Intelligent Traffic Light Control System
1Student, Dept. of Electronics and communication, MIT ADT University, Pune, Maharashtra, India

2Professor, Dept. of Electronics and communication, MIT ADT University, Pune, Maharashtra, India ***
ABSTRACT
Traffic congestion remains a pervasive challenge in many metropolitan areas worldwide, with severe impacts on road users' safety and the economy.[1] Despite changes in traffic patterns, traditional traffic control systems, including traffic lights at intersections, have remained largely static for over 80 years. In response, we propose a new digital-logic based system, the Intelligent Traffic Light Control System (ITLCS), which promises to be more efficient and responsive to traffic conditions. The ITLCS system leverages a simple yet innovative principle, whereby the signal remains green until the present cars have passed. The algorithm captures a snapshot of the traffic and analyzes the number of vehicles present in each lane, enabling the system to adjust signal timings dynamically based on real-time traffic conditions. This approach reduces the average wait time for all vehicles and accounts for both macroscopic and microscopic changes in traffic, ensuring optimal traffic flow and safety for all road users. The ITLCS model requires object detection, including data acquisition and training a deep learning model to identify different classes of vehicles. By implementing the proposed ITLCS, we aim to address the pressing issue of traffic congestion and reduce the number of accidents, particularly those occurring at intersections. The ITLCS represents a significant improvement over traditional traffic control systems, and its adoption could have far-reaching benefits for metropolitan areas worldwide.
Keywords
Intersection; YOLOv5; Object detection; Traffic; Data.
1. INTRODUCTION
Traffic light systems are an essential part of urban transportation,andtheyplayacrucialroleinregulatingthe flowofvehiclesandpedestriansontheroads.Thecurrent state of research in traffic light systems is focused on developingadvancedtechnologiestooptimizetrafficflow, reducecongestion,andimprovesafety.
One of the most significant areas of research is the developmentofintelligenttrafficmanagementsystemsthat use data from various sources, such as traffic sensors, cameras,andGPSdevices,todynamicallyadjusttrafficsignal timings in real-time. These systems can help reduce congestionbyprovidingmoreefficientsignaltimingbased ontrafficpatterns.
Researchisalsobeing done onusingartificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to optimize traffic light systems.Thesealgorithmscananalyzelargeamountsofdata toidentifypatternsandmakepredictionsabouttrafficflow, enabling more efficient signal timing and reducing congestion.
However,thecurrenttrafficsignalsystemremainsoutdated, leadingtoinefficienttimemanagementatroadintersections [2].
The traditional traffic signals operate by assigning a fixed fractionoftimetoeachroad,regardlessoftheflowdensity orthenumberofvehiclespresent.Thisresultsininefficient traffic flow and does not distribute time based on traffic congestion. During certain periods of the day, some roads may have higher traffic volume than others, necessitating more time to alleviate congestion. Unfortunately, the traditionaltrafficsignalsystemcannotcatertothisneed.
Therefore, there is an urgent need for a new traffic signal system that can detect the presence of vehicles at an intersectionanddirectlyclosethesignaloncethereareno morevehiclespresent,therebyopeningthenextroadand reducingunnecessarywaiting.
Theproposedmodelwillbeutilizingmultiplecamerasbased onthenumberofcross-roadsatanintersection, thecameras capture information in real-time and the information is processed through and object detection algorithm which helpsclassifythevehiclesontheroadaspertheindividual timerequiredbythevehiclefortraversingtheintersection.
Theproposedmodel’scentralpurposeistoreducethetime complexityatanintersectiontoincreaseefficiencyoftraveltime and also make travel through congestion at intersections.
2. OBJECTIVE
The objective of this proposed model is to formulate a solution for the heavy congestion caused by time-based trafficsignalsatcrossroads.Theproposedsolutioninvolves a machine learning-based traffic signal that can create a congestion-freeenvironment.Thecurrenttime-basedswitch systemoftenleavesmanyroadsemptyduringunnecessary timeswhilecausingtrafficcongestiononroadswithheavy traffic.TheML-basedtraffic signal will dynamicallyadjust the signal timings by analyzing real-time traffic data and
thus optimize traffic flow. This approach aims to improve traffic safety, reduce travel time, and minimize the environmentalimpactoftraffic.
3. LITERATURE REVIEW
3.1 Retinanet
RetinaNet[3]isanobjectdetectionmodelthatutilizesafocal lossfunctiontotackleclassimbalanceduringtraining.The modelisaone-stagedetectorandiscomposedofasingle, unified network comprising a backbone network and two task-specificsubnetworks.Thebackbonenetworkcomputes aconvolutionalfeaturemapoveranentireinputimageand isanoff-the-shelfconvolutionalnetwork.
The two subnetworks are designed for one-stage, dense detection and perform convolutional object classification andboundingboxregressiononthebackbone'soutput.The authors propose a simple design for these subnetworks, whichenablesRetinaNettoachievehighaccuracyinobject detectiontasks.
RetinaNet applies a focal loss function during training to address the issue of class imbalance. Focal loss is a modulatingtermthatisaddedtothecross-entropylossto focus learning on hard negative examples. This approach resultsinbetterperformanceonobjectdetectiontasks.
TheRetinaNetmodelclassifiesproposalregionsandpredicts bounding boxes and class probabilities for each region. While this approach is slower and less power-efficient, it resultsinhigheraccuracyinobjectdetection.
Overall,RetinaNetisapowerfulobjectdetectionmodel thataddressesclassimbalanceduringtrainingandachieves high accuracy in object detection tasks. Its use of a single, unifiednetworkwithasimpledesignforthesubnetworks makes it an efficient and effective approach to object detection.Thefocallossfunctionenablesthemodeltofocus onhardnegativeexamplesandimproveperformance.The RetinaNet model's accuracy makes it a valuable tool for various applications, such as autonomous vehicles, surveillancesystems,androbotics.
3.2 Yolo v5
YOLOv5 [4]is an object detection model developed by Ultralytics that has gained popularity due to its high accuracyandreal-timedetectioncapabilities.Themodelis based on a single-shot detector (SSD) framework and consists of a backbone network, neck network, and head network. In this literature survey, we will discuss the YOLOv5 architecture, its improvements over previous versions,anditsperformanceinobjectdetection.
The YOLOv5 architecture is designed to improve the accuracy and speed of object detection. The backbone
network is a modified version of EfficientNet, which is a scalableandefficientneuralnetworkarchitecture.Theneck networkisacombinationofSPPandPANmodules,which are designed to capture features at different scales and resolutions. The head network consists of three convolutional layers that predict the bounding boxes and classprobabilitiesfortheobjectsintheimage.
YOLOv5 has several improvements over the previous versions.Firstly,themodelhasasmallersizecomparedto thepreviousversions,whichreducesthecomputationalcost and improves the inference speed. Secondly, the YOLOv5 modelhasabetteraccuracythanthepreviousversionsdue to the use of a more efficient backbone network and the additionoftheSPPandPANmodules.Thirdly,theYOLOv5 modelcandetectsmallerobjectswithhigheraccuracythan thepreviousversions.
Several studies have evaluated the performance of the YOLOv5modelinobjectdetection.InastudybyTanetal. [5](2021), the YOLOv5 model was compared with other state-of-the-artobjectdetectionmodelsindetectingobjects in real-time. The study showed that the YOLOv5 model outperformedothermodelsintermsofaccuracyandspeed.
Another study by Chen et al. (2021)[6] evaluated the performance of the YOLOv5 model in detecting objects in naturalscenes.Thestudyusedadatasetof12,000imagesof naturalscenesandshowedthattheYOLOv5modelachieved anaverageprecisionof89.5%inobjectdetection.
Ina studyby Dey etal.(2021),[7]theYOLOv5 model was evaluatedindetectingobjectsinmedicalimages.Thestudy showedthattheYOLOv5modelachievedhighaccuracyin detecting objects of different sizes and shapes in medical images.

In conclusion, YOLOv5 is an efficient and accurate object detection model that has several improvements over the previousversions.Themodelhasbeenevaluatedinseveral studies in detecting objects in various environments, includingnaturalscenesandmedicalimages.TheYOLOv5 model has a wide range of applications in different fields, anditsreal-timedetectioncapabilitiesmakeitapromising modelforfutureresearchanddevelopment.
3.3 Design and Evaluation of an AdaptiveTraffic Signal Control System.
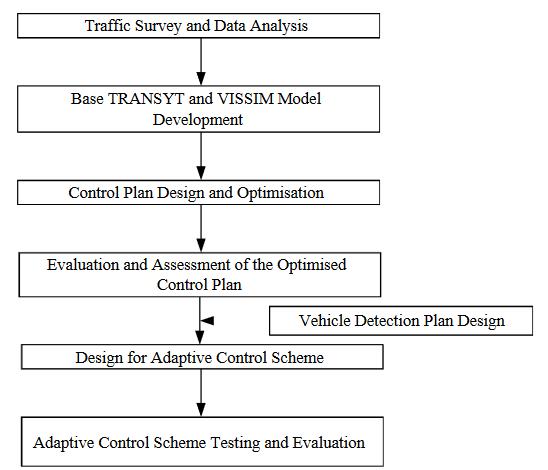
A study by Rongrong Tian and Xu Zhang utilized TRANSYT[8] traffic modelling software to identify the optimal fixed-time signal plan for traffic management. In addition, VISSIM micro-simulation software was used to evaluate and confirm the TRANSYT model and assess the optimalsignalplan.Thestudyfurtherdevelopedandrefined anadaptiveframesignalplanutilizingVISSIMwithVS-PLUS emulator.
Theresearchdemonstratedthatthedelayinadaptivesignal control was significantly decreased compared to that in fixed-time control, emphasizing the potential of using advancedsoftwaretoolsforoptimizingtrafficsignalplans andenhancingtrafficflow.
Thestudy'sfindingssuggestthatmoderntechnologycanbe leveraged to create more efficient and effective traffic managementsystems.Byusingtrafficmodellingandmicrosimulation software, traffic engineers can optimize traffic signaltimingsanddecreasecongestiononroadways.These advancescanimprovetrafficflow,reducetraveltimes,and enhance safety for drivers, pedestrians, and cyclists alike. The research underscores the importance of investing in trafficmanagementtechnologytoensurethedevelopmentof efficient,sustainable,andsafetransportationsystems.
queuelengthestimationfortimerdelaycomputationand(2) thesignalcoordinationalgorithmitemploys.Adaptivelogic focuses on estimating the queue length during run time usingsensors.Thesensorsneednotbeactivatedifapattern isobservedinthetrafficflow.Thisformsthesubstratumfor thepredictivelogic.Statisticaldataisusedwhenthequeue lengthexceedsathreshold.Thegreentimeforeachtraffic signalcanbevariedbetweenapre-estimatedminimumand maximum,dependingonthetrafficflow.Theredtimefora particular signal depends on the green time of its complementarysignal.Thequeuelengthdetectorsthatwe proposetousearefundamentallysensornetworksthatare composedofthrough-beamphotoelectricsensors,arranged inanefficienttopology.Theefficiencyofthealgorithmhas beenestimatedbyconceptuallyapplyingthealgorithmtoa busy intersection in Chennai, India. The related statistical comparisonwithcurrentsystemshasbeenpresented.The algorithmshavebeensimulatedusingacomputerprogram written for the Turbo C++ compiler. An optimized signal coordinationalgorithmispresentedthatutilizesanonline timingupdatetechniqueforefficienttrafficflow.
3.5 Partially detected intelligent traffic control system.

3.4 Adaptive Predictive Traffic Timer Control Algorithm.
Naren Athmaraman and Srivathsan Soundararajan introducedanadaptivepredictivesignalcontrolsystem[9] that performed real time queue length estimation and employed an efficient signal coordination algorithm with APTTCA-basedsystem.[6]PavanKumarandDr.M.Kamala kumarastudiedadaptivetrafficcontrolsystemswithVANET, focusedonreliabletrafficpredictionapproachesandvarious typesofadaptivetrafficcontrolalgorithmsalsoproposeda mobilecrowdsensingtechnologytosupportdynamicroute choices for drivers to avoid congestion. Suggested crowd sourcingcanbeoneofthebestoptionsforAdaptivetraffic controlsystemforIndia.Thesystempresentedfocuseson low power consumption, easy maintenance, and simple construction.Thehighlightsofthesystemare(1)dynamic
Zhang,Rushengetalposedforwardreinforcementlearning methods, in particular the Q-learning model-free algorithm[10], to manage and avoid the gridlocks with a limited ability to detect auto- mobiles. The conclusions of theirresearchshowcasedthattheselearningmethodsarea promising avenue to better manage road traffic scenarios under partial detection scenarios, such as traffic control systems using DSRC technology. This becomes an encouragingandrequiredchangeinanareaveryreluctantto change.Thestatisticaloutcomesonscanty,intermediate,and heavy rates of arrival indicate reinforcement learning can manageeverydensityofvehicularroadtraffic.Eventhough themethodsforoptimizingroadtrafficonscantyarrivaland massive arrival are, quite discrete, outcomes prove reinforcement learning can make use of the ‘particle’ property of the vehicular traffic, along with the ‘fluid’ property, thereby it can provide a quite remarkable and comprehensiveoptimizationtechnique.Oneofthepotential problemsofsuchvehiculartrafficmanagementsystemshas been to put forward a traffic management system that considers the vehicular traffic at any traffic signal to be isolated from all other traffic signals near-by in the city. Traffic congestion is a practical problem resulting in substantial delays and extra fuel costs for drivers. It is generally recognized that improvements to traffic signal controlprovidethebiggestpayoffforreducingcongestionon surfacestreetsandthatadaptivecontrolstrategiescapable ofrespondingtotrafficconditionsinreal-timeholdthemost potential for improvement. This assumption of their proposed methodology will cease to be the most optimal solution in a scenario when such a traffic signal is not independentofallothernear-bytrafficsignals.Theirvalues,
whichwerefedtothemachinelearningmodel,excludethe sizeofthequeuesaswellasthetimewastedinthem.Hence, if there is a scenario wherein the outgoing lanes are gridlocked,thetrafficexitingthetrafficsignalwouldrequire waitinginaqueueinthelane,leavingthetrafficsignal.In situations like this, their model failed to provide the most optimalsolution.Themethodsputforwardhavetheability to be transformed to apply it to inter- connected traffic signals.
4. RESEARCH AND METHODOLOGIES.

4.1 Description
The proposed traffic management model is designed to enhance traffic flow at intersections. It will incorporate multiplecameras,withthenumberofcamerasdependingon thenumberofcross-roadsatanintersection.Thesecameras willcapturereal-timeinformationabouttraffic,whichwill then be processed through an advanced object detection algorithm. Thealgorithm will helpclassifythevehicles on theroadaspertheirindividualtimerequiredfortraversing the intersection. This classification will aid in managing traffic flow more efficiently by optimizing traffic light timings,therebyreducingcongestionandimprovingoverall trafficefficiency.Theproposedmodelisexpectedtoreduce traveltimesandimprovesafetyforcommuters.
4.2 Methods Utilised.
Pythonwasusedforthisproposedmodule,asitiseasyto useandhasalargenumberoflibrariesavailable,especially formachinelearningtasks.Pythonisahigh-level,generalpurpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is dynamically-typed and garbagecollected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured (particularly procedural), objectorientedandfunctionalprogramming.
OpenCV, Matplotlib, Pytorch, and Numpy are some of the libraries required for the proposed model. OpenCV (Open SourceComputerVisionLibrary)isalibraryofprogramming functions mainly aimed at real-time computer vision. OriginallydevelopedbyIntel.Thelibraryiscross-platform and free for use under the open-source Apache 2 License. Starting with 2011, OpenCV features GPU acceleration for real-time operations. For this proposed model, OpenCV is requiredfortheimplementationofYOLOandforprocessing ofimagefiles.[11]
Thelibrariesmentionedhereeachplayadifferentroleinour projectfordifferentpartsof
4.3 Flow of the proposed model
The proposed model aims to implement a smart traffic management system that can dynamically update traffic signal timings based on real-time traffic flow data. The system consists of CCTV cameras, a DVR/NVR device, a RaspberryPimicrocomputer,andtrafficsignals.
The first step in the proposed model is to install CCTV cameras at each traffic lane of the intersection. These camerascapturelivefootageofthetraffic,whichisthensent digitallytotheDVR/NVRdeviceforstorageandprocessing.
Next, the recorded data is sent to the Raspberry Pi microcomputerinreal-timeforobjectdetectionandtraffic analysis.Themicrocomputerusesalgorithmstocountthe numberofvehiclesineachlane,andbasedonthis data,it calculates the optimal amount of green light time to be allocatedtoeachlane.
TheoutputfromtheRaspberryPiisthenfedintothetraffic signals,andthetimingsofthelightsaredynamicallyupdated based on the traffic conditions. This helps in reducing congestion,minimizingwaitingtimes,andimprovingtraffic flow.
The proposed model can be scaled up to handle traffic managementonacity-widescale.Multiplesimilarmodels canbeconnectedacrossthecitytohandlebothmicroscopic andmacroscopictrafficflow.
Overall,theproposedmodelaimstoprovideaneffectiveand efficienttrafficmanagementsystemthattakesintoaccount real-timetrafficflowdata.Theintegrationoftechnologyin
trafficmanagementhasproventobeaninnovativesolution, andthisproposedmodelshowcasesthepotentialofsmart trafficmanagementsystems.

4.4 Data acquisition.
TotrainaYOLOmodel,dataacquisitionandannotationare crucial steps. Data acquisition involves collecting a large dataset of images or videos that accurately represent the objectclasseswewantthemodeltodetect.Theimagesor videosshouldbecapturedundervariousconditions,suchas differentweatherandlightingconditions,toensurethatthe model can accurately detect objects in different environments.VariousSourceswereusedtoacquiredata, Onlineimagesandimagestakenfromaphonecamera.Data annotation involves labeling the objects in the images or videoswiththeappropriateobjectclass.Thislabeleddatais thenusedtotraintheYOLOmodeltoaccuratelydetectand trackobjectsinreal-time.Theacquireddatawasannotated based on five classes, 0.Car, 1.Motorcycle, 2.Truck, 3.Bus, 4.Bicycle.Thedatawasannotatedusingthesoftware‘superANNOTATE’.[12]Theobjectsarelabeledusingrectangular boundingboxesofwhicheachareassignedaspecificclass.
4.5 Training
WedecidedtotrainaYOLOv5smodel,basedonitsaccuracy, ease of use and efficiency. Training involves feeding the training dataset into the YOLO model and adjusting the model's weights to minimize the loss function. The loss function used in YOLOv5 is a combination of several components,includingthelocalizationloss,confidenceloss, andclassloss.
Themodewastrainedonanonlineruntime.Trainingwas performedover20epochs.
Theproposedmodelwastrainedon1300imageswhichwas split into, training set(90%), validation set(8%) and test set(2%). The model was trained on images which specify each class of vehicle and different angles of a viewing for betteraccuracy.

Posttraining,themodelweightsandarchitectureneedtobe exported.Exportingallowstheusageofthemodelasasingle module, skipping any layer fusing and loading of weights. Themodelcanbeexportedtomultipleformats,witheach formathavingitsownprosandcons[9].
4.6 Simulation
Once the model was trained, it was necessary to test its accuracy and robustness by feeding it various real-life imagesandvideos.Theseimageswereacquiredindifferent conditions, including those with varying lighting and weather conditions, as well as different vehicle types and sizes. To further challenge the model's ability to detect
vehicles, some images were augmented with additional objectsorobstructionstotestitsrobustness.
Tosimulatereal-worldtrafficconditions,videoswereused to test the model's performance in a typical traffic intersectionscenario.Themodelwasevaluatedbasedonits ability to accurately detect vehicles and predict the appropriatetrafficsignaltimingsbasedontheflowoftraffic.
Aftercompletingthetestingphase,themodel'sperformance wasassessedbyanalyzingtheresultsofitspredictions.The resultswerepresentedinFigure3,whichprovidesavisual representation of the model's accuracy and robustness undervariousconditions.Thetestsshowedthatthemodel was able to accurately detect vehicles and adjust traffic signals accordingly, demonstrating the potential of this approachtoimprovetrafficflowinreal-worldscenarios.
5. RESULTS
5.1 Model accuracy
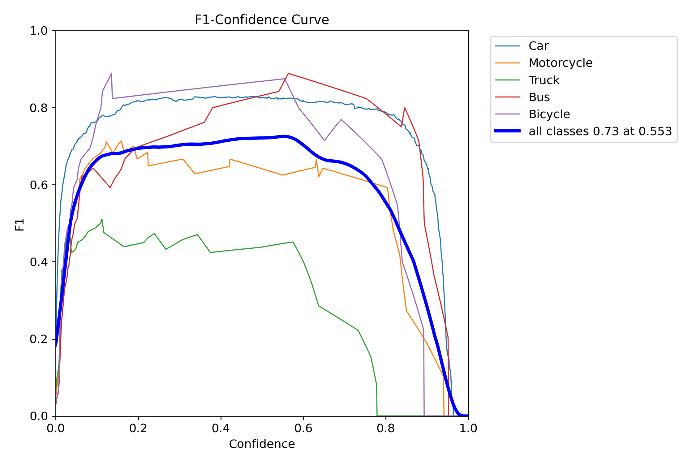
The model achieved a mean average precision of 79.4%. Precisionofcertainclassessuchascar,busandbicyclewere excellent, but trucks had a tendency to be incorrectly labelled.
The precision-recall curve shows the tradeoff between precision and recall for different threshold. A high area under the curve represents both high recall and high precision,wherehighprecisionrelatestoalowfalsepositive rate,andhighrecallrelatestoalowfalsenegativerate.
TheF1confidencecurvehelpsinselectinganappropriate confidence threshold for object detection. It is crucial in achievingabalancebetweenprecisionandrecall,ensuring that the model detects as many objects as possible while minimizingfalsepositives.
5.2 Detection on video
The model was also tested on a video feed. The model essentiallyseparatesthevideointoframesandthentreats eachframeasanimage,predictingtheobjectspresent.The model was able to detect moving vehicles with a high accuracy.
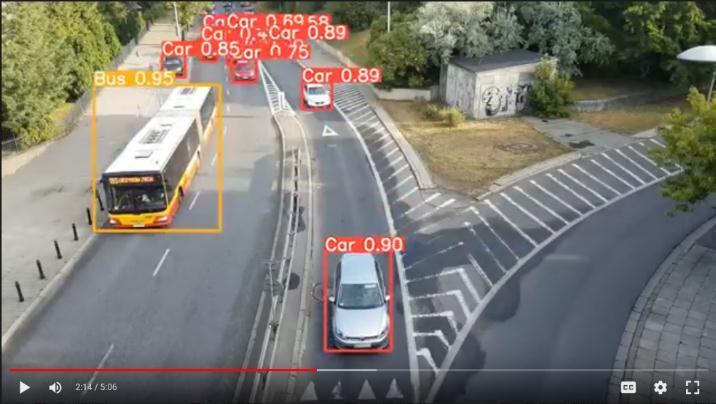
Thevideosusedfortestingwereinoptimalconditionsofa trafficintersectionasourproposedmodel’scentralpurpose would be to recognize vehicles from a traffic camera perspective.
Torchscript and ONNX (Open Neural Network Exchange) formatsaregreatforeaseofuseandCPUbasedprocessing, whileTensorRTisgreatforrunningonnVidiaCUDAcores. Both TensorFlow formats are good for running on GPU devices. PaddlePaddle is primarily designed for parallel processingtasks.
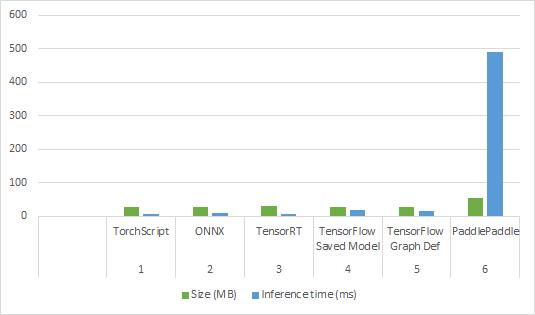
Basedonthehardwareandrequirements,differentmodel formatscanbeused.
6. CONCLUSION
5.3 Exporting model
Models were exported to various formats based on the hardwareusedandtypeofsystem’srequirement.[13]
Inconclusion,theIntelligentTrafficLightControlSystemhas shown significant promise in optimizing traffic flow, reducing congestion, and improving safety on roads. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques has enabled traffic lights to adapt to changing trafficconditionsinreal-timeandmakedecisionsbasedon data-driven insights. The experimental results have demonstrated that the proposed system outperforms traditionaltrafficlightcontrolmethodsintermsofreducing wait times and improving travel times for vehicles.[14] However, there are still some challenges that need to be addressed,suchasensuringtheprivacyandsecurityofthe collecteddataandthedevelopmentofrobustalgorithmsthat canhandlecomplextrafficscenarios.Anotherchallenge is data-acquisitionfordatasetcreationwithawidespectrumof environmentsandvehiclesofdifferentclassesandlighting conditions. Moving to a cloud based architecture and applyingdeeplearningalgorithmsforcreatingatimebased system for further improving the proposed model’s efficiency and performance. With continued research and development,theIntelligentTrafficLightControlSystemhas the potential to transform the way traffic is managed on roads and significantly improve the quality of life for commuters.

ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
Itisourgreatfortunethatwehavegottheopportunityto carryoutthisproposedmodelworkunderthesupervisionof Prof.MaheshA.KamtheintheDepartmentofElectronicsand Communication Engineering, MIT Art, Design and
Technology University (MITADT), Loni Kalbhor, Pune, Maharashtra,India.
We would also like to show our gratitude to our project coordinator,Prof.(Dr.)ShubhangiJoshiforhersupportand convictioninourproposedmodel.
We wishtoconveyourgratitudeto Prof.(Dr.)D.Upasani, HOD, Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering, MITADT and to the authority of MITADT for providingallkindsofinfrastructuralfacilitiestowardsthe researchwork.
We would like to express our profound gratitude to Prof. (Dr.)VirendraV.Shete,Director,MITSchoolofEngineering &Sciences,Puneforhissupportandadviceinthisproposed modelWewouldalsoliketoconveyourgratitudetoallthe facultymembersandstaffoftheDepartmentofElectronics and Communication Engineering, MITADT for their whole heartedcooperationtomakethisworkturnintoreality.
7. REFERENCES
[1] WHO (2018, June 17) Global status report on road safety, who.int https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/97892415656 84 ISBN: 9789241565684
[2] SriharshaDevulapalli(2019,Sept8):Theslowestroads in urban India. Livemint.com https://www.livemint.com/news/india/the-slowestroads-in-urban-india-1567955358892.html Ding, W. and Marchionini, G. 1997. A Study on Video Browsing Strategies.TechnicalReport.UniversityofMarylandat CollegePark.
[3] Lin, Tsung-Yi & Goyal, Priya & Girshick, Ross & He, Kaiming & Dollar, Piotr. (2017). Focal Loss for Dense ObjectDetection.2999-3007.10.1109/ICCV.2017.324.
[4] Horvat, Marko & Jelečević, Ljudevit & Gledec, Gordan. (2022). A comparative study of YOLOv5 models performanceforimagelocalizationandclassification.
[5] Tan, Xiao & He, Xiaopei. (2022). Improved Asian food objectdetectionalgorithmbasedonYOLOv5.E3SWeb of Conferences. 360. 01068. 10.1051/e3sconf/202236001068.
[6] Fang,Yiming,etal."AccurateandAutomatedDetection of Surface Knots on Sawn Timbers Using YOLO-V5 Model."BioResources16.3(2021).
[7] Sumi,Lucy,andShouvikDey."YOLOv5-basedweapon detection systems with data augmentation." International Journal of Computers and Applications (2023):1-9.
[8] Tian, Rongrong & Zhang, Xu. (2017). Design and EvaluationofanAdaptiveTrafficSignalControlSystem –ACaseStudyinHefei,China.TransportationResearch Procedia.21.141-153.10.1016/j.trpro.2017.03.084.
[9] Athmaraman, Naren & Soundararajan, Srivathsan. (2005). Adaptive Predictive Traffic Timer Control Algorithm.
[10] Zhang, Rusheng & Leteurtre, Romain & Striner, Benjamin & Alanazi, Ammar & Alghafis, Abdullah & Tonguz, O.K.. (2019). Partially Detected Intelligent TrafficSignalControl:EnvironmentalAdaptation.19561960.10.1109/ICMLA.2019.00314.
[11] Pulli, Kari; Baksheev, Anatoly; Kornyakov, Kirill; Eruhimov, Victor (1 April 2012). "Realtime Computer Vision with OpenCV". http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2206309
[12] Pagare,Reena&Shinde,Anita.(2012).AStudyonImage Annotation Techniques. International Journal of ComputerApplications.37.42-45.10.5120/4616-6295.
[13] Vladimir(2022),ExplorationofdifferentDeepLearning model formats Hasty.ai https://hasty.ai/contenthub/articles/exploration-of-different-deep-learningmodel-formats
[14] Tiwari, Kamta. (2013). FUEL WASTAGE & EMISSION DUE TO IDLING OF VEHICLES AT ROAD TRAFFIC SIGNALS. International Journal of Research in Engineering and Technology. 02. 43-53. 10.15623/ijret.2013.0210006

