Investigating the Corrosion Resistance of Reinforced Concrete Structures
1, 2, 3, 4, Civil dept.,Assistant Professor, Mahavir Swami College of engineering and technology, Bhagwan Mahavir University, Surat, Gujarat, India 5 Assistant Professor, Bhagwan Mahavir college of Architecture and planning, Bhagwan Mahavir University, Surat, Gujarat, India 6 Lab assistant, Mahavir Swami College of engineering and technology, Bhagwan Mahavir University, Surat, Gujarat, India.
Abstract: Reinforcedconcreteisawidelyusedconstruction material due to its excellent mechanical properties and durability. However, the corrosion of steel reinforcement in reinforced concrete structures is a major concern that can lead to severe structural damage and significant repair costs. In this study, we investigate the corrosion resistance of reinforced concrete structures by examining the effects of different environmental factors on the corrosion strength of reinforced concrete. Our findings reveal that the quality of concrete, the type of reinforcing steel, and the exposure conditions are significant factors affecting the corrosion resistance of reinforced concrete structures.
Key Words: concrete,coating,corrosiontesting,saltspray test,concretedurability
1. INTRODUCTION
Reinforcedconcreteisacompositematerialthatconsistsof concreteandreinforcingsteel.Thereinforcingsteelprovides thetensilestrengththattheconcretelacks,andtheconcrete protectsthesteelfromcorrosion.However,thecorrosionof reinforcing steel is a major problem that can lead to the degradationofthemechanicalpropertiesofthereinforced concrete structures. Corrosion can be caused by various factorssuchasthequalityofconcrete,thetypeofreinforcing steel,andtheexposureconditions.Therefore,itisimportant toinvestigatethecorrosionresistanceofreinforcedconcrete structures to ensure their long-term durability and sustainability.
1.1 Corrosion Test
Half-CellPotentialTest:Thehalf-cellpotentialtestisanondestructivetestthatmeasurestheelectrochemicalpotential ofthereinforcingsteelrelativetoareferenceelectrode.The test is based on the principle that the potential difference betweenthereinforcingsteelandthereferenceelectrodeis relatedtothecorrosionactivity.
ChlorideIonPenetrationTest:Thechlorideionpenetration test measures the amount of chloride ions that have penetratedtheconcrete.Chlorideionsareoneoftheprimary causes of reinforcing steel corrosion in concrete. The test involvesdrillingasmallholeintheconcreteandextractinga
sample for analysis. The test provides an indication of the likelihoodofcorrosionandcanbeusedtoidentifyareasof potentialcorrosion
Thetestcanbeusedtoassessthelikelihoodofcorrosionand toidentifyareasofpotentialcorrosion
CorrosionRateMeasurement:Corrosionratemeasurement involvesmonitoringtherateatwhichthereinforcingsteel corrodes.Thiscanbedoneusingelectrochemicaltechniques such as linear polarization resistance, electrochemical impedancespectroscopy,orcyclicpolarization.Thesetests provideaquantitativemeasureofthecorrosionrateandcan be used to evaluate the effectiveness of corrosion control measures
SaltSprayTest:Thesaltspraytestisastandardtestthatis used to evaluate the corrosion resistance of materials ina corrosiveenvironment.

Thetestinvolvesexposingthematerialtoasaltspraymist for a specified period and then assessing the degree of corrosion.Thetestcanbeusedtoevaluatetheeffectiveness ofdifferentsurfacetreatmentsorcoatings
RapidChlorideIonPenetrationTest:Therapidchlorideion penetration test is a quick and non-destructive test that measurestheelectricalconductivityoftheconcrete.Thetest providesanestimateofthechlorideionpenetrationdepth andcanbeusedtoevaluatethelikelihoodofcorrosion
1.2 Comparison of Corrosion Tests:
Each of the corrosion tests mentioned above has its own advantagesandlimitations.Thehalf-cellpotential testand chlorideionpenetrationtestarerelativelysimpleandnondestructive,buttheydonotprovideaquantitativemeasure ofthecorrosionrate.Corrosionratemeasurementprovidesa quantitativemeasureofthecorrosionrate,butitcanbetimeconsuming and requires specialized equipment. The salt spray test provides a standardized and controlled environmentforcorrosiontesting,butitmaynotaccurately representtheactualfieldconditions.Therapidchlorideion penetrationtestisquickandnon-destructive,butitprovides onlyanestimateofthechlorideionpenetrationdepth.
1.3 Half-cell potential measurement test
Corrosionofsteelreinforcementinconcretestructuresisa seriousproblemthatcanleadtocostlyrepairsandstructural failure. The use of half-cell potential measurement is a widelyusedmethodforidentifyingareasofconcretethatare atriskofcorrosion.Inthispaper,wediscusstheequipment requiredforconductingthetest,theprecautionsthatshould betakentoensureaccurateresults,andpresenttheresults of a half-cell potential measurement test conducted on a concretesurface.
1.4 Precautions for use the Half-cell potential measurement test
The Half-Cell Potential (HCP) test is a commonly used methodforassessingthelikelihoodofcorrosioninmetals. However, to obtain accurate and reliable results, it is importanttofollowcertainprecautionsduringthetest.Here are some precautions that should be taken during HCP testing:
Ensurepropercleaningofthemetalsurface:Beforetesting, itisimportanttocleanthemetalsurfacetoremoveanyrust, dirt,orothercontaminantsthatmayaffectthetestresults. Thesurfaceshouldbecleanedwithanon-metallicabrasive materialsuchasaplasticornylonbrush.
Avoid contact with moisture: Moisture can alter the HCP value,soitisimportanttokeepthetestareadryduringthe test.Avoidusingthetestinwetordampconditions.
Useaconsistenttestingtechnique:TheHCPtestshouldbe performed in a consistent manner to ensure accurate and reliable results. The test electrode should be held at a constantdistancefromthemetalsurface,andthetestshould beperformedforaconsistentamountoftime.
Testmultipleareas:HCPvaluescanvaryacrossthesurface ofthemetal,soitisimportanttotestmultipleareastoobtain a representative sample. The areas tested should be representativeofthemetalsurfacebeingevaluated.
Ensure proper calibration: The HCP meter should be properlycalibratedbeforeusetoensureaccuratereadings. The calibration should be performed using a standard referenceelectrode.
Interpret results with caution: HCP values provide an indicationofthelikelihoodofcorrosion,butshouldnotbe used as the sole basis for determining the presence or absenceofcorrosion.Otherfactors,suchasthemetaltype, environmental conditions, and the presence of other contaminants,shouldalsobeconsideredwheninterpreting HCPresults.
By following these precautions, the HCP test can be performed accurately and reliably, providing valuable
information for evaluating the likelihood of corrosion in metals.
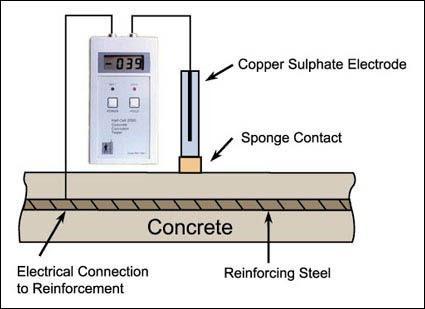
2. Equipment of Half-cell potential measurement test:
To conduct a half-cell potential measurement test, the followingequipmentisrequired:

1. A reference electrode: A copper/copper sulphate electrodeiscommonlyusedasareferenceelectrode.
2. Atestelectrode:Asteelorplatinumelectrodeistypically usedasatestelectrode.
3. Avoltmeter:Adigitalvoltmeterisrequiredtomeasure thepotentialdifferencebetweenthetwoelectrodes.
4. A wire brush: A wire brush is required to clean the concretesurfacebeforetakingmeasurements.
Fig.-1 Half-cellpotentialmeasurementtest
3 Procedure
Cleantheconcretesurfacewherethemeasurementwillbe taken,removinganydirtorloosematerial.
Placethereferenceelectrodeonthesurfaceoftheconcrete andconnectittoavoltmeter.
Insertthetestelectrodeintotheconcrete,ensuringitmakes goodcontactwiththesurfaceandisatleast5mmdeep.
Recordthepotentialdifferencebetweenthetwoelectrodes.
Move the test electrode to a new location on the concrete surfaceandrepeatsteps2-4.
Continuetakingmeasurementsatmultiplelocationsonthe surfaceoftheconcretetogetarepresentativesampleofthe corrosionpotential.
Recordthereadingsinatableorspreadsheet,includingthe location of each measurement and the corresponding potentialdifferencevalue.
Analysethereadingstodetermineifthereareanyareasof theconcretesurfacethathaveahigherriskofcorrosion,and takeappropriatemeasurestoaddresstheissueifnecessary.
4 Results:
Inthisexperimentwevisitedoneoftheoldestsite,thissite has four rooms available and the condition of column and beamwasverybad,itstestingresultisasfollows
Table-1: ProbabilityofCorrosionaccordingtohalf-cell potentialvalues
In this chart, the height of each bar represents the range betweentheminimumandmaximumHCPvaluesforeach room.Thelongerthebar,thewidertherangeofHCPvalues, andtherefore,thegreaterthepotentialforcorrosionactivity.
Based on this chart, Rooms 1 and 2 have the highest potentialforcorrosionactivity,asindicatedbytheirlonger barsandmorenegativeminimumHCPvalues.Rooms3and 4haveshorterbarsandlessnegativeminimumHCPvalues, suggestingalowerpotentialforcorrosionactivity.However, itisimportanttonotethatthischartonlyprovidesageneral overviewandadditionaltestingmaybenecessarytoconfirm thepresenceandextentofcorrosionactivityineachroom.
5. CONCLUSIONS
Table-2: MaximumandminimumvaluesoftheHCP readings
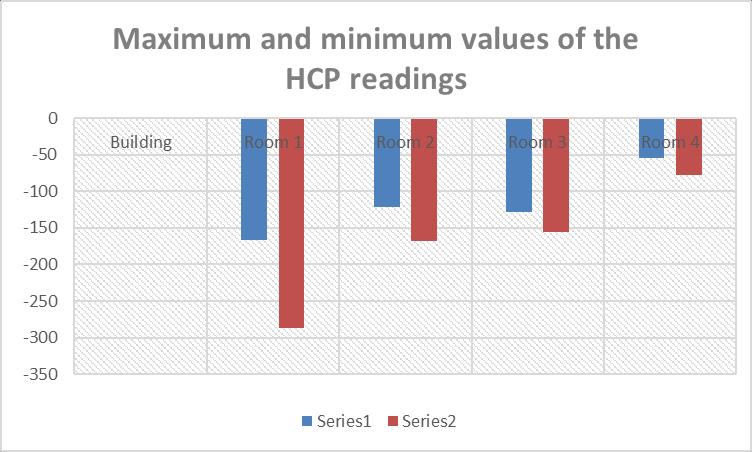
TheprovideddatashowsthemaximumandminimumHalfCellPotential(HCP)readingsforeachroom.HCPreadings areoftenusedtoassessthelikelihoodofcorrosionactivity, withmorenegativevaluesindicatingahigherprobabilityof corrosion.
In conclusion, half-cell potential measurement is a widely usedmethodforidentifyingareasofconcretethatareatrisk ofcorrosion.Theequipmentrequiredforconductingthetest is relatively simple and inexpensive, and the test can be conductedquicklyandeasily.However,precautionsmustbe taken to ensure accurate results. The results of our test indicatethathalf-cellpotentialmeasurementisaneffective method for identifying areas of potential corrosion in concretestructures.

Basedonthegivendata,itappearsthatallfourroomshavea maximum HCP value of 6 mV, which indicates a low probability of corrosion activity. However, the minimum HCPvaluesforeachroomvary,withRoom1havingthemost negativeHCPvalueof-287mV,followedbyRoom2with168mV,Room3with-155mV,andRoom4with-78mV.
These negative HCP values suggest that there may be a moderatetohighprobabilityofcorrosionactivityinRooms 1 and 2, and a lower probability of corrosion activity in Rooms3and4.However,itisimportanttonotethatthese HCP readings should be interpreted in conjunction with other factors such as environmental conditions, materials being tested, and the presence of other contaminants.

Additional testing may be necessary to confirm the likelihoodofcorrosionactivityineachroom.
REFERENCES
[1]. ACI222R-01:CorrosionofMetalsinConcrete.American ConcreteInstitute.

[2] Andrade, C., Alonso, C., and Rodriguez, J. (1997). Evaluation of Reinforcement Corrosion by Concrete Electrical Resistance Measurement. Cement and Concrete Research,Vol.27,No.3,pp.345-355.
[3] ASTM C876-15: Standard Test Method for Corrosion Potentials of Uncoated Reinforcing Steel in Concrete. AmericanSocietyforTestingandMaterials.
[4] ASTM C1202-19: Standard Test Method for Electrical Indication of Concrete's Ability to Resist Chloride Ion Penetration.AmericanSocietyforTestingandMaterials.
[5]Broomfield,J.P.(2007).CorrosionofSteelinConcrete: Understanding, Investigation and Repair, Second Edition. CRCPress.
[6]ConcreteSocietyTechnicalReportNo.60:Corrosionof Steel in Concrete - Prevention, Diagnosis and Remedial Measures.TheConcreteSociety.
[7]Powers,T.C.,andBrownyard,T.L.(1947).Studiesofthe PhysicalPropertiesofHardenedPortlandCementPaste.
