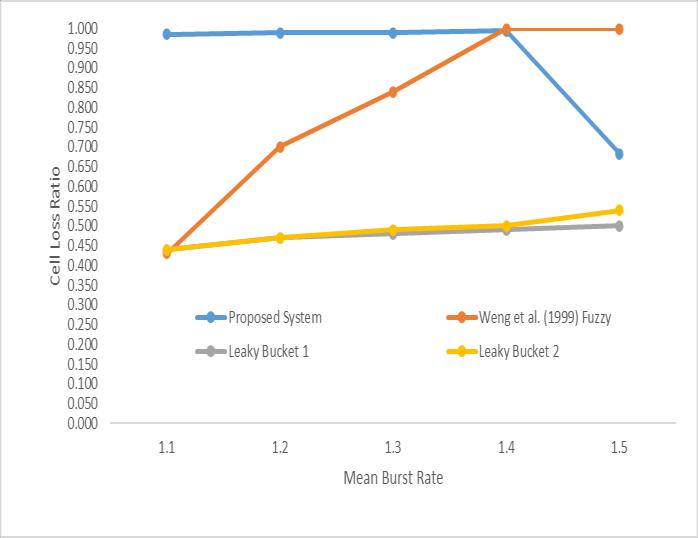
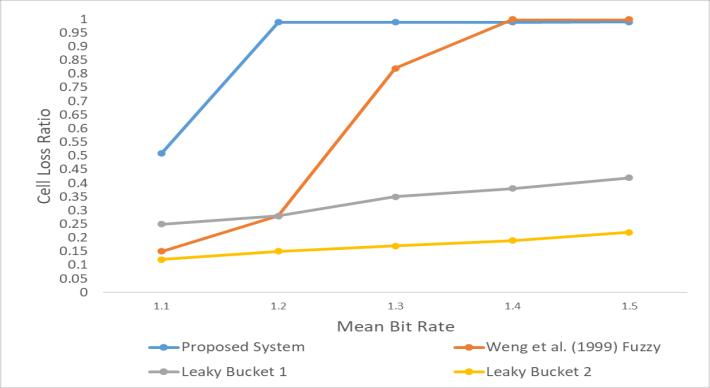
Moreover,fromFig-8thecomparisonofthecalllossratioof theproposedsystem,andtheexistingsystemsshowsthat theproposedsystemalsooutperformed[12]fuzzylogicand leakybucketcongestioncontrolmodels. Furthermore,from Fig-9,thecomparisonofthecelllossratiooftheproposed system,andexistingfuzzy,leakybucketcongestioncontrol withrespecttoCallMeanBurstRateshowsthatproposed systemproducedabetterresultthantheexistingsystems.
However,thesimulationresultsconfirmthatthedeveloped systemismoreefficientonreductionofcelllosscausedby congestion and buffer overflow in various network variations. Whenever congestion occurs in the system the developed intelligent congestion control rules from FCC signalstheFuzzyPolicertoreduceitscurrentrateofcalls delivery, by optimizing the queue capacity (state of the networkinthebuffer)withthemeanbitandburstrateof thelinguisticvariablesoftheincomingcallsanddetermine the appropriate decision to take under such network uncertainties. When the network is congestion free the transmission/cellratewillberestoredtoitsoriginalvalues. Thereby enhancing the performance of the system throughput.
3. CONCLUSIONS
The research work successfully developed an improved fuzzylogiccontrollerforaglobalmobiletelecommunication network.ItappliedthemechanismofHandoffqueue-based Call Admission Control (CAC) scheme and Fuzzy Logic artificial intelligence to developed an intelligent network congestioncontrollerforglobalmobiletelecommunication network.
The proposed system is very efficient to provide efficient qualityofservicebyintelligentlyanalyzingthedynamicof complexusercallnetworkactivities,inthemobilenetworks base station. It uses Fuzzy logic handoff mechanism to ensurethattheunadmittedcallsarenotdroppedbutassigns to free available cells for efficient delivery and moreover ensures that incoming calls are properly managed to minimize call dropping and prevents congestion in the network.

ACKNOWLEDGEMENT (Optional)
WewouldliketothankandappreciatetheDepartmentsof ComputerScience,FederalUniversityofTechnology,Owerri, ImoState,Nigeriaforprovidingtheenablingenvironment thatfacilitatedthiswork.
REFERENCES
[1] O. C. Nosiri, E. Onyenwe & E. Ekwueme, “Fuzzy logic implementation of enhance WCDMA network using selected KPIs. Advance in Science, Technology and EngineeringSystem”Journal,vol.1,2019,pp.114-124.
[2] S. Ibrahim, R. Abubakar, A. S. Nasir. & Y. Solomon, “Congestion Control Call Admission Control (CC-CAC) AlgorithmforMobileBroadbandNetworks”.European JournalofElectricalandComputerEngineering(EJECE), vol.5,2019,pp.1-5.
[3] E.E.Ekechukwu,O.C.Nosiri&M.I. Ajumuka,“Efficient call admission control algorithm for mobility managementinLTEnetworks”,InternationalJournalof NetworkandCommunication”.12(1),2022,pp.28-38.
[4] I.Georgios,D.G.Tsiropoulos.&E.E.T.Strtogianms “Call Admission Control in mobile and wireless networks, Mobile & Wireless Communication network layer and Circuitleveldesign” 2010

[5] S. Ahmed, C. Hasna, R. Saadane & C. Abdellah, “Call Admission Control Optimization in 5G in Downlink Single-CellMISOSystem.ProcediaComputer”Science. 192,2021,pp.2502-2511.
[6] H. P Uguta & L. N Onyejegbu, “An Intelligent Fuzzy Logic System for Network Congestion Control”, CurriculuminComputerScience.2(11),2017,pp.23-30.
[7] A.Ozovehe,&A.U.Usman,“PerformanceAnalysisofGsm Networks in Minna Metropolis of Nigeria. Computer, Telecommunications,Software,Electrical&Electronics Engineering”, African Journals online (AJOL), vol. 34, 2015,pp.359-367.
[8] O.C.B.TokpoK.Djouani&A.Kurien,Afuzzyapproach forcalladmissioncontrolinLTEnetworks,2014.
[9] R.Kadioglu,Y.Dalveren,&A.Kara,“QualityAssessment: AcaseStudyonPerformancebenchmarkingofcellular network operators in Turkey”, Tuirkey Journal of Electrical Engineering andComputer Sciences vol. 23, pp 2015,548-559
[10] S.Ravi&T.Sanjiv,“Analysisofhandoffqueuingbased Call admission control scheme in CDMA networks” . ICEMC2,Mysore.2008,53-59.
[11] L. N. Onyejegbu & N. I. Okafor. “Congestion Control in Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) Network. International Journal of Computer Applications”. vol. 142–No.4,2016,pp.0975–8887
[12] T.LWeng,K.K.Phang,Y.Mashkoro&T.C.Ling,(1999). “FuzzyLogicControlinATMNetwork.MalaysianJournal ofComputerScience” ,vol.12,pp.47-56.
