Smart Farming: A Machine Learning and IoT Approach
Mrs.B. Veena1 , P. Sathyapal Reddy2 , M.K.Sai Srikar M.Shilpa4Abstract - Many prime varieties of foods come from agricultural lands. Food is the most important means of survival and is a necessity for every creature. In India, there are a lot of agricultural lands and a lot more farmers who produce a wide variety of crops. There are a lot of unfortunate cases where farmers just couldn't bear the loss of a crop be it due to rainfall, droughts, or fertilizer faults. In this project, we propose a way for agriculture to be made fruitful and lush. This is done by implementing an IoT module that uses many different sensors like temperature, pH, moisture, and even rainfall sensors which detect the changes in these particular factors and process the data onto a Machine learning model. An Algorithm is then used to process and make decisions based on which irrigation is provided to the crops. This method can help to conserve water as well as give the freedom of manipulating the module using an app that controls the module and informs the farmer about it. This method also helps in healthier crop production while being cost-effective.
Key Words: IoT, Machine learning, Random-forest, Raspberry pi Model 3B, Passive infrared Sensor (PIR), Rainfallsensor,SoilMoistureSensor,TemperatureSensor (DHT11).

1. INTRODUCTION
ThisSmartfarming,alsoknownasprecisionagriculture,is an emerging approach that uses upcoming technologies such as machine learning and the internet of things (IoT) to increase the efficiency and productivity of agriculture. By integrating digital technologies into agriculture, farmers can monitor and optimize the use of resources such as water, fertilizer, and pesticides, while also improving crop yield and quality. Machine learning algorithmsareusedtoanalyzedatacollectedfromvarious sources such as sensors, weather stations, and drones. These algorithms can identify patterns and provide insightsthathelp farmers makeinformeddecisionsabout when to plant, irrigate, and harvest their crops. In addition, IoT devices such as soil moisture sensors, temperaturesensors,andsmartirrigation systemscan be usedtoautomateandoptimizethefarmingprocess.Smart farming has the potential to address many of the challenges facing the agriculture industry, such as food insecurity, climate change, and resource depletion. It can help farmers reduce waste, increase efficiency, and
improve sustainability, while also reducing the environmental impact of agriculture. However, implementing smart farming practices can be a complex and costly process. It requires significant investment in technology, data analytics, and infrastructure. Additionally, there may be challenges related to data privacy and security, as well as the need to train farmers and other stakeholders on how to use these technologies effectively.Despitethesechallenges,thepotentialbenefits of smart farming are significant, and many farmers and agricultural companies are already embracing this approach. With continued advancements in machine learning and IoT technologies, the future of agriculture looks bright, with the promise of increased efficiency, productivity,andsustainability.
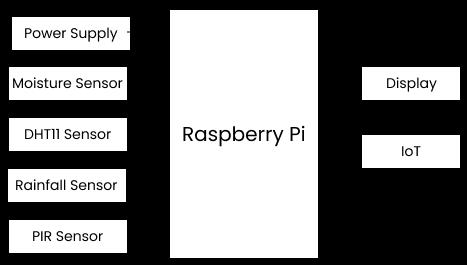
1.1 Block diagram
Raspberry Pi is used as the main IoT module to which multiplesensorsareconnectedtoobtaintherequireddata as shown in fig1. Moisture sensor is used to obtain informationaboutthe wetness presentin thesoil andwill resultinswitchingontheirrigationsystemincaseitisdry. DHT11 sensor is used to measure the temperature and humidity present in the soil and will respond via accordingly incase the threshhold temperature goes up. Rainfall sensor is sensitive to changes in weather and will beactivewhilethereisrainfall.PIRsensorismainlyuseful indetectinganimals/movementviainfraredraysandcan help in notifying the breach to the owner. Finally all the dataissentviaahotspottothecloudwherethedatacanbe updatedinrealtime.
2. IMPLEMENTATION

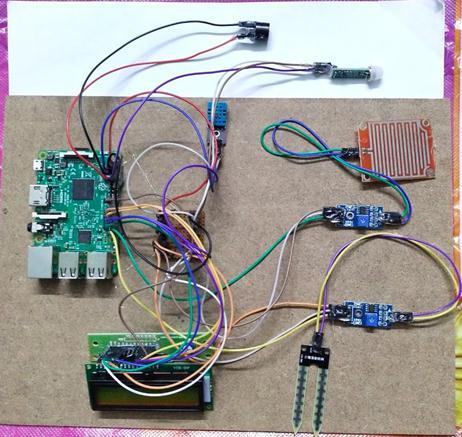
2.1 Hardware Implementation
In the hardware implementation (as shown in fig 2) we have used the raspberry pi with various sensors like SMS, DHT11,PIR and rainfall sensor including with buzzer. The PIR sensor given the output in digital format whether the objectisdetectedornormal.Andwhenthetemperatureis abovethe38oCthebuzzerwillbeactivated.Theresultand sensor data will be displayed in LCD and app which was connectedthroughthenetwork.
Other interfaces include the camera interface, which is usedtoconnectacamera moduletotheRaspberryPi,and theaudiointerface,whichisusedtoconnectaudiodevices. These interfaces make the Raspberry Pi a versatile platform for various projects, from home automation to roboticsandmore.
b) Sensors:
1. Soil moisture sensor:

2.1.1 Hardware Requirements
a) Raspberry Pi:
Raspberry Pi, on the other hand, is a single-board computer that is widely used in IoT applications. It has a range of GPIO (General Purpose Input Output) pins that can be used to connect to various sensors and devices. Raspberry Pi's working principle involves executing code on a microcontroller that processes input data from various sensors and sends output signals to other devices overa network.Itisa creditcard-sizedcomputerthatcan perform various computing tasks. It uses a small and efficient ARM processor and runs on various operating systems. It has multiple interfaces like USB, HDMI, Ethernet, GPIO, and more that can be used to connect various devices and peripherals. The USB interface canbe used to connect external storage devices, keyboards, and mice.HDMIinterfaceisusedtoconnecttheRaspberryPito adisplayorTV.TheEthernetinterfaceisusedtoconnectto theinternetoralocalnetwork.TheGPIO(GeneralPurpose Input/Output)interfaceisasetofpinsthatcanbeusedto connect various sensors and other devices like LED lights, motors,andmore.

The insertion of moisture sensor in the soil, it predicts the percentage of moisture and water content present in the soil. The ADC is used in connecting the soil moisture sensortotheraspberrypiinwhichtheoutputispresented in digital format whether it is WET or DRY displayed on LCD. The sensor consists of potentiometer to set the desired moisture threshold value, if the values measured by sensor is more than the threshold then the digital output goes high an LED indicates the output. Similarly, when it is less than the threshold value then the output remainslow.
2. Humidity & Temperature Sensor
Thissensorisusedtodetectthetemperaturechangein thesurroundingsandisactivated whenthetemperatureis above 38oC. This sensor consists of 3 pins namely VCC
where the power supply isgiven, Data pin is connectedto raspberrypiwhichpassesthechangeintemperature,GND.

It is an alphanumeric LCD, which stands for “Liquid Crystal Display”. The number 16*2 represents that it has displaythewordsin16characterswithinthe2rows .The significance of LCD was voltage is operating from 4.7V to 5.3VandCurrentisutilized1mA(withnobacklight).

This sensor is used to measure the amount of precipitationorrainfallinspecificarea.

Thesensorisusedtosensethemotionanddetectionof an object.Andalso measures the infraredlights whichare radiating from the objects. The below figure (as shown in fig7)showthetypicalpinconfigurationinwhichthe3pins aredefinedasVCC,OUT,GND.
2.2 Software Implementation

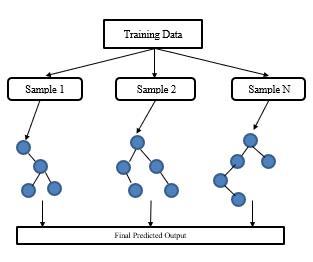
RandomforestAlgorithm
The class that is produced by Random Forest, an ensemble classifier (methods that create numerous classifiers and aggregate their findings), is the class produced by the average of the classes produced by individualdecisiontrees.Numberofvariablesandnumber of trees are the two parameters generated by RANDOM FOREST for internal structure. Random forest calculates thevariable'srelevancebyexaminingtheOOBscorewhile leaving the other variables alone.Because unimportant variables are typically found near the bottom of each tree andimportantfeaturestendtobeatthetop.
The hardware setup consists of 4 different sensors and a buzzerfornotificationconnectedtoRaspberryPi3Model B through different GPIO pins. A Led screen is setup for displaying the changes in parameters. The setup is powered via a Universal Type A adapter and will be providingdataviaahotspotontheusersmobilephone.

3. CONCLUSIONS
AlthoughIoTinagriculturehasitsfairshareofchallenges, smart farming has a bright future going ahead.There are truckload of applications in smart farming, most of which areenabledbyIoT.Manyofthesehelpthefarmingsector inimprovingthecropquality,reducingthecroplossesand lowering the costs. The proposed system has high efficiency and accuracy in fetching the live data through the four sensors used. Thus , this project focuses on understanding real-time changes and helps in understandingsmartfarmingbetter.Toincreaseyieldand tosecureproperconditions,wecanimplementtheproject on a bigger scale with more sensors for different parameters. The application can also be made more farmer friendly and provide data on a lot of different things in a presentable manner. The models can be more accuratelytrainedforbetterpredictions.
REFERENCES
[1] A.Dahane,R.Benameur,B.KecharandA.Benyamina, "An IoT Based Smart Farming System Using Machine Learning," 2020 International Symposium on Networks, Computers and Communications (ISNCC), Montreal, QC, Canada, 2020, pp. 1-6, doi: 10.1109/ISNCC49221.2020.9297341.
Once the hardware is connected to the phone via a hotspot,open theapplication on the phonewhichconsists of different fields.Changesmade to the sensors in formof heat, moisture, movement etc will immediately reflect on theappandwillproviderealtimechangessmoothly.
[2] K. Parasuraman, U. Anandan and A. Anbarasan, "IoT Based Smart Agriculture Automation in Artificial Intelligence," 2021 Third International Conference on Intelligent Communication Technologies and Virtual Mobile Networks(ICICV), Tirunelveli, India, 2021, pp. 420-427,doi:10.1109/ICICV50876.2021.9388578.
[3] G. Abraham, R. R. and M. Nithya, "Smart Agriculture Based on IoT and Machine Learning," 2021 5th International Conference on Computing Methodologies and Communication (ICCMC), Erode, India, 2021, pp. 414-419, doi: 10.1109/ICCMC51019.2021.9418392.

[4] G. S. Nagaraja, A. B. Soppimath, T. Soumya and A. Abhinith, "IoT Based Smart Agriculture Management System," 2019 4th International Conference on Computational Systems and Information Technology for Sustainable Solution (CSITSS), Bengaluru, India, 2019, pp. 1-5, doi: 10.1109/CSITSS47250.2019.9031025.
[5] H. Youness, G. Ahmed and B. E. Haddadi, "Machine Learning-based Smart Irrigation Monitoring System for Agriculture Applications Using Free and Low-Cost IoT Platform," 2022 International Conference on Microelectronics (ICM), Casablanca, Morocco, 2022, pp.189-192,doi:1109/ICM56065.2022.10005419.

