Smart Bicycle-Sharing System
Tejas Bobale1, Atharva Ghule2, Sanket Jadhav3, Savita Sangam4 Shivajirao S. Jondhale College of Engineering, Dombivli (E.) University of Mumbai
Abstract Students who can’t afford vehicles or have to stay away from their hometown to seek education may sometimes encounter the problem of traveling to places where public transport services are not available. Bicycling is an alternative means of transport for shortdistance movement. It is important to make the rental bicycle usable and available to the person in need at the appropriate time and place. Inevitably, providing the college with a steady supply of rental bicycles becomes a major concern. Rental bicycles are popular in many urban areas to help people expand their mobility. Public bicycle rental systems have become popular in recent years. Considering this, many universities and colleges provide bicycle-rental pilot programs for faculty, staff, and students. The expanded program provides people on campus with quick, accessible transportation with added features like a tracking device, SOS distress signal button, and gesture-controlled taillight indicator. This paper presents a prototype model of a smart bicycle-sharing system. The proposed system incorporates an Android Application which lets you book a bicycle; the provided bicycles have taillights that indicate the direction of the turn using the motion of the rider’s hand. Bicycles consist of a tracker which sends notifications to the admin’s smartphone of their current location and an SOS button that will send an alert to the admin when pressed.
Keywords RFID, MPU6050, A9G board, Arduino UNO/NANO,NRF24L01,SMS,SOS.
1. INTRODUCTION
Rental bicycles are popular in many urban areas to help people expand their mobility. Making the rental bicycle usable and available to the public at the appropriate time and place is important [1][2]. This Projectconsistsoffourmodules,AndroidApplication,a LockingMechanism,atracker,andaTaillightindicator.
In this JAVA-based Android application, students and staff can rent a bicycle from the college campus by creating their accounts on the Application. Users can register and log in using their Username and password, book bicycles, check current ride duration, update their profile, and check their history. In the android part, the front end involves XML, and the back endinvolvesAndroidJavaandFirebase.TheIDEusedis AndroidStudio[3].
The bicycle parking system with a digitally controllable locking mechanism, compatible with the system requested by the provider, such as RFID cards, tags, etc [11]. The proposed system incorporates an RFIDcardreader whichscanstheusercardandchecks for a valid user. Our innovative bicycle parking system, well thought-out from all aspects, enables the user to safely lock the bicycle in seconds without having to carry any lock. The ingenious locking mechanism locks thebicycle’sfrontwheel[12].
The tracker has an Ai Thinker A9G GSM/GPRS Development Boardwhich has a SIM slot in it. The admin can send predefined text messages (e.g., “SEND LOCATION”) on the phone number of the inserted SIM and then the tracker will send back a message with its GPScoordinatesandGooglemaplink alongwithit.The tracker comes with an SOS button which the rider can use if he/she is lost or not feeling safe with the surrounding. When the rider presses the button, the tracker will send an alert message and also call on the admin’sphone[15].
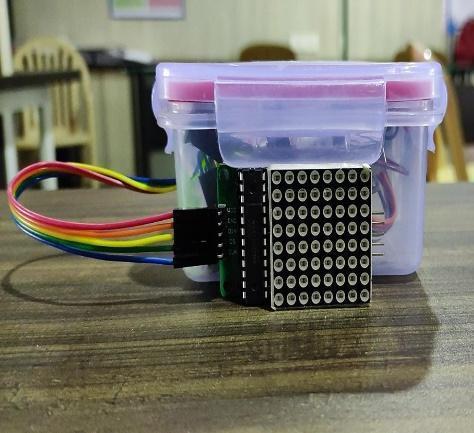
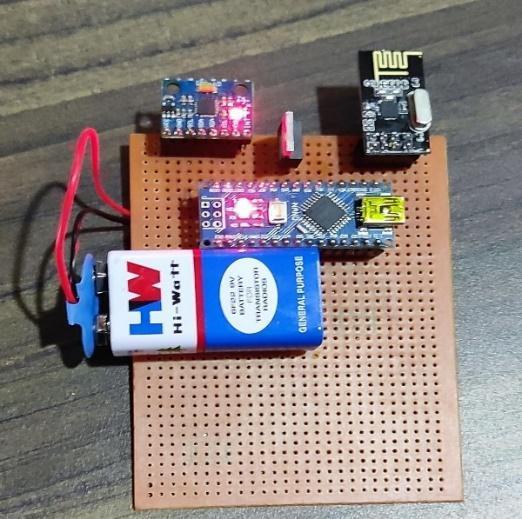
The Gesture-controlled taillight indicator consistsof2keycomponents,thegesture-controlglove to be worn by the user and an indicator unit (8x8 LED matrix)tobemountedbelowtheseatofthebicycle.The 2 devices wirelessly communicate with each other to achieve the desired output. The Arduino Nano board initializes the gyroscope (MPU6050 module) that collects data and sends raw values to Arduino. The Arduino code uses a tiny machine learning model with gesture recognition: each hand movement is analysed andrecognized(handtiltedtotheleft,right,front,etc.).
Then this signal is sent with the help of the NRF24L01 2.4GHz Wireless Transceiver Module to another NRF24L01 Module connected to Arduino Uno which showstheoutputwithan8x8LEDmatrix.Accordingto the signal received by the Arduino Uno, some patterns lightupontheLEDmatrix,sothatotherroaduserscan seewhatthecyclistisgoingtodo(willtakerightorleft turn)[19][20].
2. RELATED WORK
Literature survey of the existing system

A sustainable transportation system is currently necessary since car CO2 emissions contribute to the greenhouse effect [7][8]. These polluting vehicles are being utilized more frequently and for far shorter distances on college campuses right now. The purpose of this study is to design a reliable and affordable bicycle-sharing system for a college campus-based bicycle-sharing system [3][4]. Different conditions and scenariosmakeitdifficultforthealgorithmtoruninthe real environment due to the following reasons: using a real-time clock instead of the internal timer of the Arduino that will not reset in case there is a power failure and using GPS to track bicycle location. [1]. The bicycle industries lack efficient management techniques, such as production management, theft prevention, and sale certification, so these industries are looking to RFID to address their issues. An antenna toreceivethedataandanidentificationcodeencodedin a chip make up most of the non-contact automated identification technology known as RFID. The bicycle industry now favours installing RFID. The problem of insufficient power supply will be solved by integrating solarpanels[13][14].Inlocationslikeuniversitytowns, where bicycles are one of the quickest and most economical methodsforstudentsto getaround, bicycle theft is a major issue. For instance, Gottingen reports 1,200 bicycle thefts annually, while Germany reported more than 300,000 thefts in 2014. The paper offers a battery-saving architecture that may be used to locate bothstolenandlostbicycles[17].Thisarchitectureuses opportunistic communication with collection nodes positionedinbusyareasto trackthelocationsofstolen bicycles. Although lowering power consumption when bicycles are under the radar, the program is also intended to protect owners of bicycles that have not been reported as stolen from losing their privacy [18]. The location estimates errors will still be higher than those of a pure GPS solution and users privacy is not preservedasbikesareinastatewheretheycanalways betracked[3].
OurapproachistoprovideaBicycleSharingSystem which will allow students to easily book a bicycle for themselves also in consideration of the safety of the riderandthebicycleeachbicyclewillbeprovidedwith atrackingdevicewithanSOSbuttoninstalledinitused by rider whenever they are feeling uncomfortable with their surroundings. With one push of the button, they can make send an alert message sending their location directly to the Admin [10]. The provided bicycle also comes with a gesture-operated indicator light which is easy to use and helpful for the rider to give indications beforetakinganyturn[19][20].
3. METHODOLOGY
Flowchart
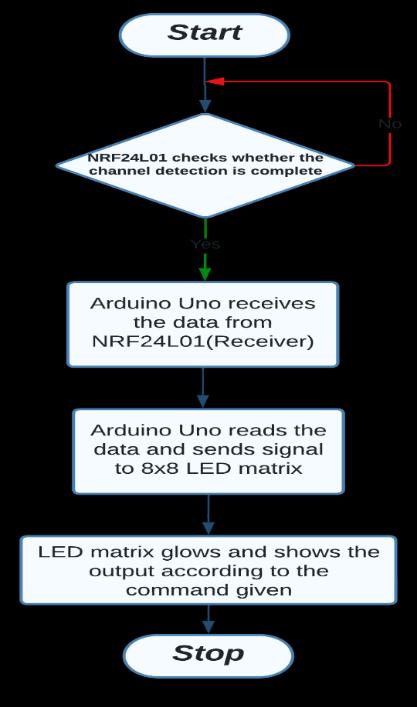
Fig.2 shows the working of the gesture-controlled glove used for transmitting the signals for every hand movement made by the rider. The gesture control glove controlstheindicatorlightonthebackofthebicycle.The glove has an MPU6050 module on it which acts as a gyroscope, it gives the reading of the X, Y, and Z axis in which direction the user rotates his/her hand. The Arduino Nano gets those readings and transmits the informationusingtheNRF24L01transmittingendtothe NRF24L01receivingend[19].
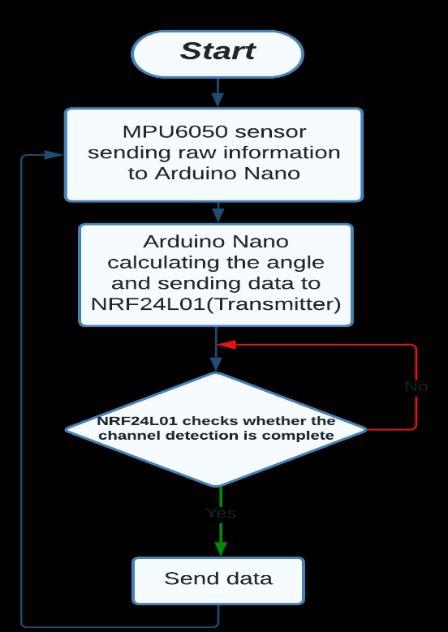
Fig.3 shows the working of receiving end of the NRF24L01. The NRF24L01 receiving ends get data and passittoArduinoUnowhichreadsthedataandgivesan output signal to the 8x8 LED matrix. If Arduino Uno receives left-direction data, the 8x8 LED matrix will indicate the rider is going to turn left showing a leftscrolling arrow and vice versa. When the rider applies the break the LED matrix glows all the LEDs indicating theriderisdecelerating[20].
4. Proposed System

Software: The Android Application was built on AndroidStudio;thefrontendismadeusingXMLandthe backend is based on JAVA and Firebase database. The user will need to Register first and then Log in to the systemusingaUsernameandPassword.Whenrequired theycan change their oldPasswordtoa newone.They canAddorUpdatetheirdetailsontheProfilepage.The usercanselect“Booking”fromtheDashboardandview all the available Bikes for Ride. The rider can see bike details in the bike description system. Once the Rider selects“StartRide”thechronometerisinitiatedandwill stop only after selecting the “End Ride” option. After clickingthe“EndRide”optiontheusercanseethetotal durationofhisrideandmustpayaccordingly.Theuser canviewhis/herpreviousridesintheHistoryTab.
Hardware: Hardwareconsistsof3maincomponents:-
1. LockingMechanism
2. Tracker
3. TaillightIndicator
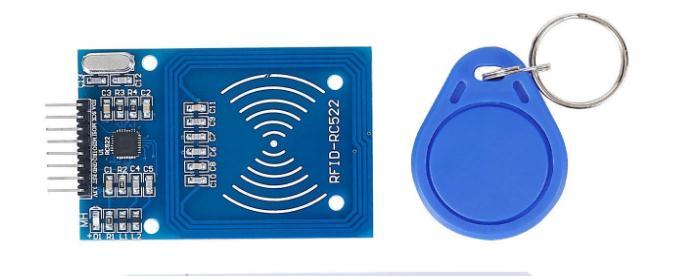
1. Locking Mechanism: - Fig shows Mifare MFRC522 RFID card reader. The RFID reader is a networkconnectedgadgetthatcanbecarriedaboutorfixedtoa surface.Itsendssignalsthatturnonthetagusingradio waves.After beingturnedon,thetag returnsa wave to the antenna, where it is converted into information. It readsRFIDcardsandverifieswhethertheuserisvalid. Thelockcanbeopenedonlybyavalidkey[11][12].
attached to it. The system includes Ai Thinker A9G Development Board: it has a built-in GSM/GPRS, GPS, and a battery circuit in it and to provide commands to this board we are using ESP32 based board which will bepoweredbya3.7vbattery,andaswitchbuttonwhich actsasanSOSbuttonwherebyjustpressingandholding onthebuttoncanalerttheadminandshareyourcurrent location via SMS. By sending one SMS you will get the GoogleMapslinkwithitscurrentlocationinit[17][18].
2. Tracker: - This is a multi-purpose tracker, which gives its current location with a Google map link
3. Taillight Indicator: - The system consists of 2 key components,thegesturecontrolglovetobewornbythe userandanindicatorunittobemountedbelowtheseat of the bicycle. The 2 devices wirelessly communicate witheachotherwiththeNRF24L01transceiver module toachievethedesiredoutput.
The Glove unit consists of a gyro sensor (MPU6050) and NRF24L01 transmitter which is controlled by an Arduino Nano. The glove unit is poweredbya9vbattery.
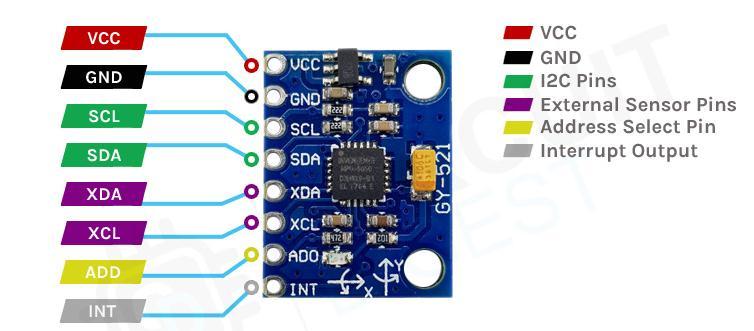
The glove controller receives tilt commands fromtheMPU6050module.TheMPU6050isaninternal 3-axis accelerometer and 3-axis gyroscope MicroElectro-MechanicalSystems(MEMS)device.Thismakes it easier for us to measure a system's or object's acceleration, velocity, orientation, displacement, and many other motion-related properties. When the user tiltstheirhandinanydirectiontheMPU6050sendsraw values to the Arduino Nano. These raw values are processed by the Arduino Nano. Arduino Nano reads
theserawvaluesandseparatesthesevaluesindifferent ranges(+X/-Xaxis,+Y/-Yaxis,and+Z/-Zaxis)[19].
5. RESULTS

TheArduinoNanothentransmitsthevaluesto receivingendwiththehelpoftheNRF24l01transceiver module.Itusesthe2.4GHzbandanditcanoperatewith baudratesfrom250kbpsupto2Mbps.Ifusedinopen spaceandwithalowerbaudrateitsrangecanreachup to100meters[20].
The indicator is a battery-powered unit integrated with an Arduino Uno, 8x8 LED matrix, and NRF24L01 receiver. When the NRF24L01 receiver receives the data, it sends that data to Arduino Uno. ArduinoUnothenreadsthedataand

checkswhichdirection(+X/-Xaxis,+Y/-Yaxis,or+Z/-Z axis) command is received and then shows the output with the help of the 8x8 LED matrix. The LED matrix glows differently for every hand movement. If it is a ‘direction’ command, the LEDs will glow and shows left/right scrolling arrows. and if it is a ‘braking' command, it glows all the LEDs together indicating the riderisdecelerating.Thus,thesystemprovidesaneasy andcomfortablebicycleindicatorsystem[20].
Calculations:
Fig.6 is the Dashboard of the Android Application. It shows the following sections: Booking, Profile, Current Ride, and History which will take them totherespectivetabs.e.g.
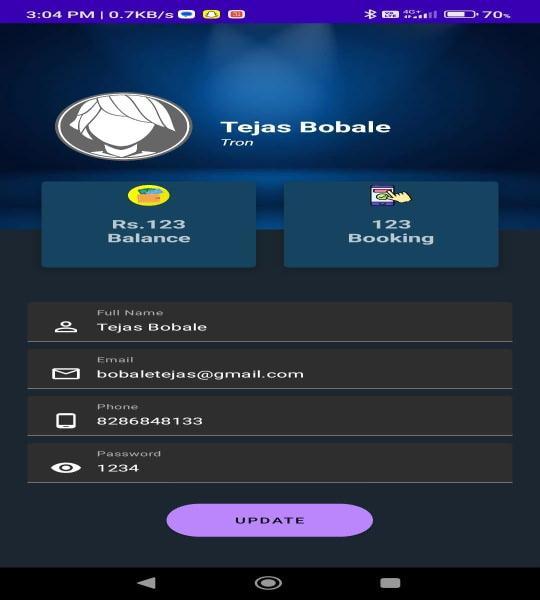
Fig.7 shows the profile details of the user. Here user can edit and update his information as he wants. Theusersimplyhastoreplacetheinformationshownin the Edit tabs and after changing the information in the tabs as they please, they have to press the ‘UPDATE’ button on the bottom of the screen. Once the ‘UPDATE’

button is pressed the data gets updated on the firebase database, if the user leaves without pressing the ‘UPDATE’buttondatawillnotchange.
Fig.10 shows the History tab of the Android application. It shows the list of previously booked rides separatedbyDates.ItalsoincludestheIDnumberofthe bicycle used, the time of the booking, and the total durationoftheriderecordedintheFirebasedatabase.
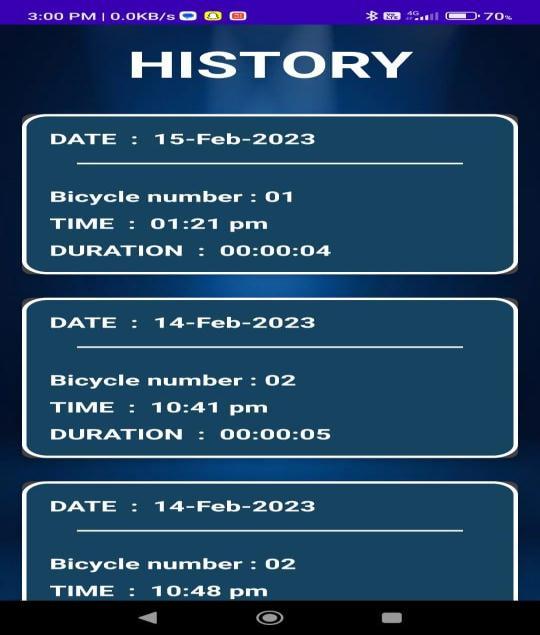

Fig. shows the Booking page of the application. Theusercanchooseanybicyclefromthelistofbicycles. Once the user books a bicycle the chronometer in the applicationwillgetstarted.Thechronometercountsthe duration of the ride of the bicycle. The chronometer stops only when the user presses the “End ride” button intheapplication.

Fig.Gesturecontroltransmitter
On the Transmitting end, the MPU6050 module gives raw values of X, Y, and Z directions. The Arduino Nano gets these raw values and calculates the proper angleofthedirectionriderismovinghis/herhand.Each direction(Left,Right,andfront) hasbeengivendifferent valuesasoutput, so whenthe rider moveshis/herhand the Arduino Nano will send a signal (set for that direction)withthehelpoftheNRF24L01module(which worksasbothtransmitterandreceiver).Thesystemgets powered by a 9v battery which in the transmitting end lastsfor15days
On the Receiving end, the NRF24L01 module receivesthesignalfromthetransmittingendoftheglove and passes it to Arduino Uno. Arduino Uno reads the signal and recognizes the hand movement. The Arduino Uno then gives the 8x8 LED matrix commands to show thedesiredoutput.
When the rider moves their wrist in the right direction the Led matrix will show a right scrolling arrow on the
LED matrix and vice versa. When the rider moves their wrist in the front direction ( while applying brakes ) all the LEDs on the LED matrix will glow and alert the vehicles behind the rider that the rider is decelarating. The system gets powered by a 9v battery which in the transmittingendlastsfor5days
In future work, we can incorporate a safe online transaction gateway for payment. Further, we can develop a system to generate virtual RFID keys which will reduce the time, resources, and human interference [22].

7. REFERENCES
[1] M. Bhandari, S. Bandodkar, A. Falcao, G. Dhawalikar andS.Mahaddalkar,"Implementationofbicyclesharing system in a college campus," 2017 7th International ConferenceonPowerSystems(ICPS),Pune,India,2017, pp.820-823,doi:10.1109/ICPES.2017.8387402
[2]R.LuoandY.Shen,"TheDesignandImplementation of Public Bike Information System Based on Google Maps," 2009 International Conference on Environmental Science and Information Application Technology, Wuhan, China, 2009, pp. 156-159, doi: 10.1109/ESIAT.2009.298.
Thisisa multi-purposetracker,itcanalso actasanSOS button wherebyjust pressingandholdingonthe button you can share your current location via SMS, and it can make a call to that SOS number it has one more feature initusingwhichyoucangetthecurrentlocationofthis A9G board by just sending an SMS. By sending one SMS you will get the Google Maps link with its current locationinit.
6. CONCLUSION
In this paper, we created Smart Bicycle renting system. The user can book a bicycle from the Android Application made on Android Studio using Java programming language and Firebase Database. The user must first book a bicycle from the application, after booking a counter will start which records the duration oftheride.Oncethecounterisstartedtheusermusttake theRFIDcardwhichisthekeytoopentheRFIDlock.The SmartBicyclecomeswithatrackerandagesture-control glove.Thetrackergivesitslocationtotheadmin’sphone when a specific command is sent through SMS to the tracker. The tracker also has an SOS button which when pressed sends an alert to the admin via phone call. The gesturecontrolgloveisusedtocontroltheindicatorlight on the back of the bicycle. The glove has an MPU6050 module on it which acts as a gyroscope, it gives the reading of the X, Y, and Z axis in which the user rotates his/her hand. The Arduino gets those readings and showsthelightindicationaccordingly.
[3] Y. Zhao, L. Chen, C. Teng, S. Li and G. Pan, "GreenBicycling: A Smartphone-Based Public Bicycle Sharing System for Healthy Life," 2013 IEEE International Conference on Green Computing and Communications and IEEE Internet of Things and IEEE Cyber, Physical and Social Computing, Beijing, China, 2013, pp. 1335-1340, doi: 10.1109/GreenCom-iThingsCPSCom.2013.232.
[4] S. Shen, C. -X. Lv, H. Zhu, L. -J. Sun and R. -C. Wang, "Potentials and Prospects of Bicycle Sharing System in SmartCities:AReview,"inIEEESensorsJournal,vol.22, no. 8, pp. 7519-7533, 15 April15, 2022, doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3160178.
[5] G. Liao and J. Zhang, "Information query for public bicycle service based on Andriod," Proceedings 2014 IEEE International Conference on Security, Pattern Analysis, and Cybernetics (SPAC), Wuhan, China, 2014, pp.126-129,doi:10.1109/SPAC.2014.6982671.
[6] W. Rao and Y. Jiang, "A Bi-level Approach for Optimizing Rental Station Locations in Public Bicycle System," 2019 4th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Engineering (ICITE), Singapore, 2019, pp. 39-43, doi: 10.1109/ICITE.2019.8880190.

[7]L.KangandC.Biao,"LessonsfromDevelopingPublic Bicycle System in Hangzhou," 2012 2nd International Conference on Remote Sensing, Environment and TransportationEngineering,Nanjing,China,2012,pp.14,doi:10.1109/RSETE.2012.6260615.
[8] X. Shi, Q. Zhou, X. Qu, G. Liu and Z. Gong, "Understanding city dynamics based on public bicycle data: A case study in Hangzhou," 2016 10th
International Conference on Software, Knowledge, Information Management & Applications (SKIMA), Chengdu, China, 2016, pp. 146-150, doi: 10.1109/SKIMA.2016.7916212.
[9]S.WangandR.Wu,"TheStaticRebalancingProblem in Bicycle-Sharing Systems with Unusable Bicycles," 201916thInternationalConferenceonServiceSystems and Service Management (ICSSSM), Shenzhen, China, 2019,pp.1-6,doi:10.1109/ICSSSM.2019.8887745.
[10]N.Stamatiadis,G.PappalardoandS.Cafiso,"Useof technology to improve bicycle mobility in smart cities," 2017 5th IEEE International Conference on Models and Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems (MT-ITS), Naples, Italy, 2017, pp. 86-91, doi: 10.1109/MTITS.2017.8005636.
[11] Kun-Ying Lin, Ming-Wei Hsu and Shi-Rung Liou, "Bicyclemanagementsystemsinanti-theft,certification, and race by using RFID," Proceedings of 2011 Cross Strait Quad-Regional Radio Science and Wireless Technology Conference, Harbin, 2011, pp. 1054-1057, doi:10.1109/CSQRWC.2011.6037138.
[12] T. T. Braun, J. Schöpfel, C. Schweer and N. Pohl, "A Harmonic Automotive Radar for Bicycle Detection with RFID Tags at 79/158 GHz," 2022 IEEE/MTT-S International Microwave Symposium - IMS 2022, Denver, CO, USA, 2022, pp. 526-529, doi: 10.1109/IMS37962.2022.9865601.
[13] A. I. Alam, M. Rahman, S. Afroz, M. Alam, J. Uddin and M. A. Alam, "IoT Enabled Smart Bicycle Safety System," 2018 Joint 7th International Conference on Informatics, Electronics & Vision (ICIEV) and 2018 2nd International Conference on Imaging, Vision & Pattern Recognition (icIVPR), Kitakyushu, Japan, 2018, pp. 374378,doi:10.1109/ICIEV.2018.8641067.
[14] K. Yamazaki and T. Nakajima, "A Risk Information Provision System on Bicycle Parking Lots," 2017 IEEE International Congress on Internet of Things (ICIOT), Honolulu, HI, USA, 2017, pp. 162-165, doi: 10.1109/IEEE.ICIOT.2017.29.

[15] A. Bochem, K. Freeman, M. Schwarzmaier, O. Alfandi and D. Hogrefe, "A privacy-preserving and power-efficient bicycle tracking scheme for theft mitigation," 2016 IEEE International Smart Cities Conference (ISC2), Trento, Italy, 2016, pp. 1-4, doi: 10.1109/ISC2.2016.7580789.
16] F. Tabei, B. Askarian and J. W. Chong, "Accident Detection System for Bicycle Riders," in IEEE Sensors Journal,vol.21,no.2,pp.878-885,15Jan.15,2021,doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.3021652.
[17]L.-W.ChenandC.-Y.Cho,"BiLight:ASmartBicycle Monitoring and Finding System for Rider Safety Based on IoT Technologies," 2022 IEEE International Conference on Pervasive Computing and CommunicationsWorkshopsandotherAffiliatedEvents (PerCom Workshops), Pisa, Italy, 2022, pp. 100-102, doi:10.1109/PerComWorkshops53856.2022.9767405.
[18] P. Dutta and U. S. G. V. Dontiboyina, "NaviRide: SmartBicycleComputerwithGPSWaypointIndicators," 2016 Second International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology(CICT),Ghaziabad,India,2016,pp.472-477, doi:10.1109/CICT.201
[19] Gesture control bicycle indicator gloves. Nevon Projects. (2022, November 30). Retrieved March 17, 2023,fromhttps://nevonprojects.com/gesture-controlbicycle-indicator-gloves/
[20] Z. Zou, Q. Wu, Y. Zhang and K. Wen, "Design of Smart Car Control System for Gesture Recognition BasedonArduino,"2021IEEEInternationalConference on Consumer Electronics and Computer Engineering (ICCECE), Guangzhou, China, 2021, pp. 695-699, doi: 10.1109/ICCECE51280.2021.9342137.
[21] X. Liu, C. Liu, M. Lu and D. Liu, "Regenerative braking control strategies of switched reluctance machine for electric bicycle," 2008 International ConferenceonElectricalMachinesandSystems,Wuhan, China,2008,pp.3397-3400.
[22] D. Zanic, R. Gotal and S. Hrabar, "Multi-band Antenna System for Fully Connected Smart E-bicycle," 2021 International Symposium ELMAR, Zadar, Croatia, 2021, pp. 43-48, doi: 10.1109/ELMAR52657.2021.9550900.
[23]Y.-X.Zhao,Y. -S.SuandY. -C.Chang,"AReal-Time Bicycle Record System of Ground Conditions Based on Internet of Things," in IEEE Access, vol. 5, pp. 1752517533,2017,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2740419.
[24] Y. Taniguchi, K. Nishii and H. Hisamatsu, "Evaluation of a Bicycle-Mounted Ultrasonic Distance Sensor for Monitoring Road Surface Condition," 2015 7th International Conference on Computational Intelligence, Communication Systems and Networks, Riga, Latvia, 2015, pp. 31-34, doi: 10.1109/CICSyN.2015.
[25] M. Zhao, S. Stasinopoulos and Y. Yu, "Obstacle detectionandavoidanceforautonomousbicycles,"2017 13th IEEE Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE), Xi'an, China, 2017, pp. 1310-1315, doi:10.1109/COASE.2017.8256281.
[26] L. Keo and M. Yamakita, "Controlling balancer and steering for bicycle stabilization," 2009 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, St. Louis, MO, USA, 2009, pp. 4541-4546, doi: 10.1109/IROS.2009.5353966.

