A Barcode-Based Prototype Authentication System Using Python Programming and Database Applications
 Soham Chakraborty, Dedipya Datta, Aritra Mondal, Barsha Saha, Koushik Pal
Soham Chakraborty, Dedipya Datta, Aritra Mondal, Barsha Saha, Koushik Pal
Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
Guru Nanak Institute of Technology, Kolkata Sodepur, Kolkata - 700140, India
Abstract - Authentication is necessary for situations where limited or selected entries are accepted. In such cases, the products are authenticated based on the amounts to make a count. So, I tried to do the job using barcodes but in a different way. In the conventional level of barcode authentication, we use a barcode reader, which consists of an infrared light source and some necessary components inside a gun-like structure. Nowadays, we can see barcode scanners in robots automating the whole process. Now, what we are trying to do is, make the system work using Python codes. From the data entry process to the end of a transaction, the whole process is automatic in our system. As a barcode scanner, there is a camera, which we all have on our mobile phones, laptops and as separate webcams. So, there will be no need for the extra effort in the process of the fruitful authentication system. We have already done research work on this topic earlier. Now, this is the whole project that we were thinking about.
Key Words: Barcode, QR code, Authentication, Python, Pandas, Segno, smtplib, Security, Camera Sensor, Scanner, Reader,Database
1.INTRODUCTION
Inolder days,authenticationswere done with barehands usingpenandpaper.Theprocesswassafeandsecurebut was a time-consuming one. Now we are blessed with technological authentication processes like RFID and Barcodeauthenticationsystems.Theseprocessestakeless timeandarealsoreliableintermsofauthentication.Inthe conventional way of barcode authentication, we use a barcodescannerwhichconsistsofinfraredlightandsome necessary hardware components inside a gun-shaped structure. We wanted to change the process of the scanning or authentication a bit and make the whole process automated using some accessories which are simply available in our daily life. We created 1D and 2D barcodesor QRcodes using data from the physical entity. These codes can be read by the camera sensor using Python intelligence. In the below explanation, we are goingthroughtheprocessofthewholesystem.
1.1 Idea of barcode
Barcode is a combination of black and white bars which are rectangular. It is the converted form of data about an object or a physical entity into a unique barcode. The Barcode was invented conceptually in the year of 1948. Two students from Drexel University named "Norman Joseph Woodland" and "Bernard Silver" created this project. It was patented in 1952. In the starting, it was a combination of black and white vertical parallel bars. These barcodes we can see in food items and grocery items. We use 2D barcodes or QR codes, a collection of vertical and horizontal bars, to get a simple and secure authenticationsystem.UsingaQRcode,itisevenpossible tostorebiometricdata.

1.2 Barcode in Authentication
The information, which can describe a physical entity uniquely, can be used to make a barcode of the corresponding physical entity. A barcode is an encoded visual form of a physical entity, so using the visible form, wecanauthenticatethatentityaspertherequirements.In our daily life, many goods and products go through the markets. It would have been hectic to count all those products manually. Barcode scanning and authentication make it much easier and faster. Nowadays, in some functions, paid entry purposes, airport entries, and railway entries also use a QR code authentication system for public entries to validate their purchases. In all these cases, they use a typical barcode scanner. We have been thinking about changes to the process of "scanning" and "validating" toa Python-basedsystem thatis fast,reliable andhustle-free.

tried to make a low-cost, fast, efficient Python-driven authenticationsystem.

1.3 What We Have Tried
After observing different places, we have got to understandthattheconventionalwayofbarcodescanning and authentication is a relatively slow process compared to what we are trying. Retail stores, industries and warehouses use IR technology to scan a barcode printed on a product. In security entries like railway stations and airports, we see fixed IR sensors which allow us to make ourbarcodesscan.Thisprocesstakesmoretime.Thereis a need for dedicated instruments for the purpose. So, usingasimplecamerawhichworksfineandtakepictures, wehavetriedtomakeasystemforscanningtheQRcode. Weallhavethistypeofcameraonourmobilephonesand laptops, which we have used for this purpose. Python makestheQRcodeorbarcodefromthesourcedatastored of a particular physical entity in the database to scan and validate it. Python has a rich library of built-in packages, which blesses us to do a lot of stuff in real. So, we have

2. Older Process vs New Acceptance
Intheearlierdays,inoffices,retailstores,bookstoresand even warehouses, people used to authenticate physical entities with paper and pen. Now, this scenario has changed a lot. Organisations started automation on every process and also in the authentication processes. Below we are going to discuss the growing use of automatic authenticationprocesses.
2.1 Procedural Changes and Acceptance
In previous days, we used to authenticate things using pen and paper. But nowadays, every organisation has a database to store all the data about the products or the physical entities with their unique identities. The modern system is better and less time-consuming than the previously manual processes. Using the data from the database, we can count all the physical entities and authenticate them as per requirements. And we are working more on the modern system to make it more robust,fastandreliable.
2.1 Usage of Modern Technology
The QR or barcode technology got introduced in 1948. Two students from Drexel University named "Norman J Woodland" and "Bernard Silver" made an encoded pictorialrepresentationofdatathatlookedlikeabullseye. After this, over the years, technology has developed a lot, and farms have started to take barcodes into everyday usage. Now it is being used in warehouses, retail stores andmanymoresectorswhereauthenticityisanissue.
2.3 Technological Growth Roadmap
1948: Barcode was first introduced in 1984 by two fellows named "Norman J Woodland" and "Bernard Silver".Atthattime,itfeaturedabullseyedesign.
1952: Thetechnologygot patented in1952,butitfailed whentechnologicalhurdlescame.
1960: The association of American Railroads sponsored the KarTrak Barcode System, the size of a refrigerator featuring13horizontallabels.
1972: The Committee on Uniform Grocery Products Code recommended barcode usage on most products in the"UnitedStates".

1974: OnJune26,1974,a"Wrigley'sGum"wasscanned. Itbecamethefirstcommercially-scannedUPCbarcode.
1974: The first alphanumeric barcode technology was invented.Thatwas"Code-29".
1975: Almost all US rail cars carried KarTrak labels, althoughtheprogramgotabandonedthreeyearslater.
1982: Thefirstcharge-coupleddevice(CCD)scannergot introduced.Itpavedthewayforthe widespreadadoption ofbarcodescanningtechnology.
1986: The first handheld fixed-beam laser scanner is patented.
1999: The two-dimensional QR code got unveiled in Japan.
2005: Airlines begin printing barcodes on passenger boardingpassestospeeduptheprocess.
2008: Mobile phones gain the required technology to displaybarcodes.
2016: The Digimarc-Barcode isa code read by machines and nearly invisible to the human eye, and is adopted by theGS1.
2.4 Usage Statistics of QR-Code
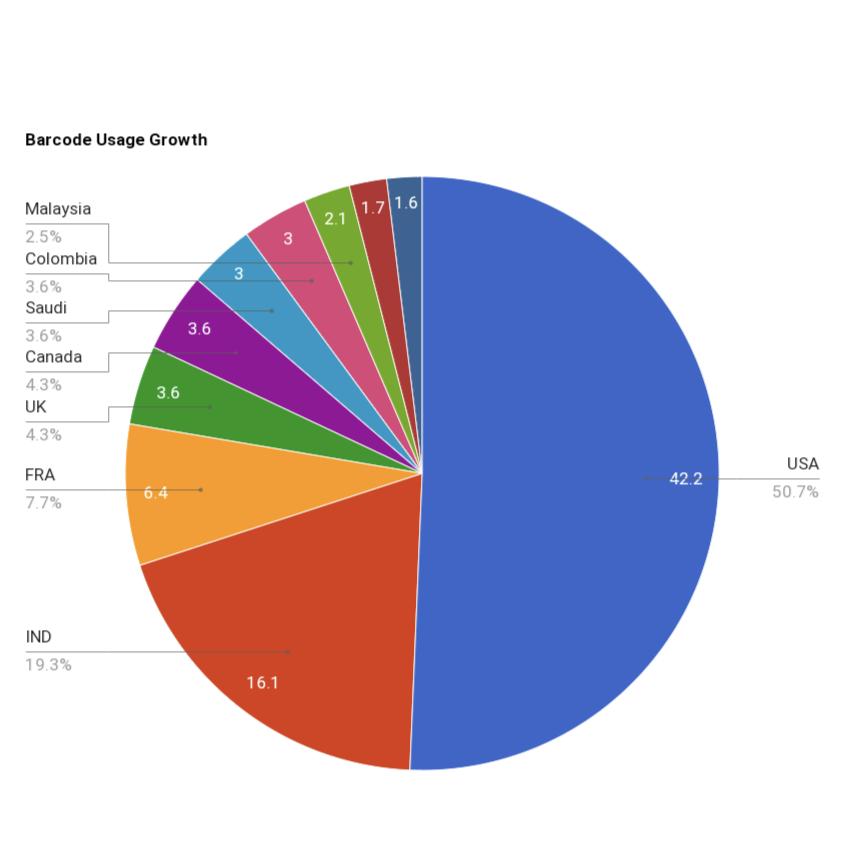
Barcode technology is much older than its subdivision, "QR-code". Now everyone has smartphones, and people use barcode or QR-Code scanning for various purposes. Only the barcode technology is 65-70 years old, and QRCodetechnologyhasgrownupin26years.Afterthecovid19 breakout, the usage of contactless transactions and all got hiked up suddenly. In the meantime, the use of QR Codesreacheditstopusercountinbetween2020to2022.
The survey from "QRCode Tiger" shows that in 2022 the scan count of QR codes in the USA is 2,880,960. The number of counts in India is 1,101,723. And five Asian countries come under the top 10 list of QR-Code usage count.75%ofthetotaluserswanttouseQR codesalsoin futurefortheireasy-to-usework.
So, looking at all those facts, we tried to make a system thatcanstandoversocietyandcreateavaluableimpact.
-5:BarcodeUsageGrowthStatistics
3. What We Created
We created a complete Python Programming based system that also has some database applications in it. There we get lots of pre-installed Python packages that make every work easy. We used some of them, which are "Pandas", "Segno", "OS", "Shutil", "OpenCV", and many more. We created this project into two parts. In the first part,wemadeaQRcodegeneratorthattakesseveraldata ofan entityfrom thedatabaseand makesa QRcode from those data. After that, it also has an email section that sendsthosecodeswithmoredatatospecificcontacts.And in the second section, there is a camera vision-based QR codescanningsectionwhichevaluatesthoseQRcodesand checksthecorrespondingdatawiththedatastoredinthe databaseearlier.
3.1 QR-Code Generation Section
Wemadeanauthenticationsystemusingthebarcodeor QR code technology. It is a system where people register their names with unique personal details, and we make the QR codes using those details. After creating the QR
codes, we made an email-generation section that automatically sends those QR codes to the corresponding personwithsomeadditionaltext.
InthisQRCodeGenerationsection,thedatacomesfrom a CSV file. People who registered their names through GoogleFormshavestoredtheirdatainourdatabase.Then wepreparedQRcodesusingthosedata.

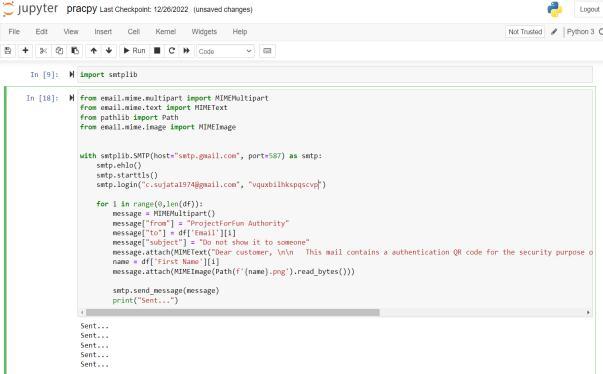
ThereisaPythonfunctionforattachingvariousdata to an email named "email.mime". Using this, I created multiple sections in the email and added some text about thevalidationoftheQRcodeandtheimageoftheQRcode. I did those activities using "email.mime.multipart", "email.mime.text", and "email.mime.image". After this, I created a login instance using "smtplib.SMTP()", which takesthehostandportasparameters.Then,usingobjectoriented programming concepts, I wrote the texts in the mail as the sender, subject, body, receiver, and all other details.
After running all these codes together, the system creates QR codes and sends them to the appropriate person via email.
3.3 Database Usage
I have used my computer hard-drive memory as the database of the project. For larger datasets, we can use databaseslike OracleDatabaseorMySQL.Inourcase, the datasetweusedwastoosmall,sowetookagoogleformto collect the data from people and managed that using google sheets. Google sheet provides a good feature by which we can export the sheet as a CSV file. After getting theCSVfile,IfetchedallthedatausingamoduleofPython namedPandasanduseditfortheproject.
Ifweneedtouseadatabaseinthisproject,wehaveto create a database using MySQL or similar tools creating databases. After that, we need to insert all the data in the databaseina tabularform. Whenthedatabasecreation is complete, we need one connector that helps to connect MySQL databases with Python. After the connection establishment, we can fetch the database using SQL commandsfromPython.
3.4 Scanning QR and Authentication

3.2 Sending QR to People
AftermakinguniqueQRcodes,sendingthosecodesto the corresponding people was the next priority. So, I imported "smtplib" from the built-in Python packages. "SMTP" stands for "Simple Mail Transfer Protocol", and I used this module to send emails to an internet machine withanSMTPorESMTPlistener.
At the time of authentication, people need to bring those QR codes to us to authenticate themselves. For this purpose,Imadeanothersectionthatcantakethevisualof the QR code and fetch the data from it. Then the system checks the fetched data with the stored data in the "strings. text" file. After that, on the window, the result of the authentication appears. If these two data are from peopleandthetextfilematches,ittellsthatthepersongot authority.Andifthedatadoesnotmatchorappearstwice, itseemsthatthepersongotunauthorizedoranyoutsider istryingtoenter.
Let'stalkaboutthetoolsandprocesses.Oursystem works based on visuals. Therefore it is necessary to get visuals of the target. For this purpose, I imported "cv2", a


Python package to operate the camera connected to the system. Then I used a command as "cv2.Videocapture(0)" and made a variable of it. From this variable, I made the capture size of the QR code scanning window using pixel representation. I also imported "decode" from "pyzbar.pyzbar" to decode the QR code. I used "with open()" function to read and write from the text files. I created every automatic step and movement using "for" and"while"loops.
For the prevention of unauthorised entries, I created twotextfiles.Onthem,the"strings.text"filewasforinitial data for every person, while another text file named "reentry.text" was empty. Whenever a person comes and authenticateshimself,correspondingdataofhimmovesto the "reentry.text" file. If a person comes with a fake QR code or a used QR code, the person gets marked because the authenticator does not accept QR's from outside or reentry.
On the camera visual, a text shows the result of the QRcode.AtthetopoftheQRcode,ittellswhethertheQR code is Authorised, Reentry or Unauthorised. If the QR is valid, a green text appears on the top of the visual of the QRcodeas"Authorised".Theresultappearsasbluetextas "reentry" when someone enters the same code twice and asredtextas"unauthorised"whenaninvalidQRcomes.

In this way, the system authenticates physical entitiesfastandefficiently.
4. Process Discussion With Screen Snippets
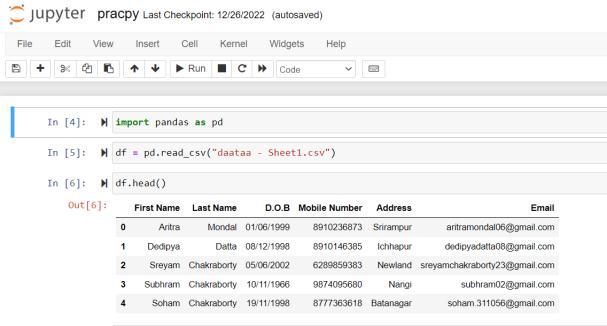
Atthestartoftheprocess,Icreateda GoogleForm to collect the data of all the people registered through our programme. I made a table with their unique details like first name, last name, date of birth, mobile number, addressandemail.
I used "Pandas" to fetch and use the data of all the registeredpersonsintheproject.Aftergettingallthedata, I exported them as a CSV(comma-separated values) file anduseditasthedatacenter.IshowedthesestepsinFig10.
In the fig-11, I showed how I created a formula to generateuniqueQRcodesandsavethemas'.jpg'images.I fetched all the personal data of people using a for-loop to make a combination of those data, which is different for everyone as the mobile number and email ids are unique foreveryone.Afterthat,Isavedallthosestringsintoafile named 'strings.text' and used 'shutil' to make a copy of that file in the QR scanner section. This text file in the scannersectionwillcheckwith thescanneddatafromthe QRcodesatthetimeofauthentication.
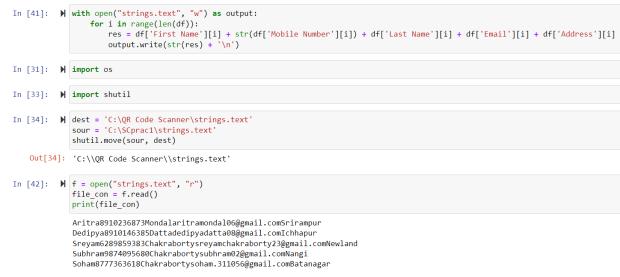
After making strings from all the personal data, I used 'Segno' to create the QR codes and saved them into the samefile.IshowedthisinFig-12.
Fig -13: DesignedtheemailandsentwithQRcodes
Then I used 'smtplib' to send those QR codes to the peopleaccordingly.Forthatpurpose,Iusedanotheremail id as the host and created a temporary password for the mail id login. Then I designed the mail subject, body and all the necessary things using MIMEMultipart. Using forloop,Ifetchedalltheemailidsandsenttheemailtothem withtheQRcodes.
I used Pycharm IDE to write and run the QR scanner sectioncodeandverifythe QRcodes.UsingopenCV,time, and many other packages, I created an efficient code that checkswhethertheQRcodeisvalidorinvalid.Pre-created 'strings' text file contains all the QR code data. When someone shows their QR code in front of the camera vision, the algorithm checks it with the 'strings' file and gives the authentication result in a GUI window named "AuthenticationResult".
Thealgorithmcheckstwotextfilesconsecutively.Ifthe QR data matches the 're-entry' text file data, it implies someoneisenteringtheirQRcodeagain.Inthissituation, the GUI window will show a blue-coloured message as "Re-Entering".Fig-15.


Fig-14:AuthenticatedMessageinGUIWindow
When someone shows a QR code to the camera vision andthedatamatchesthe'strings'filedata,theGUIshows an "Authenticated" message with a green colour in the window. It also sends the data from the 'strings' file to another file named 're-entry', and the space where it was in'strings'remainsnull.Fig-14.

The GUI window will show a red-coloured "UnAuthorised" message when the QR data is neither in the 'strings'northe're-entry'textfile.
4. Where can be used
4.1 Selective People Entries: We can use this system in urban clubs and parties where restricted or invitedpeopleareallowed.Atthetimeofdataenlistment, wecan store the data of each person in the database or a sheet,likeGoogleformorMSExcel.Afterthat,wecansend theinvitationsviatheiruniqueemailidandputtheunique QR code in the email. For authentication purposes, they willshowthoseQRcodestousontheeventdate.Theywill place their QR codes under our specified place at the entrance, and our system will ensure whether the person isallowedtoenter.Ifthesystemshowsagreensignal,the person is allowed to enter. Otherwise, we will ask the persontoauthenticatehimorherselfwithotherentities.
4.2 Railways and Bus Entries: Wecanusethissystem in railway stations and bus entries to buy travel tickets. Whenever a person buys a token, a unique QR code is generated and printed on it for them so they can use this code to authenticate themselves in the departure section. By using such systems in public places, we can get more information about the everyday activities in stations or bus-travels. Information like this can be crucial for the governmenttotrackpeople.
4.3 Other Usage: We can use this system in places where authentication of any physical entity is needed. In public sectors like government service sectors, offices, schools,taxis,heritage locationsand many others, wecan use this system as the authenticator. We can implement face recognition in this system to make it nimbler and morereliable.
5. Advantages of The System
5.1 The system will be effortless, robust and reliable. Developers and the system itself will manage all the backgroundprocessesofit.
5.2 QR code authentication system is a fast one we all know. After implementing the camera sensor as the computervisionandPython-basedsystem,it gets quicker andeffortless.
5.3 In the system, the database stores all the data. The system works based on those data, so there is no risk of losinganydata.
5.4 All the processes of the system as data collection, processing, QR-code generation, sending QR codes and authentication, are automated. So, making the system automatedmakesitmorerobustandeffortless.
6. Drawbacks of The System
6.1 I have used Python as the process control language. DevelopmenttimeislesserinthecaseofPython,butitis3 to 5 times slower than Java in runtime. Python's built-in high-level data types and some other things are responsibleforit.
6.2 Ihaven'tdevelopedany publiclyusableversionof the system. So, it is only a developer prototype version till now.Everyonecannotunderstanditanduseitseamlessly.
7. Future Improvement Scopes
7.1 We are working on it to improve the runtime of the system code. Though the system is fast enough, we are tryingtomakeitmoreefficient.
7.2 We are working on it to improve the runtime of the system code. Though the system is fast enough, we are tryingtomakeitmoreefficient.
7.3 We are looking forward to making a publicly usable versionofthesystemsothatpeoplecanuseoursystemby themselves.
8. Conclusion
The authentication process is a crucial step in every sector nowadays. We have made a system that can serve the purpose of authentication effortlessly and in an automatedway.Startingfromdatacollectiontotheendof the authentication process, it's a seamless process. Undoubtedly our system is better than the conventional authentication process, but we have to give it a userfriendly user interface that everyone can use. Soon, our system can be grown to a new height and serve society withgoodvalue.
REFERENCES
[1] Barcode Recognition System, N. M. Z. Hashim, N. A. Ibrahim,N.M.Saad,F.Sakaguchi,Z.Zakaria
[2] Barcode Based Student Recognition System, Samira Nigrel,AkshayKumarPrajapati,KunalLad,SachinJhaveri,

[3] IoT(Internet of things) and Its Application_0 LEVEL Book M4:R5_BILINGUAL BOOK(ENGLISH-HINDI) by T BALAJIPUBLICATION
[4] DataStructuresandAlgorithmsinPython,1stEdition - 5 July 2013 Michael T. Goodrich, Roberto Tmassia, MichaelH.Goldwasser
