Detection of Skin Cancer Based on Skin Lesion Images UsingDeep Learning
Prof. Bharath Bharadwaj B S 1 , Saniya Anjum 2 , Shaguftha Afreen 3 , Spoorthi T C 4,Keerthana M 51 Assistant professor, Dept. of computer Science and Engineering, Maharaja Institute of Technology Thandavapura
2,3,4,5Students , Dept. of Computer Science and Engineering, Maharaja Institute of Technology Thandavapura ***
Abstract - An adding number of inheritable and metabolic anomalies have been determined to lead to cancer, generally fatal.Cancerouscellsmayspreadtoanybodypart,wherethey can be life- changing. Skin cancer is one of the most common types of cancer, and its frequence is adding worldwide. The main subtypes of skin cancer are scaled and rudimentary cell lymphomas, andcarcinoma, whichisclinicallyaggressiveand responsible for utmost deaths. Thus, skin cancer webbing is necessary. One of the stylish styles to directly and fleetly identify skin cancer is using deep literacy (DL). To insure better prognostic and death rates, early skin cancer identification is pivotal, yet solid excrescence discovery generally relies substantially on screening mammography with shy perceptivity, which is also validated by clinical samples. Cancerwebbingand treatmentresponseevaluations aregenerally notapplicableusesforthisapproach. Anadding number of healthcare providers are using artificial intelligence (AI) for medical diagnostics to ameliorate and accelerate the opinion decision- making procedure
1 INTRODUCTION
The willful development of napkins in a specific bodyareaisknownascancer.Themostsnappilyspreading complaintintheworldlookstobeskincancer.Skincanceris a complaint in which abnormal skin cells develop out of control. To determine implicit cancer rapid-fire early discoveryandaccurateopinionareessential.Melanoma,the deadliestformofskincancer,isresponsibleforutmostskin cancer-related deaths in developed countries. The skin cancertypescompriserudimentarycell melanoma,scaled cellmelanoma,Merkelcellcancer,dermatofibroma,vascular lesion,andbenignkeratosis.
1.2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
TheGLOBOCANcheckalsopointsoutthatfurther thanhalfofthecancerdeathsdoinAsiaabout20ofcancer deathsareinEurope.Likewise,theareasmostaffectedby skincancerarearoundtheglobe.NorthAmericareckoned for half of the aggregate. Roughly 9,500 Americans are diagnosedwithskincancereveryday.Thegoodnewsisthat the five-time survival rate is 99 if caught and treated beforehand.
Earlydiscoveryofskincancercanbegetbynastylesionsis pivotalfortreatmentasitwouldincreasethesurvivalrateof
cases. Still, a conventional discovery system similar to ABCDE criteria possesses colorful limitations such as subjectivity and trip, due to the different experience positionsofdermatologistsandthecharacteristicsofnasty skinlesions.Either,thecurrentstate-of-the-artindetecting skin lesions using deep neural networks substantially focuses on the skin lesions. Also, deep literacy model infrastructures similar to ‘Resent’ used to perform these tasks are frequently complex, heavy in size, slow, and delicatetoapply.
1.3 OBJECTIVE
The skin cancer detection project is to develop a frameworktoanalyzeandassesstheriskofmelanomausing dermatological photographs taken with a standard consumer-grade camera. This step can be performed because many features used to the risk of melanoma are derivedbasedonthelesionborder.Ourapproachtofinding the lesion border is texture distinctiveness-based lesion segmentation
1.4 SCOPE
Skin cancer indications can be quickly and easily diagnosedusingcomputer-basedtechniques.Byanalyzing imagesoflesionsontheskin,wedevelopedforquicklyand accuratelydiagnosingbothbenignandmalignantformsof cancer.
2 LITRATURE SURVEY
[1] Title:-Detection of Skin Cancer based on skin lesion images
Authors:-WalaaGouda,NoorZaman
Publication Journal & Year:-IRJET,2022.
Summary:-Byassayingimagesoflesionsonthe skin, we developed a fashion for snappily and directly diagnosingbothbenignandnastyformsofcancer.The suggestedsystemusesimageimprovementapproaches to boost the luminance of the lesion image and reduce noise. Resnet50, InceptionV3, and Begrudge inception werealltrainedontheupperedgeofthepreprocessed lesion medical images to help to over fit, as well as meliorate the overall capabilities of the suggested DL

styles.TheInceptionmodelhadanoveralldelicacyrateo f85.7,whichissimilartothatofeducateddermatologists.
[2] Title:-SkinCancerClassificationUsingImageProcessing andMachineLearning
Authors:-ArslanJavaid,MuhammadSadiq,FarazAkram
Publication Journal & Year:-IJASRT,2021.

Summary:-Inthiswork,anovelmethodofskincancer classification using machine learning and image processing is implemented. In the first step, a novel methodofcontraststretching based on themean and standard deviation of pixels for Dermoscopy image enhancement is proposed. Then OTSU thresholding is performedforsegmentation.
[3] Title:-Detection of Skin Cancer Lesions from Digital ImageswithImageProcessingTechniques
Authors:-Minakshi Waghulde, Shirish Kulkarni, Gargi Phadke
Publication Journal & Year:-IJCDS,2020.
Summary:-Ourresultsareharmoniouswithcurrentart onDNNstransferknowledgeisagoodidea,asisfinetuning. We anticipated that transferring knowledge from a related task (in our case, from Retinopathy, anothermedicaltypetask)wouldleadtobetterresults, especiallyinthedoubletransferscheme.
[4] Title:-Detection and Classification of Skin Cancer by UsingaParallelCNNModel
Authors:-Noortaz Rezaoana, Mohammad Shahadat Hossain,KarlAndersson
Publication Journal & Year:-IEEE,2020.
Summary:-In this work, we propose GAN-based methods to generate realistic synthetic skin lesion images.Malignancymarkersarepresentwithcoherent placement and sharpness which result in visuallyappealingimages.
[5] Title:- SkinCancerClassificationusingDeepLearning andTransferLearning
Authors:- KhalidM.Hosny, MohamedA.Kassem, MohamedM.Foaud
Publication Journal & Year:-IJASRT-2019.
Summary:-wehaveproposedanimprovedU-Netwhichis named as NABLA-N and the model is evaluated for skin cancer segmentation tasks. Three different models are investigatedwithdifferentfeaturefusionbetweenencoding
and decoding units which are evaluated on the ISIC2018 dataset.Thequantitativeandqualitativeresultsdemonstrate betterperformancewiththemodelcomparedtothemodel.
3 EXISTING SYSTEM
SampleSkincancerisontheupswing,thishasbeen true for the last 10 times. Because the skin is the body’s centralpart,it'sreasonabletoassumethatskincanceristhe most frequent complaint in humans. The first step for identifyingwhethertheskinlesionisnastyorbenignfora dermatologististodoskin vivisection.Inskinvivisection, the dermatologist takes some part of the skin lesion and examinesitunderamicroscope.Thecurrentprocesstakes nearly a week or further, starting from getting a dermatologistappointmenttogettingavivisectionreport.At present, to check the skin malice of a case, he needs to witnesssingularwebbingbyadermatologisttofetewhether they'veskincomplaintornot.
4. PROPOSED SYSTEM
There is a need for accurate as well as reliable systemsthatcanhelpnotonlycliniciansbutaswellpersons todescrytypesoflesionsatearlystages.Thisproposedskincancerdiscoverysystemisdevelopedasaclinicaldecision support tool that uses computer vision which can help croakers to diagnose skin cancer types by simply using images with good delicacy. This design aims to dock the current gap to just a couple of days by furnishing the predictivemodelusingComputer-backedopinion(CAD).
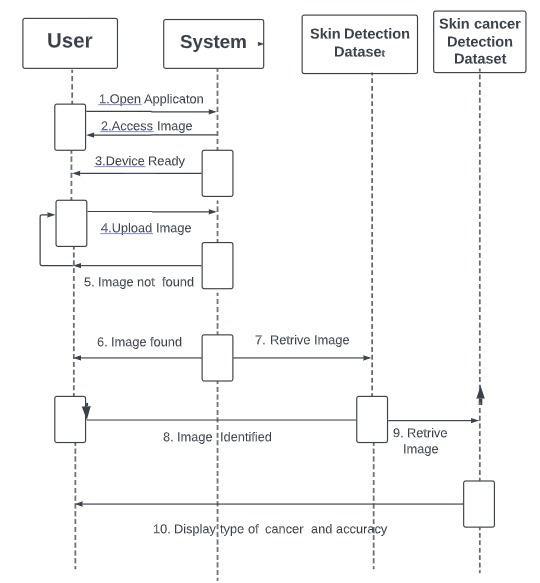
5. METHODOLOGY
Fig. 2: Flowchart
5.1 IMAGE ACQUISITION
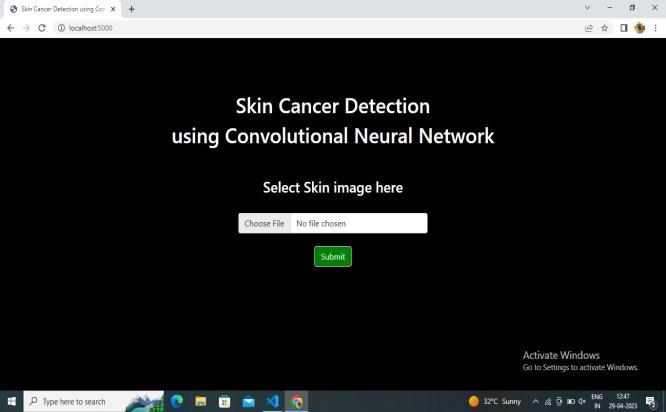
The general end of any image accession is to transfigureanopticimage(real-worlddata)intoanarrayof numerical data which could be latterly manipulated on a computer.Imageaccessionisachievedbysuitablecameras. We use different cameras for different operations. In this design,thewebcamisusedforimageaccessionwherethe stoner'sfaceiscaptured.
5.2 IMAGE PREPROCESSING
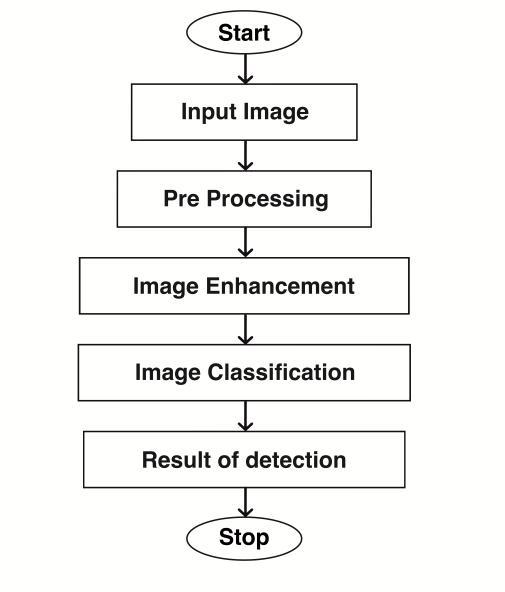
Thisprocessinvolveddataaddition,imageenhancement using (ESRGAN), image resizing, and normalization. Approachessimilartosuper-resolutiongenerativeinimical networkenhancedSR-GANcanhelpamelioratethediscovery ofskinlesions.Theenhancededitionofthesuper-resolution GAN(Ladingetc.)usesaflexible-in-residualblockratherthan anintroductoryresidualnetworkorasimplecomplication boxwhenitcomestobitsy-positionslants.Also,themodel doesn'thaveabatchnormalizationsubcasteforsmoothing downtheimage.Consequently,thesharpedgesoftheimage vestigescanbebetterapproachedintheimagesproducedby ESRGAN. When determining if an image is real or false, ESRGANemploysarelativisticdiscriminator(penetratedon 10April2022).
This system yields more accurate results. Perceptual differences between the factual and false images are combinedwiththerelativisticaveragelossandthepixel-wise absolutedifferencebetweentherealandfakeimagesasthe lossfunctionduringinimicaltraining.Atwo-phasetraining schemeisusedtoedgethecreator’schops.Thisreducesthe pixel-wiseL1distancebetweentheinputandtargetshighresolutionimagestoavoidoriginalminimawhenbeginning
with complete randomization in the first phase of the algorithm.Inthealternatestage,thethingistoupgradeand amelioratetherepairedimagesofthelowestvestiges.The final trained model is fitted between the L1 loss and the inimicaltrainedmodelsforaphotorealisticreconstruction.A discriminatornetwork wastrained to distinguishbetween super-resolved images and factual print images. By rearrangingthelightnessrudimentsinthesourceimages.
5.3 AUGMENTATION
Foreachimageinthedataset,upgradedimageswith associated masks including gyration, reflection, shifting, brilliance, and resizing were produced. Discovery and assessmentareconfinedby thepoorqualityofrawlesion images generated by electronic sensors. There was an aggregateof1440benignand1197nastytrainingimages. Afterconductinganaddition,therewasanaggregateof1760 benignand1773nastyimages.Theimbalanceddistribution ofclasseswasaddressedbyperformingoversamplingonthe nastyimages.
Toavoidprejudicedvaticinationconsequences,the ISIC2018datasetwasresolvedintothreemutuallydistinct sets(training,confirmation,andevaluationsets)toaddress theoverfittingissuecausedbytheshortnumberoftraining photos. The affair of the image addition process after applyingdifferentadditionparameters.

5.4 DATA PREPARATION
Image Accession factors can vary because certain printsinthedatasethavelowpixelconfines,andallimages shouldberesized.Eachaccessiontoolhasitsownuniqueset ofcriteria;hence,thelesionimagedatasetislikelytocontain a variety of images. To corroborate that the data were harmoniousandfreeofnoise,thepixelstrengthofallimages wasformalizedwithintheinterval.Normalizationreckoned usingEquationassuredthatthemodelwaslesssusceptible tominorweightchanges,easingitsenhancement.
5.5 EMOTION DETECTION MODULE
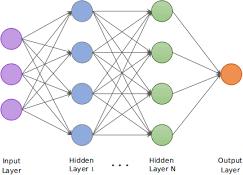
For point birth, CNN is used. For the emotion recognitionmodule,we'vetotrainthesystemusingdatasets containingimagesofhappy,angry,sad,andneutralfeelings. To identify features from dataset images for the model construction, CNN has the special capability of automatic literacy. CNN can develop an internal representation of a two-dimensionalimage.Thisisrepresentedasathree(1) dimensionalmatrixandoperationsaredoneonthismatrix fortrainingandtesting.
Five-Subcase Model This model, as the name suggests, consists of five layers. The first three stages correspondtoconvolutional and maximum-poolinglayers each,followedbyacompletelyconnectedsubcasteof1024 neurons and an affair sub caste of 7 neurons with a soft-
maximumactivationfunction.Thefirstconvolutionallayers employed 32, 32,and64kernelsof 5 *5, 4 * 4,and5 * 5. These convolutional layers are followed by maximumpoolinglayersthatusekernelsofdimension3*3andstride 2,andeachoftheseusedReLufortheactivationfunction.
Delicacycanbeincreasedbyaddingthenumberof agesorbyaddingthenumberofimagesinthedataset.The input will be given to the complication sub caste of the neural network. The process that happens at the complicationsubcasteisfiltering.Filteringisthecalculation behind matching. The first step then'stolineupthepoint and image patch. Also, multiply each image pixel by the corresponding point pixel. Intermittent Neural Network remembershistoryanditsopinionsaretoldonwhatithas learned from history. Note Basic feed-forward networks “flashback” effects too, but they flashback effects they learnedduringtraining
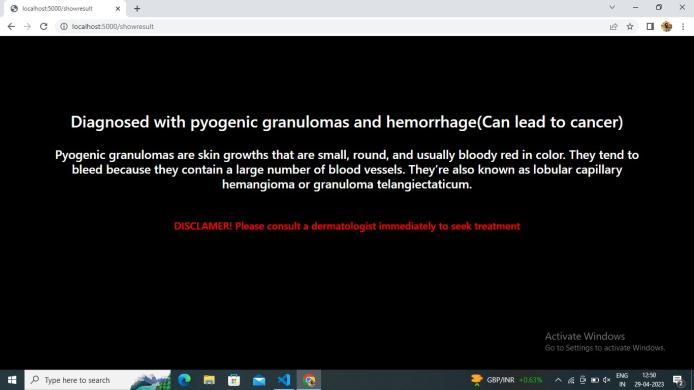
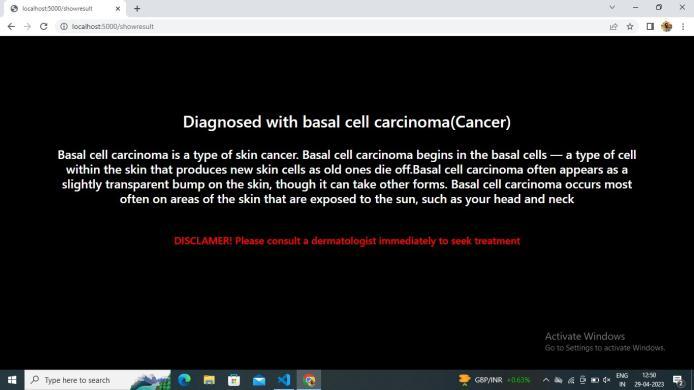
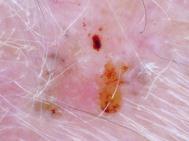
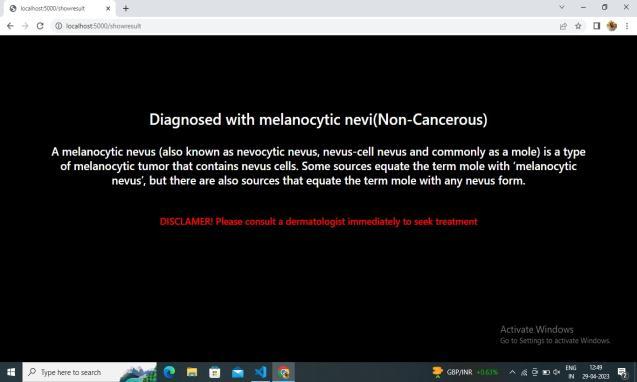
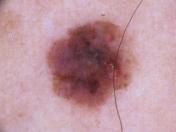

7. CONCLUSION
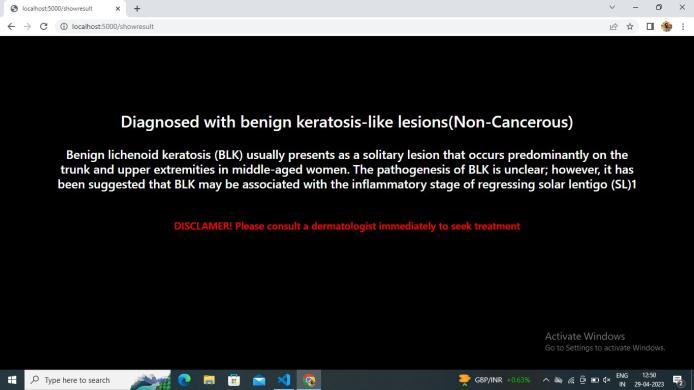
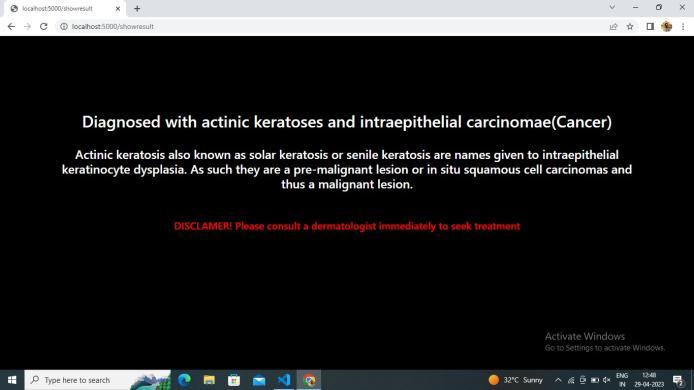
In this project, it is found that most existing skin lesion diagnoses with deep learning technology stop at deep learningmodelingandwithoutanyfurtherdeploymentor integration with a readily available device such as a smartphone.However,theadvantageofintegratingobject detectiondeeplearningtechnologyandsmartphoneinthe medical field has been discovered throughout the project. This technology can provide a low-cost diagnosis without requiring years of skin lesion diagnosis experience. Moreover, users can perform diagnosis at home with a smartphone and therefore can provide a point of care to users from a remote area. Although the process of developmentischallengingduetotheimmatureplatformof objectdetectiondevelopmentTensorFlowObjectDetection API and requires experience for Android application development,thesuccessofthisprojecthasproventhatthe development of this technology is feasible and should be aware.
REFERENCES
[1] WorldHealthOrganization. GlobalHealthObservatory; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.

[2] Han, H.S; Choi, K.Y. Advances in nanomaterialmediated photothermal cancer therapies: Toward clinical applications. Biomedicines 2021, 9,305.
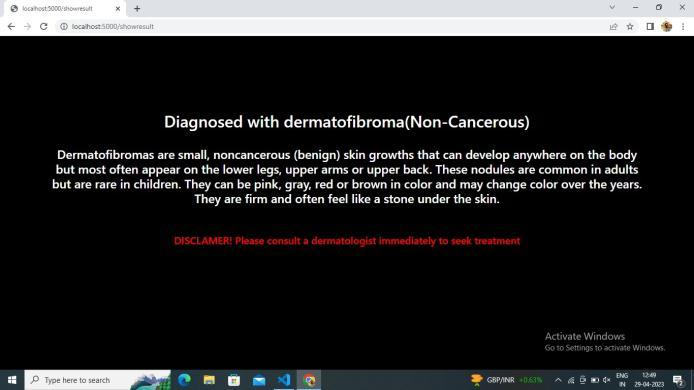
[3] Fuzzell, L.N.; Perkins, R.B.; Christy, S.M.; Lake, P.W.; Vadaparampil, S.T. Cervical cancer screening in the United States: Challenges and potential solutions for under screened groups. Prev. Med. 2021, 144, 106400.
[4] Ting, D.S.; Liu, Y.; Burlina, P.; Xu, X.; Bressler, N.M.; Wong, T.Y. AI for medical imaging goes deep. Nat. Med. 2018, 24,539–540.
[5] Wolf,M.; de Boer,A.; Sharma,K.; Boor,P.; Leiner,T.; Sunder- Plassmann,G.; Moser,E.; Caroli,A.; Jerome,N.P. glamorousresonanceimagingT1-andT2-mappingto assessrenalstructureandfunctionAmethodicalreview andstatementpaper.Nephron.telephone.Transplant. 2018,33(Suppl.S2),ii41–ii50.
BIOGRAPHIES
Bharath Bharadwaj B S Professor, DepartmentofComputer Science &Engineering, MaharajaInstituteofTechnology Thandavapura

Saniya Anjum Student,DepartmentofComputer Science &Engineering, MaharajaInstituteofTechnology


Thandavapura
Shaguftha Afreen Student,DepartmentofComputer Science &Engineering, MaharajaInstituteofTechnology

Thandavapura
Spoorthi T C Student,DepartmentofComputer Science &Engineering, MaharajaInstituteofTechnology

Thandavapura
Keerthana M Student,DepartmentofComputer Science &Engineering, MaharajaInstituteofTechnology
Thandavapura

