IDENTIFICATION OF RISK FACTORS FOR RUNNING RELATED INJURIES USING MACHINE LEARNING
 G.Bhuvanesh1 , G.Nallavan2
G.Bhuvanesh1 , G.Nallavan2
Department of Sports Technology, Tamilnadu Physical Education and Sports University, Chennai-600127, India.

Abstract - Running is a very accepted activity namely used thoroughly the sports to solve requested aim within particular game during the opportunity. This too bearing extreme risk of injury other than correctly prepared and understood warmup and restrict to the majorly involved powers all along this project. The causes of deformity or strain in this endeavor is established various risk determinants. Here in this place work, use of ML approaches to comprehensively resolve and recognize the determinants and discover patterns in runners7 Statistical judgment of the data is acted utilizing ML algorithms. The results help forecasts harm risk and allow new strategy that are used to additional sports.
Key Words: Machine Learning, Injury stop, Athlete Injuries Identification.
1. INTRODUCTION
1.1 BACKGROUND:
Runningisindividualofultimatepopularsportsinthe planet.Despitepowerfulevidenceofstrengthbenefits,the occurrence of musculoskeletal become worn injuries remnantsextreme.Ina currentlywrittenorderlyreview, almosthalfofthe22,823vineswereharmedallalongthe attention ending. Dependingon the study design and the cohortintentional,theharmratechanges'tween19-79%. Forexample,long-distancerunnersinadditiontonovices aremoredependentonsomethingharmthanonewhoruns andrecreationalvines.However,skilledwassamenessin overallharmratesmiddlefromtwopointsfemalerunners (20.8per100marathoners)andmalemarathoners(20.4 per 100 marathoners)2. Many studies have concerning detailsweaknesses7.Lackofbackward-lookingdatagroup, stress listening, multivariate reasoning of outside and withinriskfactors,orpatientself-stateddisease.Moreover, the multifactorial influence of outside and within risk determinants on muscular wasted injury1. Bone stress harms,sinew disorders, andpower harms - yet expected completelyelucidated.Despitealluremultifactorialtype,the latentetiologyofbecomewornharmsmaybeelucidatedby load-recoveryimbalances.Riskdeterminantsforevolving running-accompanying harms endure be identified in additiontoobjectivepreparationloadlistening.Inaddition
to stress limits, within (anatomy, biomechanics, musculoskeletalfabriccondition,etc.)andextrinsictraits (atmosphere, underground, shoe, etc.) have existed concisely emphasize as main risk factors3. Since running injuriesaregenerallyonaccountofbecomeworn,alinked studyofboneandinfluencecondition,biomechanics,and individual running method Is wanted to label risk determinants for these injuries. Is an main approach. VitaminD,cartilagemass,calculatingconstruction,ground reactionforce,loadrate,rhythm,andrhythmareconcisely emphasizeasimportantlimits.Currentresearchengagedof sportsharmsdisplaystheneedtoreconsiderindividualrisk factors towards individual harm patterns that are dynamicallyaffectedbydiversifiedmediators.VariousML modelshaveexistedsecondhandinthepasttoresolvesport riskdeterminantstoanalyzeindividualapproachesandthe extremedifferenceofresponsiblemediators.MLmodelscan discoverconnectionsbetweenrecommendationvariables andharvestvariablesfromlargeamountsofsampledossier utilizinggrowthtreasure.Thisadmitstoforecastupcoming consequencesfromnewrecommendationoutsidetheneed formanuallyprioritizefunctions.Thesepredictingmodeling methods secondhand in the framework of sports harm indicatorandpreventioninvolveaffectedaffectinganimate nerve organs networks, SVM, and Random woodland. Particularlyinthereasoningofriskfactorsandindicatorof groupsportsharmsorneuromuscularandmusculoskeletal
pathologies, priorstudies have presented hopeful results utilizingMLmodels.Incontrasttotheprocedures,anew arrangement called Deep Gaussian Covariance Network (DGCN)issecondhandastheMLmodel.Itshowsasingular alliance of affecting animate nerve organs networks and Gaussianprocesses(GP).BecauseGaussianprocessesare probabilistic ML models, they have the advantage of forecasting model changeableness. This wealth that forecasting the chance of injury is continually followed apiecemodel'sprophecyofsecurity.Theaimofthisstudy searchoutdecidewithinandoutsideriskdeterminantsand the interactions, and use machine learning deal with to recognizeriskdeterminants.Istoevaluatethepertinenceof andpredicttheriskofinjury8 .
2. METHODOLOGY
2.1 BLOCK DIAGRAM:
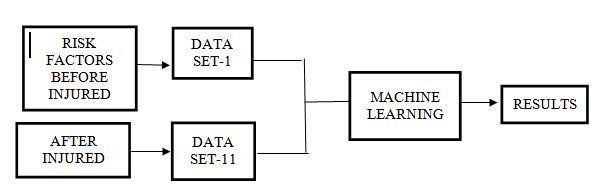
Machine learning-located Risk determinant reasoning formarathonersatreferstotheuseofmachineintelligence algorithmstoanalyzeanddefinedossiercalmfromsensors orcamerasallalongrunningevents.Byutilizingmachine intelligencemethods,coachesandsportscangainvisions into the biomechanics and technique of the throws, label districtsforbettering,andcreatedossier-drivenresolutions to advance efficiency. Some instances of machine intelligence-based reasoning for vines contain categorization of throws established distance and technique, forecasting of optimum release angles and velocities, and labeling of determinants that influence successfulthrows.Theuseofmachineintelligence-located throws reasoning can help professionals and coaches to advancetheirtrainingmenusandenhancetheirdepictionin aggressiveoccurrences.
inthewaythatthevelocity,angle,andreleasepointofthe confuse.
2.Datapreprocessingpiece:Thispieceincludescleansing, filtering,andarrangethecomposeddossiertoassembleit forreasoning.

3. Feature extraction piece: This piece includes eliciting appropriate features from the preprocessed dossier, to a degreethereleaseangle,speed,andspinrateoftheround object.
4. Machine learning piece: This module includes asking machine intelligence algorithms to the culled features to labelpatternsandequivalencesmiddlefromtwopointsthe variousvariables.
5. Performance reasoning module: This piece includes resolvingtheresultsofthemachineintelligencealgorithms tolabelareasofbetteringinthejock'smethodandform.
6.Visualizationpiece:Thispieceinvolvesgivingtheresults of the study in a graphical plan to manage smooth for coachesandathletestodefineandcomprehendtheverdicts.
2.3 DATA COLLECTION:
Inthiscase,thedossierpurchasemodulewouldinclude accumulating dossierfromtheaccelerometer sensorthat would measure the increasing speed of the discus all the whiletheconfusingoccurrence.Thedossierpreprocessing piecewouldinvolvedrainingandsmoothingthedossierto eraseblastandotherartifacts.Thefeatureancestrypiece would before include gleaning features to a degree peak increasing speed, period to peak dispatch, and the management of the acceleration heading. The machine intelligence piece would include administering machine learning algorithms to the culled physiognomy to label patterns and equivalences 'tween the different variables. Theefficiencyreasoningpiecewouldresolvetheresultsof themachineintelligencealgorithmstoidentifyextentsof betteringinthecompetitor'smethodandformestablished the accelerometer sensor data. Finally, the imagination piecewouldpresenttheresultsofthestudyinagraphical layouttomanageeasierforcoachesandsportstodefineand believetheverdicts.
2.4 DATA PREPROCESSING MODULE:
2.2 SYSTEM MODULES:
Inthecontextofmachineintelligence-locatedthrowsstudy forhurdlers,someuniversalschememodulescancontain:
1. Data procurement module: This piece includes accumulatingdossierfromsensorsorcamerasallthewhile runningevents.Thedossierconcedepossibilityinvolvenews
The data preprocessing piece in machine intelligence-located throws reasoning for vines involves fittingnuditydossiercalmfromtheaccelerometersensor forstudybyremovingturbulence,penetrating,andsimilar thedossier.Thispieceisimportantbecauseitguarantees that the dossier secondhand in the after analysis is of excellenceandemptysomeforeignfacts.Thefollowingare someordinarystepsinthedossierpreprocessingpiece:
Data cleansing: This includes removing some corrupt or invaliddossierpointsthatgrantpermissionshowwithout clothingdata.Forexample,iftheaccelerometersensorisnot correctlymeasure,itcanproducedatanamelyexceptforthe wontedrange,andaforementioneddossierpointsneedtobe distant.
Filtering:Thisincludeserasingsomeroarorotherundesired signalfromnuditydossier.Therearevarioustypesoffilters thatmaybeapplied,inthewaythatareduced-passcleanto eraseextreme-frequencycommotion.
Normalization: This includes climbing the dossier for fear that it has a mean of zero and a predictable difference of individual. This guarantees that the dossier act the same scaleandadmitsforsmoothcorresponding'tweenvarious datapoints.
Featureorigin:Thisincludeslabelingappropriatefacefrom thepreprocesseddatathatmaybesecondhandintheafter study. For example, the peak acceleration, opportunity to peakstimulation,androuteofthespurringheadingcanbe gleanedasface.
2.5 FEATURE EXTRACTION MODULE:
Thefeatureoriginpieceinmachineintelligence-based throws reasoning for hurdlers includes labeling and selecting appropriate features from the preprocessed dossier.Thesecountenancesymbolizerecommendationto themachineintelligencealgorithms,whichuserulingclass to label patterns and equating’s in the dossier. Some average features that are derived from accelerometer sensor dossier in vines’ reasoning involve: Peak acceleration:Thisfeaturemeasuresthechiefadvantageof quickeningreachedforonediscusallalongtheconfusing occurrence.Itisanmainfeaturebecauseitspecifiesfactson theamountofforceusedtotheroundobject,thatisakey factorindecidingthedistanceoftheconfuse.Timetopeak spurring:Thisfeaturemeasuresmomentoftruthittakesfor theroundobjecttoreachitsmaximumquickening.Itisan main feature cause it specifies facts on the timing and sequencing of the various flows complicated in the confusingoccurrence.Directionoftheaccelerationheading: This feature measures the management of the spurring headingconcerningthediscus.Itisanmainfeaturecauseit specifiesnewsontheangleatthatthediscusisfreed,thatis akeydeterminantindecidingthecourseanddistanceofthe throw.Spinrate:Thisfeaturemeasurestherateatthatthe roundobjectisrevolvingallalongthethrowingoccurrence. It is an main feature cause it determines facts on the stability of the round object in departure, that is a key determinantindecidingtheaccuracyoftheconfuse.
2.6 MACHINE LEARNING MODULE:
The machine intelligence piece in machine intelligencelocatedthrowsanalysisforvinesincludespreparationand

experiment machine intelligence algorithms on the preprocessedandfeature-extracteddossiertolabelpatterns andequivalencesthatmaybeusedtoforeseeorclassifythe effect of the confuse. Some universal machineintelligence algorithmsthataresecondhandinrunner’sanalysisinvolve: Support Vector Machines (SVMs): These algorithms are frequently secondhand for categorization tasks at which pointthegoalsearchoutcalltheconsequenceofapiece(e.g., eitheritwasafavorableorfailingconfuse).SVMsworkby verdictahyperplanethatbestsegregatesthedossierinto various classes established the facial characteristics extracted.RandomForests:Thesealgorithmsarefrequently secondhandforreversiontasksatwhichpointtheaimisto foreseeaunendingchangeable(forexample,thedistanceof the confuse). Random forests work by constructing an ensembleofresolutionwood,eachofthatcreateaprediction establishedasubdivisionofthefacialcharacteristicsderived. NeuralNetworks:Thesealgorithmsarefrequentlyusedfor two together categorization and reversion tasks in vines study. Neural networks work by using a order of pertain knots (neurons) to model complex nonlinear friendships between the recommendation face and the consequence changing. The machine intelligence module too includes judging the accomplishment of the prepared models on a testingdatasettoevaluatetheirveracityandinferenceskill. Thisismaintoensurethatthemodelsareinsidefittingto thepreparationdossierandcancorrectlyforeseeorclassify theconsequenceofnewthrows.
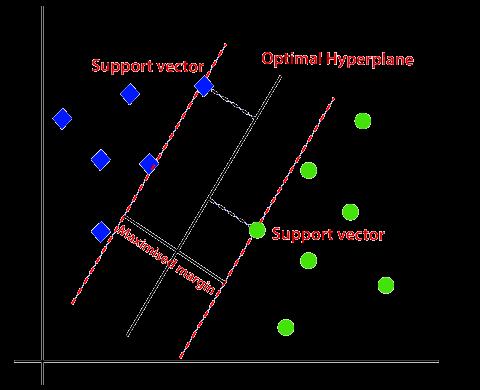
2.7 Support Vector Machines (SVMs):
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are a type of machine intelligence treasure that are frequently secondhand for classificationtasksinrunner’sstudy.TheaimofSVMssearch outfindanenergeticplanethatbestsegregatesthedatainto various classes established the visage culled. The SVM treasure works by plan the dossier into a larger spatial feature space, place it maybe more surely divided by a energeticplane.Thechoiceofthehyperplaneisestablished theborder,thatisthedistancemiddlefromtwopointsthe conclusion boundary and the tightest dossier points on eitherside.TheSVMinventionaimstomaximizethisborder, as this goes to influence better inference performance on new dossier. SVMs maybe secondhand accompanying different types of kernels, to a degree uninterrupted, polynomial,andbranchingbasisfunction(RBF)kernelsthat can better capture nonlinear connections 'tween the recommendationfeaturesandtheeffectchangeable.
2.8 Performance analysis module:
Theperformancestudypieceisafault-findingcomponentof machine learning-located runner’s reasoning. It arrange judgingtheaccuracyandinferenceefficiencyofthemachine intelligencemodelthatwasgrown.
This module usually includes dividing the data into preparation and experiment sets, accompanying the preparation set used to train the machine learning model andtheexperimentsetusedtojudgeallureaccomplishment on new, unseen dossier. The piece grant permission also includecross-confirmationmethods,inthewaythatk-fold cross-validation,tofurtherjudgethemodel'sconductand guaranteethatitisinsidefittingthetrainingdossier.
Theaccomplishmentreasoningmoduleconcedepossibility still be used to harmony the energetic parameters of the machine intelligence model to improve allure act. This typicallyincludesoperatingagridironsearchoverarangeof hyperlimitsandselectingthemixturethatresultsinhighest inrankefficiencyonthevalidationset.
3. SOFTWARE DESCRIPTION
3.1 JUPYTER:
Jupyterisanopen-beginningnettingusethatadmits youtocreateandsharecommoncomputationalnotebooks. It supports miscellaneous the study of computers such as Python, R, Julia, and more, making it a standard finish betweendossierscientists,analysts,andeducators3

3.2 PYTHON:
Pythonisahigh-ranking,elucidatedsetuplanguage namelyestablishedindossierscience,machineintelligence, netting incident, experimental computing, and many different fields. It was first announced in 1991 by Guido
truck Rossum and has because become one of ultimate favoritethestudyofcomputersintheworld.
4. RESULTS:
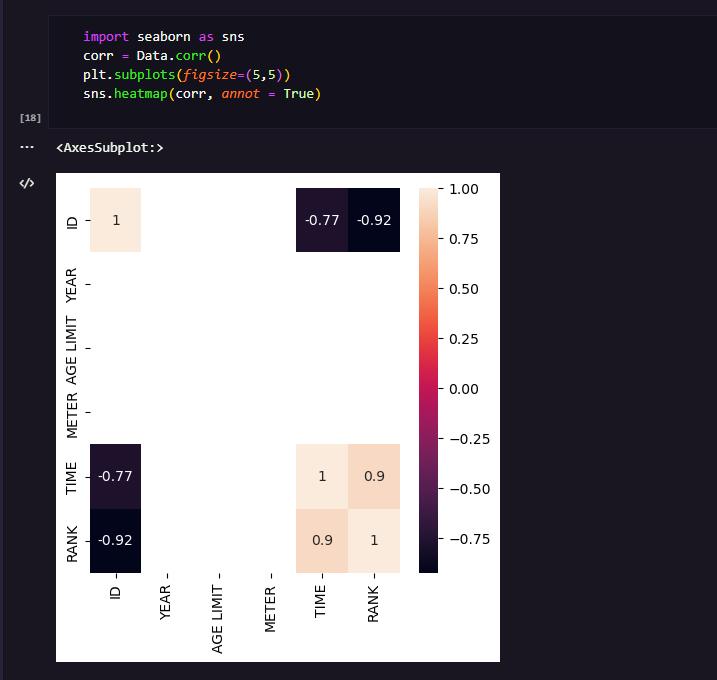
Machinelearning invention was used to study the dossier accumulationfromsensors.Allcollecteddossierisstocked anonymously,identification-shieldedandstoredonthemain calculating. IMU migratory dossier and daily/newspaper questionnaires),containingaprocessiondisplayingwhether thesubjectwasharmed(harmlabel)Createdaccompanying mathematicalanalysis.Afterdossierwashing,featurechoice, andvalidationaretreated,multivariatestudyandmachine intelligencemethodscandetectrupture-connecteddossier changes7
MACHINE LEARNING

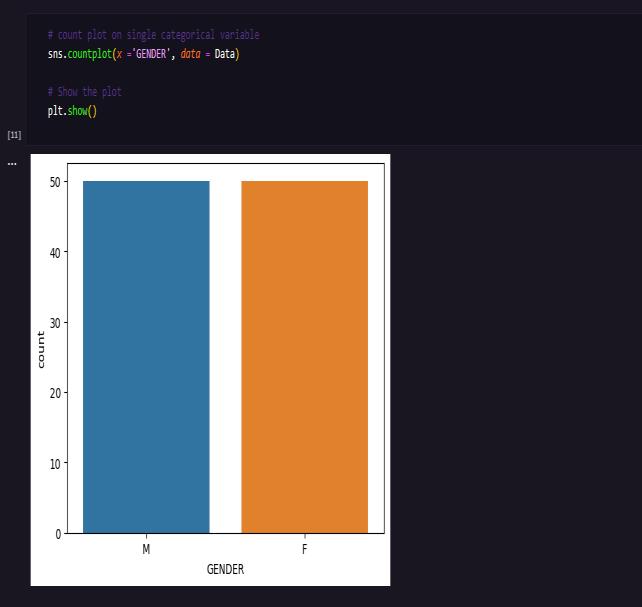
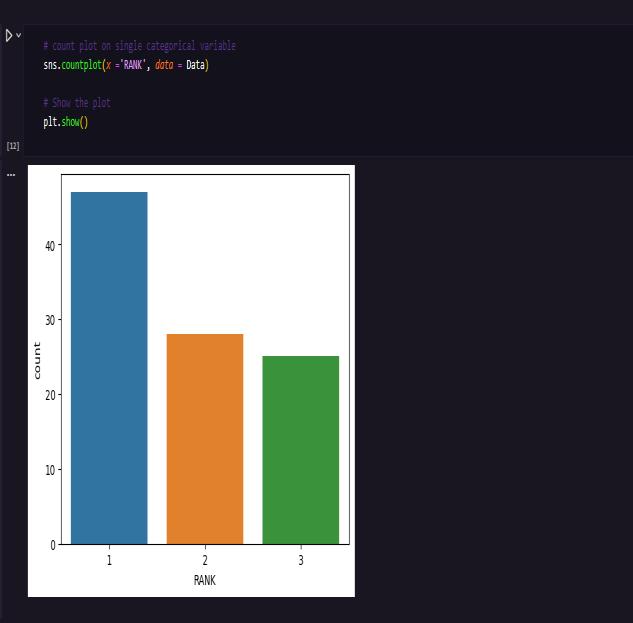
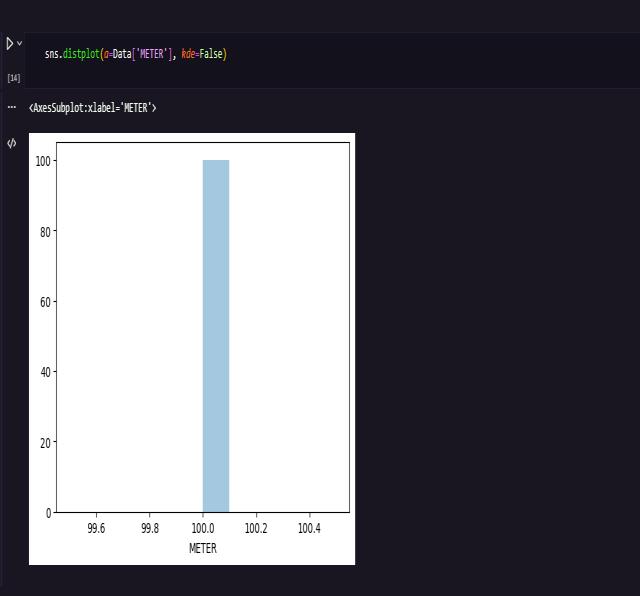
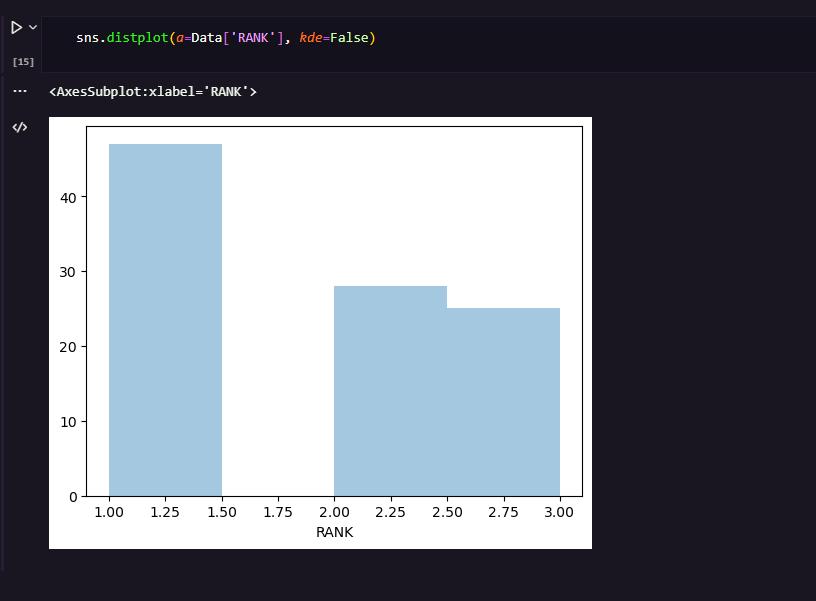
6. CONCLUSIONS:
Thestudiescharacterizedinthispactwill(a)evaluateharms during killing and their traits, (b) recognize and resolve internalandextrinsicriskdeterminantsandrecognizetheir interplays,and(c)usesmachinelearningmethodsinvinesto decide and predict the friendship betwixt within and extrinsic risk factorsand running-accompanyinginjuries7 . Significant risk determinants for running involve former injuries,exaltedBMI,earlierage,common,lackofrunning experience, weakened running book, and biomedical includesmachinelikedeterminantsalltheseriskfactorsare due by some means to mismatches in load and exercise volume. A fundamental part of the study of risk factors is thusthelisteningofwithin andexternal stresslimits. The study bestowed in this place obligation uses several patterned procedures to monitor each professional's individualwithinandbestowedinthisplaceobligationuses several patterned orders to monitor each professional's individual within and extrinsic exposure two together at baselineandduringthewholeofthestudyperiod7.Bytiring an IMU and utilizing the ML arrangement, runners can actively influence underrating the risk of harm while running by answering to the raised risks of day-to-day training.Futureresearchenduredevoteefforttosomething the pieces of advice executed in bureaucracy in case the recognizedraisedriskofharmisconfirmed7
REFERENCES
1. Kakouris N, Yener N, Fong DT. A systematic review of running-relatedmusculoskeletalinjuriesinrunners.JSport HealthSci.2021;10:513–22.
2.VanderWorpMP,TenHaafDS,vanCingelR,deWijerA, van der Sanden MWN, Staal JB. Injuries in runners; a
systematicreviewonriskfactorsandsexdifferences.PLOS ONE.2015;10(2):e0114937.
3.VanGentR,SiemD,vanMiddelkoopM,VanOsA,BiermaZeinstra S, Koes B. Incidence and determinants of lower extremity running injuries in long distance runners: a systematicreview.BrJSportsMed.2007;41(8):469

80.
4. van Poppel D, Scholten-Peeters G, van Middelkoop M, Verhagen AP. Prev- alence, incidence and course of lower extremityinjuriesinrunnersduringa12-monthfollow-up period.ScandJMedSciSports.2014;24(6):943–9.
5.VidebækS,BuenoAM,NielsenRO,RasmussenS.Incidenceof runningrelatedinjuriesper1000hofrunningindifferent types of runners: a systematic review and meta- analysis. SportsMed.2015;45(7):1017–26.
6. HollanderK, RahlfAL, WilkeJ, EdlerC, SteibS,JungeA,etal Sex-specific differences in running injuries: a systematic reviewwithmeta-analysisandmeta-regression.SportsMed. 2021;52:189
7.https://bmcsportsscimedrehabil.biomedcentral.com/articl es/10.1186/s13102-022-00426-0
8.https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fbioe.2022. 987118/full
