COMPARATIVE STUDY OF ADSORPTION PROPERTIES OF HUMAN HAIR AND ACTIVATED CARBON IN WASTE WATER
Varsha k1 , P E Mohanan Namboodiri21M. Tech Scholar in Environmental Engineering, Department of Civil Engineering, M. Dasan Institute of Technology, Kozhikode, Kerala, India

2Assistant Professor, Department of Civil Engineering, M. Dasan Institute of Technology, Kozhikode, Kerala, India ***
Abstract - An adsorption study in a batch and column was carried out by using human hair and activated carbon as bioadsorbents for the removal of oil and grease from automobile service center waste water. In batch study the adsorbent dosage, contact time, pH and temperature are considered. The batch study shows that 24 grams of human hair can remove 76 % of oil and grease from the waste water in contact time of 60 minutes and 40 grams of activated carbon can remove only 50 % of oil and grease from waste water in contact time of 80 minutes so these values is taken to be the optimum in the batch study. The maximum removal efficiency 81% of oil obtained at pH of 7.5 and 80% at 210C temperature with 24 g/l of human hair in 60 minutes time of contact. On the basis of batch the column study was conducted with adsorbent bed depth of 7.5 cm and 10.5 cm respectively and varying the rate of flow as 15 ml/min/cm2 and 10 ml/min/cm2. The combination mixture of human hair and activated carbon at 10.5 cm and rate of flow 10 ml/min/cm2 shows the highest removal efficiency of 74% in column study. After that human hair adsorbent required regeneration. In which hibiscus leaf juice (Thaali) used for regeneration, and obtained about 80% of regeneration of oil content in the saturation point.
Key words: Activatedcarbon,Adsorbent,Automobileservice station,Batch,Humanhair,OilandGrease,Regeneration.
1.INTRODUCTION
Manypeoplegettheirhaircutdailyacrosstheworld,large quantitiesofhumanhairwastebeingproducedinsaloons. Thehairwasteisdisposedofatlandfillsorincinerated,with negativeeffectsontheenvironment.Incineratinghairleads to air pollution as hair has high composition of Nitrogen, SulphurandotherinorganicelementsBurningofhairleadsto thereleaseofNitrogenintheformofnitrousoxide(N2O), Sulphur in the form sulphur dioxide (SO2), and carbon dioxide(CO2),intotheatmosphere.
Water scarcity will be a key issue for the sustainable development of a country in future. Now India is facing a water crisis and coming years it is estimated that India's population will be affected adversely by severe water scarcity.Largequantityofwateriswastedinservicestations during the washing of vehicles. We have to consider the possibilitiestorecycleorreuseofthewastewatergenerated
fromautomobileservicestations.Automobileservicestations varyfromauthorizedservicecenterstosmallscaleservice stations, which under taker pair, washing and servicingof vehicles.Thespeedygrowthofcarwashservicecentrehas seriouslyincreasedthecontributionofpollutionintobodies ofwater.Theservicestationwastewaterrepresentsoneof theheavilycontaminatedwasteswithhighimpurities.Itwas due to presence of sand and particles, oil and grease, surfactants, detergent, phosphates and hydrofluoric acid. Therefore, the direct disposal for waste water in to the drainageexacerbatesthenaturalwaterpollution.
Industrial growth has accelerated the emission of variousoilywastefromthesourcessuchaspectrochemical industries,metallurgicalindustries,automobiles&domestic sewage.Theseoilywastesareoneofthemajorpollutantof the aquatic environment. Oil water separation processes using polymeric or inorganic membranes have been proposed as effective & cost competitive alternative to conventional oil removal technologies but in present the commercial use of membrane in waste water treatment is currentlylimitedbytheirlowefficiencyaswellashighcapital &operatingcost[1].
Hair is found to be a good adsorbent for oil. Oil pollution is the emerging threat to the environment. Thus utilizationofwastehairinoilremovalwillleadstoreducethe wasteaccumulatedinenvironment.Themainoil pollution threat rising from land based activities is due to service station and workshop wastewater. Two major sources of such oils are auto motive crank case oil and used oil from smallgaragesandworkshops.Thisgiveshighcontributionto theoilpollutionmainlytechnologicallybackwardcountries, duetolowefficiencyofequipmentsandmachines[9].
2. MATERIALS AND METHODOLOGY
2.1 Adsorbent Used
The materials that are required for the adsorption and regeneration process are activated carbon, human hair as wellasthoseusedforthefiltermediahastobecollected.The humanhairiscollectedfromsaloonsandactivatedcarbonis purchased online and the hibiscus leafs (regenerant) collectedfromnearbyareasofcollege.
2.2 Adsorbent Preparation
Hairofdifferentageswascollectedfromabarbershopand saloonsinulliyeriandproperlyseparatedbycombing.The properlyseparatedhumanhairsweresoakedinhotwaterin one hour using detergent to ensure it is free from contamination.Then,theywererinsedwithhotwaterand dried under natural sunlight for 48hrs after it is kept in a glasscontainer.
Activated carbon is purchased online. Activated carbon is widelyusedasaadsorbentinwatertreatmentplants.Itis also widely available in developing countries, usually in granular size and generally called carbon. There are numerouswaystousecarbonasanadsorbent,includingto crusheditintoapowderbeforeaddingittowater,stirring anddecantinginthewaterforafewsecondsandwaitingfor thesolidstosettle.

2.3 Sample Collection
The selected site is the service station near Ulliyeri, Kozhikode which is easily accessible after the comparison withotherservicestationsinthenearbyareas,thisservice stationisselectedforstudy.Themajorworksthatarecarried out in the service are the repair and washing of vehicles, mainlyheavyvehiclessuchaslorries.Thesampleiscollected fromthewastewaterpitintheautomobileservicestation. Thewastewatercomingfromtheservicestationisofvarying concentrationoftheparameters.Acleanplasticcontaineris usedforsamplingandthesampleishandledcarefully,sothat thecharacteristicdoesnotchangeduringtheduecourseof storage.
2.4 Batch Study
To study the effect of various controlling parameters like adsorbentdosage,contacttime,temperature,pHontheoil and grease removal capacity of human hair and activated carbon. The batch experiments were conducted using a samplevolumeof250mlforeach.Theadsorbentdosageis takenas4g/l,8g/l,12g/l,16g/l,20g/l,24g/l,28g/l,32g/l and40g/landthecontacttimeof5minutes,10minutes,20 minutes,30minutes,40minutes,50minutes,60minutes,70 minutes,80minutesand100minutesandthreedifferentpH of 4.3, 7.5 and 10.48 and 21℃, 27℃, 32℃ and 45℃ are consideredasthetemperaturesforthis batchexperiment.
2.5 Column Study
Thecolumnexperimentforremovalofoilandgreasefrom the service centre waste water by human hair was performedusing5.5cmdiameterand35cmlengthcolumn, anditisattachedaflowcontrolvalveforadjustingtheflow through the column. The adsorbent is placed between the layers of pebbles to prevent the loss of adsorbents in the column. In column study two types of adsorbent beds are prepared,onewhichcontainedonlyhumanhairandother
onecontainedthecombinationmixtureofactivatedcarbon andhumanhair.Thedepthofadsorbentsisconsideredas7.5 cmand10.5cmandtwodifferentflowrateof10ml/min/cm2 and 15 ml/min/cm2 .The waste water is allowed to pass throughtheadsorbentsinthecolumnandthesamplewere collectedinfourdifferenttimes45minutes,50minutes,60 minutesand75minutes.
2.6 Regeneration Study
Theenvironmentalaspects,humanhairnegativelyaffectthe environment because it contains different types of compounds so regeneration of adsorbent is important, we need to regenerate the adsorptioncapacity ofhumanhair. Moreover,disposingofoiladsorbedhairismoredangerous totheenvironmentthattheoriginalhairoroilbeingthrown intheopen.Hereweareusinghibiscusleafjuice(Thaali)for regeneration.Thissolutionpassedthroughthecolumninthe saturationpointtofindtheremovalofoilfromtheadsorbent bed.
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
3.1 Batch Study
In the batch study adsorbent dosage, contact time, temperatureandpHaretheparametersmainlyconsidered. The detailed results of parameters are included in the followingsections.
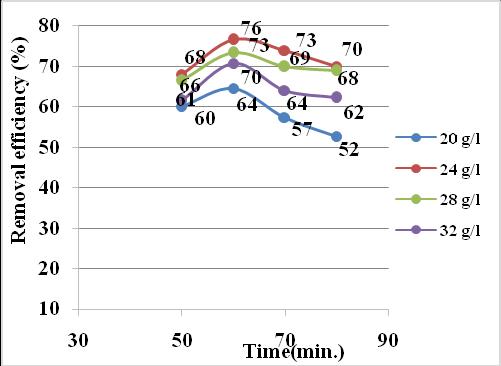
(i)Effectofadsorbentdosageandcontacttimeonhuman hair
Thestudyoftheeffectofadsorbentdosageontheremovalof oilandgreasewascarriedoutwiththedosageof4g/l,8g/l, 12g/l,16g/l,20g/l,24g/l,28g/l,32g/land40g/landthe contact time of 5 minutes, 10 minutes, 20 minutes, 30 minutes,40minutes,50minutes,60minutes,70minutes,80 minutesand100minutes.Thetable4.1showstheamountof adsorbedoil(ml/l)inthehumanhairadsorbentwithvarying adsorbentdosageandcontacttime.
Initiallythereisanincreaseinremovalefficiencyfrom20g/l to24g/lofadsorbentdosageat50minutesto60minutesof contacttime.After24g/lofadsorbentdosagetheefficiency willstartstodecline.Themaximumremovalefficiencyofoil (76%)obtainedat24g/lofadsorbentdosageat60minutes ofcontacttime.Soitwillbetakenastheoptimumpointin batch by using human hair as the adsorbent. From the analysisitisclearthat24g/lofhumanhairastheadsorbent showsbetterremovalthantheotherdosage.
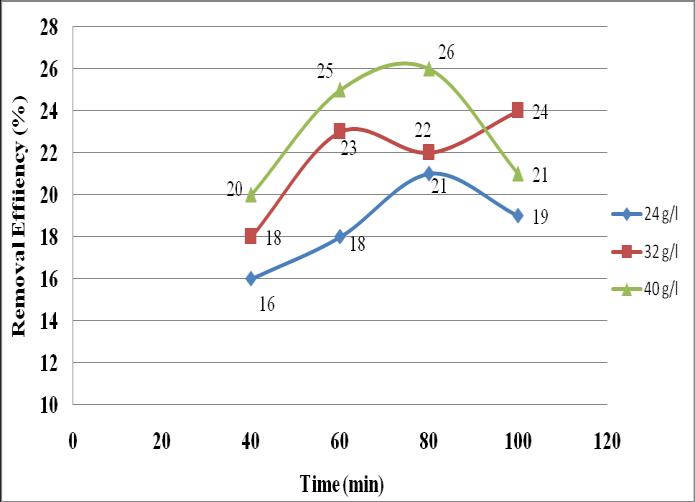
(ii)Effect of adsorbent dosage and contact time on Activated Carbon

Fig -3 EffectofTemperatureonOilRemovalbyUsing HumanHairasAdsorbent
Themaximumremoval80%obtainedat21℃andminimum removal of oil 69% in 45℃. As temperature increases the removalefficiencyofoilfromservicecenterwastewaterby usinghumanhairwasdecreases.
(iv)Effect of pH
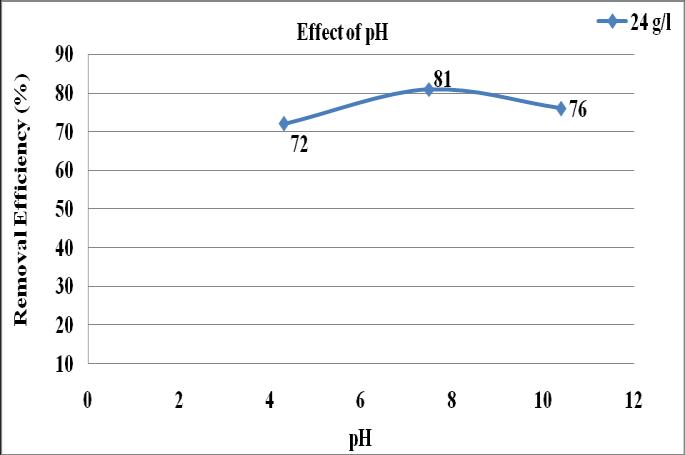
Fig-2 EffectofAdsorbentDosageandContactTimeonOil RemovalbyActivatedCarbon
From this study we can see that the removal efficiency of activated carbon increases by increasing the adsorbentdosage.The50%ofremovalefficiencyisobtained atthedosageof36g/lofactivatedcarbonin80minutessoit can be taken as the optimum value. Gradual increase in adsorptionobtainedinitiallyafterthatremovalefficiencyis decreasesto42percentageat80minutescontacttime.
(iii)Effect of Temperature
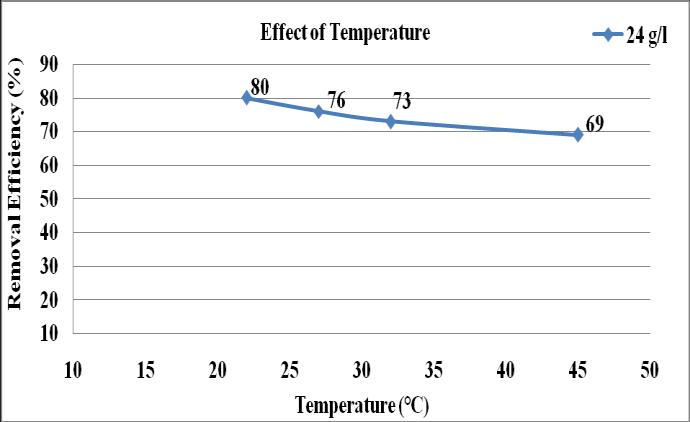
Thestudyoftheeffectoftemperatureontheremovalofoil andgreasewascarriedoutbyfourvaryingtemperature21℃, 27℃, 32℃ and 45℃ keeping the adsorbent dosage as 24 g/ml,contacttimeof60minutesandinitialoilconcentration of52.18mlin250mlofwastewater.
ThestudyoftheeffectofpHontheremovalofoilandgrease was carried out by three different pH of 4.3, 7.5 and 10.4 keepingtheadsorbentdosageas24g/ml,contacttimeof60 minutesandinitialconcentrationofoil52.18mlin250mlof wastewater.
Fig-4showstheeffectofpHontheremovalefficiencyofoil and grease by using human hair. In this experiment three different pH of 4.3,7.5and10.48samples areused. AspH increasesadsorptioncapacityofhairwasincreasestillthepH was7.5,Thenitwasdecreasesto76%atpHof10.48. The gradualdecreaseinremovalefficiencyofoillevelisobserved afterpHof7.5.The72%ofoilremovalobtainedatpHof4.5 keepingadsorbentdosageas6g/mlandcontacttimeof60 minutes.
3.2 Column Study
Fromthebatchstudywenotedthathumanhairshowsbetter performancethanactivatedcarbonandforaninitialoiland greasecontentof200ml/lfor60minutesatanadsorbent dosage of 24 g/l. In the column study we are mainly consideringtheparameterssuchasdepthofadsorbentbed andtheflowrate.
(i)Effect of Adsorbent Bed Depth
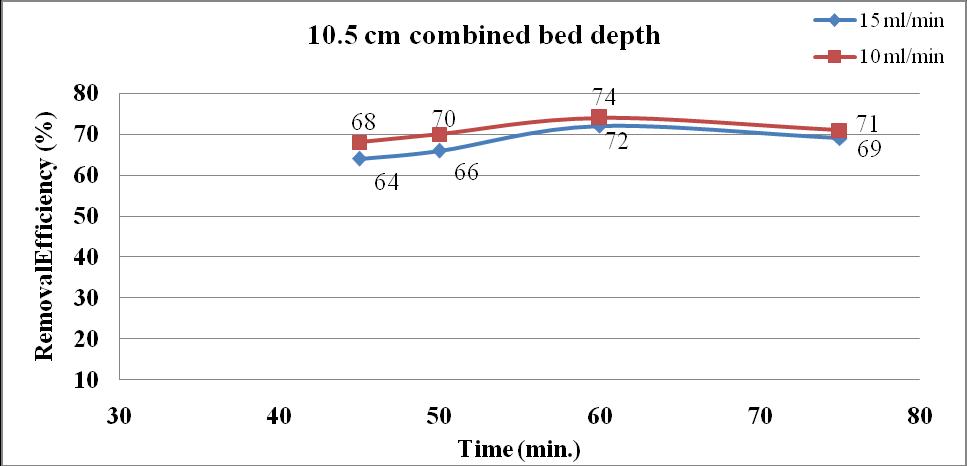
Forthissetofexperimentthebeddepthistakenas7.5cm and 10.5 cm and 200 mg/l of oily waste water is passed throughthecolumn.Samplesarecollectedatanintervalof45 minutes,50minutes,60minutesand75minuteswithrateof flows15ml/minand10ml/min.Thecombinationmixtureof humanhairandactivatedcarbonbeddepthof10.5cmgives the highest removal efficiency 74 % at rate of flow 10 ml/min.Atarateofflow15ml/min.shows72%removalof oil.Thehumanhairbeddepthof10.5cmgives71%removal of oil and 70 % removal obtained in 7.5 cm bed depth respectively.Fromthisstudywecananalysesthatremovalof oilfromwastewaterusingacombinationofbothadsorbents. Theremovalofoilincreasesbyincreasinginbeddepth.
(ii)Effect of Flow Rate

In the column study 15 ml/min/cm2 and 10 ml/min/cm2 dischargeisconsidered.The10ml/min/cm2flowrateshows betterremovalinalladsorbentbeddepthconsidered.In15 ml/min/cm2showslessremoval,whichisduetothetimeof holdingthewaterintheadsorbentislessinhigherflowrate andwhichishigherinlowflowrate.For10ml/min/cm2the removal of oil is 56.17 mg/l. The maximum removal of oil obtained at 10 ml/min/cm2 of discharge in 10.5cm of combination of two adsorbents bed depth and minimum removal obtainedin15ml/min/cm2 offlowratein7.5cm humanhairadsorbentbeddepth.In15ml/min/cm2flowrate finaloilcontentis52.48mg/lat60minutes.Thatisflowrate increasestheadsorptiondecreases.
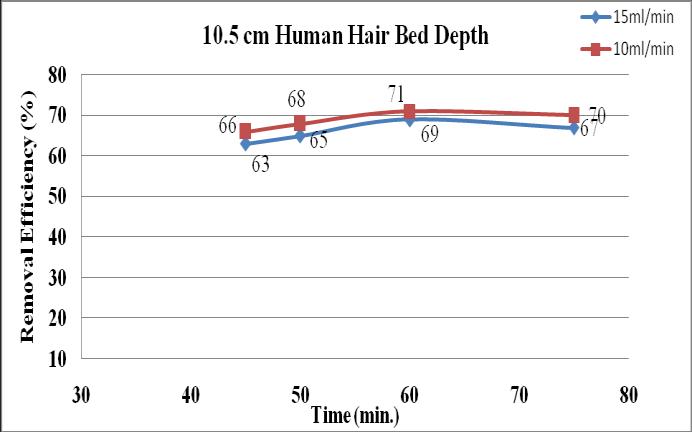
Figure-5showsthemaximumremovalof71%getsin10.5 cm adsorbent bed depthat10 ml/min/cm2 flow rate. The minimum removal efficiency (69%) of oil at 10.5 cm bed depth in 15 ml/min/cm2 flow rate. In the case of 10 ml/min/cm2 flowrateinitialremovalefficiencyis66%at45 minutes of contact time and it gradually increase till 60 minutes.After60minutesofcontacttimeefficiencydeclined into70%andfor15ml/min/cm2rateofflowinitiallyithave 63%removalefficiencyandstartstoincreasetill60minutes and declined to 67 % at 75 minutes contact time. So we concludedthat10.5cmhumanhairbeddepthcanremove maximumamount(71%)oilfromwastewater.
Fromthefigure4.10themaximumremovalefficiency74%is obtainedin10.5cmcombinationmixtureofhumanhairand activatedcarbonbeddepthat10ml/min/cm2flowrate.At15 ml/min/cm2 flow ratein the 10.5cmcombined beddepth shows72%removalefficiency.Inthisweconcludedthatthe combinationoftwoadsorbentsinthecolumnbeddepthcan increasetheremovalofoilfromthewastewateritisof74%. While comparing the above graphs we can find that the removalefficiencygraduallyincreasestill60minutescontact timeafterthatremovalefficiencywilldecreases.Wecansee thatsaturationpointobtainedin60minutesafterefficiency willdecreases,thismayduetothelackofactiveadsorption siteintheadsorbents.
3.3 Regeneration Study
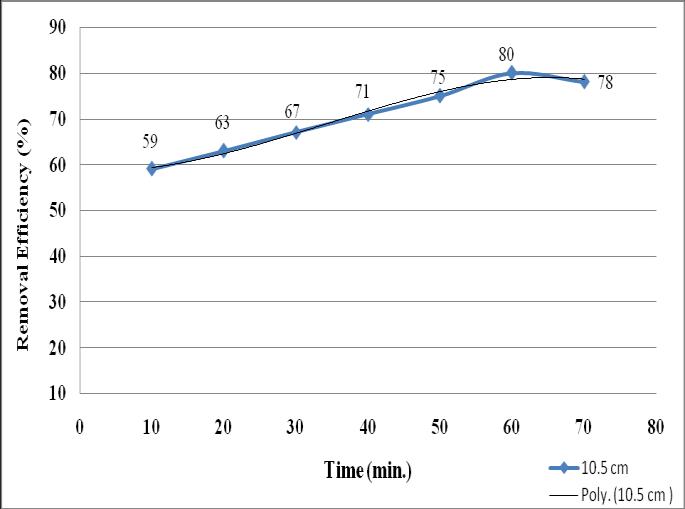
Regenerationstudyoftheadsorbentisstudiedbecauseafter certainperiodtheadsorbentisdesorbedofthematterthatit adsorbed.Inthiscasehumanhairislikelytoproducetoxic elements when improper treatment is provided. So reusabilityofhumanhairisimportantandweneedtocheck the possibility of regeneration of the adsorbent. Hibiscus leavesaretraditionallyusedtoremoveoilfromhair,whichis takenasanideaforitsuseinthecase.200mlofhibiscusleaf juiceispassedthroughthe10.5cmhumanhairadsorbent bedcolumnandget80%removalat60minutes.
Fig - 7 RegenerationStudyofOilfromHumanHair
In the above graph, initially a gradual increase in removal efficiencyofoilfrom10minutesto60minutes.In10minutes theremovalefficiencyis59%anditisincreasesto63%at20 minutes.In30minutestheremovalefficiencyagainincreases to 67% and at 40 minutes it will be 71%. In 60 minutes maximumregenerationisoccurs,80%oilcandesorbedfrom humanhair.After60minutesefficiencyreducedto78%this mayduetotheunavailabilityofadsorptionsitethatcausethe reductionofadsorptioncapacityoftheregenerant.Fromthe results of regeneration study we can analyse that hibiscus leafjuice(Thaali)usedtoregeneratethehumanhairanditis economicalandeco-friendlyregenerant.
4. CONCLUSIONS
The auto mobile service station waste water is mainly characterizedbyhighamountsofoilandgrease,highCOD andhighamountsofdissolvedsolidsetc.Thehumanhairand activatedcarbonasabioadsorbentsareusedtheremovalof oil and grease from the automobile service station waste water,astheyarecommonlyavailablematerials,inexpensive andlesstoxic.
In this study batch study and column study are conducted.Inbatchstudy,thefourparametersconsidered are Adsorbent dosage, Contact time, Temperature andpH. Theadsorbentdosageis4g/l,8g/l,12g/l,16g/l,20g/l,24 g/l,28g/l,32g/land36g/l.Thecontacttime5minutes,10 minutes,20minutes,30minutes,40minutes,50minutes,60 minutes, 70 minutes, 80 minutes ,100 minutes and three differenttemperatureandpHalsoconsidered.Afterthebatch experimentswiththisparameter,weobtainedhighremoval efficiencyofoilandgreaseforadsorbentdosage24g/lat60 minutescontacttimebyusinghumanhairastheadsorbent. The optimum oil and grease removal of 76% obtained at temperatureof27℃andpHof10.48byusinghumanhair keepingadsorbentdosageas24g/l.Themaximumremoval efficiencyof81%obtainedatpHof7.5and80%removalat temperatureof 21℃. The 50% removal of oil obtainedby using activated carbon as adsorbent keeping adsorbent

dosage as 36 g/l at time of contact 80 minutes. From the comparison of adsorption capacity of the two adsorbents usedwecanseethathumanhairismoreefficientthanthe activatedcarbon.
Onthebasisofbatchstudyresultcolumnstudyis conductedusing5.5cmdiameterand35cmheightcolumn, consideringtwotypesofadsorbentbeddepthof7.5cmand 10.5 cm and two rate of flow 10 ml/min/cm2 and 15 ml/min/cm2. From this experiment we can find that maximumremovalof74%obtainedin10.5cmcombination mixtureofhumanhairandactivatedcarbonbeddepthata flow rate of 10 ml/min/cm2. In this 10.5 cm bed made by equal amount of 15 grams of human hair and activated carboninthecolumn.Theremovalefficiency71%obtained at10.5cmbeddepthofhumanhairin10ml/min/cm2flow rate. In column study shows the maximum removal of oil fromthewastewaterobtainedinthecombinationmixtureof human hairandactivatedcarbon bed depth10.5cmat10 ml/min/cm2rateofflowthanthehumanhairbeddepth10.5 cmat10ml/min/cm2 rateofflow.
Fromtheregenerationstudyusinghibiscusleafjuice (Thaali),wefindoutthat80%ofoilcanremovedfromthe humanhairadsorbent,sothisadsorbentcanreused.Thereis a gradual increase in removal till 60 minutes after that efficiencywillreducedinto78%atatimeof70minutes.The adsorptionofoilonhumanhairisasurfacephenomenonand it shows the regeneration property by using hibiscus leaf juice (Thaali) also used adsorbents and regenerant are inexpensiveandeco-friendly.
FUTURE SCOPE
Regeneration of hair after adsorption of oil and grease is important in making use of the material for further adsorptionandsafedisposalofhair.Adsorptionisasurface phenomenonwheretheadsorbateremainonthesurfaceof absorbent.Theadsorbatecanbeseparatedfromthesurface of the adsorbent by applying an external force on the adsorbent surface. The use of natural materials such as hibiscusleafjuicewillmakeiteco-friendly.Butthequantity ofthismaterialandwaterforregenerationrequirestoFor thissetofexperimentthebeddepthistakenas7.5cmand 10.5cmand200mg/lofoilywastewaterispassedthrough the column. Samples are collected at an interval of 45 minutes,50minutes,60minutesand75minuteswithrateof flows15ml/minand10ml/min.Thecombinationmixtureof humanhairandactivatedcarbonbeddepthof10.5cmgives the highest removal efficiency 74 % at rate of flow 10 ml/min.Atarateofflow15ml/min.shows72%removalof oil.Thehumanhairbeddepthof10.5cmgives71%removal of oil and 70 % removal obtained in 7.5 cm bed depth respectively.Fromthisstudywecananalysesthatremovalof oilfromwastewaterusingacombinationofbothadsorbents. Theremovalofoilincreasesbyincreasinginbeddepth.
REFERENCES
[1] A S Jadhav, M Y Nani wadekar, NH Shinde,S V Aneka (2018) ‘Study Of Adsorption Of Oil From Oily Water UsingHumanHair’Vol3,27-31.
[2] Aleeya NatashaRamli1 and Rozidaini MohdGhazi1., (2020)RemovalofOilandGreaseinWastewaterusing Palm Kernel Shell Activated Carbon. International Conference on Tropical Resources and Sustainable Sciences.
[3] A. K. Balaji, H. Amarnath, A. L. Bala subramaniyan. (2018)RemovalofOilandGreasefromWastewaterby usingNaturalAdsorbent. International Journal of Applied Engineering Research. ISSN 0973-4562 Volume 13, Number10pp.7246-7248.

[4] Ankush Gupta. (2017).’Human Hair ‘‘Waste’’ and Its Utilization:GapsandPossibilities‘National Institute of Science, Technology, and Development Studies, Vol 1, pp818.
[5] Nitin W. Ingole, Sanju S. Vinchurkar, Sachin V. Dharpal (2015).’AdsorptionofOilfromWasteWater byUsingHumanHair’ Journal of Environmental Science, Computer Science and Engineering & Technology, Vol 3,pp207-217.
[6] Mueller, S. A., Kim, B. R., Anderson, J. E., Gaslightwala, A. and Szafranski, M. J (2003),Removal of oil and grease and Chemical Oxygen Demand from oily Automotive waste water by adsorption after chemical de-emulsification, Practiceperiodical of hazardous and radio active waste management,3,156162
[7] Mazumder, D. and Mukherjee, S (2011),Treatmentof AutomobileservicestationwastewaterbyCoagulation and Activated sludge process, International Journal of Environmental Science and Development,2,1,64–69
[8] Peter R.U., Ikwut, Akpevwe K. I., Christopher T. I., AbiyeAseminasoandTamunotonjoObomanu (2018) –FederalPolytechnicofOilandGas,Bonny,RiversState, Nigeri. International Journal of Scientific & Engineering Research,Volume7,Issue8,ISSN2229-5518.
[9] S.S. Krishnan, A. Cancilla and R.E. Jervis (2018).’ Waste Water Treatment For Heavy Metal Toxins Using Plant And Hair As Adsorbents‘ Vol 4,pp 267-276.
[10] IS 3025 – 39 (1991) : Methods of sampling and test (physicalandchemical)forwaterandwastewater,part 39:oilandgrease[CHD32:EnvironmentalProtection andWasteManagement]
