International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net

International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN: 2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net
1,2,3,4 Organization Name:- VPPCOE & VA Department :- IT University Name:- University Of Mumbai ***
Abstract: One of the leading causes of death worldwide, inbothmenandwomen,islungcancer.AccordingtoWHO, theestimatednumberoflungcancercasesperyearistwo million. The overall 5-year survival rate for lung cancer patientsincreasesfrom16to56%ifthediseaseisdetected in time Computed Tomography (CT) scan can provide valuableinformationinthediagnosisoflungdiseases This work's primary goals are to identify cancerous lung nodules from the provided input lung image and to categoriselungcanceraccordingtoitsseverity.Thisstudy employs cutting-edge Deep learning techniques to locate the malignant lung nodules. This study employs cuttingedgeDeeplearningtechniquestolocatethemalignantlung nodules. Cancer patients' CT scanned lung images are obtained from various facilities. using image processing techniques like pre-processing, segmentation techniques such as watershed algorithm and feature extraction, area of interest is separated. Features such as texture, geometric,volumetricandintensityfeaturesareextracted. Finally,thesefeaturesareclassifiedusingCNN
Keywords- Lung Cancer, CT, Deep Learning, Watershed, CNN.(Key words)
Lung cancer disease is the second largest death threat totheworldafterheartattack,asthiscancerisresponsible forthelargestnumberofdeaths,comparedtothenumber ofdeathscausedbyanyothercancertype.[1].Lungcancer is characterised by unchecked cell proliferation that results in the development of lung nodules. It is reported that lung cancer is responsible for around 19% deaths globally mostly due to alcohol and tobacco consumption. The rate of survival is assured by only 15% survival chances, for a survival period of 5 years. [2]. The main reason for such a high fatality rate is because therapy is delayed due to discovery occurring at a later stage. Chances of survival can rise by 50–70% if lung cancer is discovered sooner. Non-small cell lung cancer and small cell lung cancer are the two major groups into which the lung cancer can be classified based on the cell characteristics. [7] non-small cell lung cancer is the most commontypeoflungcancercontributingtoabout85-90% of total lung cancer cases, while the other 10-15% of the casesisdiagnosedwithsmallcelllungcancer.Theleading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide is lung cancer. The ultimate stage of lung cancer is when the symptoms
become apparent so it is very tough to identify in its beginning stage Because of this, compared to all other cancerforms,lungcancerhasaparticularlyhighmortality rate. The two kind of lung disease which develop and spread in an unexpected way, are small cell lung malignancies (SCLC) and non-little cell lung tumors (NSCLC) [1]. The phase of lung disease alludes to the degree to which the growth has spread in the lung. The World Health Organization reported that more than 7.6 million people worldwide lost their lives to lung cancer each year. Moreover, the death rates of lung cancer are expectedupontokeeprising,towinduparound17million worldwidein2030[2]. Despitebeingthebestimagingtool in the medical sector, clinicians find it challenging to interpret and detect cancer from CT scan data. In year of 2005, around 1,362,825 new cancer cases are expected andaround571,590deathsareexpectedtohappendueto cancerintheUnitedStates.Itwasevaluatedthattherewill be 162,921deaths fromlungcancer, which occurs30% of all cancerdeaths. [3] The extentof the spread of cancer is the basis for the division of lung cancer into stages. It comprises of four stages namely stage I-The cancer is confinedtothelung,stagesIIandIII-thecancerisconfined to the chest (with larger and more invasive tumor classifiedasstageIII)andStageIV-Cancerhasspreadfrom thechesttootherpartsofthebody.
Therearemanytechniquestodiagnosethelungcancer such as X-rays, Computed Tomography (CT), Magnetic ResonanceImaging(MRIscan),and SputumCytology. The problem with these techniques is that it can be time consuming and makes detection possible only at later stages. Despite being the best imaging tool in the medical sector,cliniciansfinditchallengingtointerpretanddetect cancer from CT scan data. Hence, computer assisted diagnosismightbeusefulforclinicianstopreciselyidentify the malignant cells. Computer aided techniques such as Deep learning and image processing have been implemented. In our proposed algorithm we have tried to solvethese problems. Our developed algorithm can detect cancer affected cell and the corresponding stage such as initial, middle, or final stage. If no cancer affected cell is found in the input image, then it checks the probability of lungcancer.

For many diagnostic and therapeutic purposes, automatic fault detection in CT scans is crucial Tumor segmentation and classification are exceedingly difficult because of the large amount of data present in CT scans and the hazy boundaries. To improve accuracy, yield, and speed up diagnosis, one automatic lung cancer detection methodhasbeenintroducedinthiswork
2019-Arnaud A. A. Setio, Francesco Ciompi, Geert Litjens, Paul Gerke, Colin Jacobs, Sarah J. van Riel, Mathi-Pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutionalnetworks
January 2018-Anum Masood,Bin Sheng-Computer Assisted Decision Support System in Stage ClassificationonCTimages
January 2019-Moffy Vas1, Amita Dessai2-Lung cancer detection system using lung CT image processing
October 2020 -Bijaya Kumar Hatuwal1, Himal Chand Thapa2 -Lung Cancer Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network on HistopathologicalImages
Imagesarecollected fromthehospitalsorfromgoogle. The CT images of lungs acquired from the hospital database. We will analyze how CNN algorithm helps us to distinguishbetweencancerousandnon-cancerousimages.
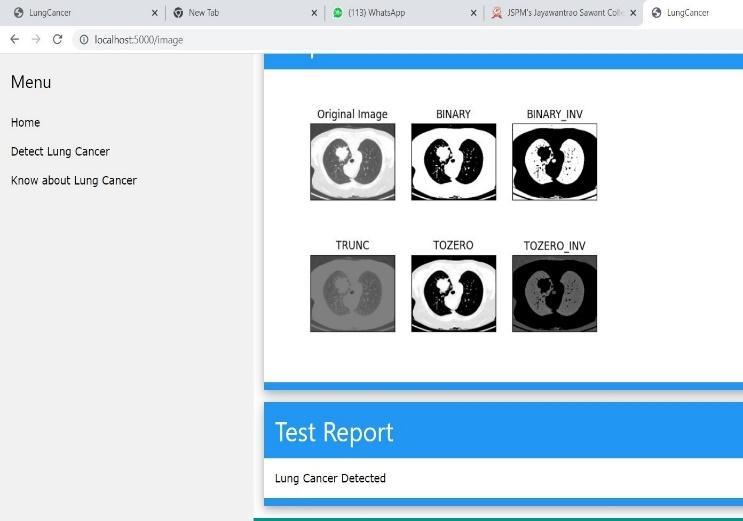
Cropping of the image in first step is done to eliminate theunwantedportionsfromtheimageNextmedianfilters are applied to the images, which are basically used to get ridofthesaltandpeppernoisepresentintheimages. The usage of a 3*3 median filter and its contribution to the improvementofthephotographs.
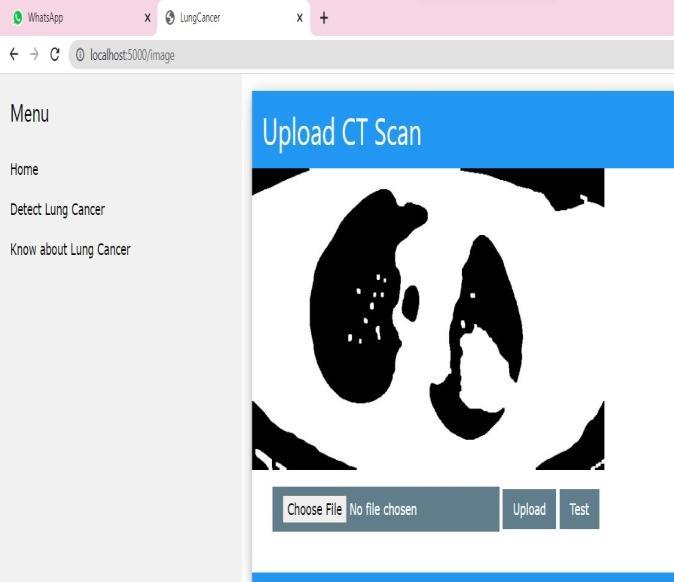
It is necessary to convert the images to binary in order to morphologically segment the lungs, which also lessens computational complexity and storage problems. The opening operation using the periodic line structuring element tends to remove some of the foreground pixels fromtheedgesoftheregionofforegroundpixels.
Feature extraction helps in extracting out significant itemsofdata whichserveasaninputtotheclassifier. The first step is to resize the image into three different resolutions.
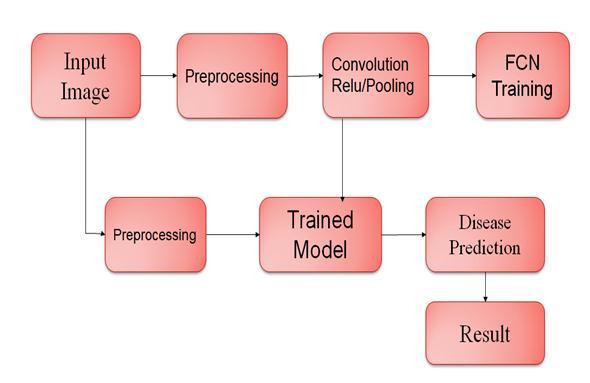
Forlungcancer DetectionweuseCNN methodologyto find accurate result. The methodology adopted in this projectwascarriedoutinfivestepswhichareshownwith thehelpofaflowchartinFig.shows Eachstepoftheflow chartisexplained.
The three components that go into the convolution are as follows:
1. Inputimage
2. Featuredetector
3. Featuremap
Two CNN architectures were tested for patch classificationintonormalandtumorclass:VGG,thewinner of ImageNet competition 2014, and Res Net which won ImageNetchallengein2015.Moreprecisely,hereweused VGG16(with 16 layers) and ResNet50 (with 50 layers). In VGG architecture all convolutional layers use filters with small receptive field of size 3x3. Part of convolutional layers are followed by max spatial pooling over 2x2 window and stride 2 what effectively down samples resolutionbyfactor2.2fullyconnectedlayers,eachhaving 4096channels,andlayerwith2sigmoidactivatedoutputs correspondingtonormalandtumorclassareconnectedto thelastpoolinglayer.OverviewofVGG16CNNisshownin figure.

average pooling layer followed by fully connected layer with 2 sigmoid activated outputs. For both tested architectures weights pre-trained on ImageNet are used for initialization to speed-up convergence. Using outputs from CNN, 256-times down sampled tumor heat map is createdbyassigningeachpatchprobabilityofbeingtumor.
We want to accomplish that since photos are inherently non-linear.Anyimageyoulookatwillshowyouthatithas a lot of non-linear elements (example, the transition between pixels, the borders, the colors, etc.). In order to compensateforwhateverlinearitywemightimposeonan image when werun it throughtheconvolution procedure, therectifierworkstofurtherbreakupthelinearity.
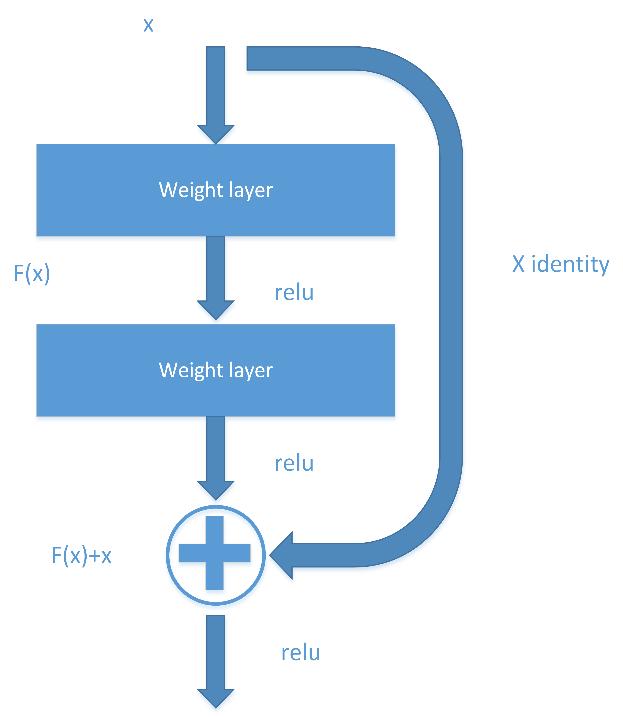
Res Net architecture is built with Res Net blocks to solve the accuracy degradation problem when creating deeper architectures with more layers. Instead of learning mappingfunction,theresidualblockfitsresidualmapping. Main hypothesis here is that it is easier to find residual mapping that original one. If H(x) denotes original mapping (figure 3), stacked layers models mapping F(x) = H(x) � x. At the top of ResNet50 network we added
Again, max pooling is concerned with teaching your convolutionneuralnetworktorecognizethatdespiteallof these differences that we mentioned, they are all images aresame.Inordertodothat,thenetworkneedstoacquire a property that is known as "spatial variance." This property makes the network capable of detecting the object in without being misled by variations in the textures, distances from the locations where they were taken,angles,oranythingelse.
Thiswillbeabriefbreakdownoftheflatteningprocess and how data move from pooled to flattened layers when workingwithConvolutionalNeuralNetworks.
You end up with a long vector of input data after the flattening stage, which you then run through the artificial neural network to create it processed further which is calledpooling.Typesofpooling:Mean,Max,Sum
CT scan
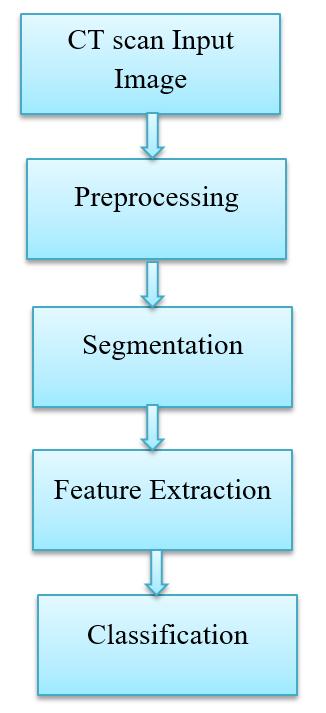
ComputertechnologyisprimarilyusedinCTscans to create or display digital images of the human body's internal organs, which aids medical professionals in visualising the body's interior. The advanced x-ray and computer technology used in a CT scan. A combination of softtissue,bone,andbloodarteriesmaybevisibleonaCT scan.CertainmalignanciescanbeidentifiedwithCTscans, which can also aid in the detection of edoema, bleeding, and bone and tissue calcification. The contrast material usedduringaCTscanisofteniodine.TheCTscanimageof lung cancer is an input for this proposed algorithm. The imagefromtheCTscanishazy.Thenoiseispresentinthis image.Noisedisturbancesmaycausebecauseofelectronic imaging sensors, sensor temperature, insufficient Light levels, film granularity, and channel noise. So preprocessing is essential for such images to remove blurrinessfromitandmakeitsharper.
WeproposeCTScanimagequalityenhancementandits application using CNN Algorithm. For developing dependable and ordinary techniques to identify the brain tumor,extractthequalityofitformedicinaldetermination, visualization, and the presence forecast. IT is Robust and scalable CNN based image segmentation and features extractionbyconsideringdifferenttypesofthedatasetwith minimum computation efforts. The use of appropriate featureextractionandreductionmodelsmayhelptoreduce thedetectiontimeandimprovingtheaccuracy.
Steps of CNN algorithm:
• Arrange material in folders with labels, such as photographsoflungcancer.
• Readdataset
• Readtheattributesofeachimageandlabelitwith thedatasetfolder'snamebelow.
• Storeitinmodelfile
• Getinputimage
• Readfeaturesofinputimage
• Comparefeaturesofstoredfeatures
• Display the label as a near-matching feature prediction.
Lung cancer Detection Comprises of the following steps:-
• 2-DConvNets.
Pulmonarydetectionusing2-DConvNets

• DeepEmbeddedClustering(DEC)
Clustering the Pulmonary and non-pulmonary areausingDeepEmbeddedClustering(DEC)
• SphericalHarmonicsFunction
Detection of mesh malignant and benign using SphericalHarmonicsModuleGradient
Segmenting the background image using a gradient back-propagation throughout the deep networks.
This work's primary goals are to identify cancerous lung nodules from the provided input lung image and to categoriselungcanceraccordingtoitsseverity.Thisstudy employs cutting-edge Deep learning techniques to locate the malignant lung nodules. Cancer patients' CT scanned lung images are obtained from various facilities. Using image processing techniques like pre-processing, segmentationtechniquessuchaswatershedalgorithmand feature extraction, area of interest is separated. Features such as texture, geometric, volumetric and intensity featuresareextracted.Finally,thesefeaturesareclassified usingCNN.
Application of median Filter to eliminate impulse noise in the images proved to be a success. The morphological operationsalsocontributedtowardssatisfactoryresultsin the process of segmentation. Artificial neural networks proved to be a good classifier with acceptable accuracy. The methodology adopted in this project resulted in an accuracy of 92% for the hospital database. This system aims at increasing the accuracy and speed of the lung cancer detection system. It also helps in detecting the canceratearlierstages.
[1] Bijaya Kumar Hatuwal1, Himal Chand Thapa2, “Lung Cancer Detection Using Convolutional Neural Network on Histopathological Images”, “International Journal of ComputerTrendsandTechnology”October(2020).
[2] Vaishnavi. D1, Arya. K. S2, Devi Abirami. T3, M. N. Kavitha4, “Lung Cancer Detection using Machine Learning”, “International Journal of Engineering Research &Technology(IJERT)”,SpecialIssue–(2019)
[3] Alan L. Yuille4 “Deep Supervision for Pancreatic Cyst SegmentationinAbdominalCTScans”(2018).
[4] Moffy Vas1, Amita Dessai 2, “Lung cancer detection systemusinglungCTimageprocessing”,IEEE,(2017).
[5] Mario Buty1, Ziyue Xu1, Mingchen Gao” Characterization of Lung Nodule Malignancy using Hybrid ShapeandAppearanceFeatures”(2017).
[6] Buty, M., Xu, Z., Gao, M., Bagci, U., Wu, A., Mollura, D.J.: Characterization of Lung Nodule Malignancy Using Hybrid Shape and Appearance Features. In: MICCAI. pp. 662–670. Springer(2016).
[7] Mohsen Keshani, Zohreh Azimifar and Reza Boostani, "Lungnodulesegmentationusingactivecontourmodeling” MVIP,IEEE,(2016).
[8]GawadePrathameshPratap,R.PChauhan,"Detectionof lung cancer cells using image processing techniques ", 1st IEEE International Conference on Power Electronics, Intelligentcontrolandenergysystems,IEEE,(2016)
[9] Arnaud A. A. Setio, Francesco Ciompi, Geert Litjens, Paul Gerke, Colin Jacobs, Sarah J. van Riel, Mathi”Pulmonary nodule detection in CT images: false positive reduction using multi-view convolutional networks”(2016).
[10] Junyuan Xie, Ross Girshick “Unsupervised Deep EmbeddingforClusteringAnalysis”(2016).
[11]BadrulAlamMia,MohammadAbuYusuf,"Detectionof lung cancer from CT image using image processing and neural network", International conference on Electrical Engineering and Information Communication Technology (ICEEICT),IEEE,May,(2015)
[12] K Punithavathy, M M Ramya, Sumathi Poobal, "Analysis of statistical texture features for automatic lung cancer detection in PET/CT images", International Conference on Robotics, Automation, Control and Embeddedsystems(RACE),IEEE,18-20February(2015).
[13] Muhammed Anshad, S.S Kumar, Recent methods for the detection of tumor using computer aided diagnosis", International Conference on Control, Instrumentation, Communication and Computational technologies (ICCICCT),IEEEtransactions,(2014)
[14] Nooshin Hadavi, Md Jan Nordin, Ali Shojaeipour, “Lung cancer diagnosis using CT-scan images based on cellular learning automata”, International conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCOINS), IEEE, (2014).
[15] Anita Chaudhary, Sonit Sukhraj Singh “Lung cancer detection on CT images using image processing”, computing sciences 2012 international conference, IEEE, (2012)
[16] Robert M Haralick, K.Shanmugam, Itshak Dinstein, “Textural Features for_ Image Classification” IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics, 3(6), pp. 610-621,(1973).
