Volume: 10 Issue: 04
RETINA DISEASE IDENTIFICATION USING IMAGE PROCESSING
 Madhavan P1, Istamsetty Siva Krishna2, Shaik Parvez3, Paidi Sathish4
Madhavan P1, Istamsetty Siva Krishna2, Shaik Parvez3, Paidi Sathish4
1Assistant Professor, Dept. of ECE, Muthayammal Engineering College, Rasipuram.
2UG Scholar, Dept. of ECE, Muthayammal Engineering College, Rasipuram.
3UG Scholar, Dept. of ECE, Muthayammal Engineering College, Rasipuram.
4UG Scholar, Dept. of ECE, Muthayammal Engineering College, Rasipuram.
Abstract - The use of imaging and computer vision systems allows for a quantitative study of human physiology. A recent study has developed an algorithm that combines image processing and machine learning techniques to analyze retinal images and aid in the early detection and diagnosis of retinal diseases. The main aim is to apply these techniques to digital fundus images of the eye to accurately separate diseased eyes from normal ones and improve the speed and accessibility of retinal disease diagnosis and treatment. Automated analysis of retinal images is crucial in diagnostic procedures, and the approach presented in this study utilizes datasets of retinal images to classify over 180 fundus images with lesions and non-lesions, achieving an accuracy of 94.4%, a precision of 94%, a recall and f1-score of 94%, and an AUC of 95%. The proposed approach employs image processing and the Support Vector Machine (SVM) classification method to distinguish diseased eyes from normal eyes using fundus images, thus paving the way for precise and automated classification and diagnosis of retinal diseases.
Key Words: Retinal image processing, arteries, veins, segmentation,classification,identification.
1. INTRODUCTION
Medical imaging refersto thetechniquesand processes of visually representing the internal structures of the body for the purpose of analyzing and intervening in health conditions. We aim to clarify hidden internal structures covered by skin and bones, and to diagnose and treat diseases. By creating a database of normal anatomy and physiology, medical imaging can identify abnormalities in variousorgansofthebody. Imagingof excisedorgansand tissues can be done for medical reasons, but is generally consideredpartofpathologyratherthanmedicalimaging.
Inaclinicalcontext,medicalimagingusing"invisiblelight" is usually associated with radiology or medical imaging, and radiologists are responsible for understanding and sometimes capturing these images. “Visible light” medical
imaging, ontheotherhand, includesdigital videothatcan be viewed without special equipment.Diagnostic radiography specifically refers to the technical aspects of medical imaging and the acquisition of medical images Radiologists are usually responsible for obtaining high-quality medical images for diagnosis, but some radiationtreatmentscanbeperformedbyradiologists.
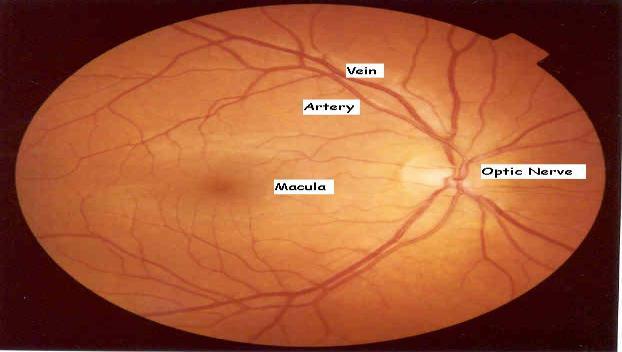
Retinal image processing plays a crucial role in the diagnosisandtreatmentofvariousdiseasesthataffectthe retina and the choroid. One such disease is diabetic retinopathy, which is a complication of diabetes mellitus that affects the retina and the choroid. The advent of retinal imaging technology has enabled optometrists to capture digital images of the retina, blood vessels, and opticnervelocatedatthebackoftheeyes.Thishasgreatly aided in the early detection and management of diseases that can affect both eyes and overall health, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, diabetes, and hypertension.
With retinal imaging technology, even the slightest changes to the structures at the back of the eyes can be detected. For instance, in choroidal neovascularization (CNV), a network of small blood vessels arises in the choroid and takes away a portion of the blood supplying the retina. As a result, the sight may be degraded and, in severe cases, vision loss may occur. Adaptive Optics (AO) has the potential to facilitate early detection of retinal pathologies. Many researchers have been working on retinal images to perform various image processing tasks forthebenefitofthehealthsector.However,theaccuracy oftheimageanalysisdependsonthequalityoftheimages, which must have high contrast photoreceptors and vasculature, as well as accurate registration.
Currently, many researchers have developed methods for automaticallyassessingthequalityofretinalimagestaken by a fundal camera, using a reference image. Recently, AO has been combined with scanning laser ophthalmoscope andopticalcoherencetomography(OCT)toobtainimages
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net
of the retinal microvasculature and blood flow, as well as three-dimensional images of living cone photoreceptors respectively.
"non-vessel" to automatically track the vessels, overcoming problems encountered in previous studies such as initialization and vessel profile modeling.
Fuzzy c-means (FCM) is a soft segmentation technique applicableformedicalimages.Itsperformancedependson the initial positions of the cluster centers, the measure of membershipdegreeforeachdatapoint,andotherfactors The centerofthecluster is modified until thediscrepancy between successive objective functions becomes significantlysmallerthanapredeterminedsmallvalue.
Moreover, several studies have shown that incomplete treatment is worse than no treatment, emphasizing the need for an automated laser system to treat the entire retina in a single session. This system is designed to scan and track the retina, applying laser energy to the entire area except for sensitive objects that may be damaged by the energy. The expected functionality of the system is to captureretinalimagesusingafunduscameraandperform accurate segmentation to extract sensitive objects in the retina, such as the blood vessel tree, optic disk, macula, and the region between the optic disk and macula. However,it'simportanttonotethatthefunduscameracan only provide an image for a portion of the retina and not theentireretina.
2. EXISTING METHODOLOGY
Theretinalmicrovasculaturehassimilarcharacteristicsto vesselsinotherpartsofthe body.Imaging techniquescan provide non-invasive views of the blood vessels in the retina,makingretinalimagesausefultoolforstudyingand diagnosing pathologies related to vessel abnormalities, such as hypertension and diabetes. The arterio-venous ratio (AVR) is often used as a marker for diseases, and retinal vessel classification techniques can be categorized as tracking-based or color-based methods. The former requires the labeling of a few vessels by medical experts and requires a vessel tracking algorithm and precise characterization of bifurcation and crossovers.
An unsupervised fuzzy algorithm for vessel tracking has been developed to detect ocular fundus vessels. The algorithm uses linguistic descriptions like "vessel" and
Where N is the number of features, C is the number of clusters which take as in search. �� is the degree of the membership of �� in the cluster j, �� is the ith of the ddimensionalmeasureddata.
3. PROBLEM ANALYSIS
Thereareseveralalgorithmsproposedforidentifyingnonvascular lesions and extracting vascular structure in retinal fundus automatic analysis. Changes in the blood vesselstructureoftheretinacanindicateretinopathy,but thiscanimpactarteriesandveinsdifferently.Tocreate an automatedtoolforretinopathydiagnosisandgrading,itis essential to distinguish arterial and venous vessels using A/V classification. However, recognizing A/V presents challenges due to variations in inter- and intra-image contrast, luminosity, and color, as well as the fading differences between vessel types in the periphery of the retina. Even after contrast and luminosity normalization, A/V can only be accurately recognized in a region around the optic disc. Vessels inside the optic disc become intertwined, making it difficult for even experts to track, while those in the periphery become thinner and almost indistinguishable.
Furthermore,thereliablerecognitionofarteriesandveins islimitedtovesselslocatedclosetoeachotheraroundthe optic disc. Vessels far apart from each other may be misclassified based solely on their image features. This appliestobothtypesofvessels,anditisassumedthatthey are evenly distributed around the optic disc at a short distance from its border. Based on these observations, a strategy was developed to create a dependable A/V classification technique. The first step was to classify vessels within a well-defined concentric zone around the optic disc. The next step was to propagate this
International Research Journal of Engineering and Technology (IRJET) e-ISSN:2395-0056

Volume: 10 Issue: 04 | Apr 2023 www.irjet.net
classification outside of this area using vessel structure obtainedfrom trackingtechniques,wherethereislittle or no information available to differentiate between arteries andveins.
4. PROPOSED METHODOLOGY
The proposed technique employs active contours to eliminate noise, enhance images, track vessel edges, compute vessel perimeters, and detect cardiomyopathies. Agraphtheorymodelisusedtosegmentbloodvesselsand calculate their perimeters. Finally, an effective infinite perimeter active contour model with hybrid region terms is proposed for vessel segmentation, which can be a powerful tool for analyzing the vasculature and managing arangeofvascular-relateddiseases.
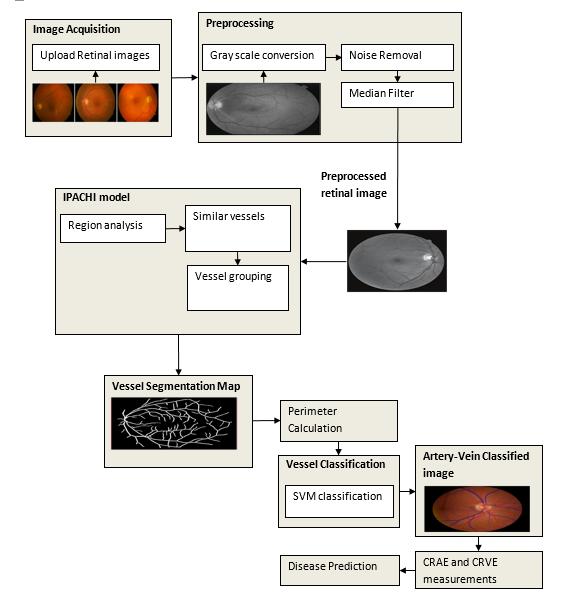
Fig - 2:SystemArchitecture
Examining blood vessels in the eye is a way to detect eye diseases like glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy. In the past, mapping the vascular network required a timeconsuming, manual process that demanded training and expertise. Automating this process enables consistency andfreesupthetimeofskilledtechniciansordoctorswho previously performed manual screening. Hence, an automatic process can be implemented to examine blood
p-ISSN:2395-0072
vessels in retinal images and detect cardio-vascular diseases.
4.1 RETINAL IMAGE ACQUISITION
Detecting and diagnosing cardiovascular diseases is crucial,andtheretinalimagesofhumansplayasignificant role in this process. Common conditions that can be identified through retinal images include stroke, diabetes, arteriosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, and hypertension.Vasculardiseasescanbelife-threateningfor individualswhodoesnottakemuchcareabouthealthand pose a challenging health issues for themselves
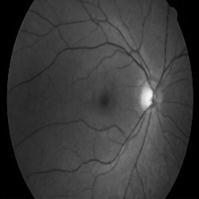
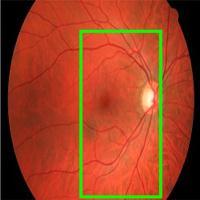
Detecting retinal images is essential, particularly the detection of blood vessels, which is the most important aspect.Changesinbloodvessels,suchaslength,width,and branching pattern, can provide information about pathological changes and help to assess the severity of diseases or automatically diagnose them. In this module, weuploadretinal images,whichshowtheinteriorsurface of the eye, including the retina, optic disc, macula, fovea, andposteriorpole.
The retina is composed of layers of interconnected neurons with synapses and contains blood vessels that mayexhibitabnormalitiesandalterationsatanearlystage. These abnormalities are often expressed through the arteriolar-to-venular diameter ratio, which is associated withhigherbloodpressurelevels.Todevelopandtestour proposed method, we constructed an image dataset using publicly available datasets like DRIVE and STAR. Each imageinthedatasetwascapturedata resolutionof760x 570 pixels with 24 bits per pixel. Initially, the proposed method was tested on normal images, which are easier to differentiate, and further testing is needed to establish its effectiveness in identifying abnormal vessel appearances. Abnormal images typically contain multiple artifacts of varying shapes and colors caused by different diseases, in addition to the blood vessels, optic disc, fovea, and background.
4.2 PREPROCESSING
Thismoduleinvolvesconvertingcoloredretinal images to grayscale to detect black-and-white illumination. Noise in colored retinal images is usually caused by noisy or distorted pixels. To preprocess and segment retinal images,asharpeningfiltercanbeimplementedtoenhance and sharpen the vascular pattern, resulting in effective preprocessing, enhancement, and segmentation.
Humanperceptionishighlysensitivetotheedgesandfine details of an image, which are mainly composed of highfrequency components. If the high frequencies are attenuated or removed, the visual quality of an image can be severely degraded. On the other hand, enhancing the high-frequency components of an image can improve its visualquality.
Enhancingtheedgesandthefinedetailsofanimagecanbe done using the Image sharpening techniques. This will interferes in adding a signal to the original image that is proportional to a high-pass filtered image of the original image. The high-pass filter extracts the high-frequency components of the original image, and a scaled version of thehigh-passfilteroutputisaddedtotheoriginalimageto produceasharpenedversion.Thehomogeneousregionsof theimage,wherethesignalisconstant,remainunchanged.
4.3 VESSEL SEGMENTATION
In this section, a graph theoretical model is employed to perform feature extraction and vessel segmentation. The model utilizes an active contour, nearest neighbor measure, and neighborhood function to create a vascular network Amapisusedtodepictthenetwork,whereevery intersection point in the vascular tree is denoted by a node,andeachvesselsegmentconnectingtwointersection points is indicated by a link. To generate the graph, an active contour method is used to extract nodes from the centerline image. Bifurcation points are identified by considering pixels with more than two neighbors, while endpoints or terminal points are identified by pixels having just one neighbor. The links between nodes are found by removing all bifurcation points and their neighborsfromthecenterlineimage,resultinginanimage withseparatecomponentsthatrepresentvesselsegments
The binary mask for vessel segmentation is generated by identifying the edges of the vessels from the sharpened image. The blood vessels are marked by assigning the value of one to the pixels that belong to the vessels and zero to those that do not. A final refined vessel segmentation mask is produced using an active contour model, which is also known as snakes. Snakes are deformable splines that minimize energy and are influencedbyconstraintsandimageforcesthatguidethem towards objectcontours, whilealsoresisting deformation. Theyareaspecifictechniquewithinthebroaderapproach of matching deformable models to images through energy minimization.Intwodimensions,theactiveshapemodelis adiscreteversionofthisapproachthatleveragesthepoint distribution model to limit the shape range to a specific
domain learned from a training set. Ultimately, the segmentation mask is provided for the preprocessed retinalimages.
4.4 VESSEL CLASSIFICATION
The blood vessels are divided into arteries and veins for correct analysis of heart diseases, which affect them differently. The extraction of blood vessels leads to the creation of a feature vector based on the properties of arteries and veins. This vector is generated from the centerlineextractedimage,witheachcenterlinelabeledas eitheranarteryorveinpixel.Thefinalgoalistoassignthe A/V classes to each label using SVM classification, which utilizesbothstructuralandintensityinformation.Toallow thefinalclassificationbetweenthearteriesandveinsalong with the vessel intensity information has to be used. The trainedclassifieristhenusedtoassignA/Vclassestoeach (Ci j , j = 1, 2) sub-graph label i, with the probability of a label that can be an artery calculated based on the number of integrated centerline pixels classified by the LDA. The probability for an artery with the label Ci j is
Pa(Cij)=naCij/(naCij+nvCij) -(2)

Where na Ci j is the number of centerline pixels of a label classified as an artery and nv Ci j is the number of centerline pixels classified as a vein. Each subgraph will have labels for pairs of categories, and the label with the greater likelihood of being an artery will be classified as such, while the other label will be classified as a vein. In order to avoid incorrect classifications caused by inaccurategraphanalysis,wewillcalculatetheprobability ofeachindividuallinkbeinganarteryoravein.
4.5 DISEASE DIAGNOSIS
This module uses the AVR ratio, which is based on measurements of CRAE and CRVE, to diagnose diseases. These measurements are real, positive numbers that have been found to be correlated with cardiovascular disease risk factors. Smaller CRAE is primarily determined by higherbloodpressure,whilewiderCRVEismainlycaused by current smoking, higher blood pressure, inflammation, and obesity. Individuals with higher blood pressure have, on average, smaller CRAE and wider CRVE, with an average of 4.8 microns to 2.6 microns, than those with lower blood pressure. A recent study found a strong negative correlation between renal function and retinal parameters (CRAE and CRVE) in healthy individuals, indicating a shared determinant in pre-clinical organ damage.CRAEisuseful inpredictinghypertensionaswell
asotherconditionslikestrokeanddiabetes.Narrowingof arterioles,asindicatedbyadecreaseinCRAE,isassociated withanincreasedriskofstroke,whileanincreaseinCRVE is linked to diabetic retinopathy, its progression, proliferative DR, and macular edema in diabetes patients buthasnocorrelationwithCRAE.

5. ALGORITHM
5.1 GRAPH THEORITICAL MODEL
This project introduces a novel approach to segmenting images with uneven object boundaries that have constant colorvalues.Theproposedmethodisamodificationofthe regioninformationtechnique.Theobjectiveisto preserve the intricate details and irregularities of the object boundaries while also removing any additional Gaussian noisepresentintheimage.Themodel'senergyisgivenby:
In this study, the width of the vessels is an essential feature for classification. By using the SVM classifier, the vesselscanbeefficientlyseparatedintoarteriesandveins.
SVMs possess several appealing characteristics, such as superior generalization ability compared to other classifiers. Moreover, they have fewer parameters to adjust, and it is not necessary to determine the architecture experimentally.TheSVMalgorithmseparates input pattern classes usinga hyperplane with a maximum margin.Theconstructionofthishyperplaneinvolves:
Wherethefeaturevectoris given byxand wisthevector thatisperpendiculartothe hyper plane ‖��‖ Specifies theoffsetfromthebeginningofthecoordinatesystem. To leveragetheadvantagesofnon-lineardecisionboundaries, the separation is conducted in a feature space F that is established by a non-linear mapping of the input patterns throughφ.Themappingisdefinedasfollows:
Where is the 2D Lebesgue measure, is the information of nth region and N is the total number of different region terms. is the first term that gives the areaof neighborhoodoftheedgeset .Hereweconsider
for an even and large number which is an approximation of the neighborhood area of thegivenimage ��
5.2 SUPPORT VECTOR MACHINE
TheSVMclassifierisusedforclassification.Overtheyears, SVM classifiers have proven to be highly effective in solvingarangeofpatternrecognitionproblems.Theinput space is transformed into a feature space with high dimensions. Then, a hyperplane is constructed that maximizes the separation margin between classes. The points that are nearest to the decision surface are identified as support vectors, and their location plays a direct role in classification. When classes cannot be separated, the optimal hyperplane is the one that minimizestheprobabilityofclassificationerror.Theinitial inputimageisconvertedintofeaturevectors.
Next, the feature vectors are transformed into the feature space using a kernel function, and the classes in the trainingdata areseparated bycomputinga divisioninthe featurespace.Topreventoverfittingandaccuratelydivide the training examples, an SVM requires a global hyperplane. This SVM phenomenon is superior to other artificial intelligence-based machine learning techniques.
The transformation of the original feature space into F is representedbythekernelfunction. Afterward,wecanuse the Artery vein ratio as a parameter to examine retinal vascular geometry, which is a high-quality measure. This measure was developed to determine the ratio between the normal diameters of the arterioles and venules and consists of two components: the central retinal artery equivalent (CRAE) and the central retinal vein equivalent (CRVE). These components are expressed as a quotient and are calculated by iteratively combining the mean widths of consecutive pairs of vessels in the arteries and veins,respectivelyasfollows:
Where�� �� apairofwidthvalues,thenArteryveinratio canbecalculatedas,

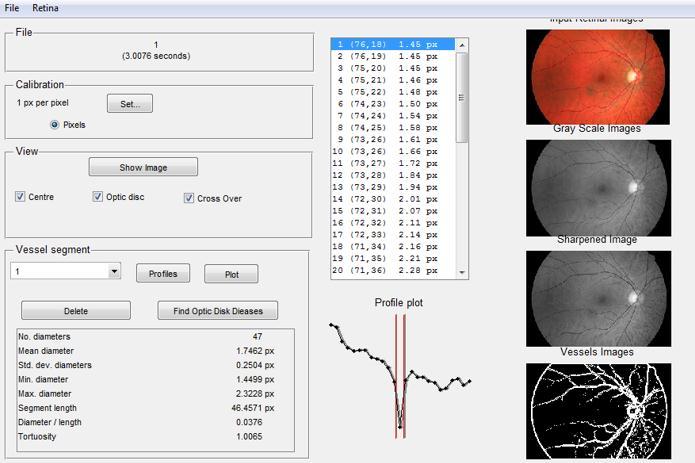
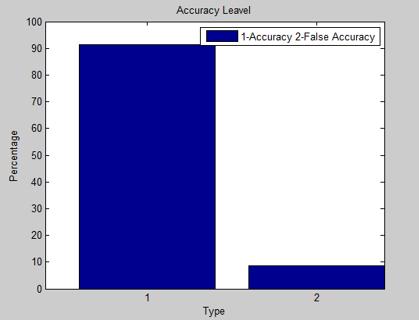
To test the effectiveness of our proposed method, we implementeditusingMATLAB2012bonasystemwithan i3processorand4GBRAM.Weusedtwosetsofimagesfor validation purposes. The first set contained six different images with six different diseases selected from planet Earth, while the second set consisted of approximately eight images. The results are divided into two categories: (A)correctlyidentifyingtheinfectedareaordiseaseonthe plant leaf, and (B) classifying the type of leaf disease. To evaluate the performance of our proposed method in correctly identifying the affected area or disease on the plantleaf,weusedtwoquantitativeevaluationparameters based on the statistical performance of the ground truth image and the segmented image. The most crucial aspect of our work is the classification of diseases. We assessed the performance of our proposed method in correctly classifyingdiseasesbyutilizingtwoentropyfunctions:the validation evaluation partition coefficient (Vpc) and the validationevaluationpartitionentropy(Vpe).
7. CONCLUSION
In conclusion, our proposed system was successfully implemented and accurately identified true vessels to obtain correct retinal ophthalmology measurements. We implemented a post-processing step to segment vessels, whichtrackedalltruevesselsandfound theoptimalones, thereby overcoming the issue of wrong diagnosis of crossovers by simultaneously identifying blood vessels fromtheretina.Theultimateaimofourproposedmethod istofacilitatetheearlydetectionofdiseasesrelatedtothe blood vessels of the retina. Its main advantage is its full automation, which does not require any intervention by clinicians and releases necessary resources (specialists), thereby reducing consultation time and facilitating its use in primary care. We also recognized that the classification of arteries and veins in retinal images is crucial for the automatic assessment of vascular changes. Our graph theoretical method, combined with Support Vector Machines (SVM), outperformed the accuracy of the SVM classifier by incorporating intensity features, demonstrating the significance of using structural information for A/V classification. Furthermore, we compared the performance of our approach with other recently proposed methods and concluded that our methodachievedbetterresults.
REFERENCES
[1] B. Zhang, L. Zhang, L. Zhang, and F. Karray, “Retinal vessel extraction by matched filter with first-order derivativeofGaussian,”Comput.Biol.Med.,vol.40,pp. 438–445,2010.
[2] M. Palomera-Prez, M. Martinez-Perez, H. Bentez-Prez, and J. Ortega- Arjona, “Parallel multiscale feature extraction and region growing: application in retinal blood vessel detection,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed.,vol.14,pp.500–506,2010.

Where,TruePositive(TP)referstothenumberof pixels that are correctly classified, while False Positive (FP) refers to the number of pixels that are incorrectly classified. True Negative (TN) represents the number of pixels that are correctly misclassified, and False Negative (FN) represents the number of pixels that are incorrectly misclassified. The sensitivity and specificity values range between 0 and 1, with a result of 1 indicating perfect segmentation
[3] Y. Wang, G. Ji, P. Lin, and E. Trucco, “Retinal vessel segmentation using multiwavelet kernels and multiscale hierarchical decomposition,” Pattern Recogn.,vol.46,pp.2117–2133,2013.
[4] G. Lathen, J. Jonasson, and M. Borga, “Blood vessel segmentation using multi-scale quadrature filtering,” PatternRecogn.Lett.,vol.31,pp.762–767,2010.
[5]M.M.Fraz,P.Remagnino,A.Hoppe,B.Uyyanonvara,A. R. Rudnicka, C. G. Owen, and S. A. Barman, “Blood vesselsegmentationmethodologiesinretinalimagesa survey,”Comput.Meth.Prog.Bio.,vol.108, pp.407
433,2012.
[6] K. Sun and S. Jiang, “Local morphology fitting active contour for automatic vascular segmentation,” IEEE Trans.Biomed.Eng.,vol.59,pp.464–473,2012
[7] C. Lupascu, D. Tegolo, and E. Trucco, “FABC: Retinal vessel segmentation using AdaBoost,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol.Biomed.,vol.14,pp.1267–1274,2010.
[8] J. Orlando and M. Blaschko, “Learning fully-connected CRFsforbloodvesselsegmentationinretinalimages,” in Med. Image Comput. Comput. Assist. Interv., 2014, pp.634–641
[9] C. Li, C. Xu, C. Gui, and M. Fox, “Distance regularized level set evolution and its application to image segmentation,”IEEETrans.ImageProcess.,vol.19,pp. 3243–3254,2010.
[10]A.Perez-Rovira,K.Zutis,J.Hubschman,andE.Trucco, “Improvingvesselsegmentationinultra-widefield-ofview retinal fluorescein angiograms,” in Proc. IEEE Eng.Med.Biol.Soc.,2011,pp.2614–2617.

