Volume: 10 Issue: 05 | May 2023 www.irjet.net

2395-0072

Volume: 10 Issue: 05 | May 2023 www.irjet.net

2395-0072
1Student, BTech, Mechanical Engineering, Delhi Technological University
2Professor, Department of Mechanical Engineering, Delhi Technological University ***
Abstract -Transportation is regarded as one of the most important development factors for any country because it maximizes mobility for individuals and moves loads for the industry. Tires play an important role in ensuring end-to-end connectivity. Tires and their structures have evolved to meet the needs and applications of the time. Many changes have been made to solve problems that, if resolved, may improve the performance of tyres. We are attempting to solve the problem of tyre punctures in this paper. The solution is airless tyres, or non-pneumatic tyres (NPT), which do not support the concept of compressed air.
This paper presents four distinct spoke structures of a Non-Pneumatic Tire model. The structure and material investigation of airless tyres is carried out by contrasting them with pneumatic tyres. A thorough structural analysis of several airless tyres spoke geometries has been done, and these spokes have then been further analyzed for important parameters like total deformation, stress, and strain. Solidworks was used for the 3D modeling of these various designs, while Ansys Software handled the in-depth analysis.
Key Words: Non-pneumatic tyre, Honeycomb spokes, Triangular spokes, Curvy spokes, Diamond Spokes, Ansys.
An airless tyre's basic construction is similar to that of a pneumatic tyre. They all have an internal core that contains pressurizedair,whichissubsequentlywrappedwithalayerofrubbercalledatreadthatcomesindirectcontactwiththe ground. The tread aids in maintaining road traction and guards against sliding and skidding. Because the tread tends to weardownovertime,ifthetyrehasnotgoneflat,itisnormallyreplacedatthispoint.
TherearethreesectionstotheNPT:arigidhub,deformablespokescapableofwithstandingverticalloads,astrengthened shearband,andarubbertreadthatmakescontactwiththeground.Rollingresistance,Contactpressure,andcarryingload capacityofNPTcanbechangedbymodifyingNPTmaterialsanddimensions.
TheimportanceofNPTisnowunderstoodonaglobalscale.Themostcrucialfeaturesof NPTthatdistinguishitfromordinarytyresare:
1. Because of its shear band, additional suspension, and lower rolling resistance, the NPT tyreaims at performance standardsabovethosemadeachievablebyconventionalpneumatictechnology.
2. It offers comfortable rides, and a load-carrying capability similar to pneumatics, and because it lacks a cavity for pressurizedair,itcannotmalfunctionduetoalossofairpressure.
3. Its strong lateral rigidity for improved handling without compromising comfort can be achieved, and it may eventuallybeabletooutperformconventionaltyres.
4. The conventional tyre is replaced with an NPT tyre, which is lighter than a regular tyre and helps to improve engineeconomybyloweringtheoverallweightofthevehicle.
5. Rightnow,tyremanufacturersmustdiscoverameanstorecyclethehugepileofbaldtyresthatisdestroyingthe landscape or come up with a material that is both durable and recyclable. because composite materials are typicallyusedinairlesstyres.Becausemostmodels'treadlivesarelongerthanthatofpneumatictyres,therubber doesnotneedtobechangedallthatfrequently.
TheabovefactorsconfirmedtheneedforvalidatingtheNPTtyreperformanceandthespecificationsthatcanleadtobetter results.Thus,differentNPTspokestructuresarechosentodeterminewhichstructurecanwithstandthestructural ability of pneumatic tyres. As per the currently available literature on NPTs, the static validation of tyre structure is illustrated under a single type of loading scenario only, and the structural validation under different loading conditions is yet to be researched.Inthispaper,dynamicconditionsarenottakenintoconsideration,andtheresultsandinferencesarebasedon static loading analysis. Section II discusses the geometry or 3D modelling of different tyre structures using Solidworks 2020, which contains the CAD of the tyre and will form the physical domain for the static structural analysis. Section III consistsofthevariousinferencesandgraphicalrepresentationsobtainedafteranalysisdoneusingAnsysR18.1
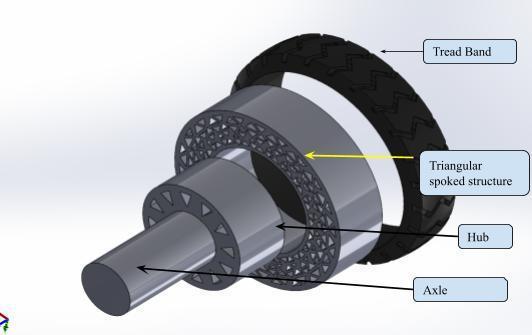
With the 3D modelling programme Solidworks, four different spoke designs Honeycomb, Diamond, Triangular, and CurvedSpokeStructures havebeendeveloped.Thewheelhub,spokestructureandshearbandwithtreadsmakeupthe threemainpartsoftheseNPTtyremodels.Tofacilitateanalysis,ahub-centredaxlehasbeenaddedtothemodel.Thisaxle servesasthecentrefromwhichthevehiclewillreceiveloadandpower.
SOLIDWORKS 2020 is the design software used for developing the CAD model.

Thespokestructureswereselectedduetotheirtheoreticallystabledesigns.

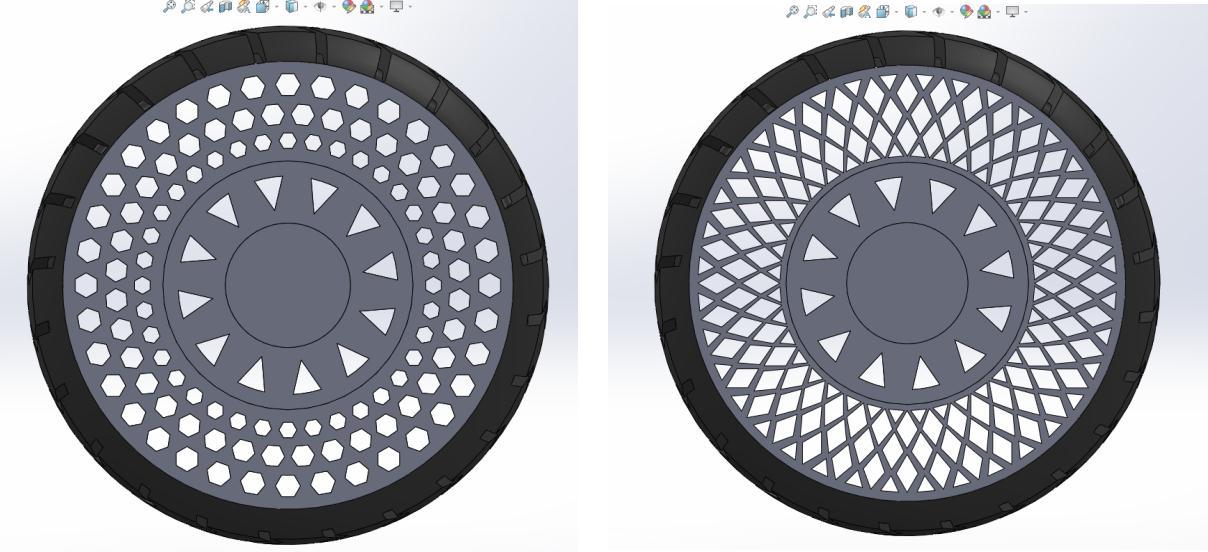
1.Honeycomb-Duetoitsevenlybalancedangleof60degreesintheregularhexagons,thisstructureisoneofthemost geometrically stable ones. The fundamental advantage of these structures is their lightweight, which allows them to beutilizedforstructuralprotection,thermalisolation,andenergyabsorption.
2. Diamond-Whencomparedtotheprecedingconstructions,thisstructurecantolerateheavierloadsbeingappliedto the tyre; additionally, because of its sturdy construction and structural design, this structure only experiences a minimaltotaldeformation.
3.Triangular(Equilateral)-Duetothefactthatjustoneforceisactingoneachofthetriangle'ssidesatonce,thetriangle asageometricshapedoesnotbend.Thespokeconstructionisstrengthenedbythisfeature,whichhelpswithoptimal forceandweightdistribution.
4.Curved Spokes- The curved spokes can take some of the force of variable torque (rapid speed variations) without breaking. Also, because of the angle of the curve, the wheels have an aerodynamic advantage because less air resistanceiscreatedwhenpassingthroughthem.
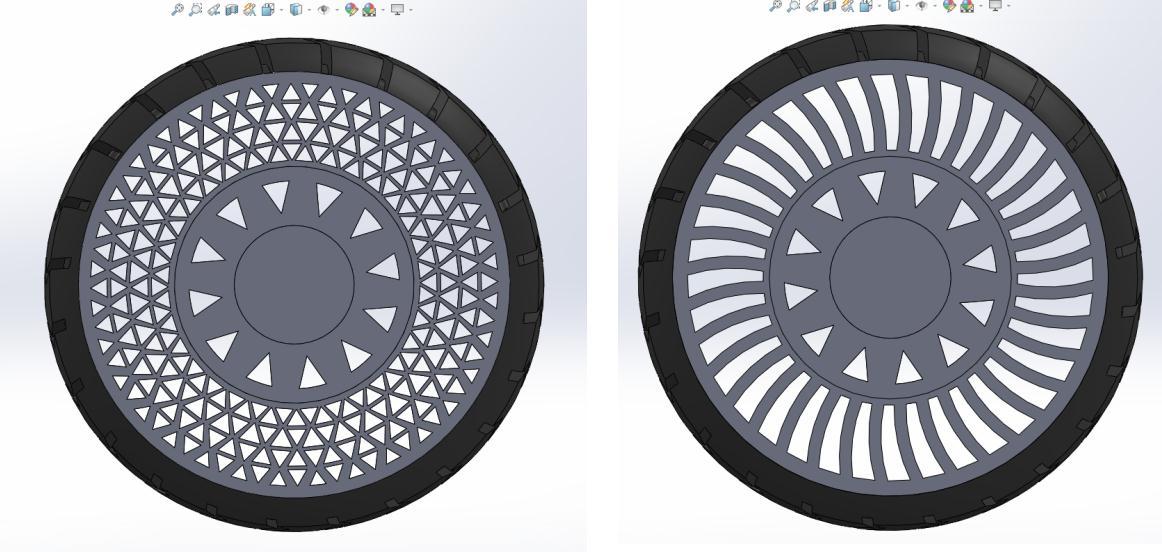
Following are the figures representing CAD assembly model of : (a) Honeycomb spoke structure (b) Diamond spokes structure(c)Triangularspokesand(d)curvyspokesstructures.

Aluminium alloy, polyurethane, alloy steel, and nitrile rubber are the materials employed in this analysis for the four distincttyreswithvariousspokestructures.Thesematerialswerechosenprimarilyduetotheirvastrangeofmechanical qualities,includinghighflexibility,high-temperatureresistance,highstiffnessandresilience,hyperelasticity,etc.Thetable belowincludesthechosenmaterial'sproperties. Table
1. Wheelsize=ɸ794mm
2. Theouterhubdiameteris=ɸ400mm
3. Innerhubdiameter=ɸ100mm

4. Hubthicknessis=200mm
5. Theouterdiameterofthewheelis=ɸ794mm
6. Thewidthofthewheelis=180mm
Innerandouterbandlayerscombinetoformthecompositestructureofanairlesstyre.Inairlesstyres,steelringsarealso employed as reinforcing components. The most common cause of tyre failure is heat accumulation. It's important to determine the mechanical stability of an airless tyre under the applied load in order to improve its design. It is also important to look into the simultaneous development of stress and strain energy distribution. The prediction of metallic elementswasvalidatedusingthepneumatictyredata.
Connections
● Contact:BetweenAxleandHub-Bonded
BetweentheHubandSpokestructure-BondedBetweentheSpokestructureandShearBand-Bonded
● VerticalLoadonabottommostpatchofeachwheel=(1800*10)/4=4500N
● FixedContact=Axle
● MeshElementShape-Tetrahedron
● ElementSize:10mm(Fine)
Theresultobtainedaftermeshingindifferentspokestructuresofthetyreisshownbelow. AnsysR18.1isusedformeshing.Here,weuseda Tetrahedron element formeshing.
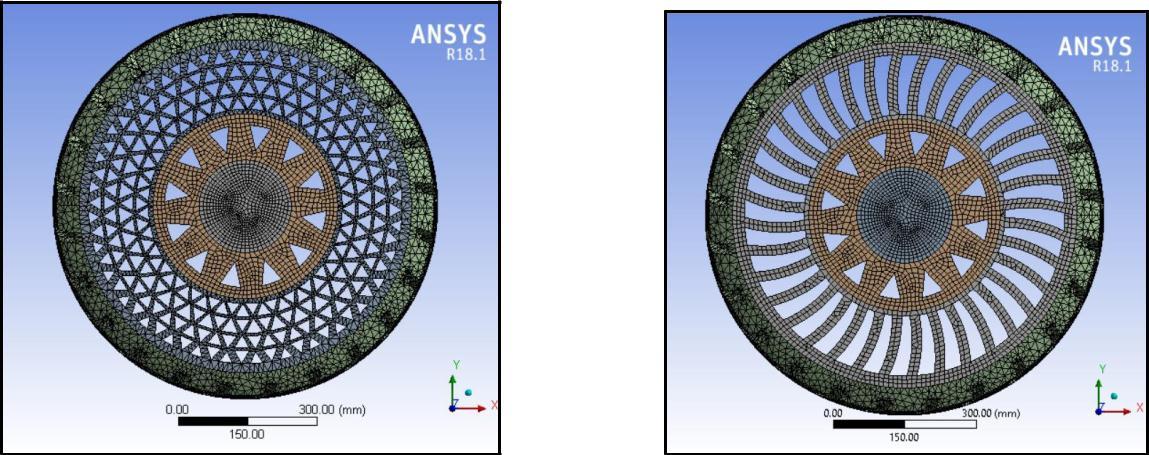
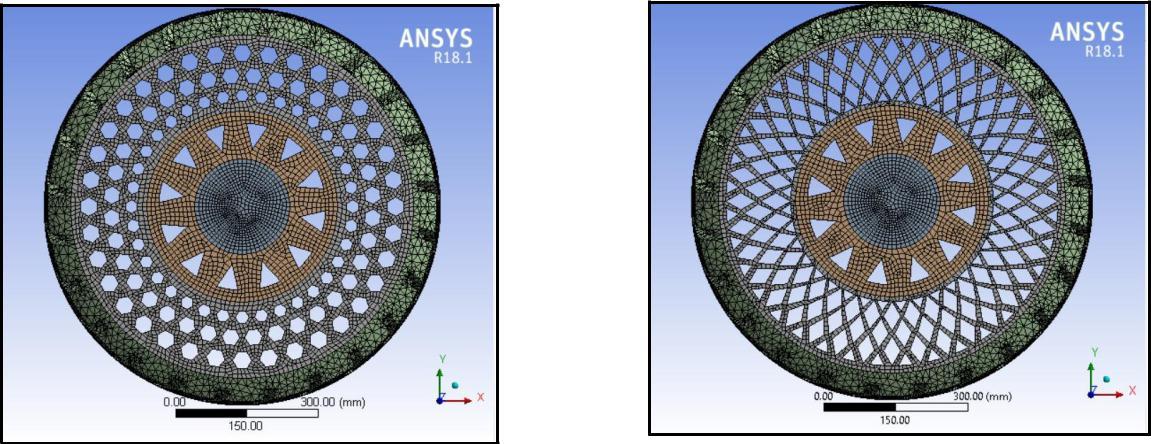

AnalysisResults
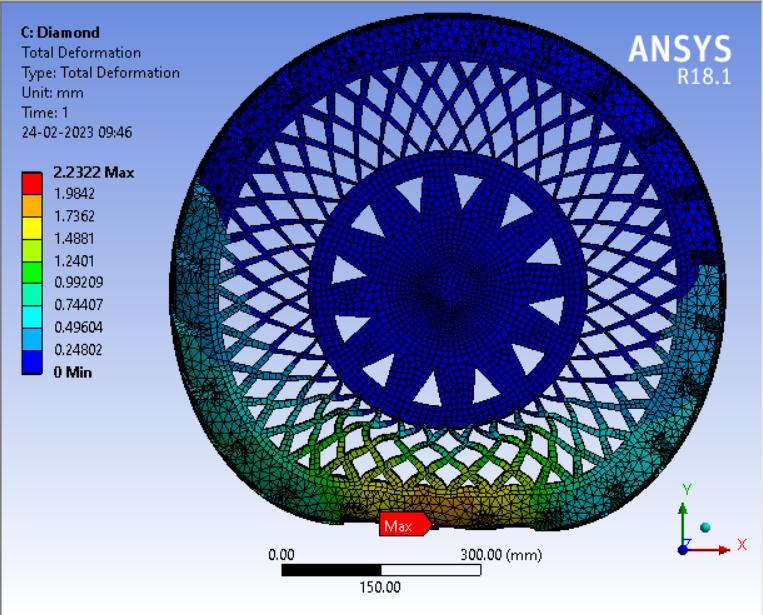
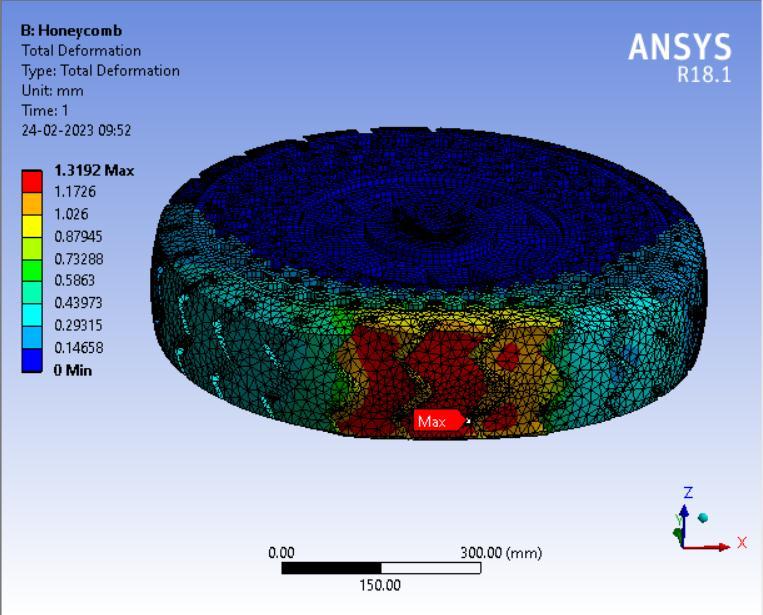
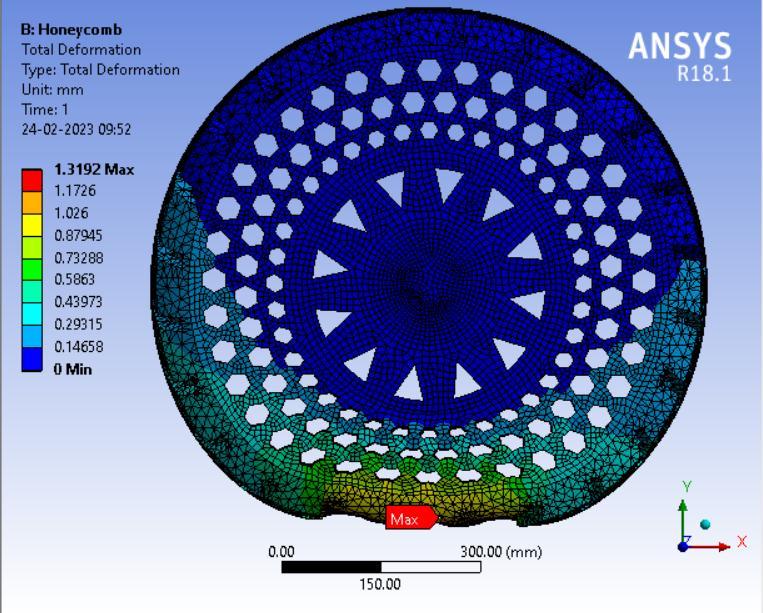

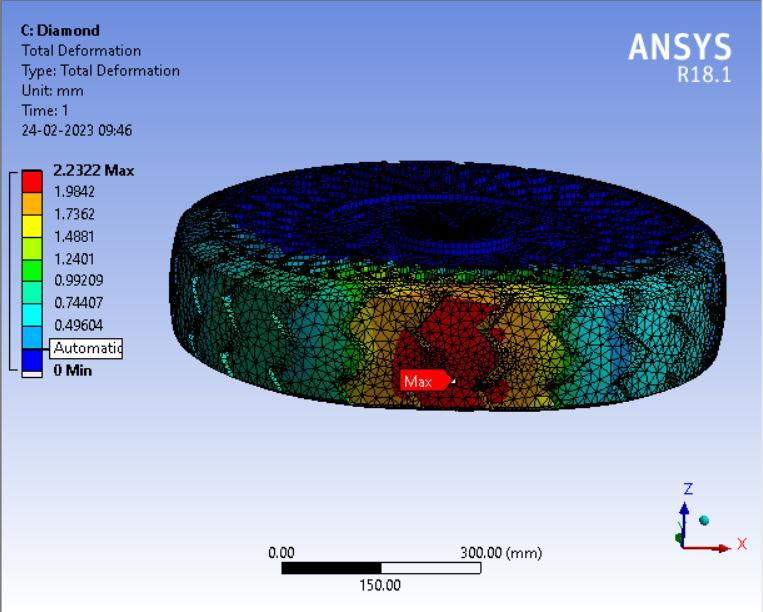
● Thepictorialpresentationinthemethodofcontourplotsof Total Deformation

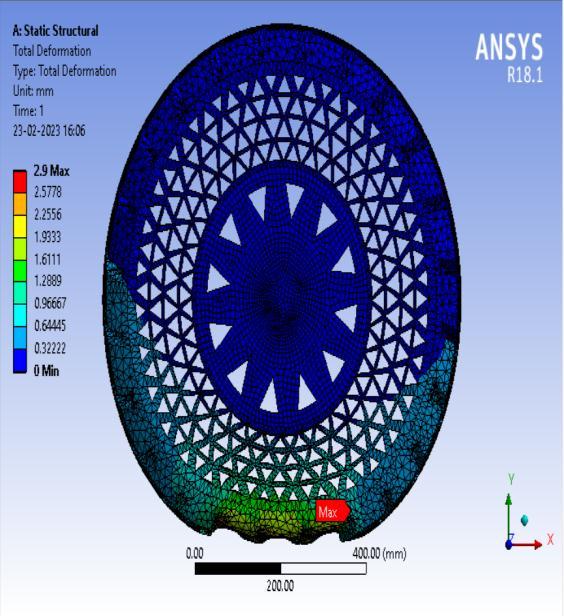
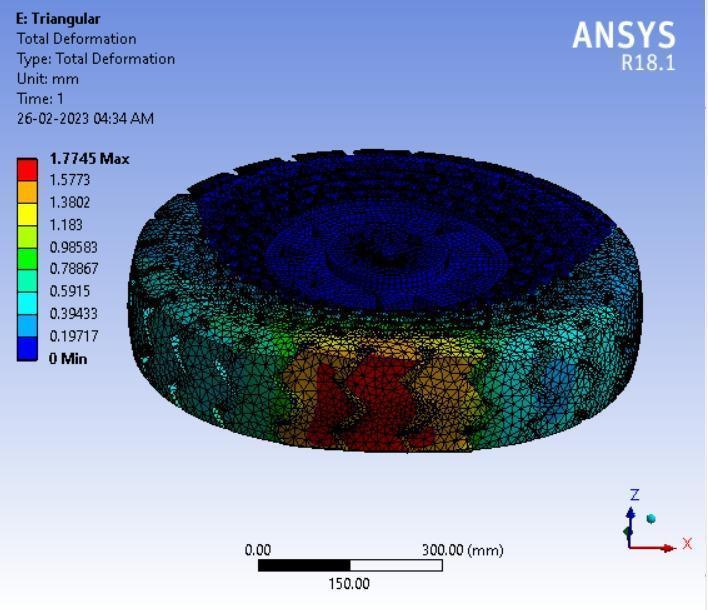
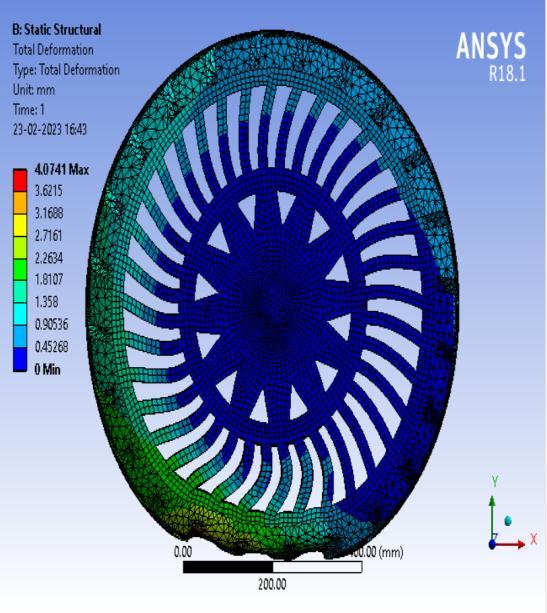

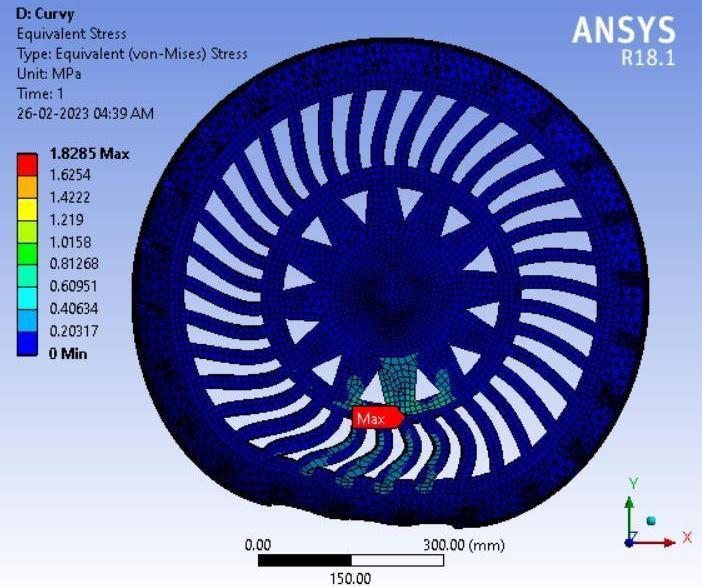
● ThepictorialpresentationinthemethodofcontourplotsofEquivalent(Von-Mises)Stress
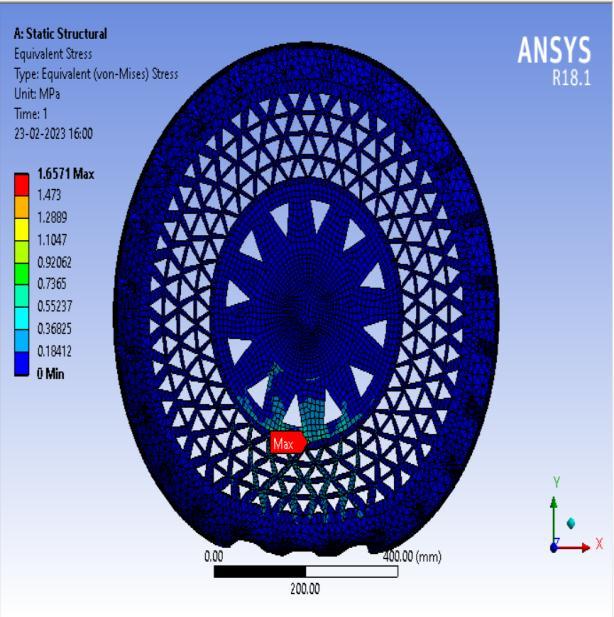
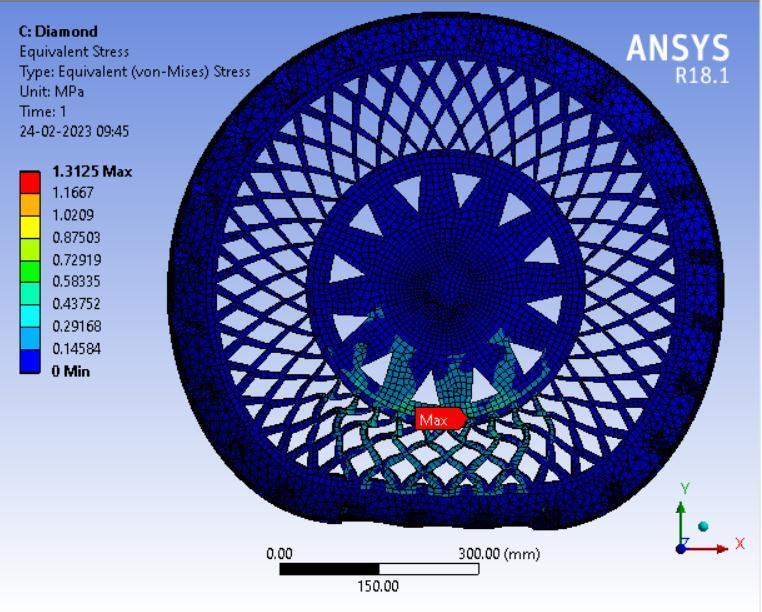
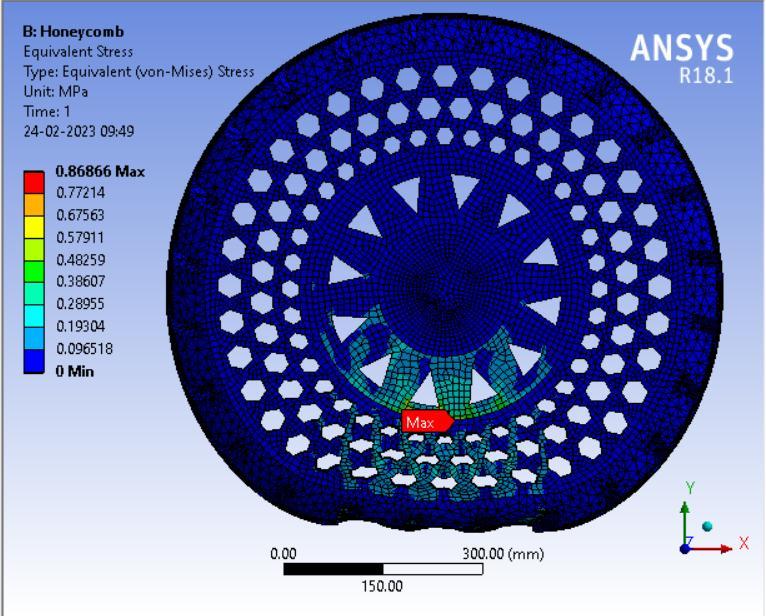

● ThepictorialpresentationinthemethodofcontourplotsofMaximumPrincipalElasticStrain
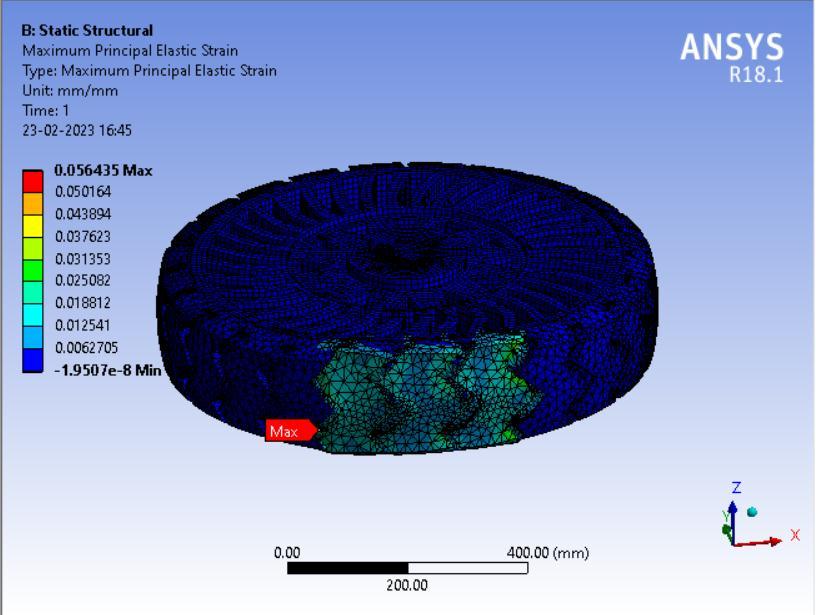
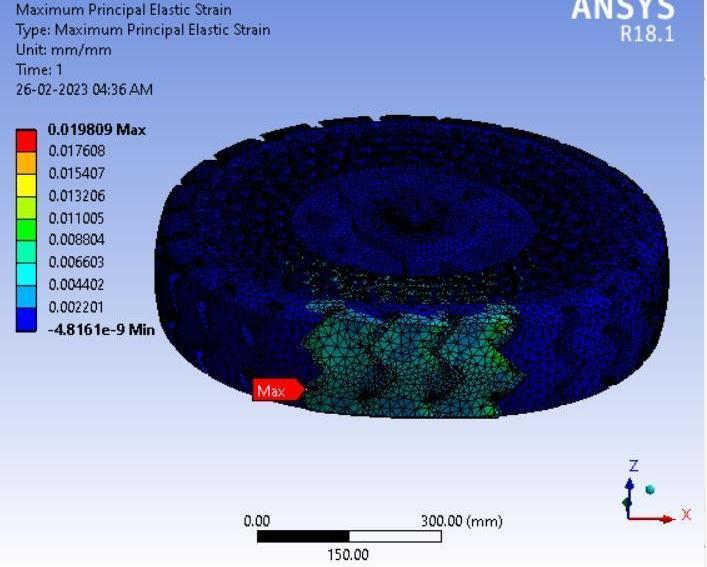
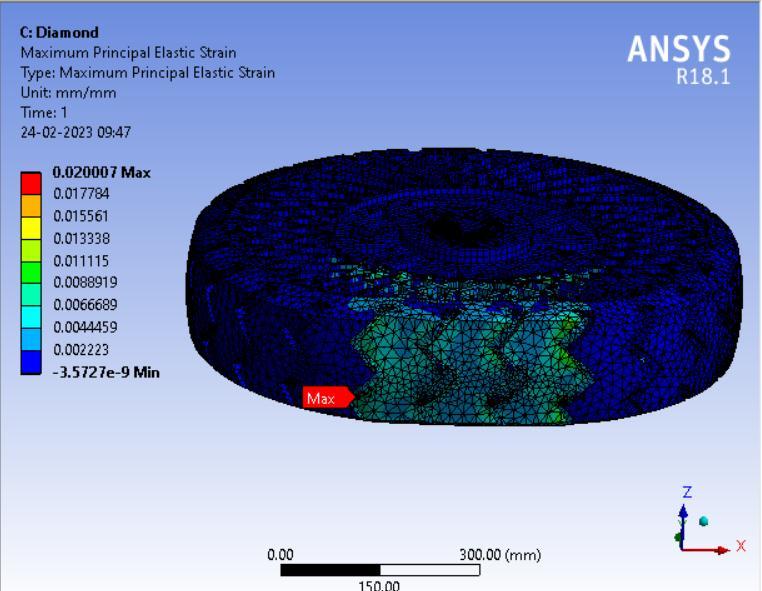
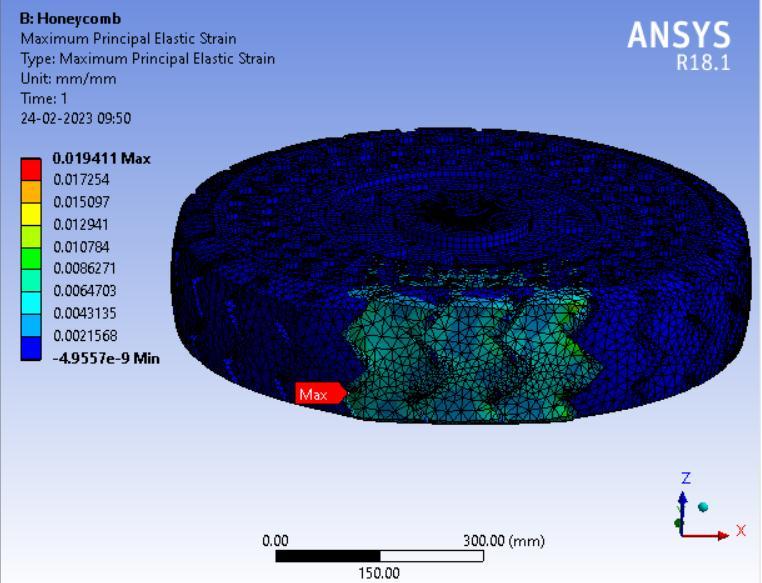

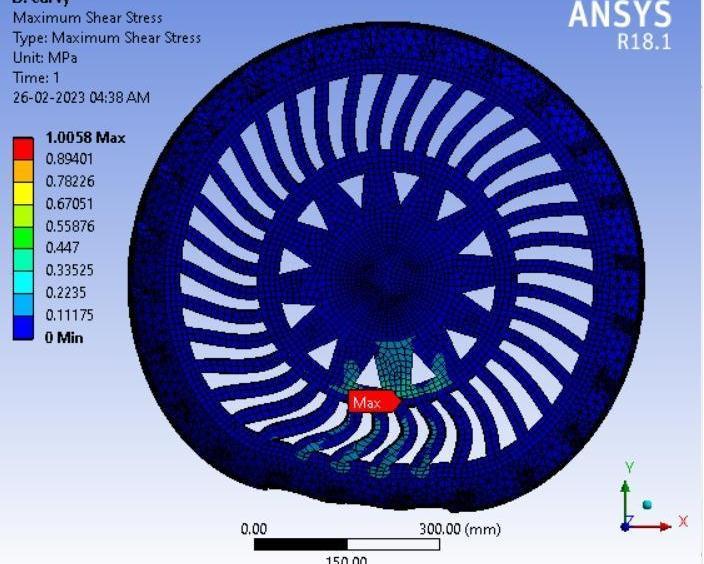
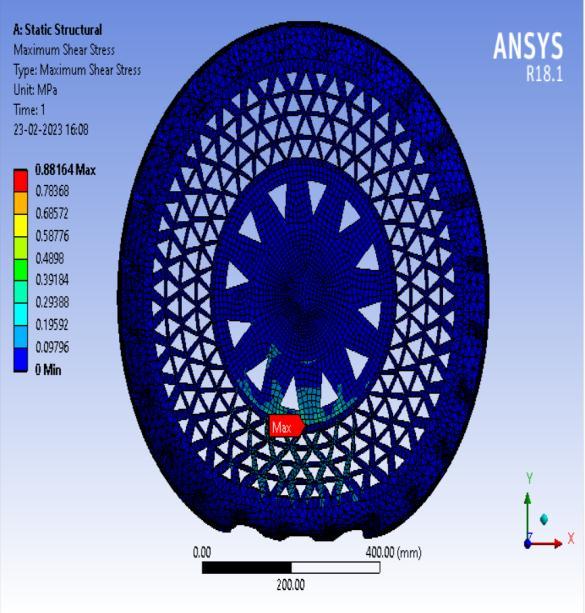
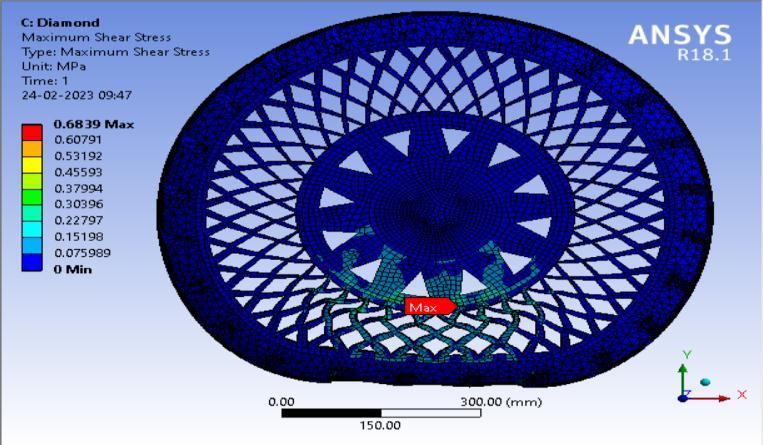
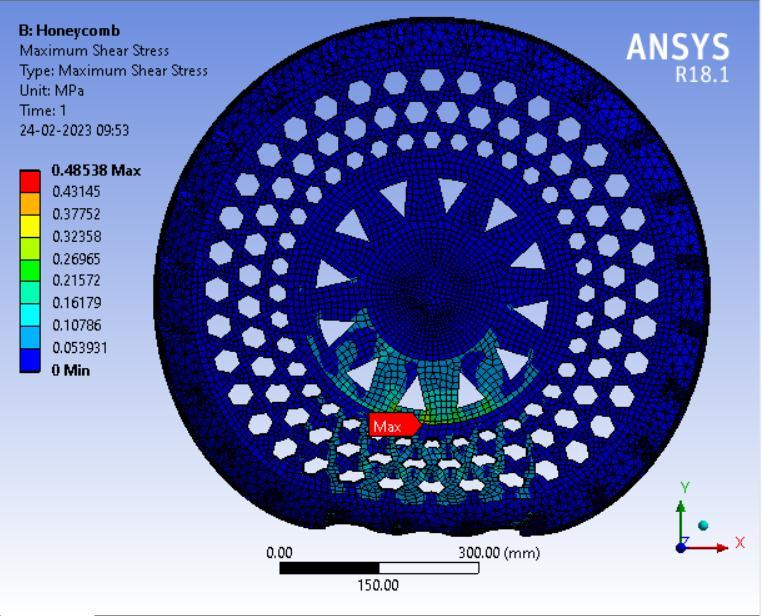
● ThepictorialpresentationinthemethodofcontourplotsofMaximumShearStress
Triangular
Curvedspokes
7: ResultcontourofShearStress
The results obtained by comparing the different spoke structures using a mix of materials that were examined are compiledbelow.

● Total Deformation
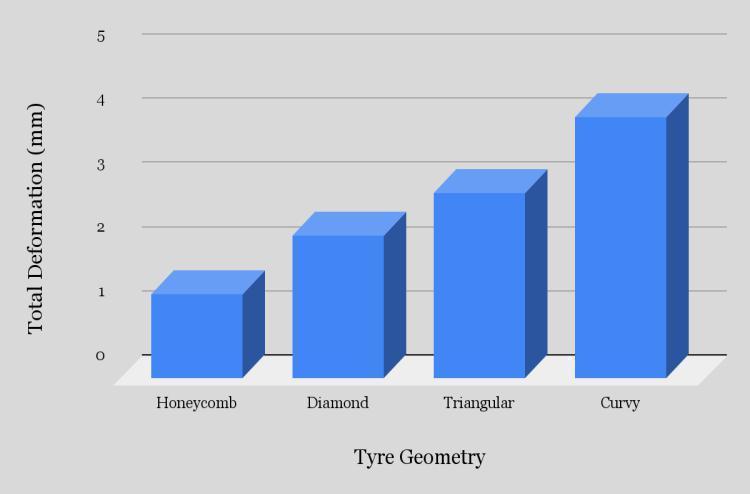
Table 3: Maximumtotaldeformationvaluesindifferentspokesstructures.
Inference-
From the above data it’s pretty evident that the Honeycomb structure has the least deformation whereas the Curvy structure has the largest deformation. Thus it can be concluded that the Honeycomb structure will give the Highest loadcarryingcapacityamongstthe4spokestructurescomparedandwouldbesuitableforheaviervehiclesincontrasttowhich theCurvystructurewouldbesuitableforlightervehicleswithlessloadandcouldprovidemorecushioningeffect.
Chart1:Totaldeformation(mm)Vs.TyreGeometry
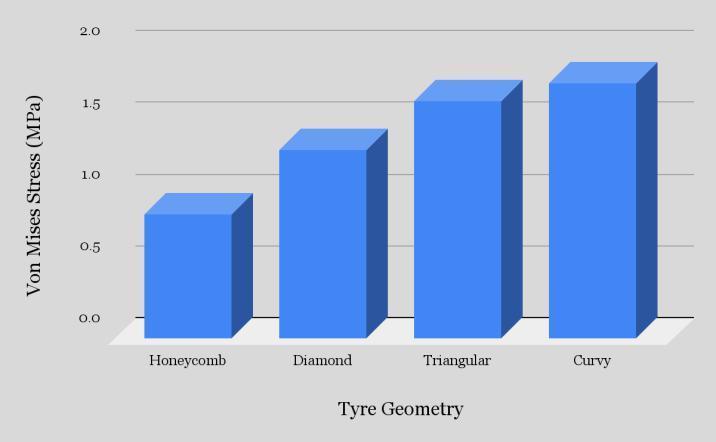
● Equivalent(Von- Mises) Stress
Table 4: MaximumVon-MisesStress(MPa)valuesindifferentspokesstructure.
Graphical Representation: Von Mises Stress(MPa) Vs. Tyre Geometry
Inference-
Fromthedatacollectedusingthetableabove,HoneycombspokestructurecamewiththeleastVonmisesstresscompared to other spokes structure. Thus, this can be said that Honeycomb spoke structure will have the highest Compressive strength. NPT with honeycomb spokes offered minimum stress concentration which is important for Fatigue resistant designs.

● Maximum Principal Elastic Strain Table 5:MaximumPrincipalelasticStrainvaluesindifferentspokesstructure.
Graphical Representation: Maximum Principal Elastic strain Vs. Tyre Geometry
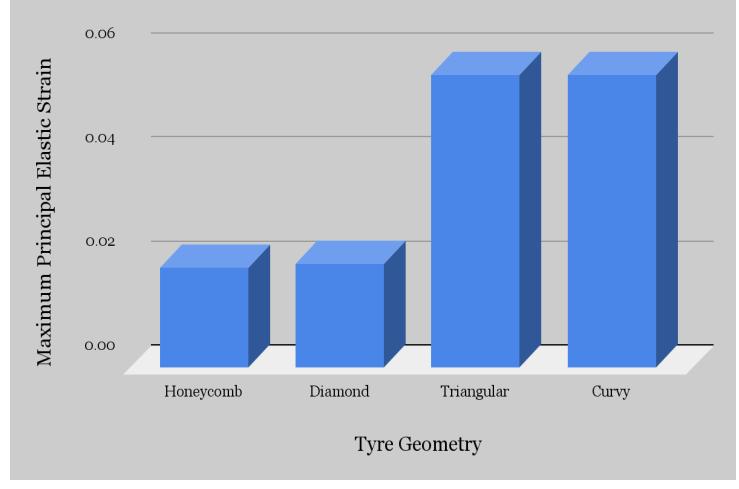
Inference-
Here, Honeycomb spokes structure shows the least value of maximum principal elastic strain value while triangular and curvyspokesstructuredesignhassimilarresults.Thus, wecansaythatHoneycombstructuredesignintyreswill leadto longerlifebyreducingtherateofwearandtear.

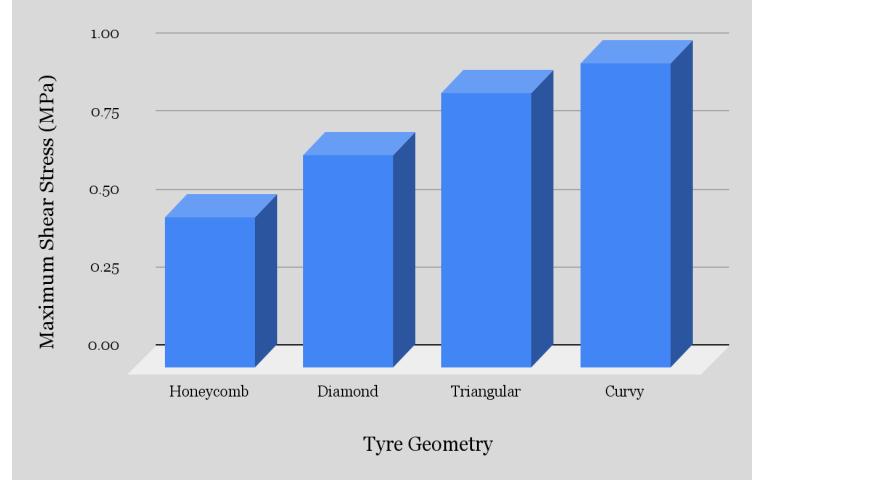
Inference-

The maximum shear stress that the tyre can withstand under a load of 4500 N is shown in the above table. For easier comparisonanddatavisualisation,theshearstressofthevariousspokesinthetyredesignaredisplayedgraphicallyinthe rightcorner.
In this instance as well, the honeycomb spoke structure had the lowest maximum shear stress value when compared to otherspokestructures.
Table below illustrates the compiled results of total deformation, equivalent von-mises stress maximum principal elastic strain, and maximum shear stress for different spoke structures in a non-pneumatic tyre. It also gives a comparative analysisoffourdifferentspokesstructuresusedforthesame.
Fromtheresultshownintheconsolidatedtableabove,wefoundthattheHoneycombspokestructuremodel gives better results than the other spoke structures of the tyre model. Similarly in different spokes structure constraints, with mentioned analysis parameters, the Honeycomb spoke structure yields better results. So for the given boundary conditionsandappliedload,theHoneycombspokestructureairlesstyreismorerigidanddurable.
TherearemanyadvantagesthatNonPneumatictyreshaveingeneraloverPneumatictyres.Someofthefactorsthatcanbe countedincludes:EliminationofairLeakageortyreblowouts,Consistenteconomyandhandlingasthereisnoissuewith gaspressure,Itsflexibilityprovidesariseinextentofcontact,Nomaintenancerequirement,Elongatedtreadlife,Facilitate utilisation,makingavehiclelotmoreeconomicalwithhighlateralstrengthforhigherhandlingwithoutanylossincomfort, Vehicleremainsinrestrainteveninparkingbrake, Remainsmobileevenwithanumberofthespokesbrokenormissing, hashighSturdiness&LongLifeandLessenvironmentalimpact.
● The results obtained from static structural analysis confirms major of the factors stated above and It can be concludedthatHoneycomb spokesstructureoftyreare morestablestructureastheyhavecomparativelyhigher capabilitytowithstandmoreload.
● ItisfoundthatHoneycombspokesdesignconstitutesleaststress,strainsanddeformationsvaluesincomparison to other designs because the honeycomb structure is more geometrically stable for the same material and symmetrical which can sustain and uniformly distribute large amount of force thereby exhibiting more compressiveandshearstrength.
As per the analysis done on different spoke structure designs, the honeycomb spokes structure design that has given the resultswithleastdeflectionisadvisableandisconcludedtobemostsuitableforheavierloadapplicationpurposes.
[1] R., Sanjeev Kumar & Kumar, K Vetrivel & Ramakrishnan, T. (2021). Design optimization of Airless Tyre - Numerical Approach.IOPConferenceSeries:MaterialsScienceandEngineering.1057.012032.10.1088/1757-899X/1057/1/012032.

[2]Mathew,NibinJacob,DilipKumarSahoo,andE.MithunChakravarthy.2017.“DesignandStaticAnalysisofAirlesstyre toReduceDeformation.” IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering 197(1):012042.
[3] Thirumoorthy, Prabhuram & S C, Meenakshi Sundaram & Jegadeeswer, S. & Kannan, V.. (2020). Static analysis of differentspokestructuresofairlessandconventionaltyres.IOPConferenceSeries:MaterialsScienceandEngineering.923. 012017.10.1088/1757-899X/923/1/012017.
[4]Mohan,Aravind&Johny,C&Tamilarasu,A&Bhasker,Pradeep&Krishnaiah,Ravi.(2017).DesignandAnalysisofNonPneumatic Tyre. IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering. 263. 062061. 10.1088/1757899X/263/6/062061.
[5]Kumar,Nikhil&Mhatre,Pranavee&Pandey,Rinkesh&Pandey,Ashutosh&Ospanova,A..(2022).OptimizationofNonPneumatic Tyre. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science Engineering and Technology. 11. 1455-1459. 10.15680/IJIRSET.2022.1104074.
[6] Thirumoorthy, Prabhuram & S C, Meenakshi Sundaram & Jegadeeswer, S. & Kannan, V.. (2020). Static analysis of differentspokestructuresofairlessandconventionaltyres.IOPConferenceSeries:MaterialsScienceandEngineering.923. 012017.10.1088/1757-899X/923/1/012017.
[7] Ali, M., Maarij, M. & Hussain, A. Design and structural analysis of non-pneumatic tyres for different structures of polyurethanespokes. J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 69,38(2022).
[8]Abhishek,Raj,andAnupKumar.“Non-PneumaticTyredesignwithHoneycombspokestructure.” IJISET - International Journal of Innovative Science, Engineering & Technology, vol.7,no.6,June2020,p.6.

[9] Prabhuram, T., Sundaram, S.M., Jegadeeswer, S. and Kannan, V.S., 2020, September. Static analysis of different spoke structuresofairlessandconventionaltyres.In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol.923,No.1,p. 012017).IOPPublishing.
[10] Pewekar, M.M. and Gaikwad, S.D., 2018. Strength validation of hexagonal cellular spoked non-pneumatic tyres for automobilesthroughfiniteelementanalysis. Int J Sci Res Sci Technol, 4(5),pp.1044-1055.
[11] Shashavali, S., Reddy, C.R. and Yadiki, G.K., 2016. Design and analysis of four-wheeler airless tyre. Int J Adv Technol Innov Res, 8,pp.4298-4305.
[12] Genovese, A., Garofano, D., Sakhnevych, A., Timpone, F. and Farroni, F., 2021. Static and dynamic analysis of nonpneumatictyresbasedonexperimentalandnumericalmethods. Applied Sciences, 11(23),p.11232.
[13] Mathew, N.J., Sahoo, D.K. and Chakravarthy, E.M., 2017, May. Design and static analysis of airless tyres to reduce deformation.In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering (Vol.197,No.1,p.012042).IOPPublishing.
[14] Mohan, A., Johny, C.A., Tamilarasu, A., Bhasker, J.P. and Ravi, K., 2017, November. Design and analysis of nonpneumatictyres.In IOP conference series: materials science and engineering (Vol.263,No.6,p.062061).IOPPublishing.