Bibliometric review of application of blockchain in supply chain management
Akash Mishra1 , Ayush Saini2 , Ansh Jini3, N. Yuvraj41Student, B.Tech (Mechanical Engineering), Delhi Technological University, New Delhi, India
2 Student, B.Tech (Mechanical Engineering), Delhi Technological University, New Delhi, India
3 Student, B.Tech (Mechanical Engineering), Delhi Technological University, New Delhi, India
4Associate Professor, Dept. of Mechanical Engineering, Delhi Technological University, New Delhi, India

Abstract - This paper analyzes the current state and potential of blockchain technology in supply chain managementthroughbibliometricanalysis.Thestudyemploys bibliometricdata-drivenanalysisusingtheWebofScienceand Scopus databases to collect relevant literature from 2013 to 2023. The Vos Viewer software is used to visualize the collaborative relationships and themes among the sampled literature.Theco-wordanalysisrevealsthatthedevelopment of blockchain technology is centered on supply chain management, traceability and transparency, supply chain financing, and sustainability. The study highlights the potential of blockchain technology in facilitating developed supplychains,anditscombinationwiththeInternetofThings, that can drive significant changes across various industries and supply chains. This paper provides valuable insights for academic researchers and industrial managers in adopting blockchain to improve supply chain management performance. The study identifies the technical features of blockchainthatcanaddresschallengesinSCMandhighlights its potential to improve consumer trust, secure transactions, andefficientmanagement.However,technicallimitationsand the need for ongoing research and development remain challenges for large-scale implementation.
Key Words: Supply Chain Management, Blockchain Technology, Smart Contract, Vos Viewer Software, Scopus, IOT, financing, sustainability
1. INTRODUCTION
Efficientsupplychainmanagementpracticesarecriticalfor boosting performance and efficiency, but a fundamental challengeremainsthelackoftrustacrossvariousparties[1]. Blockchain technology, with its openness, visibility, and disintermediation qualities, offers enormous promise for addressingsecurityissuesinthetradeprocessandbuilding mutual confidence among all supply chain participants. However, its present supply chain use is restricted, and additional study is required to incorporate it into ecommercesupplychainmanagement.
Blockchain has been widely adopted in many areas of life and industrial sectors in China as a strategic frontier technology. It efficiently tackles the issue of information opacityandasymmetrywhileensuringtheconfidentialityof
operational data[2]. While there are several studies on blockchainindustrialapplications,therehasbeenminimal study on its integration into e-commerce supply chain management.
Thispaperillustratesbibliometricanalysistowitnesshow blockchain technology has been used into supply chain management.Wegatheredacademicarticlesonblockchain and supply chain management that had been published internationallyusingScopus,abibliographicdatabase.The searchreturned19,062researcharticleswiththekeywords "blockchain"and"supplychainmanagement,"allofwhich werewrittenbetween2016and2023.
The paper analyses how blockchain technology has the potentialtoimprovesupplychainmanagement,notablyin theareasofpaymentandsupplychainmanagement.TheVos Viewer software was used to build visualizations of the linkages and themes in the gathered literature on blockchain-poweredsupplychains.
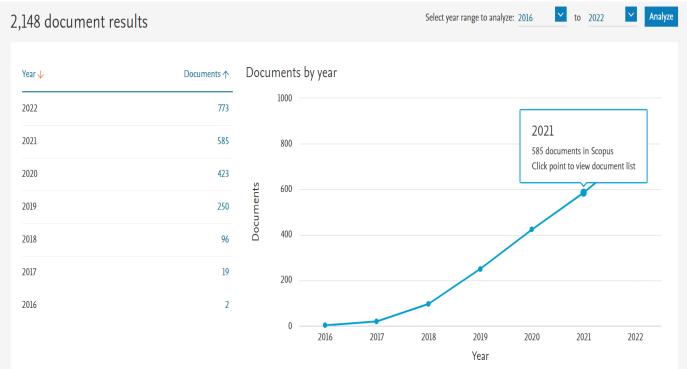
The analysis discovered that the number of blockchain studies was modest in the years after 2016, but that the number of relevant studies increased substantially from 2018to2022.Thisincreasewasmostlikelycausedbythe adventofnewdataconnectedtothepropertiesofblockchain technology, such as the Internet of Things and big data. Furthermore, extensive blockchain research and implementation are related with the introduction of new technologies.
A co-word analysis diagram was developed using 4,106 keywords to comprehend the new advancements in the domainsbeingaddressedandtouncovernewlinksbetween pre-existing scientific fields. According to the findings, blockchaintechnologydevelopmentiscentredintheareasof supply chain management, traceability and transparency, supplychainfinancing,andsustainability.
The methodology and study strategy of a bibliometric analysisexaminingtheintegrationofblockchaintechnology insupplychainmanagementarediscussedinthispaper.The researchonblockchaintechnologyisalso centered onthe sectors of supply chain management, traceability and transparency,supplychainfinancing,andsustainability.
2. Theoretical Background

A digital transaction ledger called a blockchain allows numerouspartiestosafelyandopenlyshareandaccessdata without the need for middlemen. Blockchain technology allows users to validate and add transactions to a safe, impenetrabledatabase.
2.1 Blockchain Technology
Transactionsinablockchainareorganizedintoblocksand added to the ledger in chronological order. Each block contains a one-of-a-kind code known as a "hash" that uniquelyidentifiestheblockandallitstransactions[3].This hash also includes the hash of the preceding block in the chain,formingachainofblocksandgivingrisetotheterm "blockchain."
One of the key benefits of blockchain technology is its decentralized nature. The blockchain, rather being dependingonacentralauthorityormiddlemantorunthe network,iscontrolledbyadistributednetworkofnodesthat collaboratetovalidatetransactionsandmaintaintheledger [4].Becauseofthisdecentralization,theblockchainismore resistant to hacking and fraud, while simultaneously increasingtransparencyandtrustbetweenparties.
Numerous uses for blockchain technology are available, including voting systems, supply chain management, cryptocurrencies,andmore.Itoffersasecureandeffective methodofstoringandmovingdatawithouttheinvolvement of middlemen, which has the potential to change how we interact and conduct business. Blockchain technology, however,alsohasdrawbacksandrestrictions.
2.2 Integration of Blockchain in Supply Chain
Asblockchaintechnologycontinuestoexpand,itisfinding itswayintovariousindustries,andthesupplychainsectoris not left out. Blockchain integration in supply chain managementisbecomingincreasinglypopularasitprovides awaytoimprovetransparency,accountability,andsecurity inthesupplychain.
Blockchaintechnologyisessentiallyadecentralizeddigital ledger that records and stores data in a secure and transparentway.Whenintegratedintothesupplychain,it helps to create a decentralized system that allows all stakeholdersinthesupplychaintohaveaccesstothesame information simultaneously, without the need for intermediaries. One of the key benefits of blockchain technology in the supply chain is the ability to increase transparency.Withblockchain,allparticipantsinthesupply chaincanviewtheentire transactionhistoryofaproduct, from the manufacturer to the end consumer. This level of transparency helps to prevent fraud, counterfeiting, and other illegal activities that can occur within the supply chain[5]
Anothersignificantbenefitofblockchaintechnologyinthe supplychainisimprovedtraceability.Byusingblockchain, manufacturersandsupplierscaneasilytrackproductsfrom theirorigintotheirdestination,providingcustomerswith more information about the product's quality and authenticity.
Additionally, blockchain technology also offers improved security.Byusingcryptography,blockchaincanensurethat alltransactionsaresecureandtamper-proof,whichreduces the risk of cyberattacks and data breaches. Several companieshavealreadyimplementedblockchaintechnology intheirsupplychainmanagement[6].Forexample,Walmart, one of the world's largest retailers, uses blockchain technologytotrackitsfoodsupplychain.Thesystemallows thecompanytoquicklytracetheoriginofcontaminatedfood productsandremovethemfromstoreshelvesbeforethey causeanyharmtocustomers.
Another example is Maersk, the world's largest container shippingcompany,whichpartneredwithIBMtodevelopa blockchain-basedplatformcalledTradeLens.Theplatform enablesallstakeholdersinthesupplychaintoaccessrealtime information about the location of their shipments, reducingtheriskofdelays,theft,andotherdisruptions.
Inconclusion,theintegrationofblockchaintechnologyinthe supply chain sector provides several benefits, including increased transparency, traceability, and security. Companies that have already adopted this technology are reapingthebenefitsofreducedcosts,improvedefficiency, and enhanced customer satisfaction. As more companies continue to integrate blockchain into their supply chain management,wecanexpecttoseeevenmoreadvancements inthisfield.
2.3 Hash Algorithm
Blockchainisadecentralizeddigitalledgerthatsecurelyand transparentlyrecordstransactions.Thehashfunction,which isresponsiblefortransformingdataintoafixed-lengthvalue known as a hash, is a key component of blockchain technology. The hash function is an important feature of blockchain because it protects data integrity by making it impossible to change the data without changing the hash value.
Ahashfunctiontakesanysizeinputandreturnsafixedsize output.Becausetheoutput,orhash,isuniquetotheinput data, even minor changes in the input data result in an entirelynewhashvalue.Thehashfunctionissupposedtobe a one-way function, which indicates that determining the originalinputdatafromthehashresultisverydifficult[7]
Inblockchain,thehashfunctionisusedtogenerateahash for each block, which is subsequently put to the block's header.Theblockheaderprovidesinformationsuchasthe block's timestamp, the preceding block's hash, and the
currentblock'shash.Byconnectingtheblockswiththehash function,atamper-resistantchainofblocksisformed.
The hash function is also used to verify the validity of blockchaintransactions.Eachtransactionisassignedaoneof-a-kindidentificationknownasatransactionhash,which isgeneratedbyapplyingthehashfunctiontothetransaction data.Thehashvalueofthetransactionisthenaddedtothe blockchain,ensuringthatthetransactioncannotbechanged withoutmodifyingthehashvalue.
To summarize, the hash function is an important part of blockchaintechnologysinceitmaintainsthedata'sintegrity and security. It is used to generate a unique identifier for each block and transaction on the blockchain, making tamperingwiththedataalmostdifficult.Thehashfunctionis an essential component in the creation of a decentralized andsecuredigitalledgersystem.
2.4 Smart Contract
Smartcontractshavebeenaroundforalongtime,buttheir useinindustrialpracticeshasgrowninpopularitywiththe arrival of blockchain technology[8]. A smart contract is a scriptrecordedonablockchainthatexecutesautomatically withouttheinterventionofthecontract'ssigner.Itishighly secureanddoesnotrequiremiddlemen,makingitasuitable optionforawiderangeofsectorslikeinsurance,healthcare, andsmartcities.
Blockchain-based smart contracts can be used in the insurance business to handle and analyze pay-as-you-go vehicle insurance data. Smart contracts can help the healthcare business by assuring safe access to electronic health information. Smart contracts may also be used to promoteinteroperabilitybetweeninstitutionsandnational healthcaredeliverycapacities,aswellastosecurehealthcare privacy[9] Smart contracts in the supply chain sector can shorten cash flow cycles and minimize supply chain operatingrisksintraditionalsupplychainfinancemodels. Smart contract transaction information is commonly employed in this industry because to its benefits such as traceabilityandirreversibility.
Smart contracts are also being used in the agricultural supplychaintoboosttransactionreliabilityandoperational efficiency.Furthermore,smartcontractsmaybeemployedin smart city contexts to perform autonomous distributed administration of community electricity grids and smart metretechnologies[10]

Overall,smartcontractsprovideahighlysafeandefficient method of conducting transactions without the use of middlemen,makingthemasuitableoptionforawiderange ofsectors.Withthecontinuousadvancementofblockchain technology,smartcontractusecasesareexpectedtoevolve andspreadevenmore.
3. Research Design
Thesystematicreviewanalysisisperformedinthisstudyby employing a bibliometric analysis. This part of the paper presentstheresearchdesignandmethodologyofthisstudy, andtheideaofapplicationoftheblockchaintechnologyin theareaofsupplychainmanagementhasbeenprofoundly explored and discussed to help to better understand this buddingintegrationofthetwomassiveareasofstudy.
3.1 Data Collection
Adataofallresearchpaperspublishedacrosstheworldon ourtopicofstudyonintegrationofblockchainandsupply chain management were collected via Scopus. For the purpose of research, previous publications concerning blockchainandsupplychainmanagementweregatheredas samples. Scopus is a crucial tool for accessing global academic information. In order to gain a deeper understandingofthedevelopmenttrendsofblockchainin thefieldofsupplychainmanagement,thisstudyutilizedthe coredatabaseofScopus.Scopusisabibliographicdatabase andatoolforaccessingglobalresearchliteratureinvarious disciplines, including natural sciences, social sciences, engineering, and health sciences. The search for relevant researchpaperspublished between2016 to2023utilized thekeywords"blockchain”and"supplychainmanagement", yieldingatotalof19,062researchpapers.Inthenextsection theseresearchpaperswillbeanalyzedthoroughlyinorder todrivekeyinsightsandshareareasofbuddinginterestand research
3.2 Bibliometric Study
Bibliometric analysis is a quantitative approach used to analyzeandevaluatescholarlypublicationsandtheirimpact. It involves the statistical analysis of bibliographic data, including citation counts, authorship patterns, and publication trends, among others. Bibliometric analysis is commonlyusedintheevaluationofresearchproductivity, impact,andcollaboration,aswellasinidentifyingemerging researchtrendsandgaps.Bibliometricindicatorssuchasthe h-index and impact factor are widely used to measure researchimpactandinformdecision-making
Therefore,thispapertriestodisclosethedevelopmenttrend ofblockchaintechnologyanditsapplicationinsupplychain management by employing a bibliometric analysis. The complicatedinteractionsofobjectiveitemscouldbedepicted and reflected through the similarity definition realized by theVosViewermappingtechnology.VosViewerenablesusto explorethestructureandcharacteristicsoftheresearchfield or a set of publications through bibliometric maps, which showrelationshipsbetweenauthors,institutions,keywords, and other bibliographic elements. VOSviewer allows us to create maps based on co-citation analysis, co-authorship analysis,andkeywordanalysis,amongothers.Thepurpose of the VosViewer technology is to reflect the similarity
betweeneachpairofitemsinatwo-dimensionalspacebased ontheirspacingdistanceasaccuratelyaspossible.
3.2.1 Co Word Analysis
Co-wordanalysisisabibliometricmethodusedtoidentify and analyze the relationships between words or concepts withinasetofdocuments Co-wordanalysiscanbeusedto mapthestructureofaresearchfieldortoidentifyemerging trends and topics. It involves several steps, including selecting a relevant set of documents, identifying the key concepts or keywords in those documents, creating a cooccurrence matrix that counts the frequency of pairs of words, and using various statistical and visualization techniquestoanalyzetherelationshipsbetweenthewords. Tohelpbetterunderstandthistopic,theVosVieweranalysis is employed to draw a keyword co-occurrence network diagramtoexploretheevolutionofblockchaintechnology, contributingtosummarizingtheoveralldevelopmenttrend andfutureresearchopportunities
3.2.2 Network Analysis
Networkanalysisisamethodusedtostudytherelationships between entities in a network or system. It involves analyzing the connections between nodes or entities, to identify patterns, trends, and important features of the network. The analysis typically involves identifying the nodesandlinksbetweenthem,andthenmeasuringvarious propertiesofthenetwork,suchascentrality,clustering,and connectivity.Centralitymeasurestheimportanceofanode withinthenetwork,whileclusteringmeasuresthedegreeto which nodes tend to cluster together in subgroups. Connectivity measures the overall connectedness of the network, such as the number of links between nodes. Network analysis in our research involves creating visual representations of the network, using VosViewer, to help identifypatternsandtrends.Throughthenetworkanalysis, wecanjudgethediversifieddevelopmentoftheapplication ofblockchainindifferentfields.Furthermore,throughthe co-occurrence matrix of high-frequency feature words construction,thedevelopmenttrendandresearchhotspots canbefiguredout
3.2.3 Research Framework
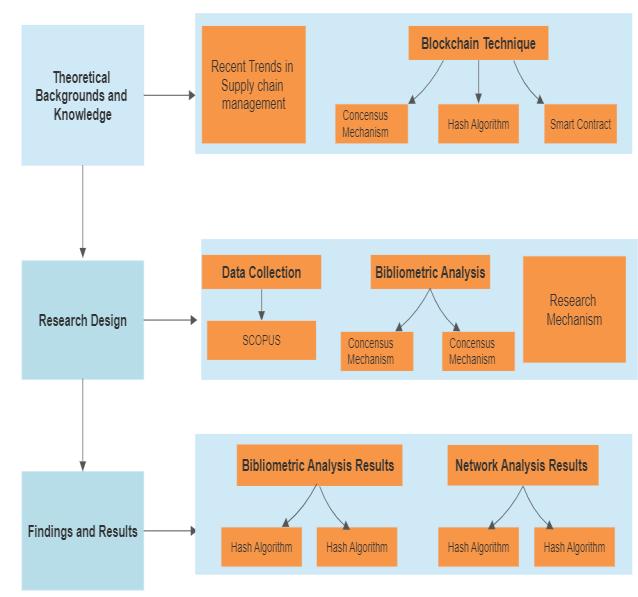
This paper performed and bibliometric analysis by addressingthecollectedliteratureonblockchainandsupply chain management from 2016 to 2023. According to research,theuseofblockchaintechnologyhasthepotential to facilitate developed supply chains, particularly in the areasofpaymentandsupplychainmanagement.Thestudy employedbibliometricanalysiswithVosViewersoftwareto reveal the intricate visualizations and interconnections of blockchain-poweredsupplychains.Theresearchresultsand themesarethensummarized.
Fig3.1:ResearchFramework

4. Findings and Results
4.1 Overview Analysis Results
4.1.1 Source Level Analysis
Toexamineacademicresearchonblockchain,wesearched forrelatedpapersinthecoredatabaseofScopususingthe keywords "blockchain," and "supply chain management[13]." This bibliometric analysis collected 21,148 references. Our findings indicate that academic research on blockchain began in 2016 and has steadily increaseduntil2022,asillustratedinFigure2.Althoughthe number of studies on blockchain was minimal in the followingyearsafter2016,therelevantstudieshavegrown rapidly since 2018, with the most rapid growth occurring from2018to2022.Wecanspeculatethattheemergenceof newdata,suchastheInternetofThingsandbigdata,which are related to blockchain technology's characteristics, has ledtoblockchain'sdevelopment.Additionally,wefoundthat thewidespreadresearchandapplicationofblockchainare associatedwiththeemergenceofnewtechnology.
Figure4.2presentsthatthetop10countriesinblockchain researchbasedonthenumberofpublications.Indiaexhibits its predominance in production and influence with 446 papers, followed distantly by the USA and China. USA has lessthanhalfasmanypublicationsasIndia.Theworldwide distributionofblockchainpublicationsshowsthatacademic research on blockchain is being published and pursued aggressivelyinallregionsoftheworld.
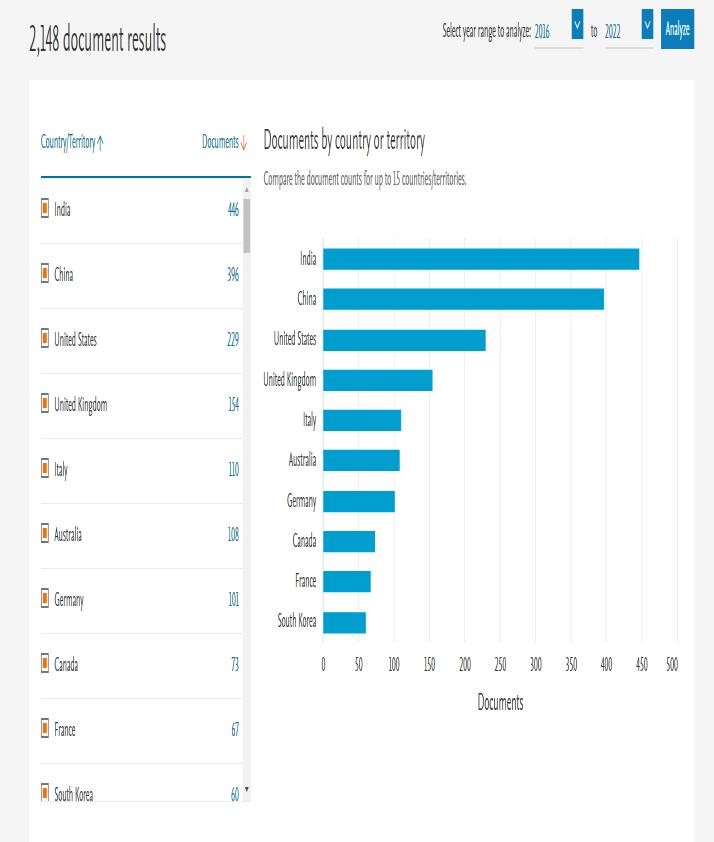
Thisfigureshowsthecountrywisedistributionofresearch papers published per country since 2016 till 2022 on the overlap of topics ‘Supply Chain Management’ and ‘Blockchain’.
This graph depicts the countries in the world who are headingtheinnovationsandresearchinthisuniqueoverlap ofthesebigfieldsofscience. Moreover, itdepicts howthe top 3 countries’ researches are easily outnumbering the othercountriesquantitatively.
Allofthesekeyinsightswerefetchedusingthedatabaseof scopuswhichprovideduswiththedataofthesepublications visavistheircountriesandpublicationyear.
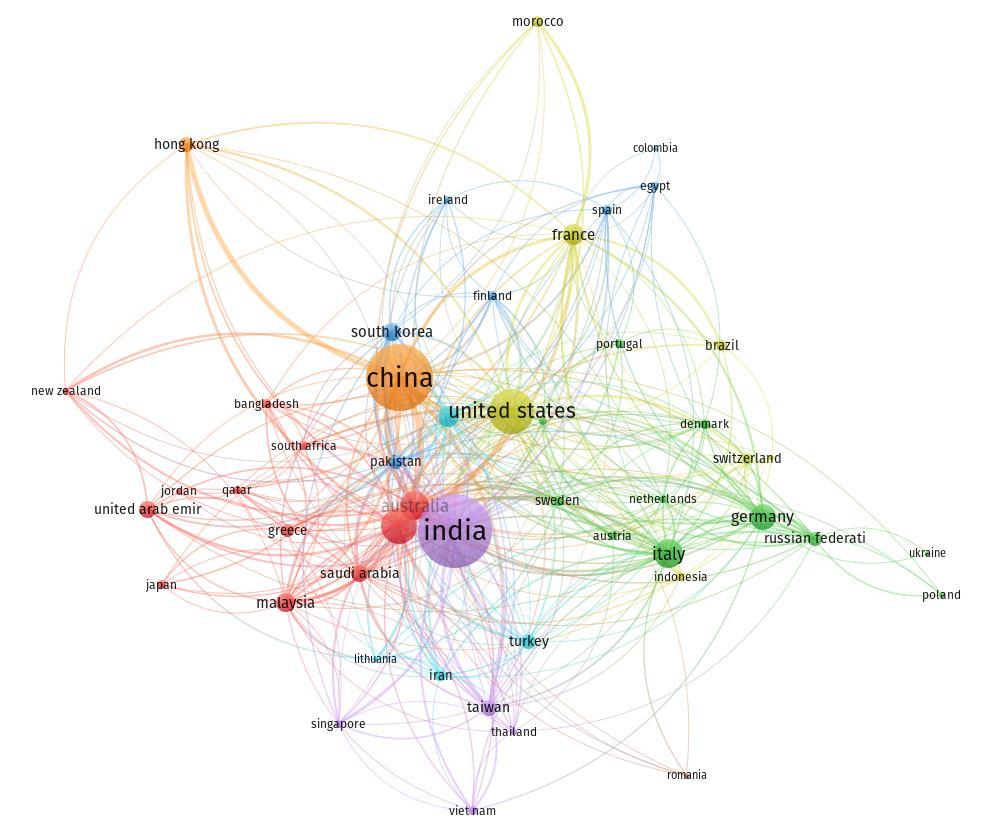
AccordingtoFigure4.3,Chinaleadsinblockchainresearch with a total link strength of 214, followed by the United Kingdomwithatotallinkstrengthof191.Othercountries such as India, Australia, USA, and France also show a significant interest in blockchain technology. This global attentionandinvestmentinblockchaintechnologysuggest itspotentialtorevolutionizevariousindustries.
As a result, numerous countries are prioritizing its development as a strategic technology for the future, particularlyChinaandtheUnitedKingdom.
4.2 Network Analysis Results
4.2.1 Literature Analysis
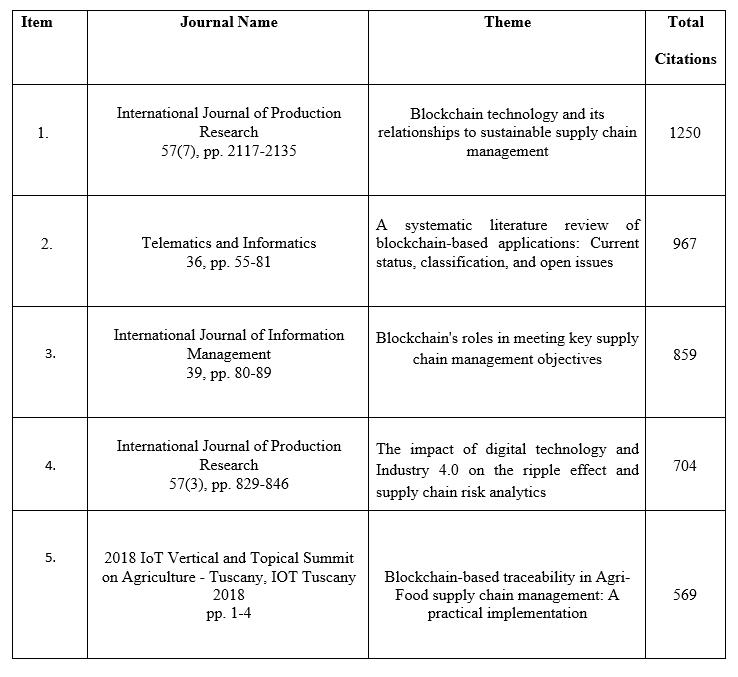
Table1presentsthetop5highcitedpapersinblockchain research. According to the highly cited papers, the mainstream research direction was explored thoroughly. Mostofthesearticlesdiscusstheapplicationofblockchain and AI in various aspects of supply chain management. Blockchainhasgreatdevelopmentprospectsinsupplychain, agriculture, and other fields. The role of blockchain is examinedinachievingkeySupplychainmanagementgoals for enterprises by establishing a framework. The combination of blockchain and the Internet of Things will drive major changes across multiple industries and their supplychains,aswellasthedevelopmentofnewbusiness modelsanddistributedapplications.

Thefollowingtableshowsusthemostcitedpapersinthe domainbeingstudied.
Cluster 1 pertains to the use of blockchain technology in diverse industrial sectors such as big data, AI, logistics, monitoring, and supply chain. The decentralized and immutable nature of blockchain enables its potential for broadapplicationsinseveralfields.Forinstance,blockchain enablestransparenttrackingoflogisticsprocesses,thereby allowingbothbusinessesandconsumerstoaccessreal-time information, ultimately improving information flow efficiency.Additionally,blockchainfacilitatesthetraceability ofproductsinthesupplychain,ensuringconfidentialityfor allpartiesinvolved.Asaresult,blockchaintechnologyhelps to establish a robust network with a complete trust mechanisminthesupplychain.
Table4.1:Top5mostcitedpapers

4.2.2 Co-Word Analysis
Using the 4,106 keywords gathered by the authors, we createdaco-wordanalysisdiagramdepictedinFigure5.Coword analysis is a content analysis technique that can proficiently showcase how keywords co-occur in datasets andexposethestructuralnetworkrelationships.Thishelps us understand the new developments in the fields being discussed as well as find the new linkages between preexistingscientificfields.Thisgivesusaclearunderstanding on the thought and ideas of existing researches in the discussedfields[14] Theco-wordanalysisisbasedonthe proposed formula T = (-1 + sqrt(-1 + 8I))/2 where I1 represents the number of words with frequency 1, and T denotes the minimum frequency value of high frequency words.TheTindexisusedtodistinguishthehighfrequency andlowfrequencywords,andtheTvaluecalculatedinthis studyis41.Therefore,wechosekeywordswithmorethan 41 occurrences as the analysis content to ensure the effectivenessofthenetworkdiagram.VosViewerutilizesthe VOSclusteringalgorithmforconductingclusteringanalysis Tocapturetheprominentareasofresearch,onlynodeswith afrequencyofoccurrenceexceeding41wereconsideredfor clustering, resulting in the identification of three distinct clusteringgroups.Figure5depictsthenodesinproportion to their frequency of occurrence, with larger nodes indicatinghigherfrequencies.Eachnodeiscolor-coded to reflecttheresearchhotspotataparticularstage,whilethe connecting lines depict the knowledge flow transitioning frompurpletoyellow,representingthechronologicalorder.
Cluster2showstheindepthanalysisoftheuseofblockchain technologyinthevariedfieldsandthetechnologybehindit. It talks about the concept of smart ledgers, consensus mechanism and the entire tech side of blockchain and its application.Italsotalksabouttheintegrationofgametheory and blockchain in order to enhance the efficiencies of modernsupplychains.Thesepartsofthisclusteraresimply informingusaboutallthetechnologiesandtheoriesthatare beingdiscussedundertheconjunctionofthesetopics.This getsustopacewithalltheresearchbeingcarriedoutfrom 2016.
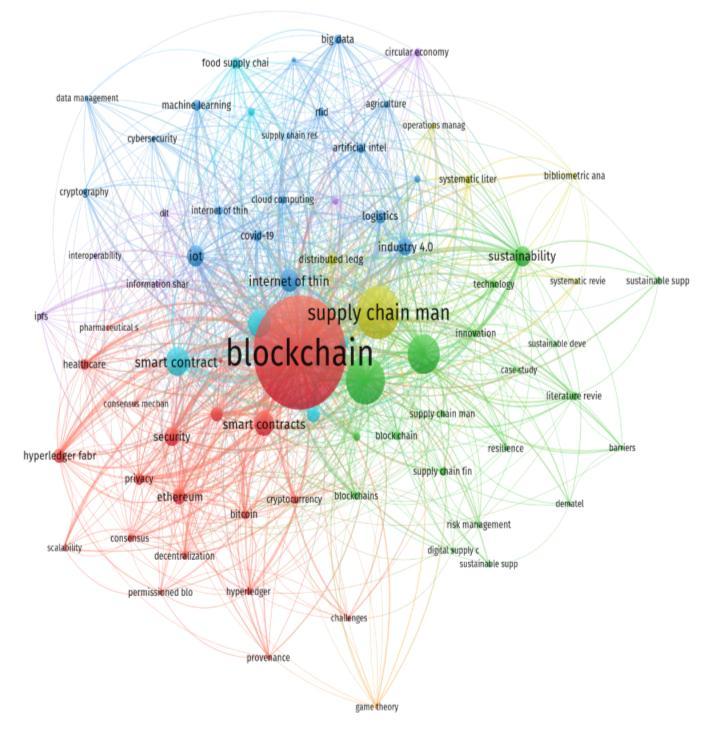
Figure4.4:Co-occurrenceofkeywodsbyauthor-keywords
Cluster 3 lastly discusses sustainability and other case studies on the application of blockchain to supply chain managementdiscussingtheexecutionandimplementation sideofthings.Ittalksabouttheapplicationofblockchainand bigdatainfoodandhighvaluegoodssupplychain.Italso discussestheriskmanagementaspectofthesupplychains as blockchain will be a big driving force to making these
supplychainsriskaverseandsafeforallofitsbeneficiaries. Thelogisticspartofthisamalgamationisbeingdiscussedin thiscluster.Moreoverthetalksandmovestowardsmaking these supply chains more sustainable has also been discussed.
Our findings indicate that most of the research conducted betweenearly2019andApril2019predominantlyfocused onblockchaintechnologies,specificallyexploringconsensus mechanismsandsmartcontracts.Subsequently,fromApril to August 2019, research interest shifted towards the integrationandimplementationofothertechnologies,such as the Internet of Things, supply chain management, personalprivacyprotection,cloudcomputing,datasharing, and traceability. In 2020, the research focus was on exploringtheindustrialapplicationsofblockchainindiverse sectors, including but not limited to personal analysis, services, resource management, trust management, smart cities,publickey,andIndustry4.0.
4.3 Research Themes
Based on the bibliometric analysis of blockchain developmenttrends,itisevidentthatresearchonblockchain technology is particularly concentrated in the domains supply chain management, traceability and transparency, supplychainfinancing,andsustainability.Thissectionaims toexaminetheresearchtrendsofblockchaintechnologyin thesetopics
4.3.1 Traceability and Transparency in Supply Chains

Supply chain management involves the coordination of variousactivitiesandpartnersinvolvedintheproduction, transportation,anddeliveryofgoodsandservices.Ensuring transparencyandtraceabilityinsupplychainsiscrucialfor improvingtheefficiency,accountability,andsustainabilityof thesupplychain.Blockchaintechnology, withits inherent characteristics of decentralization, immutability, and transparency, can be used to provide a secure and transparent platform for supply chain management. By utilizing blockchain technology, businesses can create a digitalledgerofalltransactionsandactivitiesinvolvedinthe supplychain,fromthepointoforigintothedestination
Withblockchaintechnology,everyparticipantinthesupply chain can have access to the same information, and every transactionandactivitycanberecordedin real-time.This enables stakeholders to have complete visibility of the supplychain,includingtheoriginofgoods,theirmovement throughout the supply chain,and their final destination. Transparency in supply chains provided by blockchain technology can help businesses identify and address inefficiencies and bottlenecks in the supply chain. It also promotes ethical practices and accountability by enabling businessestotracktheenvironmentalandsocialimpactof theirsupplychainactivities.Bymaintainingatransparent
and traceable supply chain, businesses can also mitigate risks associated with counterfeiting, fraud, and product recalls. Blockchain technology can also facilitate the implementationofend-to-endtraceabilityinsupplychains. End-to-endtraceabilityinvolvestrackingtheentirejourney of a product from its origin to the end consumer. This enables businesses to monitor the quality of the product, ensurecompliancewithregulations,andprovideconsumers withinformationontheoriginandsafetyoftheproduct.
End-to-endtraceabilityprovidedbyblockchaintechnology canbeparticularlybeneficialinindustriessuchasfoodand pharmaceuticals, where safety and quality are of utmost importance.Byutilizingblockchaintechnology,businesses cantracetheoriginofrawmaterials,monitortheproduction process, and track the distribution and sale of the final product.
4.3.2 Supply Chain Financing Using Blockchain
Supply chain financing refers to the practice of providing financial solutions to businesses that are involved in the supplychainprocess.Thegoalofsupplychainfinancingisto improvetheefficiencyofthesupplychainbyoptimizingcash flow and minimizing the risks associated with the supply chain.Onetechnologythathasthepotentialtorevolutionize supplychainfinancingisblockchain.Blockchaintechnology isadecentralized,distributedledgerthatallowsforsecure and transparent transactions without the need for intermediaries. It provides a way for businesses to share information and conduct transactions in a secure and efficientmanner,withouttheneedforacentralauthorityto verifyandprocessthetransactions.Thismakesitanideal technologyforsupplychainfinancing,wheretherearemany parties involved in the process and a need for secure, transparenttransactions.
One of the main benefits of using blockchain for supply chain financing is that it can improve transparencyandreducetheriskoffraud.Byusing a decentralized ledger to record transactions, all partiesinvolvedinthesupplychaincanhaveaccess tothesameinformationinreal-time.Thisallowsfor greatervisibilityintothesupplychainprocessand can help to prevent fraud by identifying and addressing any discrepancies or errors in the supplychain.
Anotherbenefitofusingblockchainforsupplychain financingisthatitcanimprovetheefficiencyofthe process by reducing the need for intermediaries. Currently,manybusinessesinvolvedinthesupply chain process rely on banks and other financial institutions to provide financing solutions. However,withblockchain,businessescandirectly interact with each other, without the need for intermediaries. This can help to reduce costs and streamline the supply chain process. Overall, the
useofblockchainforsupplychainfinancinghasthe potentialtorevolutionizethesupplychainindustry. Byimprovingtransparency,reducingtheneedfor intermediaries, and providing greater security, blockchaincanhelptostreamlinethesupplychain process and make it more efficient and costeffectiveforbusinesses.
4.3.3 Sustainability in Supply Chain using Blockchain
Sustainabilityhasbecomeanincreasinglyimportantfocus forbusinessesacrosstheglobe,andthesupplychainisno exception.Supplychainsustainabilityreferstothepractice ofcreatingenvironmentallyandsociallyresponsiblesupply chainsthatareabletomeettheneedsofthepresentwithout compromisingtheabilityoffuturegenerationstomeettheir ownneeds.Blockchaintechnologyhasthepotentialtoplaya significant role in enhancing the sustainability of supply chainsinthefollowingways:-
byprovidinggreatertransparencyandtraceability. Blockchain enables the recording of data in a tamper-proof manner, meaning that once data is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted. This makes it an ideal technology for tracking the movement of goods and materials through the supplychain,fromtheirorigintotheirdestination Byprovidinggreatertransparencyandtraceability, blockchain can help to ensure that products are sourcedandtransportedinanenvironmentallyand socially responsible manner. For example, a blockchain-based platform could be used to track the movement of goods and materials from their origin to their destination, providing real-time visibility into the entire supply chain. This could helptoidentifyanypotentialsustainabilityissues, suchasexcessiveuseofresources,unethicallabor practices,orenvironmentaldamage.Byidentifying these issues early, businesses can take proactive stepstoaddressthemandensurethattheirsupply chainsaremoresustainable.
Another way in which blockchain can support supplychainsustainabilityisbyprovidinggreater accountability.Byrecordingdatainatamper-proof manner, blockchain can help to ensure that businesses are held accountable for their sustainabilitypractices.Forexample,ablockchainbasedplatformcouldbeusedtorecordinformation aboutabusiness'ssustainabilitypractices,suchas their use of renewable energy sources or their effortstoreducewaste.Thisinformationcouldthen besharedwithstakeholders,suchascustomersand investors, providing greater transparency and accountability.
Finally, blockchain can also support supply chain sustainability by enabling the creation of decentralized networks. Decentralized networks are networks that are not controlled by a single entity,butratheraregovernedbyaconsensusofall participants. This can help to promote greater collaborationandcooperationbetweenbusinesses inthesupplychain,enablingthemtoworktogether to address sustainability challenges. For example, businessescoulduseablockchain-basedplatform to share information and resources related to sustainability, such as best practices for reducing carbonemissionsorstrategiesforreducingwaste. In conclusion, blockchain technology has the potentialtosignificantlyenhancethesustainability ofsupplychains.
By providing greater transparency and traceability, enablinggreateraccountability,andpromotinggreater collaboration and cooperation, blockchain can help to ensurethatsupplychainsaremoreenvironmentallyand sociallyresponsible.Asbusinessescontinuetoprioritize sustainability,wecanexpecttoseeanincreasinguseof blockchaintechnologyinthesupplychainindustry.
5. CONCLUSIONS
This paper provides a comprehensive analysis of the existing literature on the use of blockchain in supplychainmanagement,highlightingitspotential toaddresschallengesinthisarea.
The research hotspots in recent years mainly focused on the Internet of Things, supply chain, intelligentcommunity,cloudcomputing,chemical industry,aviation,andotherfields.Inaddition,we focused on analyzing the research trends of blockchaintechnologyinsupplychainmanagement domainmainlypertainingtofinancing,traceability, transparencyandsustainability.Wealsofoundthat application of blockchain in these areas can help resolve issues pertaining to consumer trust, awareness, secure transactions, cost savings and efficientmanagement
Inaddition,thisstudyalsorevealssometheoretical enlightenments and practical significances. The blockchain technology can help supply chain to carry out flexible management and efficient allocation of resources by innovative managreementpractices.

6. REFERENCES
[1] Hsu,C.-C.,Li,Y.-C.,&Chen,M.-C.(2019).Ablockchainbased approach to enhancing supply chain network efficiency.JournalofIndustrialInformationIntegration, 15,27-34.
[2] Bai,Y.,Lu,Y.,&Liang,C.(2018).Blockchain-baseddata sharingandcollaborationinsupplychainmanagement. InternationalJournalofProductionResearch,56(1-2), 431-447.
[3] Wu,Z.,Zhao,Y.,&Luo,X.(2020).Abibliometricanalysis of blockchain research in supply chain management. Sustainability,12(9),3864.
[4] Zhang,Y.,Zhang,C.,Yang,M.,&Zhu,Y.(2019).Anovel blockchain-based integrity verification system for medicaldata.JournalofMedicalSystems,43(7),173.
[5] Wang,X.,Liu,Y.,Wang,H.,&Li,K.(2019).Blockchainbasedsecureandefficientdatasharingforsupplychain management. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics,15(1),354-362.
[6] Liu, Y., Liu, H., Li, W., & Chen, M. (2018). Blockchainenabledsecureanddynamicsupplychainmanagement. IEEETransactionsonEngineeringManagement,65(2), 240-252.
[7] Biryukov,A.,Khovratovich,D.,&Pustogarov,I.(2016). Deanonymisation of clients in Bitcoin P2P network. Proceedings of the 25th USENIX Security Symposium, 1271-1288.
[8] Zheng,Z.,Xie,S.,Dai,H.,Chen,X.,&Wang,H.(2017).An overview of blockchain technology: Architecture, consensus, and future trends. IEEE International CongressonBigData,557-564.
[9] Domingo-Ferrer, J., & Martínez-Balleste, A. (2018). Blockchainandsmartcontractsforprivacy-enhancing technologies.IEEESecurity&Privacy,16(4),14-21.
[10] Khodabandelou, G., Abbasi, M. S., & Mirtaheri, S. L. (2019). A survey of smart contracts: Challenges, advances, and applications. Journal of Network and ComputerApplications,132,95-113.
[11] Li, Z.; Zhong, R.Y.; Tian, Z.G.; Dai, H.-N.; Barenji, A.V.; Huang, G.Q. Industrial Blockchain: A state-of-the-art Survey.Robot.Comput.-Integr.Manuf.2021,70,102124.
[12] Feng, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Lai, K.-H. Corporate social responsibilityforsupplychainmanagement:Aliterature review and bibliometric analysis. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 158,296–307.
[13] Esmaeilian,B.;Sarkis,J.;Lewis,K.;Behdad,S.Blockchain forthefutureofsustainablesupplychainmanagement in Industry 4.0. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2020, 163, 105064.
[14] Wang,C.;Lim,M.K.;Zhao,L.;Tseng,M.-L.;Chien,C.-F.; Lev, B. The evolution of Omega-The International JournalofManagementScienceoverthepast40years:A bibliometricoverview.Omega2020,93,102098
[15] S.Saberi,M.Kouhizadeh,J.Sarkis&L.Shen,“Blockchain technologyanditsrelationshipstosustainablesupply chainmanagement,InternationalJournalofProduction Research,PagesVol.57,Pages2117-2135

[16] Rosanna Cole, Mark Stevenson, James Aitken “Blockchaintechnology:implicationsforoperationsand supply chain management”, Emerald insight, ISSN:1359-8546,Vol.24No.4,pp.469-483.
[17] Yulin Luo, Shenxing Xu, Q. Zhou, “Application of blockchain technology in supply chain management”, ICIMTECH21,ArticleNo.:205
[18] PankajDutta,SurabhiSomani,RichaButala&Tsan-Ming Choi,“Blockchaintechnologyinsupplychainoperations: applications, challenges and research opportunities”, Elsevier,1366-5545,Volume142
[19] AbderahmanRejeb,JohnG.Keogh&HorstTreiblmaier, “Leveraging the internet of things and blockchain technologyinsupplychainmanagement”,MDPI,Volume 11,Issue7.
