Analytical Methods Development And Validation For Estimation Of Rivastigmine Drug Used For Alzheimer’s Disease: A Systematic Review
Ashwini R Walave 1, Hemlata S. Bhawar 2, Mayur S. Bhosale 31 Research schollar, Pravara Rural College of pharmacy, Pravaranagar, Maharashtra, India.
2 Professor, Dept. of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Pravara Rural College of pharmacy, Pravaranagar, Maharashtra, India.

3 Professor, Dept. of Pharmaceutical Chemistry, Pravara Rural College of pharmacy, Pravaranagar, Maharashtra, India.
***
Abstract - Quality assurance and quality control of pharmaceutical formulations and bulk pharmaceuticals both heavily rely on pharmaceutical analysis. The demand for innovative analytical techniques has increased as a resultofthepharmaceuticalindustries'rapidexpansionand medication production across the globe. Development of analytical methods has therefore evolved into the core function of analysis. Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive memorydefeatandimpairmentinbehaviour,language,and visuospatial skills. Rivastigmine is a carbamate-derived acetylcholine esterase inhibitor that is primarily used to treat mild to moderate Alzheimer's disease. The primary goal of this review was to highlight spectrophotometric, reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), high-performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC), and liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy (LC-MS) techniques that can be used for method development and validation for Rivastigmine drug . The review is a collection of information that includes the various analytical techniques used, the various columns used, the mobile phase used, flow rate, various detectors, and detection wavelength and retention time. The purpose of this review is to stimulate research into the creation of new, more accurate, precise, and specific methods for estimationofrivastigmine.
Key Words: Alzheimer’s disease, Rivastigmine, Dementia, Method development, Analytical techniques.
1.INTRODUCTION
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is the most prevalent serious neurocognitive impairment in the world today, affecting up to 47 million individuals. It is the sixth most common causeofdeathintheUS,accountingfor29.4fatalities per 100,000 people, according to the most recent statistics from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). cardiovascular disease deaths have fallen by 14% between 2000 and 2014, whereas complications from AD have shot up by 89% during the same period. The stress
that carers go through is equally significant, and it has an impact on their physical and emotional health. In low to middle income and high income nations, respectively, barely 5-10% and 40–50% of individuals have gotten a formaldiagnosisofAD,inspiteofitssocietalimpact.[19]
It is believed that Dr. Alois Alzheimer, a German psychiatrist and neuropathologist, first described the dementing illness that subsequently came to be recognised as AD. [5] The financial cost of Alzheimer's disease(AD)isamongthehighestintheworld.50million people worldwide were estimated to have Alzheimer's diseasein2019.[14]
The hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD), a neurodegenerative disorder, are neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles in the medial temporal lobe and neocortical regions of the brain. Clinically, the disease showsupasagradualdeclineincognitiveandbehavioural abilities. Dementia, the most common form of the illness, already affects 50 million people globally, and by 2050, experts expect that number to increase to 152 million cases, doubling every five years.[4] Dementia is a clinical condition(acollectionofrelatedsignsandsymptoms)that is characterised by a steady decline in mental capacity.
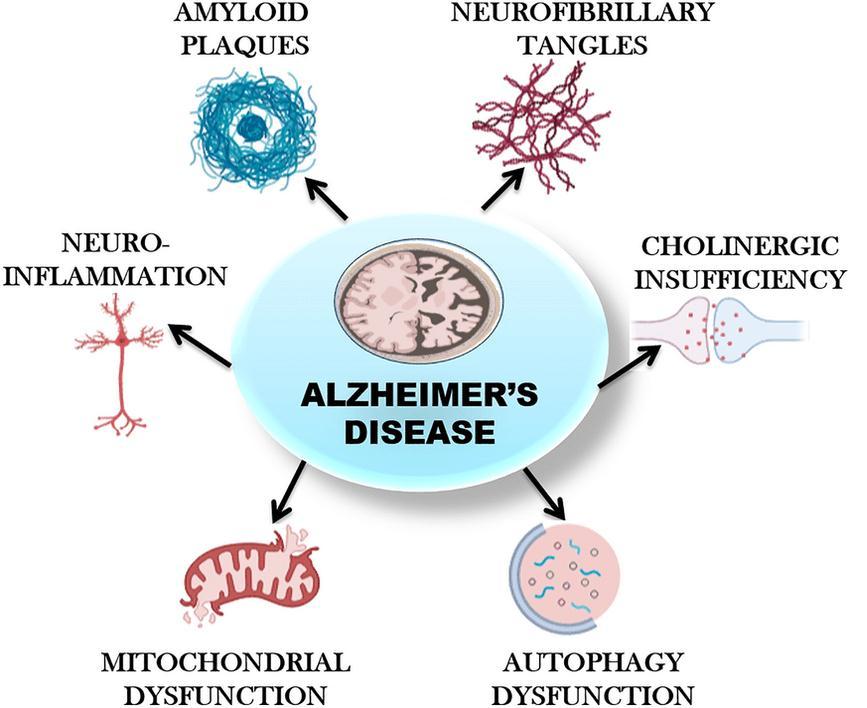
Dementia can impair a variety of cognitive functions, including memory, language, thinking, decision-making, visuospatial function, attention, and orientation. Changes in personality, emotional control, and social behaviours arefrequentcoexistingsymptoms of cognitive impairments in dementia patients. Dementia affects a person's capacity to carry out daily tasks including driving, shopping, cleaning the house, cooking, managing finances, and taking care of oneself. This is significantsincethesechangesincognitionandbehaviour can interfere with job, social interactions, and relationships.[5]
It is unclear what causes Alzheimer's disease. It is estimated that hereditary factors, usually involving numerousgenes,accountforaround70%oftheaetiology. A history of head traumas, depression or hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, obesity, etc. are possible contributing factors. The diagnosis is made using the patient'smedicalhistory,cognitivetesting,andbloodtests to rule out other potential problems. Early symptoms are frequently confused with ageing. A definitive diagnosis requirestheexaminationofbraincells.TheriskofADmay beloweredviamentalandphysicalexercise,aswellasby avoiding smoking, high blood pressure, diabetes, and obesity.[12] The first-line treatment for Alzheimer's disease and some other dementias, such as dementia in Parkinson's disease, is thought to be a cholinesterase inhibitor, such as donepezil, galantamine, and rivastigmine. According to one theory, cholinesterase inhibitors function by preventing the enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE), which degrades the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, from doing its job. For more uncommon dementias linked to neurological disorders, cholinesterase inhibitors may also result in clinicalimprovement.[20]
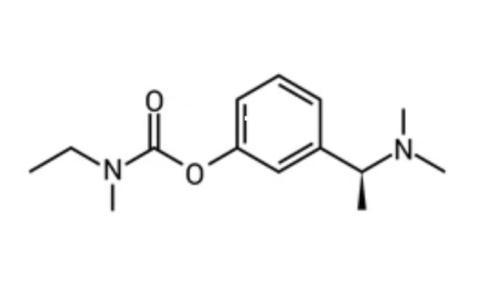
A parasympathomimetic and reversible cholinesterase inhibitor called rivastigmine is recommended for treating mild to severe Alzheimer'srelated dementia. [7] Rivastigmine is a carbamate derivative that is structurally unrelated to donepezil and tacrine but is linked to physostigmine. Rivastigmine's exact mechanism is still unknown, however it is hypothesised that it inhibits acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterasebybindingtoandinactivatingthem, preventing acetylcholine from being hydrolyzed and increasing the amount of acetylcholine at cholinergic synapses. Rivastigmine's anticholinesterase activity is more focused on brain acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase than it is on peripheral tissues.[8] Cholinergic neuronal pathways that connect the basal forebrain to the cerebral cortex and hippocampus are involved in pathological alterations in AD. Memory, attention, learning, and other cognitive processes are thought to be tightly related to these pathways. They are carried out by lowered levels of acetylcholine, which are controlled by the cholinesterase enzyme. This enzyme, which is neuronal in origin, breaks down acetylcholine at synapses throughout the nervous system. Acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that supports human memory and cognition,isbrokendownbycholinesterase.Acetylcholine is made more readily available to the patient for memory and cognitive function by suppressing cholinesterase. Since AD patients have much lower amounts of acetylcholine than persons who are otherwise healthy. . The enzyme that deactivates the transmitter in the synapticcleftisblockedbythesemedications.Itshouldbe mentioned that ChEI treat AD's symptoms rather than its cause.Acetylcholinelevels inthebrainareraisedbyChEI. Levels of butyrylcholinesterase rise while levels of acetylcholinesterase gradually decrease as AD advances and cortical neurons are destroyed. When acetylcholinesterase is gone, butyrylcholinesterase can and does take over the role of metabolising acetylcholine atthesynapses.Rivastigmine,butnotitsrivals,blocksthe activity of both acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase by covalently attaching to their active sites. The first and most crucial stage in the degradation of rivastigmine, which is not metabolised in theliver,isthebreakingofthesecovalentbonds.[21]

2.RESULTS AND DISCUSSION:
Rivastigmine
Rivastigmineisacarbamateof3-[(1S)-1-(dimethylamino) ethyl]phenyl.[8]Itisoffered asa capsuleunder the brand namesExelon,Rivagem-3,andRivamer.Ithasamolecular weightof250.3,apKaof8.85,aLogPof2.3,atherapeutic dosage of 3 mg/day, a half-life of 1 h, a half-life of 1.5 h, 40% protein binding, and 36% oral bioavailability.[15] The development and validation of Rivastigmine drug used in Alzheimer’s disease estimated quantitatively by spectrophotometric, reverse phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), high-performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC), and liquid chromatography-mass spectroscopy (LC-MS) method. Method development and validation of Rivastigmine can be studied by chromatographic techniques by various authors,theresultscanbediscussedasbelow.
For the analysis of Rivastigmine in pharmaceutical dosage forms, an isocratic RP-HPLC method has been createdandvalidated.ThermoHypersilC4column(25cm X 4.6 mm, 5 m) with a mobile phase of orthophosphoric acid and acetonitrile (60:40, v/v) adjusted to pH 4.0 at a flowrateof1.0mLmin-1producedthebestseparation.At 220 nm, UV detection was carried out. An internal standard was atrovastatin. Rivastigmine and Atrovastatin haveretentiontimesof
4.75 and 8.83 minutes, respectively. Specificity, linearity, precision, accuracy, limit of quantification, limit of detection,robustness,andsolutionstabilityofthemethod wereallvalidated.[6]
Another author proposed and validated a simple, accurate,andefficientRP-HPLCmethodfortheestimation of Rivastigmine effect by improving cholinergic function, in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. Ortho phosphoric acid was used to bring the pH of the mobile phase, which was 2.02 g of 1-octane sodium sulfonate, to 3.0 before filtering through a 0.45 mm Pal Pharma nylon 66 membrane filter. By combining buffer and acetonitrile ina70:30v/vratio,themobilephasewascreated.Column 4.6mm'250mm,ODS,Xterra RP18,5mmorsimilar,flow rate 1.0 ml/min, detection 217 nm, injection volume 40 ml, and run duration 15 min are the specifications of the chromatographicsystem.[7]
The different conditions applied by another author using RP-HPLC for the determination of Rivastigmine from Bulk dosage form by reverse phase HPLC.TheC18column(Inertsil,C18,250x4.6mm.5)was utilized. The sample was analyzed using Potassium phosphate mono basic buffer (pH 2.5± 0.05): Acetonitrile (70:30) as a mobile phase at a flow rate of 1.0ml/min. uv detection done at 217 nm. Rivastigmine's retention time wasfoundtobe3.66minutes.AccordingtoICHguidelines, the stability assay was carried out and validated for accuracy, precision, linearity, specificity, and sensitivity.
The method was validated and found to be precise, rapid, accurate,specific,reliable,andreproducible.[8]
Fortheanalysisofrivastigminehydrogentartrate intransdermaldrugadministrationsystem,arapidsimple sensitive exact, accurate and reproducible RP-HPLC method was designed and validated. Water was used as thesolventbecauserivastigminetartrateiswatersoluble. TheC-18RP-HPLCcolumn,whichwasmaintainedatroom temperature, was used to conduct the separation. The mobile phase, which was delivered at a rate of 1ml/min, was made of 0.01M ammonium acetate buffer and acetonitrile(70:30v/v).UsingaUVdetectorwitha219nm wavelength, the analysis was found. The method's accuracy,precision,robustness,linearity,andrangeareall validated.Fortheconcentrationrangeof50–100g/ml,the techniquewasdiscoveredtobelinear(r2=0.999).It was discovered that rivastigmine had a retention time of 4.40 minutes. The chromatogram's overall run time was around 10 minutes. A % R.S.D. value of less than 2 shows accuracyoftheprocedure..Thementionedmethodwasa simpleandcost-effectivequality-controltoolforanalysing Rivastigmine Hydrogen Tartrate in Transdermal Drug DeliverySystemonaregularbasis.[11]

Spectrofluorimetric approach was created For the quantification of rivastigmine in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations, that is rapid, accurate, simple, and cost effective. In triple-distilled water, rivastigmine's relative fluorescence intensity was determined at 220 nm for excitationand289nmforemission.Therangeoflinearity was found to be 100 to 4000 ng/ml. According to ICH guidelines and USP standards, the procedure was validated for a number of parameters. The quantitation anddetectionlimitswerefoundtobe20.5and62.1ng/ml, respectively. The results show that the method is quick, simple,accurate,precise,andreproducible. The outcomes and label claims were discovered to be in good agreement.[22]
The development and validation of a sensitive, focused,andpreciseHPLCtechniqueforthemeasurement ofrivastigmine(RSM)inraturine.Theprocedurecallsfor the straightforward liquid-liquid extraction of RSM and pyridostigmineasaninternalstandard(IS)fromraturine using tertiary methyl butyl ether. RSM and IS were separated chromatographically using a Kromasil KR-100 with a 20 mm ammonium acetate buffer (pH 6.5) and acetonitrile (65:35, v/v) given at flow rate of 1 mL/min. The technique had a linear range of 50 to 5000 ng/mL. The validation was carried out in accordance with FDA regulations, and the outcomes satisfied the requirements foracceptance.[23]
A rapid and sensitive liquid chromatography–tandemmassspectrometry(LC–MS/MS)methodhasbeen developedandvalidatedfortheestimationofrivastigmine
86.20 for rivastigmine and m/z 308.10 → 235.10 for zolpidem. The method involves a rapid solid-phase extraction from plasma, simple isocratic chromatographic conditions and mass spectrometric detection that enables detection at sub-nanogram levels. The proposed method has been validated for a linear range of 0.2
inhumanplasma.Rivastigminewasextractedfromhuman plasma by using solid-phase extraction technique. Zolpidemwasusedastheinternalstandard.ABetabasic-8 column provided chromatographic separation of analytes followed by detection with mass spectrometry. The mass transitionion-pairwas followed asm/z251.20→ 206.10,
20.0 ng/ml with a correlation coefficient ≥0.9988. The intra-run and inter-run precision and accuracy were within 10.0%. The overall recoveries for rivastigmine and zolpidem were 86.28% and 87.57%, respectively.Thetotalruntimewas2.0min.[24]
Tocreateafasterseparationmethodwithshorter runtimes, a precise and accurate stability-indicating gradient reverse phase ultra-performance liquid chromatographic (RP-UPLC) method was developed. This methodusesaphotodiodearraydetectortoquantitatively determine RIV and its impurities in both the drug substance and drug product. The method was applied to the active pharmaceutical ingredient, its pharmaceutical dosage form, degradation products, and process-related impurities. The Acquity UPLC BEH Phenyl column was usedforchromatographicseparation,withamobilephase containing a gradient mixture of solvents A and B. The compoundselutedinjust10minutesandweremonitored at 210 nm with a flow rate of 0.4 mL/min and a column oven temperature of 40°C. The resolution of RIV and its eleven impurities (positional and potential) was greater than2.0forallpairsofcomponents.Thisnewlydeveloped method was validated as per ICH guidelines with respect to specificity, linearity, limit of detection, limit of quantification,accuracy,precision,androbustness.[25]
The stability-indicating high-performance thin-layer chromatographic technique for rivastigmine analysis in the bulk drug and in a capsule formulation has been developed and validated. Chloroform-methanol 4:6 (v/v) was used as the mobile phase, and chromatographic separation was achieved on aluminum-backed silica gel 60F 254 HPTLC plates. At 210 nm, absorbance mode was used for the densitometric measurement of rivastigmine. The technique produced a compact spot for rivastigmine (RF 0.53 0.02) and was found to enable effective
separationofarivastigminedegradationproduct(RF0.32 0.02). The method's accuracy, precision, linearity, recovery, detection and quantitation limits, robustness, andotherpropertieswereallvalidated.Excellentlinearity was seen in the concentration range of 200–1600 ng per spot; the correlation coefficient was 0.9916–0.008. Limits of detection and quantitation were 30 and 100, respectively.[26]

ForthequantitativedeterminationofRivastigmine hydrogen tartrate, a cholinesterase inhibitor in bulk medications and pharmaceutical dosage forms, an isocratic, reversed-phase liquid chromatographic (RPLC) method was developed. The established approach is also useful for the analysis of Rivastigmine Hydrogen Tartrate inBulkDrugs,arelatedchemical.Aqueous0.01Msodium1-heptane sulphonate (pH: 3.0 with dilute phosphoric acid)-acetonitrile (72:28, v/v) was used as the mobile phase to produce the chromatographic separation on a WatersXTerraRP18(250mm4.6mm,5m)column. limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantitation (LOQ) were discoveredtobe100and300ng/ml,respectively.[27]
Forthepurposeofquantifyingrivastigmineinrat plasma and brain, a high-performance liquid chromatographic fluorescence detection method has been developed and validated. RSM was extracted from brain and plasma, respectively, using protein precipitation and one-stepliquid-liquidextractionprocedures,accompanied with an internal standard. With the use of a column inertsil ODS-3V and a mobile phase made up of acetonitrile and ammonium acetate buffer (20 mM, pH 4.5) and delivered at a flow rate of 1 ml/min, the chromatographic separation was accomplished. For both matrices, the developed method's lower limit of quantificationwas10ng/mL.[28]
heptanesulphonate(pH:3.0 withdilutephosphoricacid)acetonitrile(72:28,v/v)
3. CONCLUSIONS
An attempt was made to review current trends in the method development and validation for rivastigmine in this article. Well designed, independent cost effective analyses of Rivastigmine are lacking. According to a review, there may be cost effective method for Rivastigmine.Thereisalotofcurrentresearchbeingdone ondevelopingandvalidatinganalyticalmethodsastargets for treating AD with Rivastigmine. Hence, it is hoped that the combination of all these ongoing research areas will resultinabetterunderstanding.
REFERENCES
1. Birks,J.S.,Chong,L.Y.,&GrimleyEvans,J.(2015). Rivastigmine for Alzheimer's disease. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, (9), CD001191. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD001191.pub4
2. Sinha, S., Dwivedi, M., Chaurasia, R., & Kumar, D. (2018).Analyticalmethoddevelopmentandvalidation of Rivastigmine Tartarate by RP-HPLC in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form. Journal of

Chromatographic Science, 56(10), 982-987. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmy068
3. Lane, C. A., Hardy, J., & Schott, J. M. (2018). Alzheimer's disease. European Journal of Neurology, 25(1),59-70.doi:10.1111/ene.13439.
4. Uwishema,O.,Mahmoud,A.,Sun,J.,Correia,I.F.S., Bejjani, N., Alwan, M., et al. (2022). Is Alzheimer’s diseaseaninfectiousneurologicaldisease?Areviewof the literature. Brain and Behavior, 12, e2728. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.272
5. I. O. Korolev, "Alzheimer's disease: a clinical and basic science review", Medical Student Research Journal,vol.4,pp.24-33,2014.
6. S.Alexandar,RohiniDiwedi,T.Ashok,andM.J.N. Chandrasekhar. (2011). A validated RP-HPLC method for estimation of rivastigmine in pharmaceutical formulations. Der Pharmacia Lettre, 3(3), 421-426. ISSN 0975-5071. CODEN: DPLEB4. Retrieved from http://scholarsresearchlibrary.com/archive.html
7. Choudhary, A., Pai, K. V., Dey, S., & Mandade, R. J. (2011). RP-HPLC Method For The Estimation of Rivastigmine in Bulk and in Dosage Forms. Journal of Pharmacy Research, 4(4), 1007-1009. ISSN: 09746943
8. Radhakrishnan,K.,Karuppasamy,C.,Sabarikumar, K., Varatharajan, P., Manikandan, K., et al. (2012). Method development and partial validation of the rivastigmine drug in bulk dosage form by RP-HPLC. International Journal of Pharmacy & Therapeutics, 3(1),73-77.ISSN2229-7456.
9. Gopalan, D., Patil, P. H., Jagadish, P. C., Kini, S. G., Alex, A. T., Udupa, N., et al. (2022). QbD-driven HPLC method for the quantification of rivastigmine in rat plasma and brain for pharmacokinetics study. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science, 12(06), 056-067. doi:10.7324/JAPS.2022.120606.
10. Nataraj, K. S., Suresh Kumar, S., Badrud Duza, M., & Raju, D. B., et al. (2011). Quantification method development and validation for analysis of rivastigmine in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage form by RP-HPLC. Int. J. Chem. Sci.: 9(2), 517-523. ISSN 0972-768X.
11. Kale, M. N. "Development of validated RP-HPLC method for quantitative estimation of rivastigmine hydrogen tartrate in transdermal drug delivery system." International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Research 5, no. 5 (2014): 1892-1902. EISSN:0975-8232;P-ISSN:2320-5148.
12. Sivagami, B., Chandrasekar, R., Pavan Kumar, V., Sreesha, R., & Reddy Padmaja, B., et al. (2017). An analytical review on method development and validation of drugs used for Alzheimer’s disease. International Journal of Advances in Pharmaceutical Analysis, 07(04), 32-37. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7439/ijapa.2017.04.004
13. Shaik Firdose, P Prashanth, V. Srikalyani, S. MadhaviandBuchiN.Nalluri."Analysisofrivastigmine in in vitro transdermal permeation studies by RPHPLC-PDA method." Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research 5, no. 11 (2013): 436-442. ISSN:0975-7384.
14. Sadasivuni, H., & Gundoju, N. R. (2020). A review on: Analytical techniques on drugs for Alzheimer's disease. International Research Journal of Engineering andTechnology,7(4),6165-6170.
15. Kesharwani, S., & Mehta, P. (2021). A Review on: Analytical Techniques Development and Validation of Drugs Used for Alzheimer's Disease. Journal of
Pharmaceutical Research International, 33(55A), 228243.doi:10.9734/jpri/2021/v33i55A77777

16. Marucci,G.,Buccioni,M.,DalBen,D.,Lambertucci, C., Volpini, R., & Amenta, F. (2020). Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacology, NP 108352. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2020.108352
17. Reddy, P. R., Narsimha, R. Y., & Sreenivasulu, R. (2016). A validated stability-indicating HPLC method for the determination of Rivastigmine in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage forms. Journal of Chromatographic Science, 54(8), 1319-1325. https://doi.org/10.1093/chromsci/bmw078
18. Ray,B.,Maloney,B.,Sambamurti,K.,Karnati,H.K., Nelson, P. T., Greig, N. H., & Lahiri, D. K. (2020). Rivastigmine modifies the α-secretase pathway and potentially early Alzheimer’s disease. Translational Psychiatry, 10(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-0709-x
19. Khoury, R., Rajamanickam, J., & Grossberg, G. T. (2018). An update on the safety of current therapies for Alzheimer’s disease: focus on rivastigmine. Therapeutic Advances in Drug Safety, 9(1), 1-8. https://doi.org/10.1177/2042098618750555.
20. Li Y, Hai S, Zhou Y, Dong BR. Cholinesterase inhibitors for rarer dementias associated with neurological conditions. Cochrane Database of SystematicReviews2015,Issue3.Art.No.:CD009444. DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009444.pub3. www.cochranelibrary.com.
21. Sandhya, T., Reddy, B. P., & Babu, N. R. (2018). Development and validation of stability-indicating RPHPLC method for the quantification of impurities and assay of Rivastigmine in bulk and pharmaceutical dosage forms. Chemical Data Collections, 18-19, 5-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cdc.2018.01.001
22. Kapil R, Dhawan S, Singh B. Development and Validation of a Spectrofluorimetric Method for the Estimation of Rivastigmine in Formulations. Indian J Pharm Sci. 2009 Sep-Oct; 71(5): 585–589. doi: 10.4103/0250-474X.58179.
23. Arumugam K, Chamallamudi MR, Gilibili RR, Mullangi R, Ganesan S, Kar SS, et al. Development and validation of a HPLC method for quantification of rivastigmine in rat urine and identification of a novel metaboliteinurinebyLC-MS/MS.BiomedChromatogr. 2011Aug;25(8):903-12.doi:10.1002/bmc.1455.
24. Bhatt, J., Subbaiah, G., Kambli, S., Shah, B., Nigam, S., Patel, M., Saxena, A., Baliga, A., Parekh, H., & Yadav,
G. (2007). A rapid and sensitive liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) method for the estimation of rivastigmine in human plasma. Journal of Chromatography B, 852(12),115-121.doi:10.1016/j.jchromb.2007.01.003.
25. Raju, T. S., Kalyanaraman, L., Reddy, V. V., & Swamy,P.Y.(2012).Developmentandvalidationofan UPLC method for the rapid separation of positional isomers and potential impurities of rivastigmine hydrogentartrateindrugsubstanceanddrugproduct. Journal of Liquid Chromatography & Related Technologies, 35(7), 896-911. doi: 10.1080/10826076.2011.613143.

26. Karthik, A., Subramanian, G., Musmade, P., Ranjithkumar, A., Surulivelrajan, M., & Udupa, N. (2007). Stability-indicating HPTLC determination of rivastigmine in the bulk drug and in pharmaceutical dosageforms.PC-JournalofPlanarChromatographyModern TLC, 20(6), 457-461. https://doi.org/10.1556/jpc.20.2007.6.12
27. Mallikarjuna Rao, B., Srinivasu, M.K., Kumar, K.P., Bhradwaj, N., Ravi, R., Mohakhud, P.K., Reddy, G.O., & Kumar, P.R. (2005). A stability indicating LC method for Rivastigmine hydrogen tartrate. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,37(1),57-63. doi:10.1016/j.jpba.2004.09.041
28. Arumugam K, et al. High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Fluorescence Detection Method for the Quantification of Rivastigmine in Rat Plasma and Brain: Application to Preclinical Pharmacokinetic Studies in Rats. J Young Pharm. 2011 Oct-Dec; 3(4): 315–321.doi:10.4103/0975-1483.90244.
