QUICK GLANCE: UNSUPERVISED EXTRACTIVE SUMMARIZATION MODEL
L.Sumathi 1 , A.Selvapriya 2Abstract - It is an era of fast movement, where people wants to know the essence of any document (technical or nontechnical) at the first glance in a fast manner. This motivates for the proposed GUI based unsupervised extractive summarization model Quick Glance, which summarizes the user input. The proposed approach uses BERT based pretrained sentence embedding vectors and attention model to derive attention score for each sentence present in the user input. Next, Principal component analysis is applied on the attention scores to automatically to evaluate the importance of each sentence and to determine the number of sentences to be extracted Experimental results show that the proposed model is user friendly and exhibits acceptable performance and is highly recommendable for non – criticalapplicationlike review, news glance and so on.
Key Words: Text Summarizer, BERT, PCA ,Extractive Summarization, Linear Programming
1. INTRODUCTION
In the modern era, where a vast amount of information is accessibleonline,itiscrucialtoofferanenhancedsystemfor swiftlyandeffectivelyextractingtheinformation.Itisquite challenging for humans to manually extract the summary from a lengthy written document. Finding appropriate documents from the many documents accessible and learning essential information from them presents a challenge.Automatictextsummaryiscrucialforresolving theaforementionedtwoissues.
Thetechniqueofextractingthemostsignificantinformation fromadocumentorgroupofrelatedtextsandcondensingit intoaconciseversionwhilemaintainingitsoverallmeanings is known as text summarizing. a briefer version of the information in the original text. Automatic text summary aimstodeliverthesourcetextinaconcise,semantically-rich form. The main benefit of adopting a summary is that it shortensthereadingprocess.
Choosingtoreadanarticlemainlydependsonthesizeofit andthetimetobespentonreadingit.Ifthearticlecontains lesscriticalinformationandcontainslargeamountoftextual data, people tend to skip it due to its less important informationandlargeamountoftimerequiredtoconsume it. Here, the articles with less critical information contain repetitivecontents,whichcouldbeshrunken.Butitrequires deep understanding of the semantics present in the documentinordertoextractthemostinformativepieceof
datawhichcanreducethetimethatbeingspentonreading an article. So that many different information can be acknowledged on the time that being spent on reading a singlearticle.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY
McDonald et.al [2] proposed the first ILP method for extractive summarization. It generates summaries by maximizing relevance (i.e., importance) of the selected sentences and minimizing their redundancy (i.e., similarity).McDonald et.al [2]representedeachsentenceasa bag-of-words vector with TF-IDF values. The importance scoresarecomputedbyusingthepositionalinformationof the sentences and the similarity between each sentence vectorandthedocumentvector.Thecosinesimilarityisused tocomputethesimilaritybetweensentencevectors.
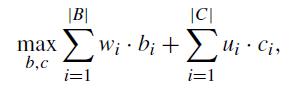

Berg-Kirkpatricket.al[3]constructed an ILP summarizationmodelbasedonthenotionof concept,which is a set of bi-grams. The distinctive characteristic of this model is that it extracts, and compresses sentences simultaneously. The model not only selects bi-grams with high importance but also chooses whether to cut (delete) individualsubtreesfromeachsentence'sparsingtree.The objectivefunctionofthismodelisthefollowing:
where bi and ciare binary variables that indicate the selection of the ithbi-gram as a summary and its deletion from the parsing tree. wiand uiindicate the weights of bigramsandpossiblesubtreecuts,respectively.Additionally, the model hasa constraintof maximumallowedsummary length, which is determined by the user. The weights are estimated by soft margin support vector machine optimizationwithbi-gramrecalllossfunction.Therefore,the model is trained in a supervised manner, which requires gold-standardsummaries.
Galanis [4] also presented a supervised extractive summarizationmodelthatextractssentencesandconcepts by maximizing sentence importance and diversity (i.e., minimizing redundancy). To represent sentences in a structured form, they leveraged various features, such as sentence position, named entities, word overlap, content wordfrequency,anddocumentfrequency.Themodelhasa
constraint of user-defined maximum summary length. Furthermore,supportvectorregression(SVR)wasusedto estimatesentenceimportance.
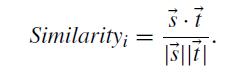
Boudin[5]proposed a purely concept-based extractive summarizationmodel.Theobjectivefunctionofthismodelis thefollowing:
where λ1, λ2, λ3, and λ4 are user-defined hyperparameters.Liuet.al[6]generatedasummarybyselecting sentenceswiththehighestscoreuntilthetotalsummarydid notexceedtheuser-definedsummarylength.
3. PROPOSED MODEL
where wiistheweightofaconcept, fkisthefrequencyof the non-stop word k in the document set, ciis a binary variableindicatingwhethertheconcept iisselected,and tkisa binaryvariableindicatingthepresenceofthenon-stopword k inthesummary.Thisvariablewasintroducedbecausethe frequencyofanon-stopwordisagoodpredictorofaword appearanceinahuman-generatedsummary.Toobtainthe concept weight, heuristic counting (such as the document frequency of each concept) was used, or the supervised model was trained. The model also hasa user-determined maximumsummarylength.Itdiffersfromothersbyapplied sentencepruning.Sentenceswithfewerthan10wordswere removedtoimprovecomputationalefficiency.
Liu[6]proposedasimpleweighting-basedunsupervised extractivesummarizationmethod.Forthe i-thsentenceina document(Si),theycalculatedsentencescoresbyleveraging term frequency, similarity, positional information, and sentencelength.Inparticular,termfrequency,positionscore, andsentencelengthscorearecalculatedasfollows:
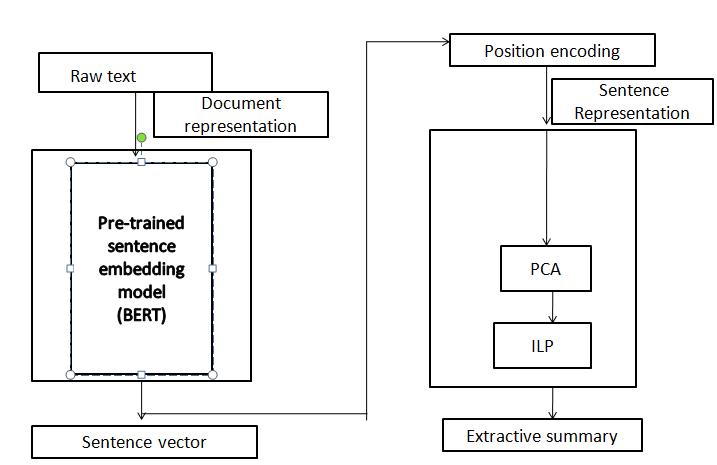
ProposedQuickGlancearchitecturedepictedinfigure1 usesJanget.al[1]two-stepprocedurefortextsummarization .It involves document representation and representative sentence selection. Document can be represented as a continuous sentence vector, with the usage of pre-trained BidirectionalEncodingRepresentationsfromTransformers (BERT)[8]model.Importanceofthesentenceisdetermined usingILPandPCAtopickrepresentativesentencesforthe summary.
where tf(w)denotesthetermfrequencyoftheword w, n represents the total number of sentences, pi refers to the position of Si, xiis the length of Si, and µ and σ denote the mean and standard deviation of the total sentence length, respectively.ForagivensentencevectorEs andtitlevector Et,similarityscoreisdefinedasthecosinesimilarityoftwo vectors:
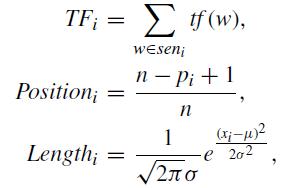

Figure 1 : Proposed System Architecture
The input document, undergoes a pre-processing step which involves tokenizing the white space, a lower-case conversion,removingthepunctuations,numbersandempty stringsfromeachtoken.
Since,thedocumentconsistsofnsentenceshaving thesequentialinformation,representingthedocumentasa sequenceofsentencesasfollows:
D=[s1,s2,...,sn]
whereDdenotesthedocumentandsk referstoitsk-th sentence.Letasentenceberepresentedasacolumnvector. Thus, Dbasic, the basic representation of D, becomes the followingmatrix:
The vectors of each sentence and article title are built basedonthetermfrequencyweightingschema.Therefore, thefinalsentencescoreiscalculatedasfollows:
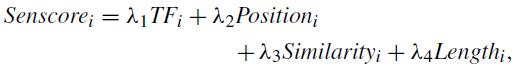
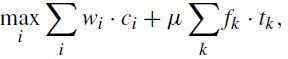
Dbasic =[sv1,sv2,...,svn]
wheresvk denotesthepre-trainedsentencevectorofsk .Dbasicisad×nmatrix,wheredistheembeddingdimension. Itispossibletouseanysortofsentenceembeddingmethod
to generatesvk. Here, the pre-trained sentence embedding modelBERT(BidirectionalEncodingRepresentationsfrom Transformers)asproposedbyDevlinet.al[8]isused,sinceit hasagoodmemorytoknowthepositionalsequence.Ithas pre-definedvectorsforeachwordinasentence.Italsohas the vector for sub-word if the word doesn’t exists. BERT generatescontextualizedrepresentsofsentenceasaT×dh matrix, where T is the number of tokens and dh is the dimension of the hidden states. As the representation of a sentence should be a vector, the average of the BERT representationsisconsideredtoobtainthedimensiondh
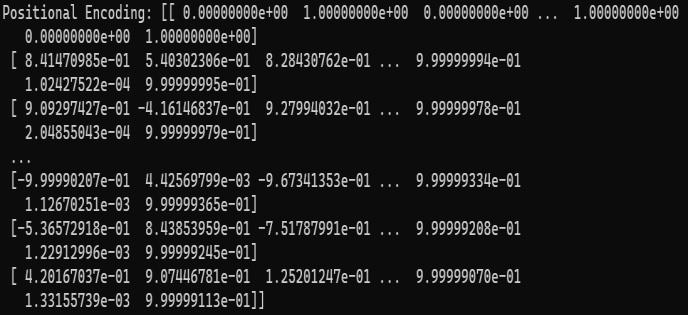
Although the matrix Dbasiccontains the intrinsic meaning of each sentence, it lacks positional information, which plays a critical role in natural language tasks. Therefore,positionalencodingisusedtoeffectivelyreflect sequential information, which employs cosine and sine functions.Inparticular,thepositionalencodingmatrixPEis calculatedasfollows:
PE(pos,2i) =sin(pos/100002i/d )
PE(pos,2i+1) =cos(pos/100002i/d )
whereposistheposition,andiisthedimension.Then,the final input embedding matrix Demb is calculated as the additionofDbasic andPE.
Demb =Dbasic +PE
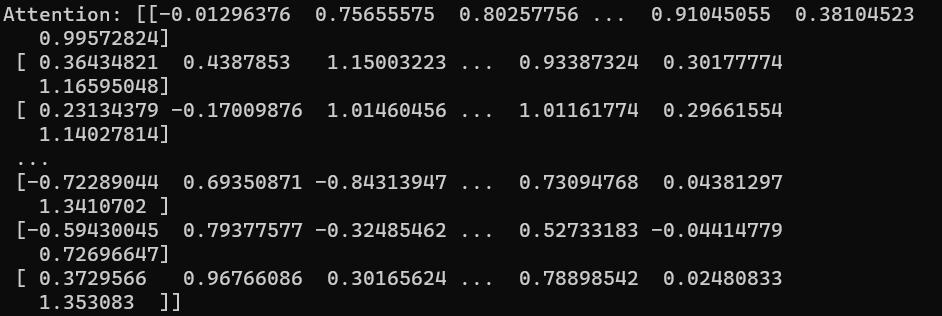
Toobtainadeeperrepresentationofthedocument, scaleddotproductattentionasproposedbyVaswaniet.al[7] is used , wherein the attention weights can be calculated withouttrainingparameters.Thematrix Q isregardedasa setofqueries.Likewise,thematrices K and V arethesetsof keysandvalues,respectively.Then,theresultofthescaled dotproductattentionisasfollows:
Attention(Q,K,V)= softmax(Q.KT /√dk )V wheredk isthedimensionofqueriesandkeys.
DeeprepresentationDdeepofthedocumentiscalculatedas
Ddeep =Attention(Demb,Demb,Demb)
whereDdeep hasdimensiond×n,thesamedimensionas thatofDemb.Therefore,thematrixDdeepcanbeconsideredthe sequenceofthedeeprepresentationvectorsofthesentences constitutingthedocument.
Ddeep =[svdeep,1,svdeep,2,..,svdeep,n]
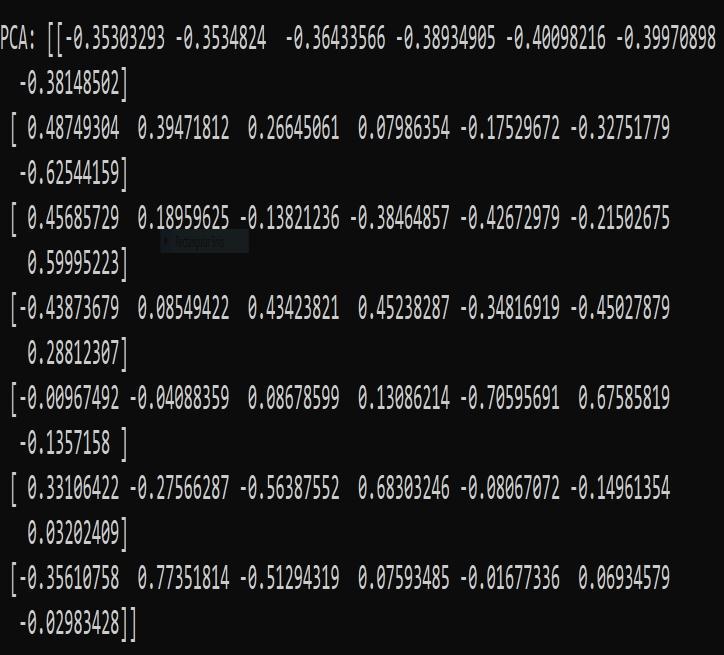
The proposed QUICK GLANCE automatically determinesthenumberofappropriatesummarysentences foreachdocumentbyPCA,andthustheimportanceofeach sentencecanbequantitativelyevaluated.PCAisamethodfor reducing high-dimensional data to lower dimensions. The principalcomponents(PCs)extractedbyPCAarecomposed
ofalinearcombinationoftheoriginalvariables.Hence,PCA hasbeenwidelyusedfordimensionalityreductionbecauseit ispossibletoexplaintheentiredatasetthroughafewPCs. ThepurposeofPCAistomaximizethevarianceofy=Xw, whichistheprojectionoftheoriginaldataX,whereXisann ×pmatrixandwisavectorofsizep×1.nisthenumberof observationsandpisthenumberofvariables.Foracentered datasetX,PCAisperformedbythefollowingoptimization:
MaxVar(Y)=wT∑w
s.t||w||=1
where∑isthecovariancematrixofX.Solvingtheabove equation for w yields the eigenvectors e of the covariance matrix.Therefore,whenthei-thlargesteigenvalueλi andits corresponding eigenvector ei are given, the i-th PC is calculatedasfollows:
yi =ei1X1 +ei2X2 +...+eipXp
Furthermore,bythefollowingequation,thevarianceofyi isλi
Var(yi)=eTi∑ei =λi

Asthetotalpopulationvarianceis∑pi=1λi ,thevariance preservationratioofyi is
αi =λi/∑pi=1λi
where αi is the variance preservation ratio of Yi . This implies that a PC yi preserves (100 × αi)% of the total variance. As Ddeep has sentence vectors as column vectors, each sentence vector is considered as a variable and the dimensionof the vector,d,as the number ofobservations. Therefore, PCA reduces the number of sentences in a document by extracting the PCs. Each PC(i.e.,) principal sentence, could be considered a vector of condensed sentencesthatcontainsasmuchinformationoftheoriginal documentaspossible.Subsequently,auser-definedspecific hyperparameter β - the variance preservation ratio that automatically decide the appropriate number of summary sentencesN.Therefore,itcouldbeconsideredthatatleast β% of the total information is preserved in N selected sentences.Thenthesentenceimportancescoreiscalculated based on the correlation between the sentence vectors of DdeepandthePS’s.AsaPSisahigh-levelvectorthatefficiently condensestheintrinsicinformationofthedocument,greater similarity of a sentence vector to a PS implies higher importanceofthesentence.Therefore,sentenceimportance scoreisdefinedby:
imp(si)=∑ k≠icos(svdeep,i,PSk )
where imp(si) is the sentence importance score of sentencesiandcosdenotescosinesimilarity.
The optimization problem is formulated as in McDonaldet.al[2],becausetheminimumextractionunitisa sentence, not a concept. The requirements for the formulationaresentenceimportancescoresandsimilarity scores between sentences. The similarity between the sentencessi andsj isdefinedasthecosinesimilarityoftheir deepsentencerepresentationvectorsasfollows:
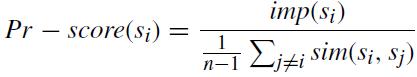
sim(si,sj)=cos(svdeep,i,svdeep,j)
Then,theappropriatenumberofsummarysentences(the length of summary sentences) for each document is automaticallydeterminedthroughPCAasfollows:
∑ni=1 xi =N
where N is the appropriate number of summary sentences.
In order to reduce the time complexity of QUICKGLANCE from O(n2 ), sentence pruning is performed to remove unimportant sentences. The sentences to be extracted are those which should have high sentence importancescoresandlowredundancyscores.Therefore,the pruningscoreofasentencesi isdefinedby
Thegiventextwillbeparagraphsbydefault,soithastobe convertedintosentencesfortextextraction.NLTKisusedfor converting the given text into sentences. Using a split() functionisagoodidea,butwithahugeamountoftextwhich mayincludeseveral quotesandspecialcharacters,it’swill not always provide a good result. So, nltk.load() has been used.
where imp(si) is the sentence importance score of sentencesi,sim(si,sj)isthe similaritybetweenthesentences si,sj

4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSIONS
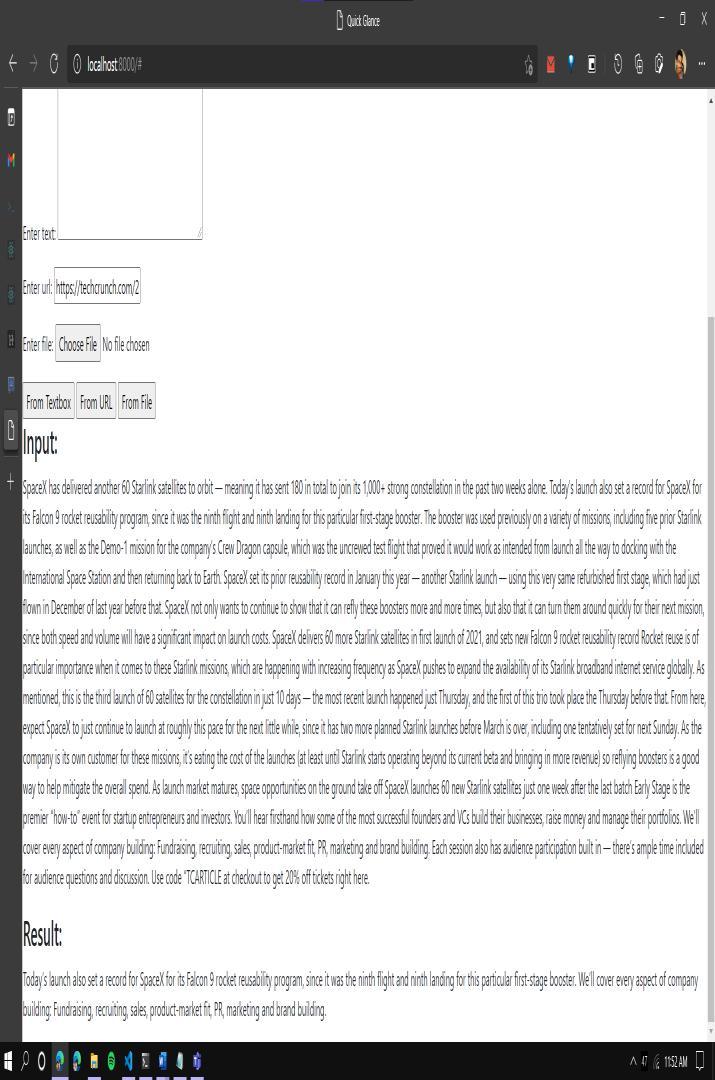
Quick Glance Text summarization application provides Graphical User Interface on the Web using Django Web Framework. Inputfromusercanbe senttotheapplication asshowninFigure2in3differentways.
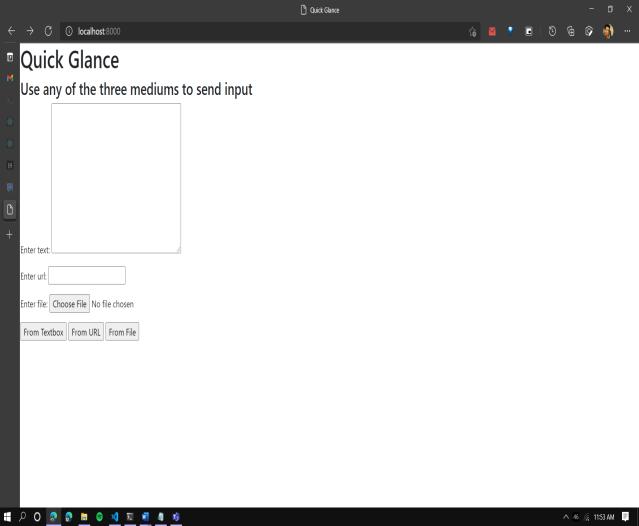
DirecttextusingTextbox
ParsedtextfromanygivenURL

Textualdatafroma.txtfile
Thedatafromthetextboxand.txtfilecanberetrievedusing simpleformsandread()methodfromDjango.Whereasthe parsed text from the URL has to be retrieved using Web scrapingthroughBeautifulSoup.
After the text has been converted to sentences, it must be cleaned.Itincludesremovingthepunctuation,removingthe needlessspaces,convertingalltexttolowercase,removing thenumbertokens.Theprocessedtextwillbeforwardedto furthersteps.ThecleanedtextisshowninFigure3.
Positional encodingisusedtoeffectivelyreflectsequential information.Thepositionalencodingmethodemployscosine andsinefunctionstocalculatethepositionofthewordinthe sentence.Resultofpositionalencodingofgiventextisshown inFigure4
Attention can attend a semantically important concept or regionofinterestandtofindtherelativestrengthofattention paid on multiple concepts. It can switch attention among conceptsdynamicallyaccordingtotaskstatusandimproves the focus on particular sentence. The calculated attention scoreforthegiveninputisshowninFigure5
In ILP, sentence scores and similarity scores between sentencesarecalculatedwhereassentencepruninghelpsto reduceunimportantsentencesandtimecomplexity

The summary of the given document is achieved and is displayedintheGUI’shomepageasshowninFigure7
Methodusedfordimensionalityreductionbecauseitis possible to explain the entire dataset through a few PC’s (Principal Components) and the same has been shown in Figure6
5. CONCLUSION AND FUTURE WORK
A user-friendly text summarizer, the QUICK GLANCE is proposed efficiently by retaining the intrinsic information. ExperimentalresultsrevisedthattheQuickGlanceprovides wellorganizedsummarywithneededinformationfornoncriticalapplicationslikereview,newsglanceetc.,inauserfriendlymanner.
Here,theappropriatenumberofsentencesinthe summary will be decided by PCA using a variance preservation ratio β. In future, PCA can be replaced with LinearDiscriminantAnalysis(LDA),andnon-negativematrix factorization (NMF). As of now, the summarized output is displayedintheGUI’sHomepage.Futureworkscaninclude thattheoutputcanalsobesenttotheuser’svalidmail.Itcan bealsoimplementedasamobileapplicationwhichwillhelp thestudentsforquickgraspingofthecontext.
REFERENCES
[1] Jang, Myeongjun, and Pilsung Kang. "Learning-Free Unsupervised Extractive Summarization Model." IEEE Access9(2021):14358-14368..

[2] McDonald,Ryan."Astudyofglobalinferencealgorithms in multi-document summarization." European ConferenceonInformationRetrieval.Springer,Berlin, Heidelberg,2007..
[3] Berg-Kirkpatrick, Taylor, Dan Gillick, and Dan Klein. "Jointlylearningtoextractandcompress."Proceedings of the 49th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Human Language Technologies.2011.
[4] Galanis, Dimitrios, GerasimosLampouras, and Ion Androutsopoulos. "Extractive multi-document summarization with integer linear programming and support vector regression." Proceedings of COLING 2012.
[5] Boudin, Florian, Hugo Mougard, and Benoit Favre. "Concept-based summarization using integer linear programming: From concept pruning to multiple optimalsolutions."ConferenceonEmpiricalMethodsin NaturalLanguageProcessing(EMNLP)2015.
[6] Liu, Maofu, Limin Wang, and LiqiangNie. "Weiboorientedchinesenewssummarizationviamulti-feature combination."NaturalLanguageProcessingandChinese Computing.Springer,Cham,2015.581-589.
[7] Vaswani,Ashish,etal."Attentionisallyouneed."arXiv preprintarXiv:1706.03762(2017).
[8] Devlin, Jacob, et al. "Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectionaltransformersforlanguageunderstanding." arXivpreprintarXiv:1810.04805(2018).
