System for Detecting Deepfake in Videos – A Survey
Abstract - nowadays, freely to be had software program grounded on device literacy methods has resulted inside the era of veritably realistic fake content that has counter accusations on society in an duration of faux news. Software including FaceApp are freely to be had and may be utilized by each person to create practical searching fake motion pictures. Such videos if used with a terrible rationale also the outcomes can be critical and may have an effect on society and people. alternatively, crucial exploration has beencompleted to be able to increase discovery styles to reduce the negative outcomes of deepfakes. This paper give a review of which are used to descry comparable manipulated d videos. We explore several techniques used to create face based totally manipulation videos and evaluate a number of deepfake discovery methods grounded on numerous parameters which incorporates generation styles, technique used, datasets and so on.
Key Words: Deepfake detection, Deep Learning, Generative Adversial Networks (GANs), Convolution Neural Networks (CNN).
1. INTRODUCTION
Thanks totheprogressin deepgetting to knowerain additiontolaptopvisionincurrentyears,asurgehasbeen seen in fa-uxfacemedia. every day, a massive variety of DF picturesandfilmsaresharedonsocialmediasystems DF movies are spreading, feedingfauxinformation and endangering social,country wide, and international ties. Human beings are-worried that what they study at the internet or watch at thenetisnow notreliableand honest On this backdrop, inJanuary2020,apopularsocial media platform introduced a brand newcoverage prohibiting AI-manipulated videos that could mislead the viewers for the duration of elections.Thetroubleis thatthat isdepending on the potential to tell the distinction among real and false videos. creation of Deepfakemoviesisbasedtotallyattheconceptofchanginga person’s face withany individualelse’s face. The requirementtoachievethisisthatthesufficientwidevariety ofphotosofeachthehumans have to be available studies carried out these days has focused on how those deepfake motion picturesare crafted anda way tounderstandthemwith the aid of analysing different
capabilities intently. But withthedevelopment in era, it has come to be an increasingnumber ofchallenging to inform apart fake movies fromtherealones
2. TECHNICAL BACKGROUND

A.CNN
ADeepLearningadvancesincomputervisionhavebeen constructed and improved over time, largely through one technique – a Convolutional Neural Net-based approach work[31]
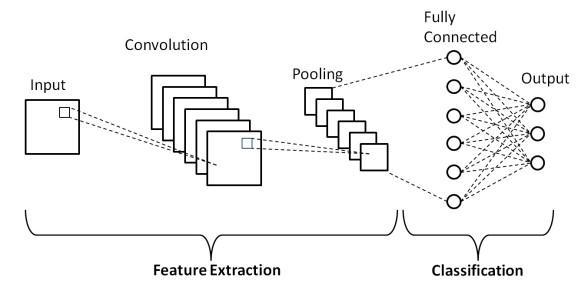
CNNs are a type of deep learning network[31]. An algorithmthatcantakeanimageasinputandgivepriorityto distinctaspects/objectsintheimage(learnablebiasesand weights)whiledistinguishingbetweenthem.ACNNrequires significantlylesspre-processingthananeuralnetwork.In contrast to other classification systems, CNN has handengineeredfiltersinitscoretechniques,whichtheycanuse with the proper training. The ability to detect these filters/featuresisdeterminedbythedesignofthebuilding. The study of Neurons in the Human Brain of the OrganizationoftheVisualCortexinfluencedtheconnectivity pattern of a CNN, which is analogous to the connectivity pattern.
TheCNN’sjobistocondensethepicturesintoaformat which is simpler to process while retaining important elements for accurate prediction. This is essential for designingan
In order to retrieve high level characteristics such as edgesfromthesourceimages,CNNisused.CNNdoesn’thave tohaveasingleConvolutionalLayer.Traditionally,thefirst ConvLayerisincontrolofcapturingLowLevelinformation like edges, color, gradient direction, and so on. The architecturegetsadjustedtotheHigh-Levelcharacteristics aslayersareadded,resultinginanetworkthatcomprehends thepicturesinthedatasetinthesamewayaswedo
AnRNN[32]isaneuralnetworkwhereintheresultofthe previousstepisbeingutilisedasinputinthefollowingstep. This in contrast to regular neural networks where all the inputs
andoutputsarenotdependentoneachother.However,in few situations, for example trying to predict the following termofaphrase,thepreviouswordsarecrucial,andthusthe previouswordsmustberemembered.Asaresult,RNNswere synthesised.Theyutilisetheintermediatelayerstosolvea problem.ThehiddenstateinRNNremembersinformation aboutthehiddensequence.RNNshave"memory”thatstores all of the results of the calculations. The memory uses the same configurations for all inputs or hidden layers. Therefore, it achieves exact same outcome by performing identicalworkonallinputsorhiddenlayers.
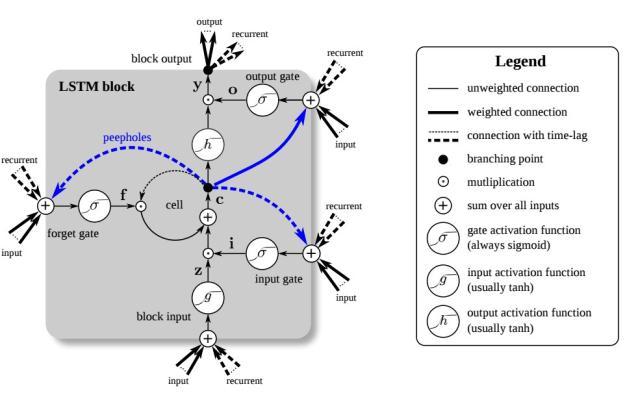
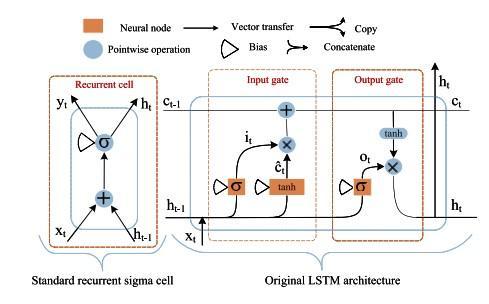
Hochreiter and Schmidhuber[33] LSTM was proposed to dealwithlong-termdependencieswhenevertheseparation among relevant data input is great. It achieves all the intriguingresultbased onRNN andhencethey have been thecentreofdeeplearning.Therecurrenthiddenlayersof RNN’s,arecomposedofrecurringcellswhoseconditionsare controlledpriorinstancesaswellasthecurrentsourcesvia feedbacknetworks.
C. GAN
Texts,imagesandvideogeneration,drugdiscovery,and textto-image conversion have all been employed in realworldapplications.

GANsareamongthemostpredominantMachineLearning techniquesdevised in recenttimes.Ina nutshell,theyare algorithms from the generative models group. These algorithmsareasubcategoryoftheunsupervisedlearning discipline, that concentrates on algorithms which understandthefundamentalstructureofthedatawithout defining a specific value. Generative models discover the inherent distribution of data input p(x), allowing them to generate
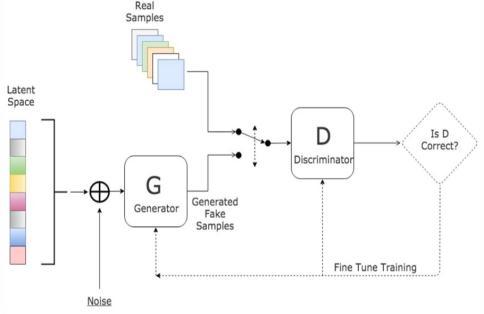
Asaconsequenceofthistraining,theDiscriminatorcan accuratelyidentifyinputdataastrueorfalse.Thisimplies that its weight values are optimised to optimise the likelihoodofanyrealinputdataxbeingclassifiedasapartof the genuine dataset whilst also reducing the likelihood of any false picture being categorized as the real dataset. In moretechnicaljargon,withthehelpofloss/errorfunction, D(x)isoptimizedandD(G(z))isminimized.
Besidesthat,theGeneratorhasbeentrainedtomisguidethe Discriminatorbyproducingdatawhichisasrealaspossible, suggestingthatGenerator’sweightshavebeenoptimizedto increasetheprobabilitythatanycounterfeit
• Thefirstmodel,referredtoasaGenerator,attemptsto developnewinformationwhichisexactlyequivalentto the simulated values. The Generator is like a person whocreatesforgedartwork.
• The next model is the Discriminator. The primary objectiveofthismodelistofindwhetheraninputdata setis’real,’indicatingitrelatestotheoriginaldataset, or’fake,’meaningaforgercreateditwascreatedbya forger.ADiscriminatorinthissituationissimilartoan art expert who attempts to determine not whether worksofartaregenuine.

Theabovegeneratorismodeledusinganeuralnetw orkG(z,θ1).Itstaskistoconvertthenoiseoftheinputv ariableztotherequireddatasourcex.(saypictures).O ntheotherhand,thesecondneuralnetworkD(x,θ2)m odelsdiscriminationandgeneratestheprobabilitythat thedataisfromrealdataonascaleof0%to100%.(0,1 ).Inbothcases,theweightorindexthatdefineseachne uralnetworkisspecifiedbythetai.
Fig. 9. Global concept of GAN
Since the neural networks represent both generator and dis- criminator, the GAN can be trained with the aid of a gradient based optimization technique picture will be categorized as belonging to the legitimate dataset. In mathematical terms, this means that the network’s loss/errorfunctionmaximizesD(G(z)).
3.FACE – BASED VIDEOS MANIPULATIONMETHODS
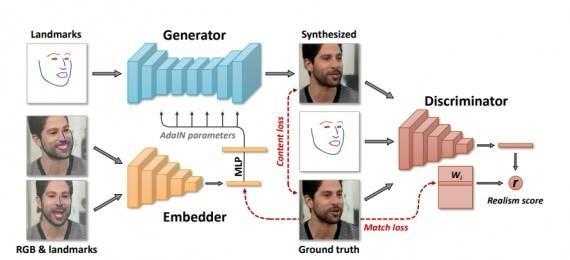
In the last twenty years, the prominence of simulated facetamperinghasshotup.Zollhoferetal.[16]provideda detailed report. Bregler et al. [17] specifically presented VideoRewrite,tocreateanewdifferentvideoartificiallyof an individual with differing mouth movements by using imagebasedmethod.Withvideofacereplacement,oneofthe very basic automatic face swap approaches [18] were proposed by Dale et al. They use single camera movies to recreateathree-dimensionalmodelofthosetwofacesand thenusetheresulting3Dmodel.Thefirstfacialreenactment expressiontransferwasaccomplishedbyThiesetal.[19].A consumerlevelRGB-Dcamerawasusedforrecreationand tracking3Drepresentationofthesourceandtargetactors both.Theanalyseddeformitiesinoriginalfacesareapplied tomodeloffacetobemodified.Toconvertthegraphically computedmodificationoffacesbacktotheiroriginalform, Kimetal.[22]learnedanimagetranslationneuralnetwork. NeuralTextures[19]improvesthetexturegeneratedusing thismethodinagreementwiththenetworktodeterminethe restored output instead of a pure translated network of imagefromanimage
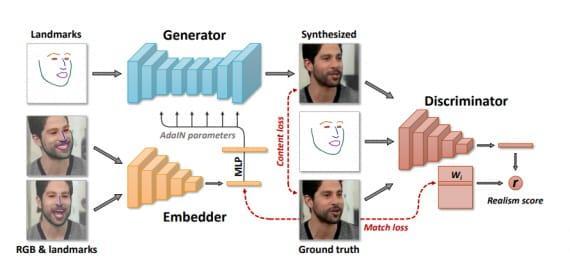
Imageto image generation
A.FACESWAP
Inputimageand targetimagewill beprovidedto cGANsnetworks, andanticipated picturewillbe accomplished
Thefollowingtableshowspopulardeepfakegeneration tools.
ManipulationMethods
TABLEI
MANIPULATIONMETHODS
Methods Deepfake Generation Techniquesused
EntireFace synthesis
Thisitcreates nonexistentfaces GAN (ex:StyleGAN)
IdentitySwap ReplacingofOne person’sfacewith anotherperson’s face
Attribute Manipulation Modificationof SpecificFeatures suchasface editing,adding spectaclestoa faceimage,andso on
Expression swap modificationofa person’sface expression
Picture Animation Regardlessofthe initialimage,itis animatedintoa talkinghead, whichisquite similartothe drivingvideo
Imageto image generation

Inputimageand targetimagewill beprovidedto cGANsnetworks, andanticipated picturewillbe accomplished
FaceSwap,ZAO mobileapplication
GAN(ex:StarGAN)
Face2Face, Neural Textures
FakeImage Animation
cGANs (conditi onalGAN)
cGANs (conditi onalGAN)
FaceSwap [9] is a method of transferring facial features fromonevideotoanother.Removethefacialareausingthe infrequently recognized facial markings. The method use scomposite images to fit these characters into 3D models. The textures from the source images are used to backproject this model to the intended image, lowering the discrepancy between both the predicted shape and the localizedlandmarks.eventually,theimageismixedwiththe rendered model, and color-variance correction is applied. Until one video ends, we repeat these processes for all source and target frames in pairs. With a lesser cost of computationtheexecutioncanberuneffectivelyontheCPU.
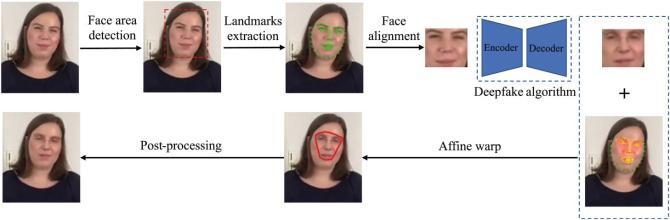
B. DEEPFAKES
Deepfakes[9] is a term that has come to refer to deeplearning-basedface substitute, but the same name is usedforadeceptiontechniquethathasexpandedviaonline platforms too. A face from the origin video or photo collectionisusedtoreplaceafaceinatargetimageorvideo. The method uses a shared encoder to train two auto encoderstocreateimagesfortrainingofthesourceandfaces tobemanipulated.Afacialrecognitionsystemisusedtocrop andalignthephotos.Thetrainedencoderanddecoderofthe sourcefaceareappliedtothetargetfaceinordertocreatea fakeimage.Theoutputoftheautoencoderisthenblended intotheimage.

C. FACE2FACE
Face2Face [9,28] is a facial reconstructive mechanismthatpassonthemanifestationsofasourcevideo to an intended video without compromising the target’s identity. The two video input streams were used by the initial implementation with a manually done keyframe selection. A dense face reconstruction made use of these frames to reintegrate the face under various lighting conditions and facial expressions. We use the Face2Face technique to fully automate the creation of reenactment alterationsforourvideodatabase.
D. NEURALTEXTURES
For their Neural Textures-based rendering approach, Thies et al. [9] used face reenactment as an example.Itlearnsaneuraltextureofthetargetindividual, includingarenderingnetwork,fromtheoriginalvideodata.
Then the models can be trained by making use of the combined losses occurred by an adversarial network and while photometric reconstruction. Tracked geometry is employedduringtrainingandtestingperiodintheNeural Textures method. These figures are generated using Face2Face’s tracking module. Only the facial emotions correspondingtothemouthregionaremodified;whilethe regionofeyeremainsintact.
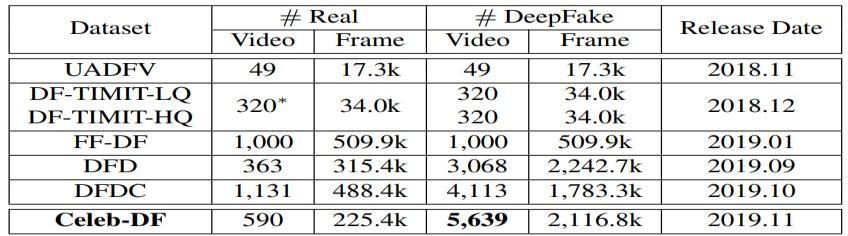
4. DATASETS
Therearemanyusefulonlineresourcesthatcanbeusedt omonitortheprogressoftechnology.Newdeeplearning modelssuchasGANshavebeenusedinrecentdevelopme ntsinhumanbasedvideointegration.TheGANmodelcons istsoftwoparts,bothofwhicharedeepneuralnetworkst rainedinseries.Thefirstisthatthemeshbuilderaimstoc reatefaceimagesasclosetorealimagesaspossible.Secon d,thediscriminationofthemeshisdesignedtodistinguish betweenthem,makingthesyntheticimageofthefaceloo kreal.
Thisisthemainideabehindcreatingdeepobjects.Therefo re,anewvideowascreatedbysuperimposingthetarget's faceononeoftheviewers.Therefore,anewvideoiscreat edfromthebeginningofthetask.
TABLEII
DATASETUSED
Datasets About

1 FaceForencic++ It is a forensics dataset made up of 1000originalvideosequenceswhich are modified using 4 different face modification techniques: Deepfakes, Face2Face, FaceSwap, and NeuralTextures.Theinputcamefrom 977 YouTube videos, all of which included frontal face which was clearly visible, allowing tampering methodstocreateplausibleforgerie
2 CelebAHQ TheCelebA-HQdatasetisanenhanced versionofCelebAwith30,000images at1024x1024pixels.
3 Flicker Theyallowustoestablishastandard forimagelocalizationoftextualentity mentions.
4 UADF This dataset contains 49 mediumqualityrealandfakevideos.
5 VoxCeleb Itisfreetodownloadandinstall,and itisavailableworldwide.Aftermany hours of work, the dataset was createdbyrecordinginterviewswith celebritiesandwell-knownpeopleon YouTube, one of the most popular websites. i)VoxCeleb1’s database contains over 100,000 samples. VoxCeleb2 has nearly a million samples.
6 CelebDF Celeb-DeepFakeDF,theDFsynthesis Algorithmisusedtocreatethevideos which is critical to improving visual quality.Itisdividedintosectionsthat addressvariousvisualdefectsfound incurrentdatasets.
Face of a specific individual asan input which is swapped withanindividualfromthesource.Zhuetal.[29]proposed CycleGAN as a strategy for improving GAN performance. Bansal et al. [30] developed Recycle-GAN, which extends previousworkbyincorporatingspatialandtemporalsignals via conditional generative adversarial networks. The two primarytypesofforensicsdatasets.FirstoneisTraditional and second is Deepfake. Classical DeepFake forensics datasets are the two main types. Traditional forensic datasets are handcrafted in less controlled environments suchascameraartifacts,compositing,painting,resampling, and rotation detection. IFSTC hosted the first Forensic MedicinePhotoContest(2013),aninternationaleventwhere participants film thousands of indoor and outdoor scenes with 25 digital cameras. There are 82 occurrences of 92 unique and 101 unique mask variants in the Wild Web Dataset(WWD)[9].WWDtriestobridgethemeasurement gap in native photography techniques. [3] Evaluate performance.TheCelebFacesAttributesCollection(CelebA) includesover200,000celebrityphotosand40featurenotes. With a total of 10,177 people, 202,599 face images, 5 geographies,and40binaryfeaturenotesperimage,CelebA hasatotalof10,177people,202,599faceimagesandrich annotations.
DeepFake datasets are the second most common type of forensicsdataset.GAN-basedmodels,whichareparticularly famousbecauseoftheirperformance,arecommonlyusedto generatethesedatasets.TheUADFV[3]ismadeupof49real videosand49DeepFakevideoscreatedwithFakeAPPand theDNNmodel.Thesefilmsareabout11:14secondslongon average, with a resolution of 294 x 500 pixels. The DeepFakeTIMIT (DF-TIMIT) dataset [3] was created by merging the VidTIMIT dataset [3] and FaceSwap-GAN; 16 similar-looking pairs of people from VidTIMIT [3] were chosen,andthedatabasegeneratedapproximately10videos foreachofthe32peopleusinglow-qualityofsize64×64, i.e.,DF-TIMIT(LQ),andhigh-qualityofsize128×128.
FaceForensics (FF) [8] is a DeepFake dataset aimed at performing forensic tasks such as facial detection and segmentationoffalsifiedimages.Over500,000frames,itis madeupof1004videos(facialvideostakenfromYouTube). Sourceto-targetmanipulation,inwhichFace2Facereenacts thefacialexpressionsofasourcevideo,andself-reenactment manipulation, in which Face2Face reenacts the facial expressions of a source video, are the two types of manipulation.
TheFaceForensics++(FF++)[15]datasethas1,000actual YouTubevideosweregathered,and1,000DeepFakevideos werecreatedusingeachofthefourfacemethods:DeepFake, Face2Face,FaceSwap,andNeural Texturearesomeofthe toolsavailable.
TABLEIII
DEEPFAKEDETECTIONMETHODS
No Titleofthepaper Techniquesused Datasetused
1 DeepfakeVideo DetectionUsing RecurrentNeural Networks
employsLSTM and RNN,CNNfor feature extraction,LSTM forsequence Processing
2 Detection of DeepFakesin VideosUtilizing Feature engineeringin DeepLearning CNNFrameworks
3 DeepLearning and Super Resolution Algorithms Combinedfor Deep FakeDetection
4 Deepfake DetectionUsing Clusteringbased Embedding
5. METHODOLGY
5 Deepfake Detectio nUsingSVM
6 DeepFakesand Beyond:ASurvey ofFakeand Detectionand Face Manipulation Databases
Methodology is a systematic, theoretical evaluation of the procedures utilized in an area of study. It involves a conceptual investigation of a collection of methods and principles related to a specific field of study. It typically includesterminologysuchasmodeofthinking,theoretical model, stages, and quantitative and qualitative methodologies.
7 Fighting deepfak ewith residual noise utilisingCNN
8 Deepfakecreation and detectio n using DeepLearning
HOHA.
DWT,CNN+SIFT False texts, voices, movies, and images areall examples offraudulent media..

CNN Resnet50 Model with Super Resolution Algorithms
Regularization Meso4algorithm, FWAalgorithm, EVAalgorithm, Multitask algorithm,and thefinal Xception-c23
DeepFake, Image Processing, SVM, GAN,DFT
CelebA and UADFV
UADFV, CelebDF, and DeepFakeDetection algorithms
CelebAdataset
CNN,RNN DFFD
InceptionResNet V2,CNNDeep Learning algorithm.
DFDC FaceForensics dataset
MesoNetCNN, DeepfakeDetection Challenge
9 DetectingCNN GeneratedFacial ImagesinRealWorldSceNarios

10 FaceForensics++: Attemptingto Detect Manipulated Facial Images
Using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) CelebA-HQ (CAHQ)
DeteUsing Steganalysis Method
Flickr-FacesHQ (FFHQ)
FaceSwap, DeepFakes, Face2Face,Neural Textures,Post ProcessingVideo Quality
Thesecriteriadefinetheformortypeofdatacollectionor,in somecases,howaresultwillbecalculated.Theprocessdoe snotdescribeaspecificprocess,butmostimportantlythety peofprocessthatneedstobedonetoachievetheworkand goals.
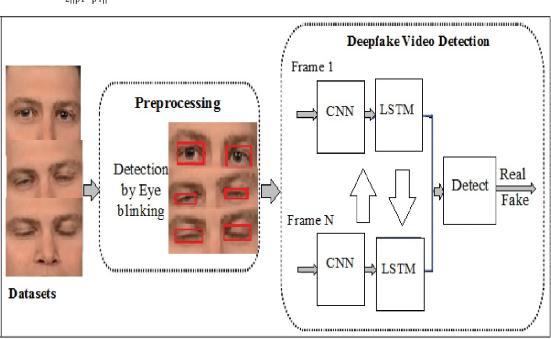
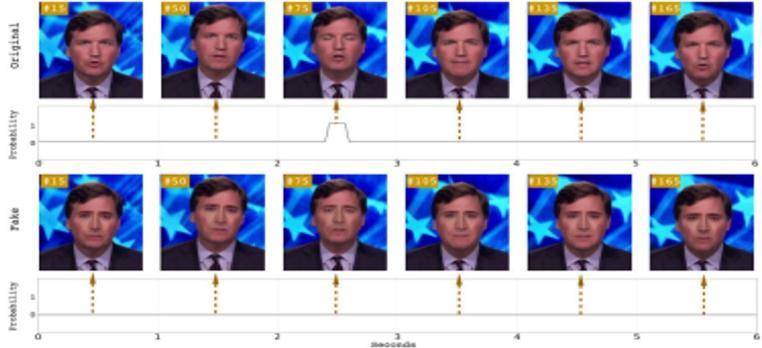
[1]proposed a timesensitive pipelineforautomatic detectio nofdeepfakevideos.Itusesaconvolutionalneuralnetwork (CNN)toextractphasefeatures.Thesefeaturesareusedtotr ainaneuralnetwork(RNN)todeterminewhetherthevideo hasbeenmanipulated.Themainresultsofthisstudyare:the analysisisperformedintwostages,theCNNextractsthesa mplestage,andthetimesensitiveRNNnetworkcapturesthe physicaldifferenceinthefaceswappingprocess.600videos, halfofwhicharedeepfakesfromvariousvideohostingsites, wereusedtotesttheproposedmethod.
Theresultofthegivenmethodisshownvisuallyintheequat ion,allowingittodecidewhetherthesuspectvideoiscorrec tornot.
Duetothelargeamountofdataframeslostaftervideocomp ression,mostimagedetectionmethodscannotbeusedforvi deoalone.Extractingvideointoframesisagreatwaytolear naboutthismedium.DWTisusedtofilterin[2]:DWTsplits theimage intofour parts. When using the Pythonlibrary Py Wavelets (HH). Vertical Detail,often referred toashighlow, HL,isaspecialoutputtouseinit.Thisdecompositionimage canbethoughtofasafrequencyfilterfortheframe.TheCNN feedwillbeanewfilter.CNNsareusedforclassification.Thi swillhelpdetecterrorsorinaccuraciesindeepfakes.Theco llectedframesaresplitinto90%trainingframesand10%te stframesbeforebeingfedintotheCNNmodel.Thisisanimp ortantstageofmodeltraining.Toincreaseaccuracy,thetrai ningprocessisprogrammedupto50times.Tuitionfeesvar yforvideos;infact,thehighertheresolution,thelongeritta kestotrainthemodel.
In[5],anewmethodisproposedthatincludesgroupbased embedding on regular basis. Open source techniques are used tomakefilmsthatcanreproducespecialfeaturesin deep flims. Clusterbased embedding normalization is incorporated into objective classification to increase local
smoothnessoftherepresentationspace,resultinginamodel thatlearnstoavoidoverlappingevents.Ourlatestdeepdata is used to test the model.Experimental results show the effectiveness of the method. The Xception network uses positive and negative models for training classification. During the training phase, the number of classes was determined as 3 and the samples formed during the test were classified as negative samples.During training, a constant loss is also used to ensure the spacing between classesandthesmoothnessoftheinclassplacementarea.
[8] proposed a method for using residual noise to be the difference between the original image and its noisefree version.Residualnoisehasbeenshowntobeusefulindeep sensingduetoitsspecificityanddiscrimination,whichcan beachievedthroughneuralnetworkswithadaptivelearning. The method was tested on two datasets: lowresolution FaceForensics++videosandhighresolutionvideosfromthe KaggleDeepfakeDetectionChallenge(DFDC).Inthisarticle, wepropose an adaptive learningbased classifier that uses convolutionalneuralnetworkstolearnthenoiseofrealand fake videos. The performance of the proposed method (DFDC) is demonstrated in two datasets, FaceForensics++ and DFDC.The aim is to determine whether the noise obtainedfromrealvideoisdifferentfromthenoiseobtained fromfakevideo.Toremovethenoise,removethenoisefree version of the frame from the frame itself. Frames are denoised using the wavelet transform function WF. Add residual noise to each frame. The backbone is the deep learningalgorithmInceptionResNetv2,a164layerCNNthat trainsoveronemillionimagesfromtheImageNetdataset.
[14] proposes a method for detecting the appearance of facial forgery, which is used at the level of mesoscopic analysis.Infact,microscopicresearchbasedonimagenoise becomes illegal in the case of video with image noise degradationaftervideocompression.Similarly,itisdifficult forthehumaneyetoclassifyfakeimagesatahigherlevel, especiallywhenimagesshowhumanfaces. Therefore,itis recommendedtouseadeepneuralnetworkwithasufficient number of layers as an intermediate method. The two designsbelow,withthelowestrepresentationandtheleast amount, yielded higher separation scores in all tests.They relyonimageclassificationnetworkscontainingclustersfor efficientconvolutiontechniquesandfeatureextraction,and use convolutional networks for classification.Meso4: This network starts with four layers of connectivity and integration,thenaddsadensenetworkwithahiddenlayer. All layers use the elimination function to increase their flexibility,whilethelayersusetheReLUfunctiontoprovide nonlinearity and bulk normalization to match their generationandgradientinhibitingeffects.Thenetworkhasa total of 27,977 teaching parameters.MesoInception4: A differentmodelusingadifferentversionoftheinitialization modulefromSzegedyetal.Toreplacethefirsttwolayersof Meso4.Thepurposeofthismodelistoreleasetheoutputof several convolutional processes with different shapes to
expand the workspace where the model can be changed. Instead of the 5×5 convolution of the original Deepfake Detection module using neural networks, 3×3 extended convolutionisusedtoavoidhighsemantics.Itcanbeseenin the cross link between the idea of using extended convolutionswithaninitialmodule.
DeepfakedetectionalgorithmsXceptionandMobileNetare discussedin[15]astwostrategiesforclassificationworkto verify deep fake movies. FaceForensics++ training and analysis data, which includes four datasets using four different and wellknown deep recognition methods, were used.Theresultsshowedhighaccuracyacrossthedata,with accuracyrangingfrom91%to98%.Avotingmachinewas alsodevelopedthatcoulddetectfakevideosbycombiningall four methods instead of one. This study discusses deep learning algorithms for implicit classification and hence detectionofdeepfakevideos.FaceForensics++wasusedasa raw video data source to train two neural networks using preliminaryimages:XceptionandMobileNet.Eachnetwork istrainedtoprovidefoursamples,oneforeachofthefour most popular deepphishing platforms. These include Deepfakes, Face2Face, FaceSwap, and NeuralTextures. Evaluation of the model shows that it can distinguish real videofromhighqualityvideo,butthisperformancedepends onthedepthmockplatformused.Tosolvethisproblem,the voting process is proposed to use the results of various modelstocreatebettersolutions.
6.CHALLENGES
Currently,therearemanydeepfakedevicesonthemarket withreasonableperformancelevels,buttherearestillmany devicesindevelopment.Incontrast,thedevelopmentofdeep fake creations, high demand for forensics and deep mastering expertise in conservation. GAN is a wellknown artificialintelligencealgorithmthatconsistsoftwotypesof discriminators and generated models that compete to produce false positives. These parodies of real people are often famous and spread quickly on social media sites, makingthemsuperadvertisingtools.Withthisfactinmind, forensicexpertswhohaveabasicunderstandingofforensic tools can use minor branches of legal protection to avoid investigations.Therefore,thecontrolmodelshouldbeable to find the accuracy of the misinformation and reduce the error.Therefore,manymethodsoflegalprotectionaimedat obscuring existing sensors are important for the developmentofmultimediaforensicsasitexposesgapsin alreadyexistingresponsesandencouragessimilarresearch formorerobustsolutions.
There are many models available today for creating or exploringdeepholes,buttheystilllackdetailsandcertain limitations.
CHALLENGES IN DEEPFAKE CREATION
• DespiteeffortstoincreasethevisibilityofDeepFakescr eation,therearestillsomeissuesthatneedtobeaddres sed.Generalization,bodyinstability,lighting,lackofori ginalityineyesandlips,handgesturesandpersonalage aresomeoftheproblemswithmakingDeepFakes.
• Generalization:Thepropertiesofgenerativemodelsare determined by the dataset used to train them. As a result,aftercompletingtrainingonacertaindataset,the model’s output reflects the learned properties (fingerprint). Furthermore, the output quality is influenced by the amount of the dataset used during training.Asaresult,inorderforthemodeltoprovide high-quality output, it must be given a dataset large enoughasinputtoattainaspecificsortoffeature.

• Temporal coherence: Other flaws involve visible fluttering and juddering among frames, as well as a dearth of temporal coherence. Deepfake creation methodswhichoperateoneveryframedonottakeinto accounttemporalinconsistencywhichleadstoseveral issues.
Fig. 14.Abnormalitiesoftemporalcoherence
• Differences in illumination: DeepFake datasets are created in a controlled environment with consistent lighting and background. In indoor/outdoor settings, however,arapidchangeinlightingconditionsresultsin colourinconsistenciesandstrangeirregularitiesinthe output.
• Lack of realistic emotions: The main challenges of DeepFake generation based on eye and lip synchronisation are an absence of emotions, disruptions,andthetarget’scommunicationtempo.
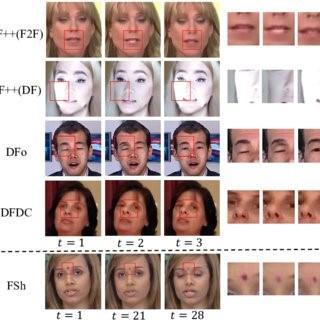
Fig. 15.Abnormalitiesofeyeblinking
•Gestures:Whenthetargetexpressesemotionswith hand gestures,thedevelopedDeepFakemodelhas difficulty matchinggestureswithemotionsexpressed bygestures.Also, it is difficult to create such deepfakes duetothelimitedinformationofthesearticles.
CHALLENGES IN DEEP FAKE DETECTION
AlthoughDeepFakedetectorshaveimprovedsignificant lyinperformance,currentdetectionalgorithmsstillhav esomeshortcomingsthatneedtobeaddressed.Deepfa kedetectionsystemsfacemanyproblems,themostimp ortantofwhicharedescribedbelow.
• NoDFdataset:DFmodeldetectionperformancedepen dsonthevarietyofdatasetusedduringtraining.Iftesti ngisdoneondownloadswithunknownfeatures,itisdi fficulttobuildadetectablemodelwithoutknowingthef unction.Duetothepopularityofwebplatforms,postpr ocessingtechniquesareusedforDFMultimediatoavoi dmisleadingDeepFakedetectors.Suchoperationscani ncluderemovingartifactsfromthebody,blurring,smoo thing,clipping,andmore
• Unfamiliar attack type:Another difficult task is developingasolidDFdetectionmodelagainstobscure sortsofassaults.Thesetechniquesareutilizedtotrick classifiersintheirresult.
• TemporalAggregation:CurrentDFdetectionmethods usebinaryframe-level classificationtodetermine ifa video frame is legitimate or fraudulent. These approaches, however, may encounter challenges like temporal anomalies and real/artificial frames appearing at regular intervals because they do not accountforinterframetemporalconsistency.
• Unlabeled data:DeepFake detection methods are typicallydevelopedusingmassivedatasets.Attimes,for example, in journalism or policing, only a limited number of dataset is available. Therefore, fostering a DeepFake detection model, unlabeled dataset is difficult.
7. CONCLUSION
This paper is about a new method, DeepFake, and this paperexaminesanewandwell-knownmethod,DeepFake. Principles,advantagesanddisadvantagesofDeepFake,GANbased DeepFake applications are explained. A DeepFake detection model is also mentioned. Most modern deep learningsearchalgorithmscannotbemodifiedandextended, whichmeansthatthesearchspaceisstillinitsinfancy.Many well-knownorganizationsandexpertsworkingtoimprove theimplementationprocessarewillingtoagree.However maintaining data integrity requires more effort and additionalsecuritymeasures.
REFERENCES
[1] DavidGuera,EdwardJ.Delp.DeepfakeVideoDetection UsingRecurrentNeuralNetworks.
[2] SonyaJ.Burroughs,BalakrishnaGokaraju,KaushikRoy and Luu Khoa. DeepFakes Detection in Videos using Feature Engineering Techniques in Deep Learning Convolution Neural Network Frameworks. 2020 IEEE AppliedImageryPatternRecognitionWorkshop(AIPR).
[3] YuezunLi,XinYang,PuSun,HonggangQiandSiwei Lyu Celeb-DF: A Large-scale Challenging Dataset for DeepFake Forensics. arXiv:1909.12962v4 [cs.CR] 16 Mar2020.
[4] NikitaS.Ivanov,AntonV.Arzhskov,VitaliyG.Ivanenko. Combining Deep Learning and Super-Resolution AlgorithmsforDeepFakeDetection.
[5] KuiZhu,BinWuandBaiWang.DeepfakeDetectionwith Clusteringbased Embedding Regularization in 2020 IEEEFifthInternationalConferenceonDataSciencein Cyberspace(DSC).
[6] HarshAgarwal,AnkurSinghandRajeswariD.Deepfake Detection Using SVM in Proceedings of the Second InternationalConferenceonElectronicsandSustainable CommunicationSystems(ICESC-2021).

[7] RubenTolosana,RubenVera-Rodriguez,JulianFierrez, AythamiMoralesandJavierOrtega-Garcia.DeepFakes and Beyond: A Survey of Face Manipulation and FakeDetection.arXiv:2001.00179v3[cs.CV]18Jun2020
[8] MarwaChendebElRai,HussainAlAhmad,OmarGouda, DinaJamal,
ManarAbuTalibandQassimNasir.FightingDeepfake ByResidualNoiseusingConvolutionNeuralNetworks in 2020 3rd International Conference on Signal ProcessingandInformationSecurity(ICSPIS).
[9] AndreasRossler,DavideCozzolino,JustusThies,Luisa Verdoliva, Matthias Nießner, Christian Riess. FaceForensics++:LearningtoDetectManipulatedFacial ImagesinarXiv:1901.08971v3[cs.CV]26Aug2019.
[10] Nils Hulzebosch, Sarah Ibrahimi, Marcel Worring. Detecting CNNGenerated Facial Images in Real-World Scenarios.
[11] HadyA.Khalil,ShadyA.Maged.DeepfakesCreationand Detection Using Deep Learning in 2021 International Mobile, Intelligent, and Ubiquitous Computing Conference(MIUCC).
[12] ArtemA.Maksutov,ViacheslavO.Morozov,Aleksander A. Lavrenov and Alexander S. Smirnov Methods of DeepfakeDetectionBasedonMachineLearning.
[13] Luisa Verdoliva Media Forensics and DeepFakes: an overviewinarXiv:2001.06564v1[cs.CV]18Jan2020.
[14] Darius Afchar, Vincent Nozick, Junichi Yamagishi and IsaoEchizen.MesoNet:aCompactFacialVideoForgery DetectionNetworkinarXiv:1809.00888v1[cs.CV]4Sep 2018.
[15] Deng Pan, Lixian Sun, Rui Wang, Xingjian Zhang and Richard O. Sinnott. Deepfake Detection through Deep Learningin2020IEEE/ACMInternationalConference onBigDataComputing,ApplicationsandTechnologies (BDCAT).
[16] MichaelZollhofer,JustusThies,DarekBradley,Pablo¨ Garrido, Thabo Beeler, Patrick Peerez, Marc Stamminger,´MatthiasNießner,andChristianTheobalt. State of the art on monocular 3d face reconstruction, tracking,andapplications.Computer GraphicsForum, 37(2):523–550,2018.
[17] ChristophBregler,MicheleCovell,andMalcolmSlaney. Videorewrite:Drivingvisualspeechwithaudio.In24th Annual Conference on Computer Graphics and InteractiveTechniques,SIGGRAPH’97,pages353–360, 1997.
[18] KevinDale,KalyanSunkavalli,MicahK.Johnson,Daniel Vlasic,WojciechMatusik,andHanspeterPfister.Video face replacement. ACM Trans. Graph., 30(6):130:1–130:10,Dec.2011.
[19] JustusThies,MichaelZollhofer,MatthiasNießner,Levi Val-¨gaerts,MarcStamminger,andChristianTheobalt. Real-time expression transfer for facial reenactment. ACMTransactionsonGraphics(TOG) -Proceedingsof ACMSIGGRAPHAsia2015,34(6):Art.No.183,2015.
[20] JustusThies,MichaelZollhofer,MarcStamminger,Chris¨tianTheobalt,andMatthiasNießner.Face2Face:Real-
TimeFaceCaptureandReenactmentofRGBVideos.In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,pages2387–2395,June2016.
[21] PaulUpchurch,JacobGardner,GeoffPleiss,RobertPless, NoahSnavely,KavitaBala,andKilianWeinberger.Deep featureinterpolationforimagecontentchanges.InIEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,2017.
[22] HyeongwooKim,PabloGarrido,AyushTewari,Weipeng Xu,JustusThies,MatthiasNießner,PatrickPerez,ChristianRichardt,MichaelZollhofer,andChristianTheobalt. Deep Video Portraits. ACM Transactions on Graphics 2018(TOG),2018.
[23] ZhiheLu,ZhihangLi,JieCao,RanHe,andZhenanSun. Recentprogressoffaceimagesynthesis.InIAPRAsian ConferenceonPatternRecognition,2017.
[24] GrigoryAntipov,MoezBaccouche,andJean-LucDugelay. Face aging with conditional generative adversarial networks. In IEEE International Conference on Image Processing,2017.
[25] David Guera and Edward J. Delp. Deepfake video detection ¨ using recurrent neural networks. In IEEE InternationalConferenceonAdvancedVideoandSignal BasedSurveillance,2018.
[26] Tero Karras, Timo Aila, Samuli Laine, and Jaakko Lehtinen. Progressive Growing of GANs for Improved Quality, Stability, and Variation. In International ConferenceonLearningRepresentations,2018.

[27] Yongyi Lu, Yu-Wing Tai, and Chi-Keung Tang. Conditional cyclegan for attribute guided face image generation. In European Conference on Computer Vision,2018.
[28] JustusThies,MichaelZollhofer,MarcStamminger,Chris¨tianTheobalt,andMatthiasNießner.Face2Face:RealTimeFaceCaptureandReenactmentofRGBVideos.In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition,pages2387–2395,June2016.
[29] Mohammed Akram Younus, Taha Mohammed Hasan. EffectiveandFastDeepFakeDetectionMethodBasedon HaarWaveletTransform
in2020InternationalConferenceonComputer ScienceandSoftwareEngineering(CSASE),Duhok, KurdistanRegion–Iraq.
[30] A.Bansal,S.Ma,D. Ramanan,and Y. Sheikh,”Recyclegan:Unsupervisedvideoretargeting,”inProceedingsof theEuropeanConferenceonComputerVision(ECCV), Washington,2018,pp.119-135.
[31] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki
[32] A.Malik,M.Kuribayashi,S.M.AbdullahiandA.N.Khan, ”DeepFake Detection for Human Face Images and Videos: A Survey,” in IEEE Access, vol. 10, pp. 1875718775,2022,doi:10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3151186.
S. Hochreiter and J. Schmidhuber, “Long short-term memory,”NeuralComput.,vol.9,no.8,pp.1735–1780, 1997.

