MOVIE RECOMMENDATION SYSTEM USING COLLABORATIVEFILTERING
1Associate Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, GITAM University, Visakhapatnam, AndhraPradesh, 530045, India. 2,3,4,5,6B. Tech Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, GITAM University, Visakhapatnam, AndhraPradesh, 530045, India.***

Abstract -
Nowadays, the recommendation system is crucial and is used bymany significant applications. The proliferation of applications, the emergence of a global village, and the availability of a large amount of information are the results of the recommendation system. Anoverview of the approaches and techniques developed by this study introduces a recommender system based on collaborative filtering,which has evolved over time to include contentbased and hybridapproaches. The study examines various techniques used forcollaborative filtering, including matrix factorization, user- basedand item-basedrecommendation. It also serves as a guide for future research in this field. By analyzing user preferences and eating habits, we extract aspect-based ratings from reviews and recommend reviews accordingly. Furthermore, theproposed movie recommendation system is tested against multiple evaluation criteria and performs better than existing approaches. Through extensive research and review of numerous papers, it was discovered that content-based filteringtypicallyreliesonasingle techniqueforconverting text into vectors for recommendations and a single approachtodetectsimilaritybetweenvectors.Thinkofitas a hybrid strategy that only uses a content-based filtering method. The way we search for exciting items has revolutionized today's recommendation systems. It is vital to advise mobile users to download OTT movie apps. To help you choose suitable movies, it thoroughly summarizes user preferences, reviews, and[SS1] feelings. It requires absolute accuracy and timeliness, yet this information filtering technique predicts user preferences. A recommender systemis a system that aims to predict or filter selections according to userchoices. OTT platforms, search engines, articles, music, videos, and other similar platforms are typicalapplications ofrecommender systems. Inthiswork,wetendtoprovideamoviedesignsystembased on a common approach. It's a supported collaborative filtering strategy that takes user-provided knowledge, analyses it, and then suggests the most appropriate movie fortheusers.
INTRODUCTION
Becauseoftherichnessofknowledgeamasseduptothe twenty- first century and the increasing rate at which informationisgushingovertheinternet,thereisagreat dealofconfusionoverwhattoconsumeandwhatnotto ingest. Even on YouTube, there are always a ton of videosavailableifyou wanttoseeoneaboutaparticular concept. Since the results are suitably ranked, there might not be much of a problem right now, but what if they weren't? In this situation, we would undoubtedly spendalotoftimelookingforthebestmoviethatfitsus andmeetsourneeds.Whenyoulookforsomethingona website, this is what happens the algorithm could be able to offer you recommendations the next time you visit a particularwebsite without you even having to search. This feature is fascinating, isn't it? A recommendersystem'smainresponsibilityistopresent the user with the items that are the most pertinent. Recommendation engines are used by Amazon, Flipkart, Netflix, and YouTube to propose videos, items, movies, and other content. Regardless of what you do on these websites, a system is in place that tracks your activity and makes suggestions for activities or products that you are very likely to be interested in. This research paper addresses the logic behind movie suggestions, conventionalmovierecommendationsystems,problems with conventional movie recommendation systems, and a suggested fix for an AI-based personalized movie recommendationsystem.Therearealreadyalotofwellknown movie recommendation datasets available on Kaggle and other sites. Movie lens, the TMDB Movie Dataset, and the Netflix dataset are a few of the wellknown datasets. Websites like Netflix, Amazon Prime, and others employ movie recommendations toincrease revenue or profits by eventually enhancing the user experience. In reality, in 2009 Netflix conducted a competitionwithaprizepoolof about$1million($1M) for creating at least 10% upgrades to the current system.Aswaspreviouslymentioned,wehaveaccess to a large amount of data, and since we are not interested in everything thatis available tous, we must filteritinordertouseit.
To filter the data, filtering tactics are needed. Different filtering methods or movie recommendation algorithms can be used to create a recommendation system. The main algorithms forfiltering or suggesting moviesareasfollow
1.1 Content Based Filtering:
A content-based recommender system tries to infer user characteristics or behavior from the characteristics of an objecttowhichtheuserrespondsfavourably.
to produce the optimal results. It is the result of the preferencesandactsofnumerousmoviegoers.
This movie recommendation system and the ML algorithm itis based on are built on the history of each user in the database. The interaction of all system users with articles is absolutely necessary for collaborative filteringto work. Sincecontent-based filtering only uses the user's input for modelling, each user of this MLbased recommender systemhas an impact on the final product. In collaborative filtering, we share a lot of similarities,someofthemareasfollows:
1.2.1Jaccard similarity:

A common proximity measurement called Jaccard Similarityisusedtocomparetwoobjects,suchtwotexts, toseehowsimilartheyare.TheJaccardsimilaritycanbe used to find similarities between two collections or two asymmetricbinaryvectors.
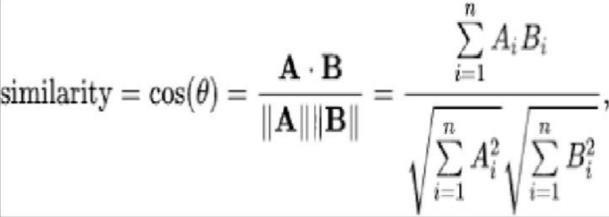
Fig.1 ContentBasedFiltering
The two columns after that both humor and action
Describethegenresofthefilm.Nowthatweareawareof which individuals favor certain genres, we may find characteristics that are uniqueto that person based on howthoseindividualrespondstofilmsinthatgenre.
Using the feature vector created to embed the user in an embedding space after we are informed of the user's preferencesprovide recommendations to the user based on those preferences. The feature vectors for the item and the user- selected feature vectors from previous recordsareusedtogeneratethesimilaritymetrics,which will be covered in more detail later, during recommendation. The best few are then suggested. Content- based filtering does not require other users' dataduringrecommendationstooneuser.
1.2 Collaborative Filtering:
Collaboration does not need the provision of item characteristics. Each user and item are described by a featurevectororembedding.
Both users and things can be embedded by it. The same embeddingspacecontainsbothusersanditems.
Theresponsesofotherusersaretakenintoconsideration whenproposing a certain individual. In order to suggest items to a particular user, it maintains track of their favouriteitemsaswellas those of users who behave and have tastes similar to theirs. It uses customer feedback on a range of products to generatesuggestions.
Asthenamesuggests,thisfilteringstrategyis basedona combination of pertinent user and other user activities. Thesystem compares and evaluates these acts in order
1.2.2 Cosine similarity:
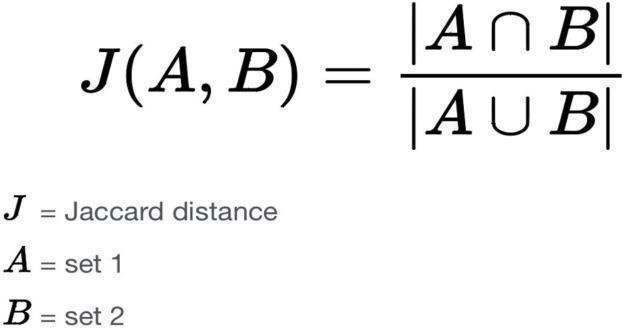
In an inner product space, two vectors are compared using cosine similarity The cosine of the angle between twovectorscan be used to calculate whether or not they arepointinginthesamegeneraldirection.
1.2.3 Pearson similarity:
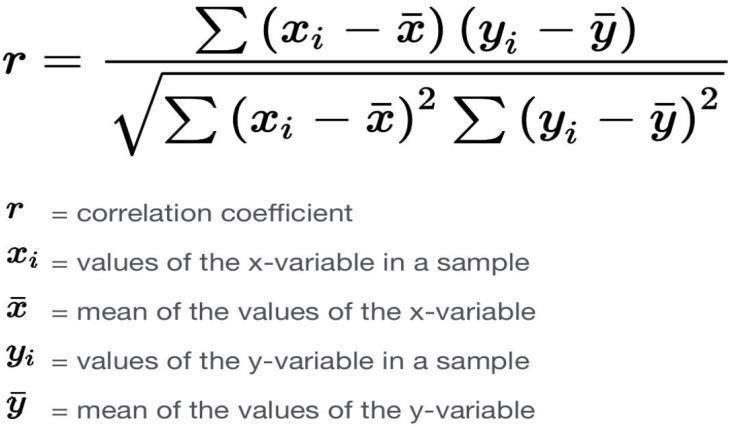
ThePearsoncorrelationcoefficientassessesthestrength ofalinearrelationshipbetweentwovariables.Itsvaluecan be between -1 and 1, where -1 denotes a total linear correlation that is negative, 0 denotes a lack of relationship, and +1 denotes a total linear correlation thatispositive..
Knowledge-based filtering:
If a recommender system provides recommendations based on the user's specific requests rather than the user'sratinghistory,itisaknowledgebase.Theusercan berequiredtoprovideasetofstandardsorspecifications aswellasanillustrationofwhatthefinalproductshould look like. Following a search of the item database, the algorithmreturnsresultsthatarecomparable.
1.4 Deep Neural Networks Model:
A deep neural network (DNN) is an ANN with multiple hidden layers between the input and output layers. Like flat ANNs, DNNs can model complex nonlinear relationships.
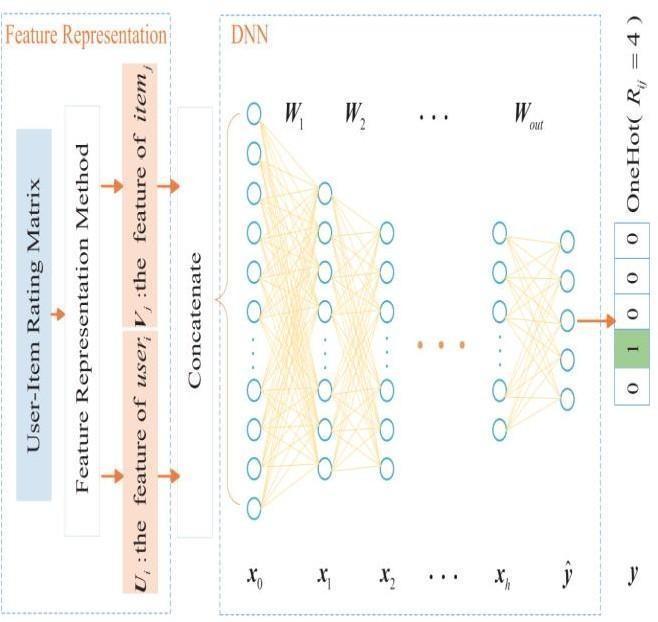
Neuralnetworks'mainobjectiveistoreceiveavariety of inputs, do more complex calculations, and produce outputs for practical problems like categorization. It solely supports transfersbetweenneuralnetworks.
Neural networks are frequently employed in supervised learning and reinforcement learning tasks. Layers are joinedtooneanothertoformthesenetworks.
Deep learning has a potentially enormous number of hidden layers,mostofwhicharenonlinear.Considerthat thereare1000layers.
Performance-wise, DL models outperform conventional MLnetworks.
Lossfunctionminimizationandnetworkoptimizationare thetwomainapplicationsofgradientdescent.
Acrucialcomponentofdeeplearningmodelsaretraining datasets. In addition, backpropagation is the most commonapproachusedtotrainDLmodels.
Large neural networks with intricate input/output transformationsaretrainedusingdeeplearning(DL).
1.4.1
Fig.2 DeepNeuralNetworks
Sources of user-item interactions:
Implicit Feedback: Based on the user's clicks, searches, and purchases, the preferences and dislikes of theuseraremonitoredand recorded.There are plenty of them,butnooneobjects.
Explicit Feedback: When a personreacts toor rates a product,theyareexpressingtheirpreferencesanddislike Althoughtherearefewerofthem,ithasbothpositiveand negativeinputs.
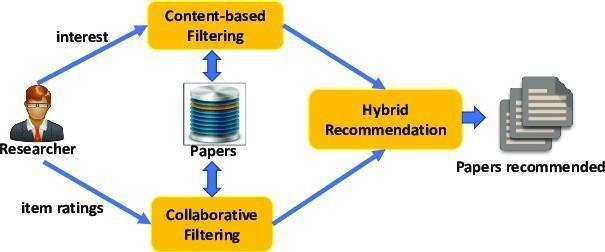
1.5 Hybrid Filtering:
A hybrid recommendation system blends collaborative filtering methods with content-based filtering approaches. Mixing collaborative and content-based filtering could help us get around the problems we run into when employing them independently, and in some situations, it might even be more effective. There are many ways to put into practise hybrid recommender system techniques, such as employing content and collaborative-based methods to produce predictions separately, then combining the predictions, or simply improvingacontent- basedapproach with collaborativebased method capabilities (and vice versa).Numerous research evaluates the effectiveness of hybrid approaches to conventional procedures and come to the conclusion that using hybrid methods yields more accuratesuggestions.

Fig.3 HybridRecommenderSystem
1.5.1 Types of Data for Generating a RecommendationSystem:
The approaches allow us to categories the data into two categories from which we can create a recommendationsystem:
-
• Explicit Feedback: data that explicitly includes user feedback. Explicit feedback is a sort of user evaluation that expresses the user's feelings towards the product,suchaswhetherheenjoyeditornot.
Implicit Feedback: This data may contain information like c licks, movies watched, music played, and other activitiesratherthantheuser'sratingorscore.
We'll discuss implicit feedback's significance because, in thispiece,we'lldeveloparecommendationsystembased on it. We attempted to define both explicitly in the previoussection.andimplicitfeedback.Solet'stalkabout a recommender that is basedonexplicitinputandmakes suggestions based on ratings, like making book recommendations based on user reviews. The recommender is now focusing on the rating; however, it does not take into account the book a user ultimately decides to read. If ratings are not available, this could result in the recommendation being in a state of incompleteinformation.
Information on which books have received the most or least votes, or which books have been selected by the majority of people, can be a useful source of information forarecommendationsystemtomakethemostofitself..
Because the user chooses which objects to rate and the left receives a blank rating, it is extremely clear that the missing ratings are more likely to be bad. Alternatively, we can say things that we don't think others will agree with.Withoutrankingthem,weleftthem.
These findings inspired us to develop a model that can function with implicit feedback. Additionally, Light FM, a library, can assist us in creating a recommendation systemonimplicitfeedback.
. Losses used by Recommendation Systems:
There are two ways we can create recommendation systems,eachusingadifferentlossstrategy:
When the user interacts favorably with the data and the ROC AUC needs to be optimized, we can utilize the Bayesian Personalized Ranking (BPR) pairwise loss approach. Using thepairwise loss, we seek to maximise the difference between predictions for positive and randomlychosennegativefeedback.
Weighted Approximate-Rank Pairwise (WARP) loss: this iscrucialwhenthereispositivefeedbackinteractionand we need to optimize particular top recommendations. Thisstrategy maximizes the rank of positive input by continually sampling the negative feedback until it finds theonethatisdefyingtherank.
2.LITERATURE REVIEW

Basedon"Content-basedrecommendationsystems,"M.J. Pazzani and D. Billsus, published in The Adaptive Web, Springer, Berlin, Germany, pages (325–341). In order to provide items to consumers, content-based recommendation systems take advantage of commonalities between items. We have reviewed and rated movies, and this recommender system makes suggestionsbasedontheirdescriptionorfeatures.
The topic of "Probabilistic matrix factorization," by A. Mnih and R. R. Salakhutdinov, in Proc.Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst., 2008, pp. (1257–1264,) is merging latent features of the individual and properties of the object to fittheappropriateratingscore.whenthesquareerrorof thelossfunctionisminimized.
For the improvement and performance of hybrid and content based X. Wang and Y. WangThe paper titled "Enhancing Content-Based and Hybrid Music RecommendationusingDeepLearning"waspresentedat the22ndACMInternationalConferenceonMultimediain 2014, with a focus on utilizing deep neural network models to improve the accuracy of music recommendation systems.Theaim ofthisapproachisto increasetheprecisionofpredictions.
E.Arisoy,T.N.Sainath,B.Kingsbury,andB.Ramabhadran, ‘‘Deepneuralnetworklanguagemodels,’’inProc.NAACLHLTWorkshop,WillEverReallyReplaceN-GramModel? 2012, pp. (20–28). is based upon Using the forward propagation approachin a deep neural network model, which uses the latent properties of users and things as inputstopredictthescore.HereweusedtheDNNmodel and ReLU is activation function and entropy for evaluatingdifferencestogetanequation.
In thED.Ciregan, U. Meier, and J. Schmidhuber, ‘‘Multicolumndeepneuralnetworksforimageclassification,’’in
Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. Pattern Recognit. (CVPR), Jun. 2012, pp. (3642–3649) based upon Our deep artificial neural network designs, which are biologically plausible, can. Convolutional winner-take-all neurons with small receptive fields produce dense networks with nearly the same number of sparsely linked neural layers.The user profile is used to generate a recommendation. Arecommendation is made by contentbased filteringbasedsolelyononeuser'sXprofile.Based ontheuser&X'sprioractivity,thesystemtriestosuggest articlesthatarecomparabletothisarticle.
3.PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION & OBJECTIVES
3.1 PROBLEM STATEMENT
The main issues with the method for suggesting movies include false user reviews, an exaggerated rating, and irateconsumers.Asanoutput,takeintoaccountnotjusta rating choice but also an "explanation" of why the user wouldenjoythemovie.
Arecommendationsystem'sobjectiveistoofferusersthe bestpossiblesolutions.
Choose the movies that consumers wish to see based on theirpost-viewingratings.
Alternativesinclude:
Create a list of movies that at least one user shouldstartwatchingastheirnextchoice.
3.2 OBJECTIVES
To increase the impact of movie review endorsement.To makeiteasierforpeopletomanagetheirtime.
To provide consumers with a pleasant user experience thatenablesthemtouseflexible.

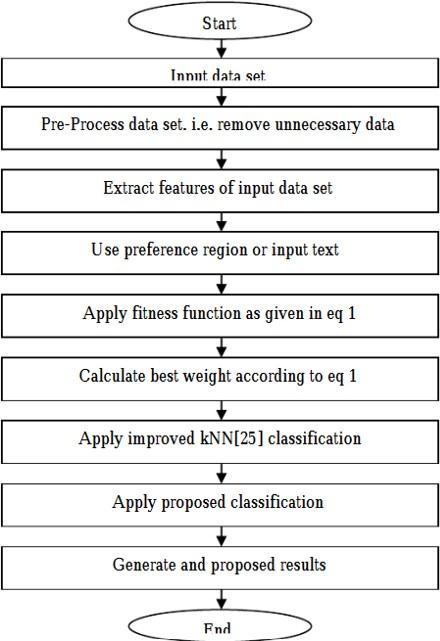
4.SYSTEM DESIGN
Fig.4 FlowchartofthecollaborativeFilteringApproach
5.IMPLEMENTATION
In the first step we import the python libraries pandas and Numpy to perform cosine similarity vectorization considerably more quickly and effectively,. To reach the highest achievable time complexity, we shall make the best useofthelibrariesastheyaremadeavailable.
Following that, we will download two Kaggle data sets containingtheinformationrequiredtomakesuggestions. We combine two data sets into a single Data Set to improveperformance.
We will next read the Data Sets and Apply Data Preprocessing operations on them. Data preprocessing functionsincludedatacleaning,removingunwanteddata rows, unidentifieddata columns, and modifying data as Nowwechangethedatatypesforthecolumnsanddefinea function to analyse the data, which allows us to understand what the data indicates and how to use it. Thenullvaluesarethenremovedfromthedatabase.
Finally,wecreatethetagattributebycombiningallofthe columns such as overview, genres, keywords, cast, crew, andsoon.
TheprimarycodeissimplymadeupofthePickleFilesthat wereceivedafterrunningtheGoogleCollabextensivelyto obtainthosepicklefilesandstreamlit.
As we know, thesePicklefiles includedata thathas been processed and vectorized in order for us to make decisionsinthefinalsection.Atthesametime,weaddeda DeepNeuralNetworkCodebymodifyingthemaincode.
HereiswherewecreateawebsitethatloadsotherURLs, suchasonethatretrievesmoviepostersfromanexternal link.
When a user inputs the proper information to receive recommendations, the website will function according to the Main code. The user is aware that they won't be able to access the pickle files; instead, all they have access to is this website, which is essentially made possiblebythemaincode.
Thiscodeservesasanintermediarybetweentheuserand thepicklefiles,data,and,ultimately,therecommendation system.
6.TECHNOLOGIES
The technologies used for the implementation are: Pythonlibraries:
Pandas:Inordertowork best withrelational orlabelled datasets, Pandas is a well-known open-source Python library fordata analysis and manipulation. It provides a variety of data structures and procedures for working with matrices and numerical data. The following are someofthemaincharacteristicsofpandas.:
Atwo-dimensionaltablewithrowsandcolumnsisknown as a data frame and is the main data structure used by Pandas. Manysorts of data can be stored and handled usingdataframes..
Pandas include powerful data manipulationtools such as filtering,sorting,grouping,merging,andreshaping.
Pandascanreadandwritedatafromandtoawiderange of file formats, such asExcel, CSV, SQL databases, and others.
NumPy: The name NumPy refers to a free and opensource Python package for scientific computing. Multidimensional array objects and processing routines are also included in this package.Arrays can be used by NumPy to execute logical and mathematical calculations. ThefollowinglistofNumPy'simportantfeatures:
A potent N-dimensional array object that can be used to represent vectors, matrices, and higher-dimensional arrays is included in the NumPy programming language. This makes applying mathematical operations to data arrayssimple.
For performing common mathematical operations like addition, multiplication, and trigonometric functions, NumPy provides optimised numerical functions. These operations are considerably quicker than comparable Python operations and are designed to work with NumPy'sN-dimensionalarrays
NumPy includes a powerful linear algebra module that includesfunctionsforperformingmatrixoperationssuch asmultiplication,inversion,anddecomposition.
Pickle:Pickle is commonly used to serialize and deserialize a Python object structure. A Python object must be transformed into a byte stream before it can be savedtoafileordatabase,maintainedacrosssessions,or sentoveranetwork.
Streamlit:A Python framework calledStreamlit makesit simple to create interactive web applications for data science and machine learning. You don't need to write HTML, CSS, or JavaScript code to design bespoke user interfaces,dashboards,andvisualizationswithStreamlit
The following are the Key characteristics of Streamlit include: Automatic responsiveness: Whenever you make changestoyourapp'scodeordata,Streamlitinstantlyrerendersit.
Widgets that are simple to use: You can easily add widgets to your app to make it responsive and interactive.
Easy integration with popular Python libraries like Pandas, Matplotlib, and Scikit-learn: Streamlit integrates withtheselibrariesseamlessly.

HTML: Webpagesaretypicallycreatedusingthemarkup language HTML (Hypertext Markup Language). Using numerous elements and tags, it is a text-based language that isused to define the organisation and content of a webpage.WebbrowsersparseHTMLcode,convertingit intoavisualrepresentationoftheonlinepage.
TherearemanydifferentcomponentsinHTML,andeach onehasaspecificfunction.
Headings,paragraphs,lists,links,pictures,andtablesarea fewtypical HTML elements. These components are used to organise the information on a web page and offer supplementary details, such as formatting and semantic meaning.
Usually, a text editor or an integrated development environmentareusedtobuildHTMLdocuments(IDE).as soonas the HTML CSS: The visual styling of HTML and
XML documents is described using the language CSS (Cascading Style Sheets). It enables web designers to isolateadocument'sdisplayfromitsinformation,making it simpler to produce appealing and consistent designs acrossnumerouspagesandwebsites.
CSS specifies font size, colour, placement, and layout by applying rules to elements insidea document. The style> tagcanbeusedtoincorporatetheserulesdirectlyintoan HTMLdocumentorinaseparateCSSfile.
Javascript:High-level programming languages like JavaScript are frequently used to develop interactive onlineapps,games,anddynamicwebcontent.Itisaclientside scripting language, which means that rather than being performed on a server, it does itonthe user's web browser.
Because it can be used for a variety of tasks, such as producinganimations,modifyingHTMLandCSS,verifying form input,andmanaging user interactions, JavaScript is renownedforitsflexibility.Itservesasthefoundationfor a number of well- known web frameworks and libraries, includingReact,Angular,and Vue. Google colab:A cloudbased development environment called Google Colab (shortfor"Collaboratory") enablesyoutocreateand run JupyterNotebookdocuments,whichletyouwriteandrun code in a web browser. Google's Colab service, which is available for free, gives customers access to powerful computingtoolsincludingCPUs,GPUs,andTPUsaswellas well-known machine learning frameworks and libraries likeTensorFlow,Keras,PyTorch,andOpenCV.
Working on Python projects, data analysis, machine learning, deep learning, and other tasks is possible with Colab. Also, youcan quickly share your notebooks and workinreal-timecollaborationwithothers.
OneofthekeybenefitsofusingColabisthateverythingis managed for you, so there's no need to set up and maintainyourowndevelopmentenvironment.
RESULT
7.CONCLUSION
A number of datasets can be used to create a movie recommendation system. However, we will use a datasetcontaining the movie's metadata for this endeavor (cast, crew, budget, etc...). This project involved creating and implementing an algorithm for a collaborative filtering recommendation system for a movie recommendation system. In this customized recommendationsystem,thetopnmovies aresuggested to the active User using the singular value decomposition approach andtheUser-basedcosinesimilarityalgorithm.
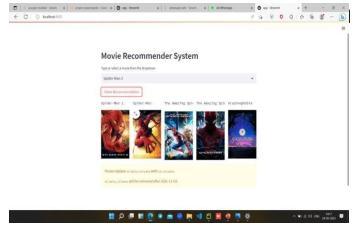
The findings demonstrate that the combined recommendations outperform the separate deep neural networkalgorithmrecommendations.
Future work will focus on investigating the performance of recommendation systems using alternative deep learning techniques, such as the convolutional neural networkapproach.
9. REFERENCES
1. D. G. Adomavicius and A. Tuzhilin, ‘‘Toward the next generation of recommender systems: A survey of the state-of- the-art and possible extensions,’’IEEETrans.Knowl. Data Eng., vol. 17,no.6,pp.734–749,Jun.2005.
2. Z. Huang, D. Zeng, and H. Chen, ‘‘A comparison of collaborative- filtering recommendation algorithms for e- commerce,’’ IEEE Intell.Syst.,vol.22,no.5,pp.68–78,Sep./Oct.2007.
3. X. Su and T. M. Khoshgoftaar, ‘‘A survey of collaborative filtering techniques,’’ Adv. Artif. Intell., vol.2009,Aug.2009,Art.no.421425.
4. D. Ciregan, U. Meier, and J. Schmidhuber, ‘‘Multicolumn deep neural networks for image
classification,’’ in Proc. IEEE Conf. Comput. Vis. PatternRecognit.(CVPR),Jun.2012,pp.3642–3649.

5. F. Richardson, D. Reynolds, and N. Dehak, ‘‘Deep neural network approaches to speaker and language recognition,’’ IEEE Signal Process. Lett., vol. 22, no. 10,pp.1671–1675,Oct.2015.
6. E. Arisoy, T. N. Sainath, B. Kingsbury, and B. Ramabhadran, ‘‘Deep neural network language models,’’ in Proc. NAACL-HLTWorkshop, Will Ever ReallyReplaceN-GramModel?2012,pp.20–28.
7. J. S. Breese, D. Heckerman, and C. Kadie, ‘‘Empirical analysis of predictive algorithms for collaborative filtering,’’ in Proc. 14thConf. Uncertainty Artif.Intell., 1998,pp.43–52.
8. J.L.Herlocker,J.A.Konstan,A.Borchers,andJ.Riedl, ‘‘An algorithmic framework for performing collaborative filtering,’’in Proc. 22nd Annu. Int. ACM SIGIR Conf. Res. Develop. Inf. Retr., 1999, pp. 230

237.
9. B. Sarwar, G. Karypis, J. Konstan, and J. Riedl, ‘‘Itembased collaborative filtering recommendation algorithms,’’inProc.10thInt.Conf.WorldWideWeb, 2001,pp.285–295.
10. T. Hofmann and J. Puzicha, ‘‘Latent class models for collaborative filtering,’’ in Proc. IJCAI, vol. 99, no. 1999,pp.1
61999.
11. K.MiyaharaandM.J.Pazzani,‘‘Collaborativefiltering withthe simple Bayesian classifier,’’ in Proc. Topics Artif.Intell.(PRICAI),2000,pp.679–689.
12. S. Vucetic and Z. Obradovic, ‘‘Collaborative filtering using aregressionbasedapproach,’’Knowl.Inf.Syst., vol.7,no.1,pp.1–22,2005.
13. J. Liu, Y. Jiang, Z. Li, X. Zhang, and H. Lu, ‘‘Domainsensitive recommendation with user-item subgroup analysis,’’ IEEE Trans. Knowl. Data Eng., vol.28,no.4,pp.939–950,Apr.2016.
14. Y. Koren, R. Bell, and C. Volinsky, ‘‘Matrix factorization techniques for recommender systems,’’ Computer,vol.42,no.8,pp.30–37,2009.
15. K. Yu, S. Zhu, J. Lafferty, and Y. Gong, ‘‘Fast nonparametric matrix factorization for large-scale collaborative filtering,’’ in Proc. 32nd Int. ACM SIGIR Conf.Res.Develop.Inf.Retr.,2009,pp.211–218.
16. B. Sarwar, G. Karypis, J. Konstan, and J. Riedl, ‘‘Application of dimensionality reduction in recommender system A case study,’’ Dept. Comput. Sci. Eng. Univ. Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, USA, Tech.Rep.TR-00-043,2000.
17. Mnih and R. R. Salakhutdinov, ‘‘Probabilistic matrix factorization,’’inProc.Adv. NeuralInf.Process.Syst., 2008,pp1257–1264.
18. R. Salakhutdinov, A. Mnih, and G. Hinton, ‘‘Restricted Boltzmann pp. 791–798.Georgiev and P. Nakov, ‘‘A non-IID framework for laborativefiltering withrestrictedboltzmannmachines,’’inoc. Int. Conf. Mach.Learn.,2013,pp.1148–1156.
BIOGRAPHIES
Dr. S.V.G. REDDY completed M- Tech (CST) from CST) from Andhra
Universityandhasobtained a PhD in Computer Science and Engineering fromJNTU Kakinada.HeisanAssociate Professor, the Department of CSE,

GIT,GITAMUniversity. His area of researchworkis data mining, machinelearning and deep neuralnetworks. He has guided various B. Tech and M. Tech projects and haspublicationsinseveraljournals.Hisareasofinterest are drug discovery, computer vision, brain-computer interface,climatechangeandwastemanagement.
Putchakayala Meher Sowjanya currently pursuing B.Tech-(CSE) from GITAM Institute of Technology, GITAM (Deemed to be University), Visakhapatnam. Her areas of research work are machine learning and deep learning. Her areas of interest are Recommended Systems and data science.

Pavan Kumar Reddy currently pursuing B.Tech-(CSE) from GITAM Institute of Technology, GITAM (Deemed to be University), Visakhapatnam. His areas of research work are machine learning and data Science.HisareasofinterestareDeep Learning and Recommended Systems.
Bavisetti Sai Saketh currently pursuing B.Tech-(CSE) from GITAM Institute of Technology, GITAM (Deemed to be University), Visakhapatnam.His areasof research work are machine learning and data science.Hisareasofinterestaredeep learninganddatascience.
Lekkala Yaswanth Kumar currently pursuing B.Tech-(CSE) from GITAM Institute ofTechnology, GITAM (Deemed to be University), Visakhapatnam. His areas of research work are machine learning and artifitial intelligence. His areas of interest are Recommended Systemsandneuralnetworks.



Karri Viswa Abhiram Reddy currently pursuing B.Tech-(CSE) from GITAM Institute of Technology, GITAM (Deemed to beUniversity),Visakhapatnam. His areas of research work are web development and machine learning. His areas of interest are artifitial intelligence andRecommendedSystems


