DECENTRALIZED VOTING SYSTEM USING BLOCKCHAIN
Shrutika Gawali1 , Deepika Khadgade2 , Shrutika Kolhe3, Nikita Vyavhare4 , Prof. Madhuri B. Babar5J D College of Engineering and Management, Nagpur Dr. Babasaheb Ambedkar Technological University, Lonere, India

Abstract - This design proposes the design and development of a decentralized voting system using blockchain technology and face recognition. The end is to produceasecure,transparent,andaccessiblevotingprocess that ensures the integrity and delicacy of election results while icing the insulation of pickers. The system will use blockchain technology to produce a decentralized and tamper-substantiationcensusofvotes,andfacerecognition technology to insure that each vote is cast by an eligible name. Thedesignaimstocontributetotheongoingsweatsto develop farther secure and accessible voting systems that enhancepopularprocessesandcovertheintegrityofchoices.
Key Words: Blockchain, Decentralized, E-voting, Voter Privacy, Face Recognition
1. INTRODUCTION
Voting schemes have evolved from counting hands in early days to systems that include paper, punch card, mechanicalswitchandoptical-scanma-chines.Anelectronic voting system which is used presently give some characteristicdifferentfrom thetraditionalvotingfashion, andalsoitprovidesbetteredfeaturesofvotingsystemover traditionalvotingsystemanalogousasdelicacy,convenience, strictness,insulation,verifiablyandmobility.ButElectronic votingsystemssuffersfromvariousdownsidesanalogousas time-consuming, consumeslargevolumeofpaperwork,no directpartfortheadvancedofficers,damagetomachinesdue tolackofattention,massupdatedoesnotallowstoners to contemporize and edit multitudinous item simultaneously etc.therefore,byadministeringadecentralizedBlockchain predicatedgarçonterrainwecanhelpdataloss.Blockchainis a distributed census technology that allows secure and transparent record- keeping of deals across a network of computers.Thetechnologywasfirstintroducedin2008by an anonymous person or group of people under the alias SatoshiNakamoto inawhitepapernamed"BitcoinAPeerto-PeerElectronicCashSystem."Atitscore,ablockchainisa database that's maintained by a network of bumps that collectivelyvalidateandrecorddealsinadecentralizedand secure manner. SHA- 256 a fixed- size 256- bit (32- byte) hash value. It's one of the most considerably used hash functions in the world and is used in various operations, including digital signatures, word storage, and blockchain technology. SHA- 256 takes an input communication of
arbitrarylengthandproducesafixed-sizeaffair,whichisa uniquedigitalpointoftheinputcommunication.Theaffair, alsoknownasthehashvalue,isgeneratedusingaseriesof fine operations that can't be re- clued, making it nearly impossibletogaintheoriginalinput communicationfrom thehashvalue.
1.1 Blockchain
Blockchainisadistributedledgertechnologythat al-lows secureandtransparentrecord-keepingoftransactionsacross anetworkofcomputers.Thetechnologywasfirstintroduced in2008byananonymouspersonorgroupofpeopleunder the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto in a white paper titled "Bitcoin:APeer-to-PeerElectronicCashSystem."Atitscore,a blockchainisadatabasethatismain-taintedbyanetworkof nodesthatcollectivelyvalidateandrecordtransactionsina decentralizedandsecuremanner.
1.2 SHA – 256 Algorithm
SHA-256 (Secure Hash Algorithm 256-bit) is a cryptographichashfunctionthatgeneratesafixed-size256bit (32-byte) hash value. It is one of the most widely used hash functions in the world and is used in various applications,includingdigitalsignatures,passwordstorage, andblockchaintechnology.
SHA-256takesaninputmessageofarbitrarylengthand produces a fixed-size output, which is a unique digital fingerprintoftheinputmessage.Theoutput,alsoknownas thehashvalue,isgeneratedusingaseriesofmathematical operations that cannot be re- versed, making it practically impossible to obtain the original input message from the hashvalue.
2. LITERATURE SURVEY
Ehab Zaghloul focuses on voter privacy through secure multiparty computation performed by parties of differing allegiances. In the security and privacy analysis, it shows thattheproposedschemeissecureagainstpotentialsecurity threats and provides voter anonymity. The purpose of [2] study is to examine and assess current research on electronicvotingsystembasedonblockchains.Theideaof blockchainanditsapplicationsareintroducedfirst,followed
by a discussion of existing electronic Voting System. The articleaddressesrecentblockchainbasedelectronicvoting system research. In the research paper [3] The proposed blockchainarchitectureshowshowBlockchainusingSmart contractsandhyperledgerFabricwillbeutilizedtohandle e-votingsystemsecurityconcerns.Thediagramsandflow charts of paper further break down into the defined proposed process intimately, which makes it a possible reality to beat the protection limitations and adoption obstaclesrelatedtotheelectroniclegalsystem.[4]Sofurther study, tells that the benefits of blockchain such as cryptographicfoundationsandtransparencytoachievean effective solution to e-voting. Also, due to the encryption mechanism,itisnotpossibleforanypersontogainaccessto allthevoteswithoutfirsttakingcontroloftheentireservice network.
3. PROPOSED SYSTEM:
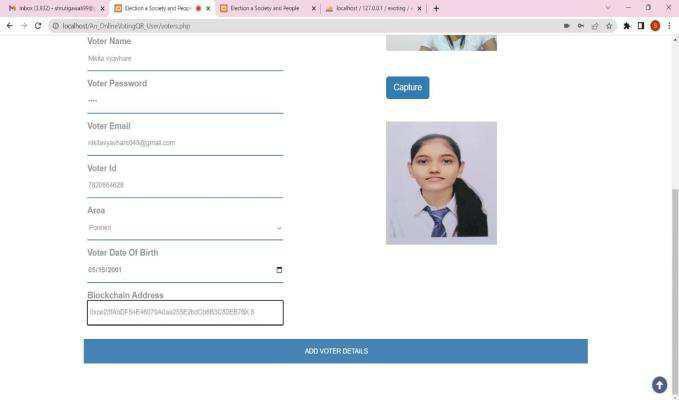
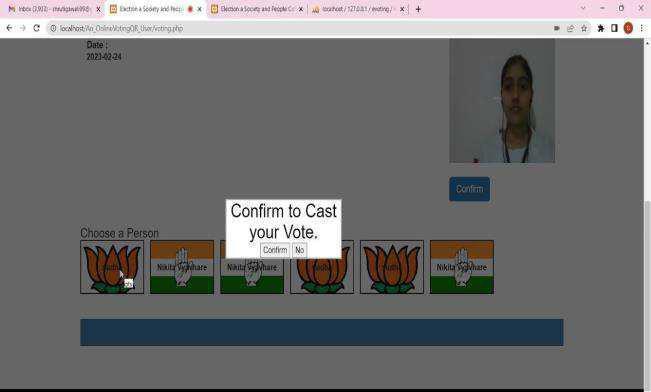
The proposed system is the Biometric online voting systemwithbiometricpointusingAadharcard.Itdetermines the particular name by his/ her point whether he she is a validnameornot.Itallowsparticularnametocastthevote online.
Thepollingprocesscontinuesuntilthevotingtimeends andmodernizethedatabaseinthegarçon.Biometriconline voting system uses Aadhar card to recoup the complete details about the name. And the votes are stored in a blockchain garçon and viewed to the public this insure a secureterrain.
4. METHODOLOGY:
The methodology for assessing the result of a decentralized voting system using blockchain and face recognitiontechnologywouldinvolveseveralways.
identify patterns, trends, and perceptively that can help melioratethesystem'sperformance.
4.ComparisonwithTraditional VotingSystemsTheresult ofthedecentralizedvotingsystemwouldbecomparedwith thetraditionalvotingsystemstoestimateitseffectiveness. The comparison would involve assaying the delicacy, security,vacuity,andcost-effectivenessofthedecentralized systemcomparedtotraditionalsystems.
5.Feedbackand improvementthefinalstepwouldbeto gather feedback from pickers, election officers, and other stakeholderstoidentifyareasforimprovement.Thefeedback would be used to upgrade the system's design and development,makingitmoreeffective,secure,andaccessible.
1. Design and Development
The first step would be to design and develop the decentralized voting system using blockchain and face recognition technology. This would involve concluding applicable blockchain technology, developingthefacerecognitionsystem,andintegratingboth technologiestoproduceasecure,transparent,andaccessible votingprocess.
2.TestingandEvaluation

Thecomingstepwouldbe to test the system and estimate its performance. This would involve conducting birdman tests with many pickers to ensurethesystemisworkingcorrectlyandtoidentifyany issuesthatneedtobeaddressed.Thesystem'sperformance wouldbeestimatedpredicatedonseveralfactors,analogous assecurity,delicacy,vacuity,andinsulation.
3.DataCollectionandAnalysisThesystem'sperformance data would be collected and anatomized to estimate the resultofthedecentralizedvotingsystem.Thedatawouldbe anatomizedusingstatisticalanddatavisualizationwaysto


6. DATA FLOW DIAGRAM:
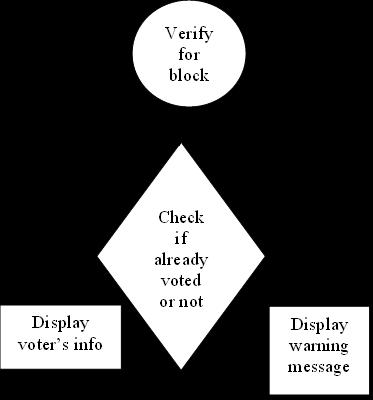
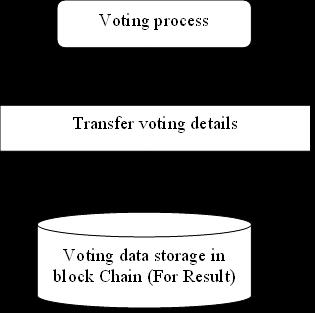
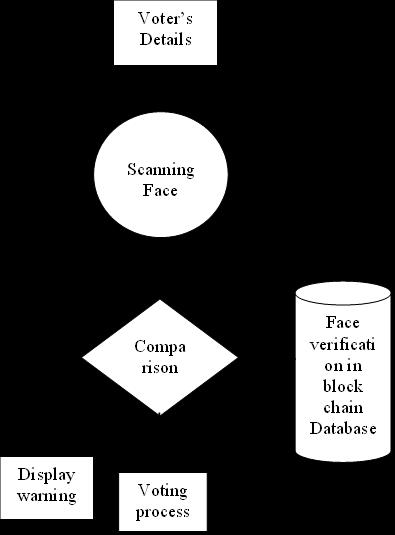
A Data Flow Diagram (DFD) is a graphical representation of the “flow” of data through an information system, modelling its aspects. It is a preliminarystepusedtocreateanoverviewofthesystem which can later be elaborated DFDs can also be used for visualizationofdataprocessing.

7. IMPLEMENTATION

Decentralizedvotingsystemsusingblockchainandface recognition technology have the eventuality to revise the votingprocessbyfurnishingamoresecure,transparent,and accessiblevotingprocess.Theuseofblockchaintechnology provides a tamper-evidence and transparent tally that ensures accurate and auditable results while guarding against fraud, manipulation,and hacking. Face recognition technology, on the other hand, can give an accessible and accessiblewaytocorroboratetheidentityofchooserswhile guarding their sequestration. Still, the perpetration of decentralizedadvancingsystemsusingblockchainandface recognitiontechnologyisn'twithoutitschallenges.Onemajor concernisscalability,asthetechnologymaynotbesuitable to handle the high volume of choosers that are present in large-scale choices. Also, the use of face recognition technology raises enterprises about sequestration and the eventualityforabuseofparticulardata.Thus,there'saneed forsequestration-conservingwaysthatensuretheobscurity ofchoosersandcovertheirparticularinformation.Likewise, standardized protocols and regulations are demanded to ensure interoperability and wide relinquishment of decentralized voting systems using blockchain and face recognition.Eventually,there'saneedforfurtherexploration on the impact of the technology on name get and participation,aswellastheusabilityandavailabilityofthe technology for all eligible choosers. Overall, decentralized voting systems using blockchain and face recognition technologyhavetheeventualitytosignificantlyameliorate thevotingprocessbyfurnishingamoresecure,transparent, and accessiblesystem.Still,thechallengesassociatedwith enforcingthetechnologymustbeannouncement-dressedto ensure its successful relinquishment and integration with beingvotingsystems.
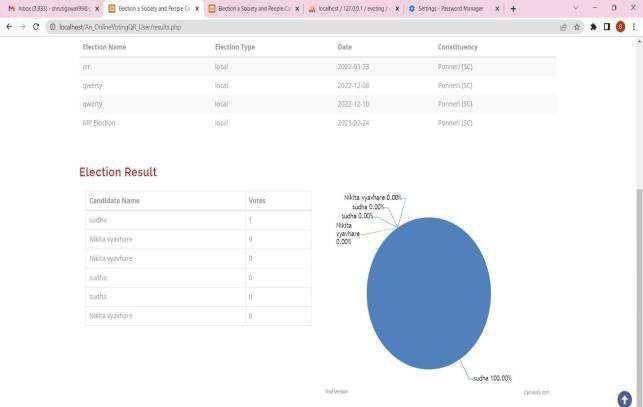
9. RESULT:
Theresultofenforcingadecentralizedvotingsystemusing blockchainandfacerecognitiontechnologywouldbeamore secure,transparent,andaccessiblevotingprocess.Theuseof blockchain technology would ensure the integrity of the voting process by furnishing a tamper-evidence and auditabletally,whilefacerecognitiontechnologywouldgive anaccessibleandaccessiblewaytocorroboratetheidentity ofchooserswhileguardingtheirsequestration.Byenforcing a decentralized voting system using blockchain and face recognition,itwouldbepossibletohelpfraud,manipulation, andhackinginthevotingprocess.Thiswouldincreasethe delicacy and translucency of election results, thereby promoting trust in the voting process and the popular system as a whole. Also, the use of face recognition technologywouldmakethevotingprocessmoreaccessible toalleligiblechoosers,includingthosewithdisabilitiesor limited access to technology. The technology could also reducetheneedforphysicalpollingstations,makingitmore accessibleforchooserstocasttheirvotefromanywhereat anytime.Still,theperpetrationofadecentralizedadvancing system using blockchain and face recognition technology
isn'twithoutitschallenges.Technical,cost,andscalability enterprisesmustbeaddressedtoensurethetechnologyisa feasible and extensively espoused result for secure and accessiblevoting.Sequestrationenterprisesassociatedwith the use of face recognition technology must also be addressedtocovertheobscurityofchoosersandhelpabuse of particular data. Overall, the result of enforcing a decentralizedadvancingsystemusingblockchainand face recognitiontechnologywouldbeamoresecure,transparent, and accessible voting process that promotes trust in the popular system and ensures accurate and fair election results.
10. SUMMARY:
Adecentralizedvotingsystemusingblockchainbyface recognitionisapromisingsolutionforenhancingthesecurity andtransparencyofthevotingprocess.Thissystemutilizes facial recognition technology to ensure the accuracy of a decentralized voting system using blockchain by face recognitionisapromisingsolutionforenhancingthesecurity andtransparencyofthevotingprocess.Thissystemutilizes facialrecognitiontechnologytoensuretheaccuracyofvoter identification, while blockchain technology provides a tamper-proofandimmutableledgerofallvotingtransactions. The use of the SHA-256 algorithm further enhances the securityandintegrityofthesystem.Overall,thistechnology has the potential to increase voter participation, enhance electionsecurity,andimprovethetrustandlegitimacyofthe democraticprocess.
11. CONCLUSIONS
In conclusion, a decentralized voting system using blockchain by face recognition has the potential to revolutionize the voting process by providing a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof system. The integration of facial recognition technology can help fraud, to prevent fraudulent voting and ensure the accuracy of voter identification, while blockchain technology can pro-vide a decentralizedandimmutableledgerofalltrans-actions.The use of the SHA-256 algorithm can further enhance the security and integrity of the system by creating unique digitalfingerprintsofvoterinformation,votes,andblocks.
However,therearestillseveralchallengesthatneedtobe addressed to ensure the widespread adoption of such a system, including concerns about the accuracy and bias of facialrecognitiontechnology,theneedforsecureandreliable hardware, and the potential for cyber-attacks on the blockchain network. Additionally, legal and regulatory frameworkswillneedtobedevelopedtoaddressissuessuch asvoterprivacy,dataprotection,andtransparency.
Despitethesechallenges,adecentralizedvotingsystem using blockchain by face recognition has the potential to increasevoterparticipation, enhanceelectionsecurity,and improvetheoveralltrustandlegitimacyofthedemocratic
process.Furtherresearchanddevelopmentinthisareacan helptoovercometheremainingobstaclesandbringabouta new era of secure and transparent voting systems. The remainingobstaclesandbringaboutaneweraofsecureand transparentvotingsystems.
12. REFERENCES
[1] D-BAME: Distributed Blockchain-Based Anonymous MobileElectronicVotingEhabZaghloul,Tong-tongLi, Senior Member, IEEE, and Jian Ren, Senior Member, IEEEINTERNETOFTHINGSJOURNAL,VOL.8,NO.22, NOVEMBER15,2021

[2] Blockchain Based Online Voting System Using RSA Algorithm Kingsle Edwin, Hepzibah Christinal and Abraham Chandy, EasyChair: Institute of Tech-nology andSciences,Coimbatore,IndiaFebruary1,2022
[3] SecuringtheElectoralE-VotingSystemUsingBlockchain TechnologyTaiwoAdekeyeDataScience5andArtificial Intelligence Bournemouth University Bournemouth, United Kingdom, uploaded by Taiwo Adekeye on 13 January2022.
[4] SecureVotingSystemusingBlockchainMethodManav Tiwari, Utkarsh Thaokar, Sahil Sangwan, Shubham Gupta,DepartmentofInformationTechnology,Sinhgad Institute of Technology, Lonavala, India. International Journal of Research in Engineering, Science and Management,Volume5,Issue1,January2022.
[5] Data Management, Analytics and Innovation Proceedings of ICDMAI 2019, Volume 1, Advances in IntelligentSystemsandComputingVolume1042,Series Editor: Janusz Kacprzyk, Systems Research Institute, PolishAcademyofSciences,Warsaw,Poland
[6] Chaintegrity: blockchain-enabled large-scale e-voting system with robustness and universal verifiability, ShufanZhang· LiliWang·HuXiong©Springer-Verlag GmbH
[7] Using Blockchain Data Security Management for EVotingSystemsErickFebriyanto,Triyono,NinaRahayu, Kelvin Pangaribuan, Po Abas Sunarya The 8th International Conference on Cyber and IT Service Management(CITSM2020)OnVirtual,October23-24, 2020
[8] ElectionBlock: An Electronic Voting System using Blockchain and Fingerprint Authentication Mohamed Ibrahim, Kajan Ravindran, Hyon Lee, Omair Farooqui, Qusay H, Mahmoud 2021 IEEE 18th Inter-national Conference on Software Architecture Com-panion (ICSAC)
[9] Digital Voting: A Blockchain-based E-Voting Sys-tem using Biohash and Smart Contract Syada Tasmia Alvi, Mohammed Nasir Uddin, Linta Islam EEE Xplore Part Number:CFP20P17-ART;ISBN:978-1-7281-5821-1
[10] Decentralized E-voting system based on Smart Contractby usingBlockchainTechnologyAliMansour Al-madani,Dr.AshokT.Gaikwad,VivekMahale,Zeyad A.T.Ahmed
[11]The Future of Electronic Voting System Using Blockchain Md. Razu Ahmed, F.M. Javed Mehedi Shamrat,Md.AsrafAli,Md.RajibMia,Mst.ArifaKhatun
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIEN-TIFIC & TECHNOLOGY RESEARCH VOLUME 9, ISSUE 02, FEBRUARY2020ISSN2277-8616

