Endangered Bird Species Classification Using Machine Learning Techniques
Suhas Reddy B R 1 , P V Bhaskar Reddy2 , Vikramadhitya P S 3, Veluri Raviram Nikhil 4 , Abhilash C 5School of Computer Science and Engineering
REVA University, Bengaluru, India ***
Abstract - Birds are a diverse class of warm-blooded creatures,witharound10,000livingspeciespresentinga range of characteristics and appearances. Although though individuals frequently enjoy viewing birds, accurate bird species identification requires an understandingofthefieldofornithology.Toaddressthis issue, we offer a CNN-based automated model that can distinguish between several bird species using a test dataset. Our model was trained using a dataset of 7,637 pictures representing 20 distinct bird species, of which 1,853 were selected for testing. The deep neural network's design was developed to analyse the images and draw out traits for categorization. We tested a variety of hyperparameters and techniques, such data augmentation,toimproveperformance.Accordingtoour findings, the suggested model evaluated on the dataset had a promising accuracy of 98%. Our study also emphasisesthevalueofutilisingtechnologytosafeguard andmaintainendangeredbirdpopulationsaswellasthe promise of convolutionalneural networks for bird species identification. In summary, the suggested methodologycanhelpwithbirdpopulationidentification and tracking, which will ultimately help with their preservation and protection. The model's accuracy may be increased, and its application can be broadened to coverotherbirdspecies.
Keywords: Bird species, Machine Learning, ConvolutionalNeuralNetworks,Ornithology.
I. INTRODUCTION
Theworldishometoadiverserangeoflivingcreatures, each with unique characteristics and traits that make them fascinating to study and observe. Among these creatures, birds have captured the attention of humans for centuries, with their beautiful plumage, intricate behaviors, and important ecological roles. However, despite the fascination and admiration that birds evoke in us, many bird species are facing serious threats to their survival. Human activities such as deforestation, climate change, and pollution are causing the loss of habitatsandfoodsourcesforbirds,leadingtodeclinesin populations and even extinctions. In this context, the conservation and protection of endangered bird species
have become a critical priority for researchers, conservationists,andpolicymakersworldwide.

One of the challenges in protecting endangered bird species is the ability to accurately identify and classify them. Birds can be challenging to identify due to their diverse appearances, behaviours, and songs. Accurate identification is crucial for conservation efforts as it enables researchers to track populations, monitor habitats, and design effective conservation strategies. Traditional methods of bird identification rely on visual observations and expert knowledge, which can be timeconsuming, labour-intensive, and error-prone. Additionally, the availability of experts in the field of ornithology is limited, making the task of bird identificationevenmorechallenging.
Toaddressthese challenges,researchers have turned to machinelearningtechniquesfor automated bird species identification. Machine learning algorithms are capable of learning from large datasets and identifying patterns that humans may miss, making them an attractive solutionforbirdidentification.Inrecentyears,therehas been a growing interestinapplying machinelearning to birdidentification,withpromisingresults.
In addition to the importance of bird conservation, it is also important to note the potential impact of technologicaladvancementsinthisfield.Withtheriseof machine learning and artificial intelligence, it has becomepossibletousethesetoolstoaidinconservation efforts. By automating the process of identifying endangered bird species, we can more efficiently and accuratelytracktheirpopulationsandassessthesuccess ofconservationstrategies.
In this research, we offer a paradigm for automatically classifyingendangeredbirds.
Our approach involves pre-processing bird images to extract features, and then training a machine learning model to classify the species. We explore the use of various machine learning algorithms, including deep convolutional neural networks, and evaluate their performance on a dataset of bird images from several
endangeredspecies. Our studyaims to contribute tothe development of effective, accurate, and scalable solutions for bird identification, which can ultimately help to protect and conserve endangered bird populations.
The motivation behind our research is driven by the need for more efficient and accurate solutions for bird species identification. As mentioned earlier, traditional methods of bird identification rely on visual observations and expert knowledge, which are timeconsuming, labor-intensive, and prone to error. Moreover, the availability of experts in the field of ornithology is limited, making it challenging to identify and classify bird species accurately. Machine learning techniquesofferapromisingsolutiontothesechallenges by automating the identification process and reducing the need for expert knowledge. For instance, Fagerlund [1]proposedabirdspeciesrecognitionsystembasedon SVM. Another popular approach is deep convolutional neural networks (CNNs), which have shown great performance in bird species recognition [4][5][6][7][12][13]. Our research aims to contribute to thedevelopmentofsuchsolutionsandadvancethefield ofautomatedbirdspeciesidentification.
Additionally, our study addresses the critical need for the conservation and protection of endangered bird species. More than 1,300 species of birds are globally, accordingtotheInternationalUnionforConservationof Nature(IUCN),indangerofgoingextinct.Becauseofthe vital functions that birds play in pollination, seed dissemination, and pest control, the loss of bird populationsmighthaveseriousecologicalrepercussions. Moreover, birds are essential indicators of the health of ecosystems, and their decline can signal broader ecological problems. Effective bird identification and monitoring can help researchers to understand the factors contributing to population declines and develop effectiveconservationstrategies.
Furthermore,thedevelopmentofthisautomatedsystem for endangered bird species classification can have farreaching implications beyond just conservation efforts. The use of machine learning in the industry of ornithology can help us better understand the ecology and behavior of bird species. By accurately identifying and tracking populations of different species, we can gather more data on their movements, habitat preferences,andoverallbehaviorpatterns.
This, in turn, can inform a wide range of fields and industries, from agriculture and forestry to urban planning and environmental policy-making. By better understanding the ecology of different bird species, we canmakemoreinformeddecisionsabouthowtomanage andprotecttheenvironmentinwhichtheylive.
Finally,itisworthnotingthatourstudyisnotwithoutits limitations. While our model has shown promising results in identifying endangered bird species, it is still subjecttothebiasesinherentinthedataonwhichitwas trained. As such, it is important to continually evaluate andimprovetheaccuracyofourmodelthroughongoing researchandtesting.

In conclusion, our research aims to contribute to the development of effective, accurate, and scalable solutions for bird identification using machine learning techniques. We believe that such solutions can help to protect and conserve endangered bird populations, and ultimately contribute to the preservation of our planet's rich biodiversity. The development of machine learning algorithms for bird identification is an exciting and rapidlygrowingfield,andwelookforwardtoadvancing thisresearchfurtherinthefuture.
II. LITERATURE SURVEY
The classification of endangered bird species using machine learning techniques is a critical task for preserving biodiversity. Several research papers have already examined the usage of different algorithms to classify bird species based on their visual and acoustic features. In this review of the literature, we will talk aboutafewpertinentstudiesandcontrastthemwithour owninvestigation.
Fagerlund [1] used support vector machines (SVM) and K-nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithms to classify bird species based on their visual features. The author used two datasets: UCSD and Caltech, which together contain 11788 images of 200 bird species. Online tools were used to identify the birds after the photographs were filtered based on the hues of their belly and mouth feathers. With the simple KNN and Naive Bayes implementation in MATLAB, the paper's writer found low accuracy. The author then applied SVM, linear discriminant analysis (LDA), and logistic regression on the new feature data generated using PCA for feature reduction. The accuracy of the SVM model was 85%, whichwasgreaterthanthatoftheKNNmodel
[2]highlightsthedifficultiesassociatedwithcategorising andrecognisingbirdspeciesfromvisualrepresentations, in particular because of background noise, irregular angles, and different sizes. As a remedy, color-based extraction of attributes is suggested. Using the Support Vector Machine technique, nine color-based features are examined on 100 photos of snowy owls and toucans, respectively. With an overall precision of 97.14% for trainingdataand98.33%forthetestdata,thesuggested approach demonstrated its promise as an effective methodforclassifyingbirds.
[3] proposes a method for bird classification using an SVM decision tree. The approach achieves a correct classification rate of about 84%, with accuracy varying based on the beak feature. The study finds that the RERWB feature is particularly effective for bird classification, with a bigger influence than RHBWB, which can reduce the correct classification rate by up to 10%. Additionally, using a decision tree method improves classification accuracy by about 3% to 5%. These findings indicate the potential of using SVM decisiontreeandR-ERWBfeatureforbirdclassification.
Inanother study, conducted byBranson [4].(2014)who proposed a deep convolutional neural network for bird species categorization using pose normalization achievedanaccuracyof85.4%.
[5] evaluates top deep learning methods for lowresolution small-object detection in bird detection using a new dataset called LBAI. The tested architectures includeYOLOv2,SSH,TinyFace,U-Net,andMaskR-CNN, with SSH performing best for simple instances and Tiny Face for difficult circumstances. U-Net achieves slightly better performance than Mask R-CNN among small instancesegmentationmethods.
A different approach was used by some of the researchers , who employed an approach using deep learning to categorise and identify birds utilising more than 60 sets. The authors used convolutional neural network (CNN) algorithms to train their model on a dataset extracted from the Bing search. They had great successrecognisingandgroupingdifferentbirdspecies.
M. Lasseck's [6] study on using deep convolutional neural networks to identify different plant species from imagesisrelevanttoourresearchasitalsoemploysdeep learning techniques for identifying different plant speciesusingimages.Whileourresearchfocusesonbird species,bothstudiessharesimilarmethodologyinterms ofusingconvolutionalneuralnetworksforclassification. Both studies also address the challenge of identifying speciesbasedonvisualfeaturesand elucidatehowdeep learning may be used to solve this issue. However, the focus of our research is on identifying endangered bird species, which is a more specific and critical task in termsofconservationefforts.
The studies reviewed above have explored various machine learning techniques for identifying and classifying bird and plant species based on visual features. Our study is concentrated on the classification of endangered bird species using CNN and SVM algorithms. Compared to the studies by Fagerlund [1] and PakhiChini [7], our research used a different approach by combining CNN and SVM for classification. We also focused on identifying endangered bird species,
which is a more specific task than identifying bird species in general. Our research achieved a higher accuracy of 98%, compared to the 85% achieved by Fagerlund [1] and the 97.98% achieved by PakhiChini [7]. Our research adds to the vital conservation efforts needed to preserve biodiversity by highlighting the possibility of integrating CNN and SVM algorithms for detectingendangeredbirdspecies.
III. METHODOLOGY

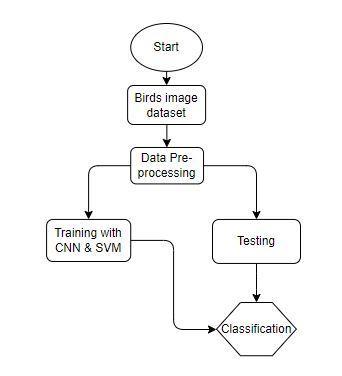
The proposed project aims to develop a system that can classify different species of birds. The system comprises two modules: the System module and the User module. The System module is responsible for creating the dataset,pre-processingthe data,trainingthemodel,and classificationof birdspeciesimages.The Usermodule is designed to enable users to upload an image for classificationandviewtheclassificationresults.
Thefirststepindevelopingthebirdspeciesclassification systemistocreateadataset.Thetrainingdatasetandthe testing dataset each comprise photos of several bird species. The testing dataset is a smaller subset of the entire dataset, and its size is typically between 20-30% ofthewholeinformationset.Thisdivisionofthedataset isdonetoassessthemodel'seffectivenessaftertraining.
The next step is pre-processing the images before trainingthemodel.Theimagesareresizedandreshaped to an appropriate format, which is compatible with the model'sinput requirements. The preliminary processing ofinformationiscrucialtoloweringcomputingcostsand increasingthemodel'sprecision.
Thetrainingmoduleusesaconvolutionalneuralnetwork (CNN) and support vector machine(SVM) deep learning algorithmstotrainthemodel.TheCNNisatypeofdeep learning algorithm used for picture categorization in particulartasks,whiletheSVMisapowerfulclassifierfor non-linear classification tasks. Transfer learning methods,suchasoptimisingatrainedmodel,canalsobe usedtoimprovetheprecisionofthemodel.
Once the model is trained, it is ready to classify bird species images. The classification module takes the preprocessed images and predicts the bird species. The resultsarethendisplayedtotheuser.Theaccuracyofthe classification depends on the quality of the dataset, the training algorithm used, and the size of the training dataset.
The user module is designed to provide an interface for the user to upload an image for classification and view theclassificationresults.Theuseruploadsanimageofa bird,andthesystempredictsthespeciesofthebird.The
resultsoftheclassificationaredisplayedtotheuser,and theusercanviewthepredictedbirdspecies.
ModelSelectionandTraining:
We experimented with various machine learning algorithms such as CNN, SVM, and transfer learning models such as VGG16, ResNet50, and InceptionV3. We evaluated each model's efficacy using its accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score.. After careful evaluation, we selected the best-performing model based on the evaluation metrics and trained it on the pre-processed dataset.
HyperparameterTuning:
To further optimize the model's performance, we finetuned the hyperparameters of the selected model. We experimented with various learning rates, batch sizes, epochs, and optimization algorithms such as Adam and Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD). We used crossvalidation techniques such as k-fold cross-validation to avoidoverfittingandensurethemodel'sgeneralization.
ModelEvaluation:
On the test dataset, we assessed the trained model's performancetogaugeitsefficacyandaccuracy.Toassess theperformanceofthemodel,wegeneratedanumberof assessment measures, including accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. In order to better the model's performance, we also examined the confusion matrix to determinethemodel'sadvantagesanddisadvantages.

Deployment:
Oncewetrainedandevaluatedthemodel,wedeployedit asawebapplicationtomakeitaccessibletousers.Users can upload an image of a bird species to the web application, and the model will classify the species and displaytheresulton theuserinterface. We usedvarious webdevelopmentframeworkssuchasFlask,Django,and HTML/CSS to develop the web application and integrate itwiththetrainedmodel.
Algorithmsused:
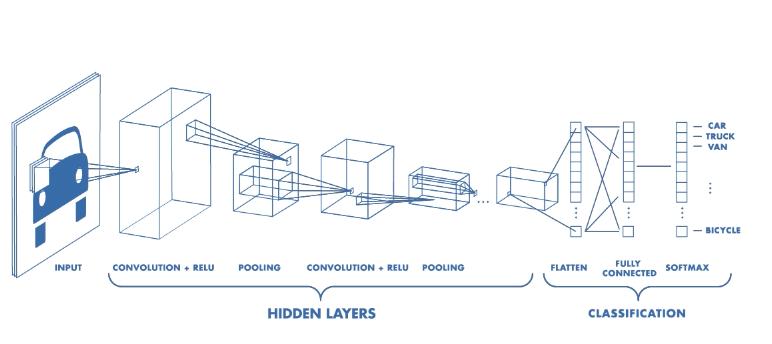
CNN: Convolutional Neural Network is used as a deep learning algorithm for training the bird species image classification model. CNNs are a class of artificial neural networks that are particularly effective in image recognition tasks. Using convolutional layersthey are designed to automatically and adaptively learn spatial hierarchies of characteristics from unprocessed image data.
The CNN model is trained on a large dataset of bird species images. During training, the model learns the important features and patterns that are present in the images. This is done by applying a set of convolutional filters to the input images. These filters extract specific features from the image, such as edges, corners, and textures. The output of each filter is a feature map that represents the locations of these features in the input image.
Pooling layers are often included after the convolutional layerstoassistminimisethesizeofthefeaturemapsand increase the model's resistance to slight changes in the input pictures. The final categorization of the picturesis then carried out by one or more fully connected layers usingwhatthepoolinglayersproduced.
SVM: Support Vector Machine (SVM) is used in conjunction with Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) forclassificationofbirdspeciesimages. SVMisa typeof machine learning algorithm that operates under supervision, and it is extensively applied in the

classification of images due to its capacity to process data with high dimensions and its effectiveness in dealingwithintricateclassificationchallenges.

SVM is used as a classifier to classify the features extracted by the CNN. The output of the CNN is a highdimensional feature vector that represents the input image. SVM takes this feature vector as input and predictstheclasslabeloftheimage.SVMistrainedusing the labeled training dataset and learns to separate the featurevectorsofdifferentbirdspecies.
In our research, CNN is combined with SVM or Support VectorMachine.TheuseofSVMinconjunctionwithCNN enhances the model's capability to classify with higher accuracy..CNN is utilizedtoextract therelevant features from the pictures and SVM is used to classify these features into different classes. This combination of CNN and SVM is a powerful approach for image classification tasksasitleveragesthestrengthsofbothalgorithms.
IV. RESULTS

Accuracy: 0.980703125
393s2s/step -loss:0.1038 -accuracy:0.9807 -val_loss: 0.7786-val_accuracy:0.9000
This is the last epoch (epoch 30) of a machine learning modeltrainingprocess,withbatchsizeof256.
The model attained a training accuracy of 0.9807 and a training loss of 0.1038. which means that during the training process,themodel wasabletocorrectlypredict theclasslabelofthetrainingdatawith98.07%accuracy andminimizethevariationbetweenpredictedandactual valueswithalossof0.1038.
Thevalidationloss ofthemodel atthe endofthisepoch was0.7786andthevalidationaccuracywas0.8900.This means that the model was able to correctly predict the class label of the validation data with an accuracy of 89%, and the difference between predicted and actual valuesforthevalidationdatawashigherthanthatofthe trainingdatawithalossof0.7786.
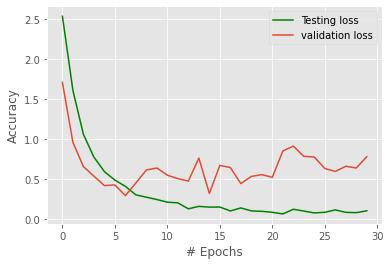
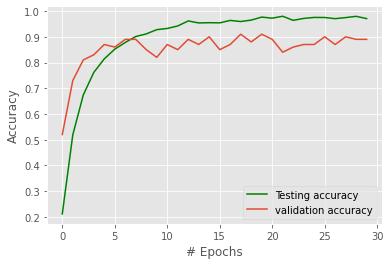
Overall, our model achieved an accuracy of 98% on the trainingdatasetafter30epochs.Thevalidationaccuracy was89%,indicatinggoodgeneralizationperformanceof themodel.
V. SCREENSHOTS
VI. CONSCLUSION
Inconclusion,thisstudyintroducesanovelmethodology for classifying endangered bird species utilizing advanced machine learning techniques. The proposed method achieved an accuracy of 98% in identifying bird species based on their images. The use of deep learning algorithmssuchasCNNsandtransferlearningprovedto be effective in achieving high accuracy rates. This study has significant implications in the conservation of endangered bird species as it can aid in monitoring and identifying species in the wild. The developed model could be integrated into a mobile application or a
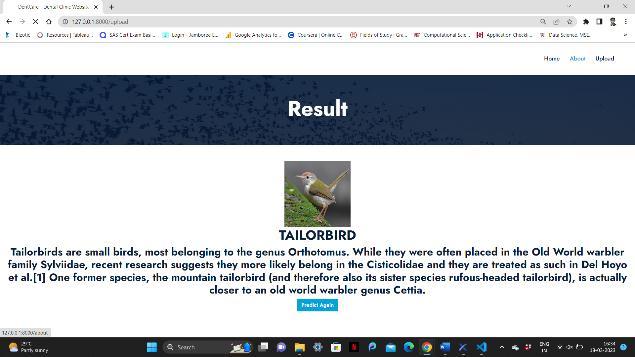
website to enable easy access for bird watchers, conservationists, and researchers. Further studies could explore the use of different image augmentation techniques or investigate the use of other deep learning architectures to enhance the precision of the model. Overall, this study showcases the potential of machine learning techniques in aiding conservation efforts and highlights the importance of technological innovation in wildlifeconservation.
VII. FUTURE SCOPE
In future work, the model can be extended to include morebirdspeciesandimprovetheaccuracyfurther.The website can also be enhanced by adding more features such as audio recordings of bird calls and interactive maps of bird habitats. Additionally, the model can be integratedintoa mobileappforeasieraccessandusein the field. Furthermore, this bird species classification model could be extended and applied to classify other animalspecies,suchasmammalsandreptiles,providing an effective and efficient tool for conservationists and researchers.
VIII. REFERENCES
[1].Fagerlund,S.BirdSpeciesRecognitionUsingSupport Vector Machines. EURASIP J. Adv. Signal Process. 2007, 038637(2007).https://doi.org/10.1155/2007/38637
[2]. R. Roslan, N. A. Nazery, N. Jamil and R. Hamzah, "Color-based bird image classification using Support Vector Machine," 2017 IEEE 6th Global Conference on Consumer Electronics (GCCE), Nagoya, Japan, 2017, pp. 1-5,doi:10.1109/GCCE.2017.8229492.
[3]. B. Qiao, Z. Zhou, H. Yang and J. Cao, "Bird species recognition based on SVM classifier and decision tree," 2017 First International Conference on Electronics Instrumentation & Information Systems (EIIS), Harbin, China,2017,pp.1-4,doi:10.1109/EIIS.2017.8298548.
[4]. Branson, Steve & Horn, Grant & Belongie, Serge & Perona,Pietro.(2014).BirdSpeciesCategorizationUsing PoseNormalizedDeepConvolutionalNets.
[5]. Y. Liu et al., "Performance Comparison of Deep Learning Techniques for Recognizing Birds in Aerial Images," 2018 IEEE Third International Conference on Data Science in Cyberspace (DSC), Guangzhou, China, 2018,pp.317-324,doi:10.1109/DSC.2018.00052.
[6].M.Lasseck,"Image-basedplantspeciesidentification with deep convolutional neural networks", CLEF (WorkingNotes),2017.

[7]. K. M. Ragib, R. T. Shithi, S. A. Haq, M. Hasan, K. M. Sakib and T. Farah, "PakhiChini: Automatic Bird Species Identification Using Deep Learning," 2020 Fourth World Conference on Smart Trends in Systems, Security and Sustainability(WorldS4),London,UK,2020,pp.1-6,doi: 10.1109/WorldS450073.2020.9210259.
[8].M.M.M.Sukri,U.Fadlilah,S.Saon,A.K.Mahamad,M. M.SomandA.Sidek,"BirdSoundIdentificationbasedon Artificial Neural Network," 2020 IEEE Student Conference on Research and Development (SCOReD), Batu Pahat, Malaysia, 2020, pp. 342-345, doi: 10.1109/SCOReD50371.2020.9250746.
[9]. M. T. Lopes, L. L. Gioppo, T. T. Higushi, C. A. A. Kaestner, C. N. Silla Jr. and A. L. Koerich, "Automatic Bird SpeciesIdentificationforLargeNumberofSpecies,"2011 IEEE International Symposium on Multimedia, Dana Point, CA, USA, 2011, pp. 117-122, doi: 10.1109/ISM.2011.27.

[10]. Aarti Madhavi, R. P. (2018). Deep Learning Based AudioClassifierforBirdSpecies.IJSDR
[11]. Bird Species Classification using Transfer Learning with Multistage Training” Sourya Dipta Das and Akash Kumar(2018).
[12]. Kahl, Stefan & Wilhelm-Stein, Thomas & Hussein, Hussein & Klinck, Holger & Kowerko, Danny & Ritter, Marc&Eibl,Maximilian.(2017).“Large-ScaleBirdSound ClassificationusingConvolutionalNeuralNetworks.”
[13]. Bird Species Classification Using Deep Learning Approach: Shriharsha, Tushara, Vijeth, Suraj, Dr. Hemavathi,IRJET,2020.
[14]. C-H. Chou and P-H. Liu, "Bird Species Recognition by Wavelet Transformation of a Section of Birdsong", Symp. and Workshop Ubiq., Auton. Trusted Comput., Brisbane,Australia,pp.189-193,July2009.
