CLOUD BASED WEB-APPLICATION FOR RAPID AND PRECISE DETECTION OF TUBERCULOSIS USING DEEP LEARNING
Dineshkumar Ganesan1 , N. Naveenkumar2
1PG Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Muthayammal Engineering College, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu.
2Assistant Professor, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, Muthayammal Engineering College, Namakkal, Tamil Nadu.
ABSTRACT - Tuberculosis (TB) is a communicable disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis, which primarily affects the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. TB is a major global health problem, and the World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that around 10 million people worldwide became ill with TB in 2019. Early detection and treatment of TB are essential for effective disease management and prevention of transmission. In this work, we have detected TB reliably from the chest X-ray images using image pre-processing, data augmentation, image segmentation, and deep-learning classification techniques. Several public databases were used to create a database of 4000TB infected and 4000 normal chest X-ray images for this study. Nine deep CNNs and SVM (ResNet18, ResNet50, ResNet101, ChexNet, InceptionV3, Vgg19, DenseNet201, SqueezeNet, and MobileNet) were used for transfer learning from their pre-trained initial weights. They were trained, validated, and tested for classifying TB and non-TB normal cases. Three different experiments were carried out in this work: segmentation of X-ray images using two different U-net models, classification using X-ray images, and that using segmented lung images
Traditional diagnostic methods for TB, such as sputum microscopy and culture-based techniques, have limitations in terms of sensitivity and specificity, particularly in detecting TB in its early stages. Machine learning algorithms, such as Support Vector Machine (SVM), have shown promise for the accurate detection of TB. However, classification using segmented lung images outperformed that with whole X-ray images; the accuracy, precision, sensitivity, F1-score, and specificity of DenseNet201 respectively for the segmented lung images. The paper also used a visualization technique to confirm that CNN learns dominantly from the segmented lung regions, resulting in higher detection accuracy. Overall, a cloud-based web application for rapid and precise detection of tuberculosis using SVM would be a valuable tool in the fight against this disease, enabling healthcare professionals to make more informed decisions about diagnosis and treatment.
Index Terms: Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Restnet, Chexnet, Tuberculosis Detection, Support Vector Machine(SVM)

I. INTRODUCTION1
Tuberculosis(TB)isacontagiousdiseasethatremainsa significant global health concern, affecting millions of people each year. Early and accurate detection of TB is critical for effective treatment and control of the disease. Support Vector Machines (SVM) is a machine learning algorithm that has shown promising results in the classification of medical images for the detection of TB. In recent years, cloud computing has become increasingly popularforitsscalability,flexibility,andcost-effectiveness. Cloud-based applications have the potential to provide rapid and precise detection of TB using SVM, which can significantly improve the accuracy and efficiency of TB diagnosis.Acloud-basedwebapplicationfortherapidand precisedetectionofTBusingSVMwouldenablehealthcare professionals to upload medical images and receive a prediction on whether or not the images contain evidence
of TB. The application could be accessible from anywhere with an internet connection, making it particularly useful in areaswithlimitedresourcesandmedical infrastructure [2]-[4]. In this project, we propose the development of a cloud-based web application for rapid and precise detection of TB using SVM. We will leverage open-source toolsandcloudservicestobuildtheapplication,whichwill be designed to be user-friendly and accessible to healthcare professionals. The SVM model will be trained usinga datasetofmedical images,andtheapplicationwill interfacewiththemodelthroughanAPI,enablingusersto upload images and receive predictions on the presence of TB. The web application could be designed to be userfriendly and accessible, with clear instructions on how to upload images and interpret the results. It could also includeadditionalfeaturessuchastheabilitytodownload the results or share them with healthcare professionals. Overall, a cloud-based web application for rapid and precise detection of tuberculosis using SVM would be a
valuable tool in the fight against this disease, enabling healthcareprofessionalstomakemoreinformeddecisions aboutdiagnosisandtreatment[6]
An increase in accuracy of TB detection from chest radiographs with a robust and versatile method can make computer aided automatic diagnostic tools more reliable [11].Theclassificationaccuracycanbeimprovedeitherby using different deep learning algorithms or by modifying the existing outperforming algorithms or combining severaloutperformingalgorithmsasanensemblemodel.
Due to the advancement of computer vision approaches and the advancement of digital techniques several CAD techniques are used recently. With this advancement, TB canbedetectedquicklyandovercomefurthertransmission when it is determined early. CAD has the ability to speed upamassscreeninginTB-spreadingareas[8]
A. Objective
The application should be able to process and analyze large amounts of data related to patients' symptoms, medical history, and test results, and provide accurate diagnosis and treatment recommendationsinreal-time.
The application should be user-friendly, easily accessible, and compatible with different devices andoperatingsystems.
It should also ensure data security and privacy, comply with relevant regulations and standards, and have robust backup and disaster recovery mechanismsinplace.
B. Data process Model
Data Collection: Collect patient data, including symptoms, medical history, and test results from various sources such as hospitals, clinics, andlaboratories.
Data Preprocessing: The collected data must be cleaned, transformed, and preprocessed before beingusedforanalysis.
Feature Extraction: Identify relevant features from the preprocessed data to create a feature setforSVM.
SVM Model Training: Use the preprocessed data to train SVM models that can accurately detect TBinpatients.
Model Validation: Validate the trained SVM models on a separate dataset to ensure the accuracyandreliabilityofthemodels.
Deployment of the Application: Deploy the trained SVM models as a web application on a cloud-basedplatform.
User Interface: Develop a user-friendly web interface for the application that allows healthcare professionals to input patient data, view analysis results, and receive treatment recommendations.
Security and Privacy: Ensure data security and privacy by implementing appropriate measures such as encryption, access control, and data anonymization.
Compatibility and Scalability: Ensure that the application is compatible with different devices and operating systems and can be scaled up to handlelargevolumesofpatientdata.
The project should adhere to ethical guidelines and regulations related to data privacy and protection, and involve extensive testing and quality assurance to ensure that the application meets the required standardsofaccuracyandreliability.
C. Need for project
The need for the development of a cloud-based web application for the rapid and precise detection of tuberculosis using Support Vector Machine (SVM) algorithmsisdrivenbyseveralfactors:
High incidence of tuberculosis: According to the World Health Organization (WHO), tuberculosis is one of the top 10 causes of death worldwide, and in 2020, an estimated 10 million people fell ill with TB globally. TB is a highly contagious disease, and early detection and treatment are critical in preventing its spread and reducing mortalityrates.
Inefficient and time-consuming diagnostic methods:ThecurrentmethodsofdiagnosingTB involve sputum microscopy, chest X-rays, and culture-based methods, which can be timeconsuming, require specialized equipment and trained personnel, and may not be readily availableinresource-limitedsettings.
Limited access to medical expertise: In many

partsoftheworld,thereisashortageoftrained healthcare professionals who can accurately diagnose and treat TB, leading to delayed diagnosisandtreatment.
Technologicaladvancements:Advancesinmachine learning and cloud computing have made it possible to develop accurate and efficient diagnostic tools that can be accessed remotely, enabling healthcare professionals to provide timelyandeffectivetreatmenttopatients.
Therefore, the development of a cloud-based web application that uses SVM algorithms for the rapid and precise detection of TB has the potential to improve the efficiencyandeffectivenessofTBdiagnosisandtreatment, especially in resource-limited settings where access to medicalexpertiseanddiagnostictoolsislimited[2].
II. DEFINITIONS
Cloud-based:Referstoatypeofcomputingthatrelieson remote servers hosted on the internet to store, manage, and process data and applications, rather than on local servers or personal computers. Web application: Also known as a web app, it is a software application that is accessed through a web browser or web-enabled device and is designed to be used over the internet. Rapid detection: Refers to the ability of a diagnostic tool or method to produce results quickly, allowing for early detection and treatment of the disease. Precise detection: Referstotheaccuracyandreliabilityofadiagnostictoolor methodindetectingthedisease,minimizingfalsepositives orfalsenegatives.SupportVectorMachine(SVM):Atypeof machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression analysis, which works by finding the optimal boundary or hyperplane that separates the different classes or groups in the data. Tuberculosis (TB): An infectious disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium tuberculosis,whichprimarilyaffectsthelungsbutcanalso affectotherpartsofthebody.Itistransmittedthroughthe air when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Diagnosis: The process of determining the nature and cause of a disease or medical condition, usually through a combination of physical examination, medical history, and diagnostic tests. Treatment: The medical care and management provided to a patient with a disease or medical condition, aimed at improving their health outcomes and quality of life. In the case of TB, treatment usually involves a combination of antibiotics taken over severalmonths.
III. LITERATURE REVIEW

Tawsifur Rahman (2020), Tuberculosis (TB) is a chronic lung disease that occurs due to bacterial infection and is one of the top 10 leading causes of death. Accurate and earlydetectionofTBisveryimportant,otherwise,itcould be life-threatening. Detection from chest radiographs with a robust and versatile method can make computer-aided automaticdiagnostictoolsmorereliable.Theclassification accuracy can be improved either by using different deep learning algorithms or by modifying the existing outperforming algorithms or combining several outperforming algorithms as an ensemble model. MobileNet structure is built on depth-wise separable convolutions except for the first layer which is a full convolution.Alllayersarefollowedbybatchnormalization and ReLU nonlinearity with the exceptionofthefinal fully connectedlayerwhichhasnononlinearityandfeedsintoa Softmax layer for classification. A final average pooling reduces the spatial resolution to 1 before the fully connected layer. Counting depth-wise and pointwise convolutions as separate layers, MobileNet has 28 layers. The proposed method with state-of-the-art performance can be useful in the computer-aided faster diagnosis of tuberculosis.
Limitation:
Itisrequireshighcomputationalpowertoconstruct CNN
TakingConsuming
Algorithm:
ResidualNetwork(ResNet)
Stochastic Gradient Descent with Momentum(SGDM)
S. K. Sharma and A. Mohan (2013), Globally, tuberculosis (TB)stillremainsamajorpublichealthproblem.Indiaisa high TB burden country contributing to 26 percent of the globalTBburden.During1944-1980,TBbecametreatable and short-course chemotherapy emerged as the standard of care. When TB elimination seemedpossibleintheearly 1980s, the global human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) pandemic resulted in a resurgence of TB. The widespread occurrence of multidrug-resistant and extensively drugresistant TB (M/XDR-TB) is threatening to destabilize TB control globally. Atypical clinical presentationstill posesa challenge.Disseminated,military,andcrypticTBarebeing increasingly recognized. Availability of newer imaging modalities has allowed more efficient localization of
lesions and the use of image-guided procedures has facilitated definitive diagnosis of extrapulmonary TB. However, drug toxicities and drug-drug interactions still constitute a significant challenge. Recently, therehasbeen a better understanding of anti-TB drug-induced hepatotoxicity and its frequent confounding by viral hepatitis, especially, in resource-constrained settings; and immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) in HIV-TB. Quest for newer biomarkers for predicting a durable cure, relapse, discovery/repurposing of newer anti-TBdrugs,developmentofnewervaccinescontinuesto achievethegoalofeliminatingTBaltogetherby2050.
Khairul Munadi, Kahil Muchtar,NoviMaulina,Biswajeet Pradhan (2018), The latest World Health Organization (WHO) study in 2018 is showing that about 1.5 million peoplediedandaround10millionpeopleareinfectedwith tuberculosis (TB) each year. Moreover, more than 4,000 people die every day from TB. A number of those deaths could have been stopped if the disease was identified sooner. Due to the low contrast of TB chest X-ray (CXR) images, they are often is in poor quality. This work assesses the effect of image enhancement on the performanceofDL techniquetoaddressthisproblem.The employed image enhancement algorithm was able to highlight the overall or local characteristics of the images, including some interesting features. Specifically, three image enhancement algorithms called Unsharp Masking (UM), High-Frequency Emphasis Filtering (HEF), and Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization (CLAHE), were evaluated. The enhanced image samples were then fed to the pre-trained ResNet and EfficientNet models for transfer learning. In a TB image dataset, we achieved89.92%and94.8%ofclassificationaccuracyand AUC(AreaUnderCurve)scores,respectively.
Limitation:
Itisrequireshigherprocessingpower
Takingmoretimetoprocess
Algorithm:
AlgorithmofConvolutionalNeuralNetwork(CNN)
ResNetandEfficientNet

IV. ALGORITHM
A. Support Vector Machine (SVM)
Support Vector Machine (SVM) is a supervised machine learning algorithm used for classification and regression analysis.SVMisparticularlyusefulincaseswherethedata
isnotlinearlyseparable,meaningthedatacannotbeeasily separated into different classes using a straight line or hyperplane.
In SVM, the algorithm tries to find the hyperplane that maximallyseparatesthedifferentclassesintheinputdata. The hyperplane is chosen such that the margin between thehyperplaneandtheclosestdatapointsfromeachclass is maximized. These closest data pointsarecalledsupport vectors.
SVM can be used for classification tasks, where the algorithmpredictswhichclassaninputdatapointbelongs to based on the features of the input data point. SVM can also be used for regression analysis, where the algorithm predictsacontinuousoutputvaluebasedonthefeaturesof theinputdatapoint.
Inthecontextoftheproposedproject,SVMwillbe used for the classification of chest X-ray images as TB-positive or TB-negative, based on features extracted from the images.SVMhasshownpromisefortheaccuratedetection of TB using chest X-ray images, and the use of SVM in a cloud-based web application can enable rapid and precise TBdiagnosis,particularlyinresource-limitedsettings.
There can be multiple lines/decision boundaries to segregate the classes in n-dimensional space, but weneed tofindoutthebestdecisionboundarythathelpstoclassify thedatapoints
• This best boundary is known as the hyperplane of SVM
• The dimensions of the hyperplane depend on the featurespresentinthedataset,whichmeansifthereare2 features(asshownintheimage),thenthehyperplanewill beastraightline
• Andifthereare3features,thenthehyperplanewillbe a2-dimensionplane.
• We always create a hyperplane that has a maximum margin, which means the maximum distance between the datapoints.
PROs:
• SVM works relatively well when there is a clear marginofseparationbetweenclasses.
• SVM is more effective inhighdimensional spacesand isrelativelymemoryefficient.
• SVM is effective in cases where the dimensions are greaterthanthenumberofsamples.
B. Convolutional Neural Network (CNN)
ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks(CNNs)areaclassofdeep learning algorithms used for processing and analyzing visual data, such as images and videos. They are specifically designed to extract and learn hierarchical patternsandfeaturesfromtheinputdata.Thefundamental idea behindCNNsistouseconvolutionallayersthatapply filters (also known as kernels) to the input data. These filters detect specific features, such as edges, textures, or shapes, by performing a convolution operation on the input.
The convolution operation involves element-wise multiplication of the filter with a local region of the input data, followed by summing up the results. This process helps capture spatial dependencies and extract relevant features. CNNs typically consist of multiple layers, including convolutional layers, pooling layers, and fully connectedlayers.
The convolutional layers perform the convolution operation, while the pooling layers down sample the output, reducing its spatial dimensions. The fully connected layers at theendofthenetwork connectall the neuronsfromthepreviouslayerstomakefinalpredictions. During the training phase, CNNs learn to recognize patternsandfeaturesbyadjustingtheweightsofthefilters and the fully connected layers. This learning process is done through backpropagation, where the network's output is compared to the ground truth labels, and the weightsareupdatedtominimizethediscrepancybetween them. The optimization is achieved by using various optimization techniques, such as gradient descent or its variants
PROs:
Hierarchical featurelearning:CNNsaredesignedto automaticallylearnhierarchicalrepresentationsof featuresfromtheinputdata.
CNNsleveragetheconceptofconvolutiontoextract localfeaturesfromtheinputdata.
V. METHODOLOGY
A. DATASET UPLOAD
ItistheUIofthewebpagewhichcontainssingleupload button.Thispagecollectstheuploadedimageandgiveitas theinputforthedetectionmodel.
A UI (User Interface) containing a single upload button can be a simple and effective way to collect chest X-ray images from users for TB detection using the proposed cloud-basedwebapplication.
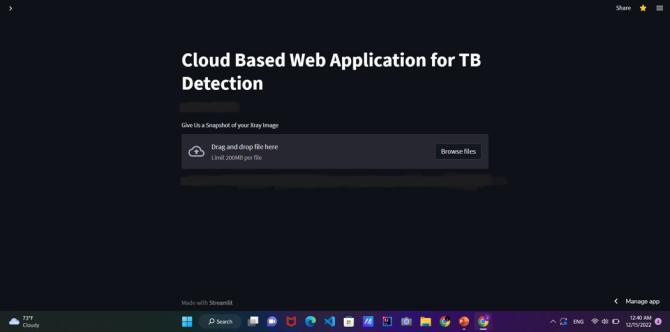
The UI can consist of a single web page with a clear and prominent "Upload Image" button. When the user clicks the button, they will be prompted to select a chest X-ray image file from their local device. Once the image is selected,itwillbeuploadedtothecloud-basedserver,and thedetectionmodelwillbetriggeredtoprocesstheimage.
The UI can also include a progress bar or loading animationtoprovidefeedbacktotheuserwhiletheimage isbeinguploadedandprocessed.Oncethedetectionmodel has processed the image, the UI can display the results of the TB detection, indicating whether the image is TBpositiveorTB-negative.
Overall, a simple and intuitive UI with a single upload button can enable easy and efficient collection of chest XrayimagesfromusersforTBdetectionusingtheproposed cloud-basedwebapplication.

B. TUBERCULOSIS DETECTION
The Tuberculosis detection model uses Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to detect weather the given patient’sdatasetisinfectiousforTuberculosis.
It uses series of ResNet’s (ResNet18, Resnet50, ResNet 101)andtotaliscalculatedbytakingaverage.
Using Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) for tuberculosisdetectionfromchestX-rayimagesisapopular approachinrecentresearch.

CNNs are a type of neural network that are particularly well-suited to image classification tasks. They work by applyingconvolutionoperationstotheinputimage,which enablesthenetworktoidentifypatternsandfeaturesinthe image. These features are then passed through a series of layersthatcanlearnincreasinglycomplexrepresentations oftheinputdata.
In the context of TB detection, CNNs can be trained on a large dataset of chest X-ray images, with labels indicating whethertheimagesareTB-positiveorTB-negative.During training, the network learns to identify features in the images thatareassociatedwithTB,andthesefeaturesare usedtomakepredictionsonnew,unseenimages.
One of the advantages of using a CNN for TB detection is thatthenetworkcanlearntoidentifysubtlepatternsinthe chest X-ray images that may not be visible to the human eye. Additionally, CNNs are able to learn from large datasets, which can improve the accuracy of the TB detectionmodel.
In the proposed cloud-based web application, the CNNbased TB detection model will take the uploaded chest Xray image as inputandoutputa predictionofwhetherthe image is TB-positive or TB-negative. The SVM algorithm canthenusethispredictionasinputtoimprovetheoverall accuracyoftheTBdetection.
C. IMAGE ENHANCEMENT
Image enhancement is performed using Deep Learning beforesubmittingthetestdatatotheDetectionModel
Performingimageenhancementusingdeeplearningbefore submittingtestdatatotheTBdetectionmodelcanimprove the accuracy and reliability of the detection results. Image enhancement techniques aim to improve the quality and visibilityoftheinputimages,whichcanhelpthedetection model to identify subtle features that may be indicative of TBinfection.
Deep learning techniques can be used for image enhancement by training a neural network to learn mappings between low-quality and high-quality images. The network can be trained on a large dataset of chest Xray images with high-quality ground truth labels and then used to enhance the low-quality test images by applying thelearnedmappings[].
One popular approach for image enhancement using deep learningistousegenerativeadversarialnetworks(GANs). GANsconsistoftwoneuralnetworks-ageneratornetwork that creates new images based on random noise, and a discriminatornetworkthattriestodistinguishbetweenthe generated images and real images. During training, the generator network learns to produce images that are indistinguishable from real images and can be used to enhancelow-qualitytestimagesbygeneratinghigh-quality versionsoftheinputimages.
In the proposed cloud-based web application, image enhancementusingdeeplearningcanbeperformedbefore submitting the test data to the TB detection model. This can improve the accuracy of the detection results and providemorereliablepredictionsforTBinfection.
D. F1-SCORE CALCULATION
F1-Scoreisthecombinedaccuracyofthemodel.
Along with the Prediction Classification Result the F1Scoreisalsodisplayedtotheuser.
Return Boolean result and the combined F1 Score of the modeltotheoutputobject.
TheaccuracyorF1-Scoreofthemodeliscalculatedby theformula
To calculate F1-score, first we calculate precision and recall:
Precision=TruePositive/(TruePositive+FalsePositive)
Recall=TruePositive/(TruePositive+FalseNegative)

where True Positive represents the number of correctly classified TB-positive samples, False Positive represents the number of falsely classified TB-positive samples, and False Negative represents the number of TB-positive samplesthatwerenotidentifiedbythemodel.

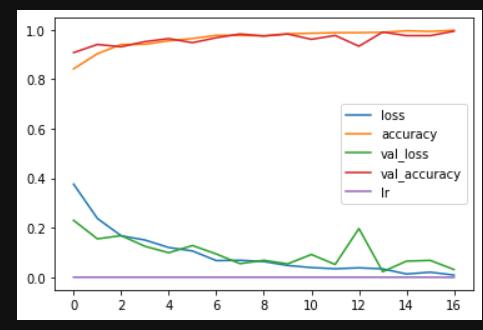
Once we have precision and recall, we can calculate F1scoreas:
F1-score=2*(Precision*Recall)/(Precision+Recall)
The F1-score ranges from 0 to 1, with a score of 1 indicating perfect precision and recall, and a score of 0 indicating no correct predictions. In general, a higher F1score indicates better performance of the TB detection model.
E. REPORT GENERATION AND DISPLAY
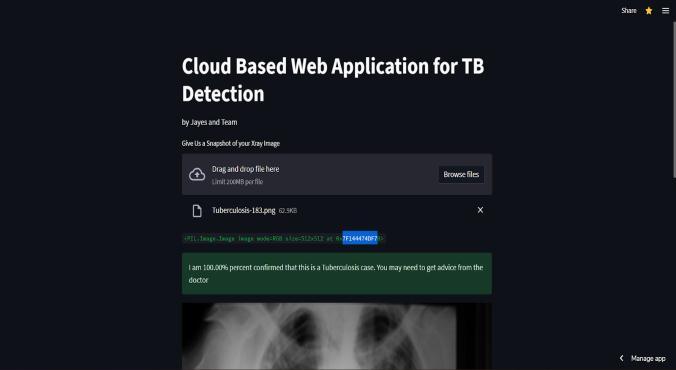
ThepositiveandnegativeresultalongwiththeF1-Scorein percentageisdisplayedtotheUserontheUI.
Displayingthepositiveandnegativeresultsalongwiththe F1-score in percentage to the user on the UI can provide valuable feedback on the performance of the TB detection model. The positive and negative results indicate whether the input sample is classified as TB-positive or TBnegative, while the F1-score provides an overall measure ofthemodel'saccuracyandreliability.
F1-score is a commonly used metric for evaluating the performance of a binary classification model like the TB detection model. The F1-score is the harmonic mean of precisionandrecall,andprovidesasinglescorethattakes bothmetricsintoaccount.
Precision is the fraction of true positive predictions out of all positive predictions, and measures the proportion of correct predictions among the positive predictions. Recall is the fraction of true positive predictions out of all actual positive cases, and measures the ability of the model to correctlyidentifyallpositivecases[17]
The F1-score is typically reported as a percentage, with a scoreof100%indicatingperfectprecisionandrecall,anda score of 0% indicating no correct predictions. By displayingtheF1-scoretotheuser,theycanquicklyassess the quality of the detection results and make informed decisionsaboutthenextstepsforpatienttreatment.
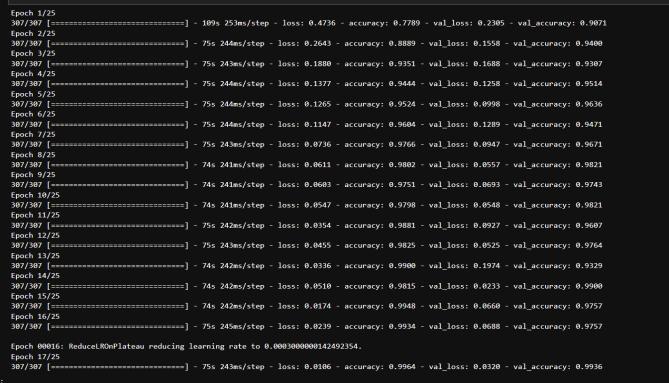
VI. RESULT & DISCUSSION
Theresultsofthecloud-basedwebapplicationforrapid andprecisedetectionoftuberculosisusingSupportVector Machine (SVM) can be evaluated based on the accuracy, precision,recall,andF1-scoreoftheTBdetectionmodel.
The accuracy of the TB detection model measures the proportion of correctly classified TB-positive and TBnegative samples out of all test samples. A high accuracy scoreindicatesthatthemodelisabletoaccuratelyclassify TB-positiveandTB-negativesamples.
Precision measures the proportion of true TB-positive cases out of all positive predictions, whilerecall measures the proportion of true TB-positive cases out of all actual TB-positivecases.Ahighprecisionscoreindicatesthatthe modelisabletoaccuratelypredictTB-positivecases,while a high recall score indicates that the model is able to correctlyidentifyallTB-positivecases.
The F1-score is the harmonic mean of precision and recall, and provides a single score that takes both metrics into account. A high F1-score indicates that the model is bothaccurateandreliableinpredictingTB-positivecases.
Overall, the cloud-based web application for rapid and precise detection of tuberculosis using SVM can provide a valuable tool for healthcare providers to quickly and accurately identify TB-positive cases and initiate appropriate treatment. The application can help to reduce the burden of TB on global health and improve patient outcomesbyfacilitatingearlydetectionandtreatment.
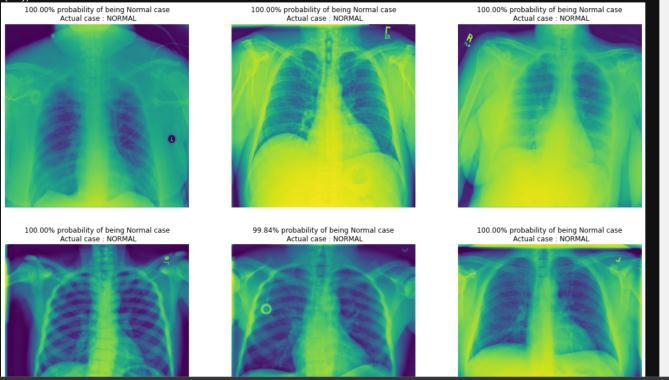

VII. CONCLUSION
Inthepresentwork,resultsofautomaticclassificationof medical images are presented in two categories: with and without tuberculosis. To carry out the classification, features are extracted using deep learning and the RESNET50 neural network. Cross-validation and the formation of training and test sets were the two classification scenarios used. The scenario with the best resultswastheoneinwhichthetrainingandtestsetswere formed with an accuracy greater than 85%. The classification method that shows the best performance in thetwoscenariosimplementedinthisworkisSVM.Ascan be seen in the results obtained in the present work, these far exceed chance and allow to carry out the classification of images in an efficient way. Computer tomography (CT) of the abdomen, CT of the head, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain, and MRI of the spine were all used inthisinvestigation.OursuggestedCNN architecture could automatically categorize these 4 sets of medical
photos by image modality and anatomic location after converting them to JPEG (Joint Photography Experts Group) format. In both the validation and test sets, we achievedoutstandingoverallclassificationaccuracy(>99.5 percent). The collected results allow us to assess the viability of the methods adopted. It also allows us to identify the best classification scenario and machine learning method to carry out the classification of radiographswithandwithouttuberculosis.
REFERENCES
[1] Abdelaziz A, Elhoseny M, Salama AS, Riad AM (2018) A machine learning model for improving healthcare services on cloud computing environment. Measurement 119:117 128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2018.01. 022.
[2] A.D. Baxevains, G.D.Bader, and D.S.Wishart Bioinformatics.Hoboken,NJ,USA:Wiley,2020.
[3] P. Brady, ‘‘Error and discrepancy in radiology: Inevitableoravoidable?’’InsightsImag.,vol.8,no. 1,pp.171–182,Feb.2017.
[4] J.Degnan,E.H.Ghobadi,P.Hardy,E.Krupinski,E.P. Scali, L. Stratchko, A. Ulano, E. Walker, A. P. Wasnik, and W. F. Auffermann, ‘‘Perceptual and interpretiveerrorindiagnosticradiology Causes andpotentialsolutions,’’AcademicRadiol.,vol.26, no.6,pp.833–845,Jun.2019.
[5] S. Graham, K. D. Gupta, J. R. Hidvegi, R. Hanson, J. Kosiuk, K. A. Zahrani, and D. Menzies, ‘‘Chest radiograph abnormalities associated with tuberculosis: Reproducibility and yield of active cases,’’Int.J.TuberculosisLungDisease,vol.6,no. 2,pp.137–142,2002.

[6] Greenspan, B. van Ginneken, and R. M. Summers, ‘‘Guesteditorial deeplearninginmedicalimaging: Overview and future promise of an exciting new technique,’’ IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., vol. 35, no. 5, pp.1153–1159,May2016.J.
[7] Hosny, C. Parmar, J. Quackenbush, L. H. Schwartz, and H. J. W. L. Aerts, ‘‘Artificial intelligence in radiology,’’ Nature Rev. Cancer, vol. 18, no. 8, pp. 500–510, 2018, doi: 10.1038/s41568-018- 00165.
[8] Kamal J AbuHassan, M. Bakhori, Benjan A. Evans. Automatic Diagnosis of Tuberculosis Disease BasedonPlasmonicELISAandColor-BasedImage
Classification In International Conference of MedicalApplicationsofAI,Oct2017.
[9] Khairul Munadi, Kalil Muchtar, Novi Manulina. Image Enhancement for Tuberculosis detection usingDeepLearning,IEEJournal,2020.
[10] Khutlang R, Krishnan S, Whitelaw A, Douglas TS (2010) Automated detection of tuberculosis in Ziehl-Neelsen stained sputum smears using two one-classclassifiers.JMicrosc237:96 102.
[11] Lee C-Y, Xie S, Gallagher P, Zhang Z, Tu Z (2014) Deeplysupervisednets.arXiv:1409.5185.
[12] OsmanMK,MashorMY,JaafarH(2012)Detection of tuberculosis bacilli in tissue slide images using HMLP network trained by extreme learning machine. Elektronika ir Elektrotechnika (Electron ElectrEng).
[13] M.I.Razzak,S.Naz,andA.Zaib,‘‘Deeplearningfor medical image processing: Overview, challenges and the future,’’ in Classification in BioApps (Lecture Notes in Computational Vision and Biomechanics), vol. 26, N. Dey, A. Ashour, and S. Borra,Eds.Cham,Switzerland:Springer,2018.
[14] Sadaphal P, Rao J, Comstock GW, Beg MF (2008) Image processing techniques for identifying Mycobacterium tuberculosis in Ziehl Neelsen stains.IntJTubercLungDis12(5):579 582.
[15] S. K. Sharma and A. Mohan, ‘‘Tuberculosis: From an incurable scourge to a curable disease-journey over a millennium,’’ Indian J. Med. Res., vol. 137, no.3,p.455,2013.
[16] H.-C.Shin,H.R.Roth,M.Gao,L.Lu,Z.Xu,I.Nogues, J. Yao, D. Mollura, and R. M. Summers, ‘‘Deep convolutionalneuralnetworksforcomputer-aided detection: CNN architectures, dataset characteristics andtransferlearning,’’IEEETrans. Med. Imag., vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 1285–1298, May 2016.
[17] Silverman, ‘‘An appraisal of the contribution of mass radiography in the discovery of pulmonary tuberculosis,’’Amer.Rev.Tuberculosis,vol.60,no. 4,pp.466–482,1949.
[18] TawsifurRahman.ReliableTuberculosisDetection using Chest X-Ray with Deep Learning, SegmentationandVisualization,IEEJournal,2020
[19] M. van Cleeff, L. Kivihya-Ndugga, H. Meme, J. Odhiambo, and P. Klatser, ‘‘The role and performance of chest X-ray for the diagnosis of tuberculosis: A cost-effectiveness analysis in Nairobi, Kenya,’’ BMC Infectious Diseases, vol. 5, no.1,p.111,Dec.2005.
[20] H. van’t Hoog, H. K. Meme, K. F. Laserson, J. A. Agaya,B.G.Muchiri,W.A.Githui,L.O.Odeny,B.J. Marston, and M. W. Borgdorff, ‘‘Screening strategiesfortuberculosisprevalencesurveys:The value of chest radiography and symptoms,’’ PLoS ONE,vol.7,no.7,Jul.2012,Art.no.e38691.

