Deep Learning-Based Approach for Thyroid Dysfunction Prediction
Tushar Bhatia Student, Department of Computer Science and Engineering, HMR Institute of Technology and Management, Delhi, India
***
Abstract – Globally, thyroid dysfunction is a major health concern caused due to irregular hormone production by the thyroid gland. Millions of populations are getting affected by this disease regularly. Accurate diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction is crucial for effective treatment andmanagement of the disease, but this is challenging given the condition’s complex and varied symptoms. In this paper, a deep learningbased neural network algorithm for generating predictions is constructed based on a dataset of approximately3772 patient records with 28 features. The Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model was trained and evaluated using standard machine learning techniques and achievedhigh-level accuracy (98.8%) in identifying instances of thyroid dysfunction. The findings demonstrate that the proposed ANN model can be a reliable and effective tool for early diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction. The suggested model has several advantages, including its ability to handle a large number of input parameters and its ability to learn intricate relationships between input and output variables. However, further research is required to assess if the suggested approach can apply to more extensive and diverse patient populations. Overall, the results of this study lay out the potential of machine learning and ANN models in the diagnosis of thyroid dysfunction and may aid in creating more precise and effective diagnostic equipment for this prevalent endocrine illness.
Key Words: Thyroid Dysfunction, Deep Learning, Neural Network, Artificial Neural Network, Machine Learning, accuracy, endocrine illness.
1.INTRODUCTION
Thethyroidglandisatiny,butterfly-shapedorgansituated inthefrontoftheneck,surroundingthewindpipe.Ourbody containsglands,whichproduceandreleasecompoundsthat help the body to perform a specific function. The thyroid gland produces hormones, namely levothyroxine(T4) and triiodothyronine(T3),whichassistinregulatingmetabolism, heartrate,bodytemperature,andotheressentialprocesses. Whenthethyroidglandisoveractiveorinactive,itcanlead tovarioushealthproblems.
Thyroid dysfunction is a widespread endocrine disorder affectingmillionsworldwide,irrespectiveofage,gender,and ethnicity.Itoccurswhenthethyroidglandeitherproduces excessorinsufficienthormones,whichcanresultinseveral healthissues.Hypothyroidism,characterizedbylowthyroid hormonelevels,andhyperthyroidism,characterizedbyhigh thyroid hormone levels, are the most common thyroid
disorders. It can affect bodily functions like energy production,weightmanagement,andmoodregulation.
Symptoms of thyroid dysfunction can vary widely and includefatigue,weightgain,depression,andanxiety.Early detectionandtreatmentofthyroiddisordersareessential for managing the condition and avoiding severe complications. Diagnosing thyroid dysfunction requires a combination of clinical evaluation, biochemical tests, and imaging techniques. However, traditional diagnostic methods are time-consuming, expensive, and require specializedtoolsandexpertise.Therefore,thereisaneedfor amethodicalandaccurateapproachtotheidentificationof thyroiddisorder
DeepLearning-basedmodelarchitecturehasemergedasa convincingtechniqueforimprovingtheefficiencyofthyroid dysfunctionprediction.ThispaperpresentsaDeepLearning Artificial Neural Network (ANN) model for making a predictionusingclinicalandbiochemicalparameters.
1.1 Deep Learning
DeepLearninglieswithinthestrataofmachinelearning(ML) andartificialintelligence(AI) Itsmethodologyisinfluenced by the human brain's structure and function. It involves training artificial neural networks, which are complex mathematicalmodelsthatcanlearntorecognizepatternsin data.
DeepLearninghasriseninprominenceinrecentyears,owing totheabundanceofextensiveamountsofdataandpowerful computingresources.Ithasenabledsignificantadvancesin several fields like natural language processing, computer vison,speechrecognition,andmedicalscience.
Oneofthecriticalstrengthsofdeeplearningisitsabilityto extractfeaturesfromrawdataautomatically.Thismeansthat it can solve problems where traditional machine learning approachesrequirehand-craftedfeaturesordomain-specific knowledge.
Deep learning models generally feature layers of interconnected nodes, or neurons, that perform a simple mathematicaloperationoninputs.Theoutputofonelayeris fed into the next, and each layer learns to recognize more complexdatafeatures.Modeltraininginvolvesadjustingthe weights of the connections between the neurons with an objective to minimize a cost function, which evaluates the differencebetweenthepredictedvaluesandactual values. This is often achieved usingan algorithm calledstochastic gradientdescent,whichiterativelyupdatestheweightsbased onthegradientofthecostfunctionconcerningtheweights.
1.2 Artificial Neural Networks
ArtificialNeuralNetworks(ANNs)aredeeplearning-based models designed to emulate the structure and function of biologicalneuronsinthebrain.ANNsareconstructedupof layersofinterconnectednodes,includinganinputlayer,one ormorehiddenlayers,andanoutputlayer.Theyareutilized foranalysingdatapatternsandmakingpredictionsbasedon information
EachneuroninanANNreceivesinputsfromneuronsinthe precedinglayer,whicharemergedandprocessedwiththe helpofanactivationfunctiontogenerateanoutput.During training, the weights of the connections between neurons arealteredtominimizethecost.
TherearenumeroustypesofANNs,eachhavingitsownset of advantages and disadvantages. Feedforward neural networks are the simplest type, with layers that process unidirectional flow of information from the input to the outputlayer.RecurrentNeuralNetworks(RNN)aresuitable for tasks involving data sequences due to their cyclic connections, allowing information to flow in cycles. Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN) are specialized for processingimagesandconsistoflayersthatapplyaseriesof convolutional filters to the input image, allowing the networktolearntorecognizepatternsatdifferentscales.
Regardlessoftheirsuccess,ANNshavesomelimitations,like therequirementforsubstantialamountsoftrainingdataand the complexity of interpreting the inner workings of the models. However, they continue to be an active area of research and development and are likely to play a pivotal roleinthefutureofartificialintelligence.
2. LITERATURE REVIEW

[1] This study utilizes a range of classification models to diagnosethyroiddisordersbasedonparametersincluding TSH(ThyroidStimulatingHormone),T4U,andgoitre.Various
classification techniques, including K-nearest neighbor (KNN),wereemployedtosupportthestudy'sfindings.Naïve Bayes and Support Vector Machine algorithms are also implemented. The test was carried out with the help of a RapidMinerinstrument.TheresultsrevealedthattheKNN was more accurate than Naïve-Bayes in detecting thyroid disorder, with a 93.44% accuracy. The suggested KNN techniqueenhancedclassificationaccuracyandcontributed to better results. KNN exhibited superior performance compared to other methods, since the factors were independentofeachother
[2]Inthisresearchpaper,theauthorsdevelopedamachine learningalgorithmtopredictthemosteffectivetreatmentfor thyroiddiseasebasedonpatientcharacteristicsandmedical history The data was collected from 282 patients with thyroidillnessandperformancewasevaluatedusingmultiple ML algorithms The findings indicated that the Random Forestalgorithmperformedthebest,gettinganaccuracyof 77.83% in predicting the most effective treatment. The authors noticed that the model could support clinical decision-making in treating thyroid disease, potentially improvingpatientoutcomes.
[3]Inthisstudy,theauthorsproposedanensemblemethod forclassifyingthyroiddiseasethatinvolvesoptimizationof features.Theyobtaineddatafrompatientsdiagnosedwith thyroiddiseaseandextractedasetofparametersrelatedto the disease. They then used an ensemble classifier that combinedseveralmachinelearningmethodstopredictthe type of thyroid disease based on extracted features. The results showed that the proposed ensemble approach outperformed individual machine learning algorithms regardingaccuracy.Thestudydemonstratesthepotentialof anensembleapproachforenhancingtheefficiencyofthyroid diseaseclassification.
[4]Theauthorsofthisresearchconstructedadeep-learning model for predicting thyroid disorders by incorporating clinicaldatafromover20,000Indianpatients.Themodelwas based on a CNN architecture and achieved an accuracy of 92.6% and a specificity of 96.3% in predicting hypothyroidismandanaccuracyof91.5%,andaspecificityof 95%inpredictinghyperthyroidism.Thestudyhighlightsthe potential of deep learning models for diagnosing and managingthyroiddiseaseinIndia.
[5] This paper proposes an ANN model for the automated predictionofthyroiddisease.Theauthorscollectedthyroid samplesandtrainedanANNmodelusingan80:20ratiosplit of data for training and testing. The model achieved an average accuracy of 85% during training and 82% during testing. The study concludes that ANNs are a flexible and robust technique for thyroid disease diagnosis, with high reliabilityindifferentsamplingsituations.
3. METHODOLOGY
TheproposedANN-basedapproachconsistsof4stages:data collection, data preprocessing, model training, and model evaluation.Thissectionlaysoutanoverviewofvarioussteps involvedinthepredictionprocess.Thefigurebelowgivesa representationoftheworkflowinvolved.
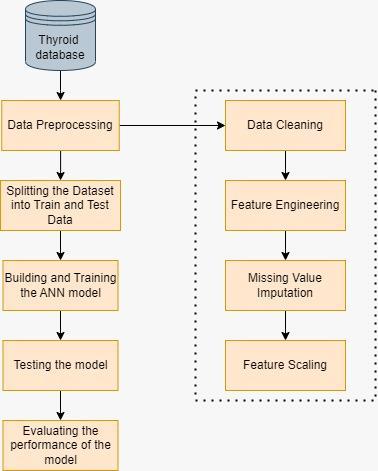
Table-1: NumericalAttributes
S.No. Attribute Name Data Type 1 age object 2. TSH object
object
Table-2: CategoricalAttributes
.No. Attribute Name label 1 sex
-2:Workflowdiagram
(I) Data collection
Toconductthisresearch,adatasetcomprisingclinicaland biochemicalparametersofpatientswithandwithoutthyroid disease was obtained from the UCI Machine Learning Repository. The dataset consists of 3772 instances, each containing28attributes,includingage, sex, thyroxineand antithyroidmedicationdetails,thyroidsurgery,pregnancy, sickness,hyperthyroidandhypothyroidqueries,tumorand psychinformation,TSH,T3,andT4levels,andvariousother chemical and biochemical parameters that are commonly usedindiagnosingthyroiddysfunction.Table-1andTable-2 showthenumericalandcategoricalattributesrespectively.

(II) Data Preprocessing

Datapreprocessingisacrucialstageinanymachinelearning project.Thefollowingstepsareperformedinthisstage:
• Data Cleaning: The 'binaryClass' column in the datasetisconvertedtonumericalvalues,'t'and'f' valuesarereplacedwith1andO,respectively,and '?'valuesarereplacedwithNaN.
• FeatureEngineering:The'sex'columnisconverted to numerical values, and the 'referral source' columnisdroppedfromthedataset.
• Handling missing values: The missing values are imputed with the mean value of the respective column.
• Splitting the dataset: The dataset is divided into trainingandtestingsetswiththe'train_test_split()' functionfromsklearn.
• Feature scaling: The training and testing sets are scaled using the 'StandardScaler()' function to ensureallthefeaturesareonthesamescale.
(III) Model Building
The proposed research involves the creation of a deep learningmodelbasedonANNarchitecturetopredictthyroid disease. The model is implemented using the Tensorflow KerasAPI.Themodel'sarchitecturecomprisesasequenceof fourdenselyconnectedlayers,whereeachneuronislinked toeveryneuroninthenextlayer.Theinputlayerhas256 neurons, which is equal to the number of features in the input dataset and uses the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activationfunction.
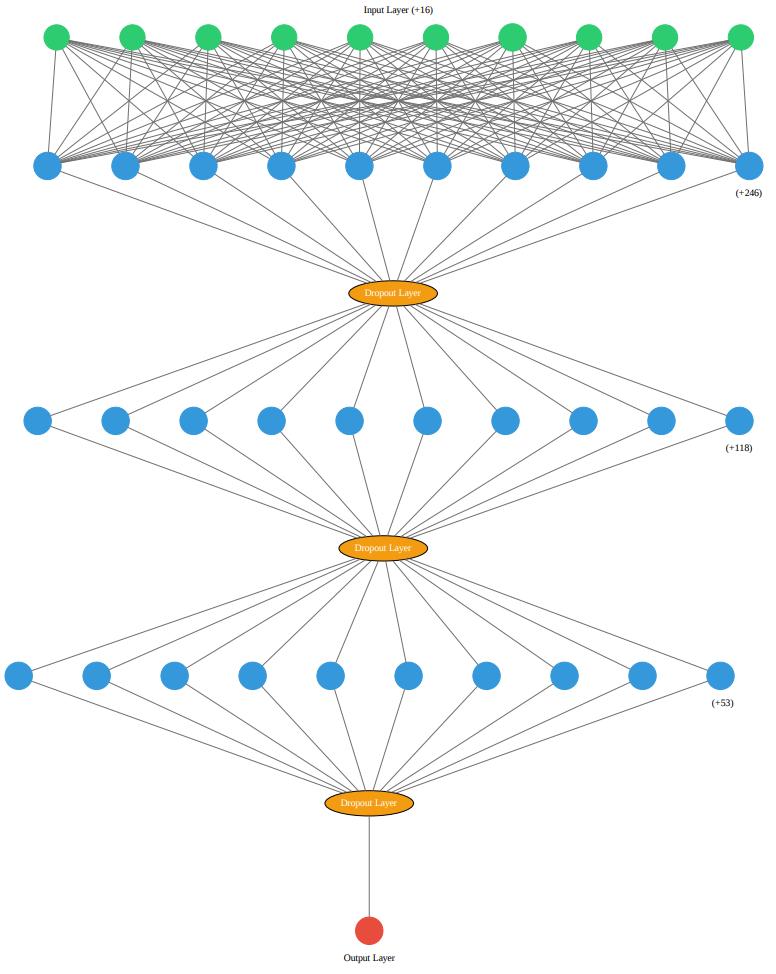
Thedropoutlayeristhenaddedafterthefirst,second,and third hidden layers, respectively, with 0.4, 0.3, and 0.2 dropout rates. Dropout is, basically, a regularization technique used in deep learning models to prevent overfitting.Itrandomlydropsoutsomeoftheneuronsinthe hidden layer during training, which reduces the codependencebetweenneuronsandimprovesgeneralization
The second hidden layer has 128 neurons, and the third hiddenlayerhas63neurons,bothactivatedusingtheReLU activation function. The final output layer has only one neuron,whichproducestheprobabilityoutputofthebinary classificationproblem(0or1)usingthesigmoidactivation function. Figure 2 visualizes the developed ANN model architecture.
Next,themodeliscompiledusingbinarycross-entropyloss andtheAdamoptimizer.
ReduceLROnPlateau,ModelCheckpoint,andEarlyStopping are the callback functions used to monitor the training
process,adjustthelearning rate,savethebestmodel,and stopthetrainingiftheaccuracybecomesstableforagiven numberofepochs.
The model is then fit using the 'fit()' method with the training data, for 80 epochs, a batch size of 48, and a validationsplitof0.1.
(IV) Model Evaluation
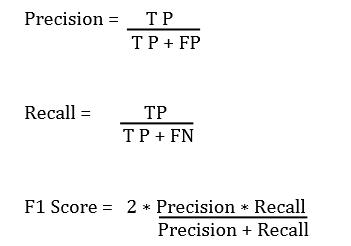
The trained model is evaluated using the test dataset that hasnotbeenusedinthetrainingprocess.Thepredictions are compared to the true labels using a confusion matrix, whichisavaluabletoolforevaluatingtheperformanceofa binaryclassificationmodel.Itisatablethatshowsthetrue positives(TP),truenegatives(TN),falsepositives(FP),and false negatives (FN) predictions of the model. From the confusionmatrix,variousperformancemetricslikeaccuracy, precision,recall,andF1scorearealsocalculated.
The accuracy metric measures the proportion of accurate predictions madeby the model anditcanbe described as follows:
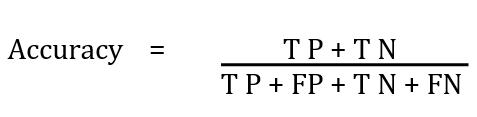
Sometimes,accuracycanbemisleadingwhenthedatasetis uneven, indicating that one class is substantially more prevalent than the other. In such instances, additional metrics such as precision, recall, andvF1-score are more informative.Theprecisionmetricmeasuresthepercentage oftruepositivesamongthepredictedpositivesandisagood indicationofthemodel'sabilitytopreventfalsepositives. Therecallmetricdeterminestheproportionoftruepositives among the real positives and is a good measure of the model's capacity to detect all positive cases The F1 score metric combines precision and recall to measure the accuracyofabinaryclassificationmodel.Itistheharmonic mean of precision and recall. The formulas for calculating precision,recall,andF1oscorearedefinedasfollows:
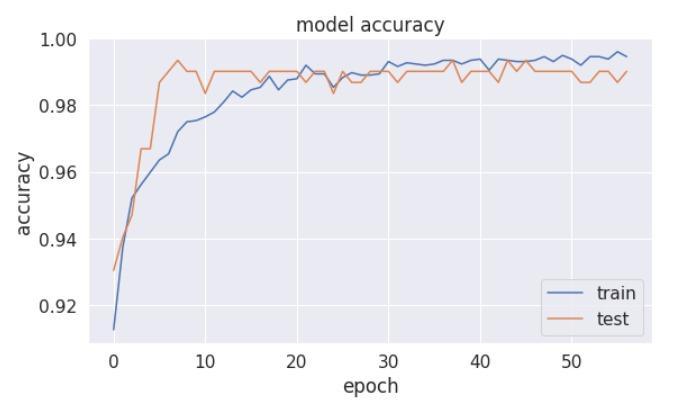
Fig -4:ANNmodelaccuracy
5. CONCLUSION & FUTURE SCOPE
Overall,evaluatingatrainedmodelusingatestdatasetand variousperformancemetricsmeasureshowwellthemodel performsonunseendataanditsability topredictpositive andnegativecasescorrectly.
4. RESULTS & DISCUSSION
Based on the evaluation metrics, the trained ANN model effectively recognized thyroid dysfunction. The confusion matrixindicatedthatthemodelpredicted691truepositive (TP)casesand55truenegative(TN)cases,withonly3false positive (FP) and 6 false negative (FN) predictions. The overallaccuracyscorewas0.9888,theprecisionscorewas 0.992, the recall score was 0.992, and the F1 score was 0.970. The curve depicted in Figure 4 depicts how the model's accuracy on both the training and test datasets evolvesthroughoutmultipleepochsandrisesovertimeas themodellearnstomatchthedatabetter.Insummary,the proposed ANN model demonstrated high accuracy and balanced performance in identifying thyroid dysfunction. Thestrongperformanceonthetestdatasetimpliesthatthe model is not overfitting to the training set. These results suggestthatthemodelcanpotentiallyassistindiagnosing thyroiddysfunction.Nevertheless,somelimitationstothis studyshouldbeconsidered,likethefactthatthedatasetwas notdiverseenoughorthattherewerepotentialbiasesinthe dataset that may have influenced the performance. Additionally,themodelwastrainedandtestedusingmedical record data, and its performance can be improved by incorporating other clinical information, such as patient historyandimagingresults.
Inconclusion,thedevelopeddeeplearningmodelexhibited highaccuracyandspecificity,whichindicatesitspotential usefulness in clinical practice. The model outperformed traditional machine learning algorithms, emphasizing the potentialofdeepLearningbasedneuralnetworkmodelsin thyroid dysfunction prediction. Future studies should concentrate on expanding the dataset, incorporating additional relevant features, and further validating the model'sperformanceondiversepopulations.Moreover,the model can be integrated into clinical decision support systemstohelpphysiciansinaccuratethyroiddiagnosisand management.
REFERENCES
[1] K. Chandel, S. Arora, S. K. Gupta, and V. K. Panchal, "A comparativestudyonthyroiddiseasedetectionusingKnearest neighbor and naïve bayes classification techniques,"CSITransactionsonICT,vol.4,no.2-4,pp. 313-319,Dec.2016.

[2] L.Aversano,M.L.Bernardi,M.Cimitile,M.Iammarino,P. E. Macchia, I. C. Nettore and C. Verdone, "Thyroid Disease Treatment prediction with machine learning approaches,"ProcediaComputerScience,vol.192,pp. 1031-1040,2021,doi:10.1016/j.procs.2021.08.106.
[3] A.ShrivasandP.Ambastha,"Anensembleapproachfor classification of thyroid disease with feature optimization," International Education and Research Journal,vol.3,no.5,pp.1–4,2019.
[4] A.Singh,S.Dubey,andS.K.Patil,"DeepLearningBased Prediction of Thyroid Disorder," in 2021 5th InternationalConferenceonIntelligentComputingand ControlSystems(ICICCS),pp.1149-1153,IEEE,2021.
[5] V.V.Hegde,andD.N.,"AutomatedPredictionofThyroid DiseaseusingANN,"InternationalJournalofInnovative ResearchinScience,EngineeringandTechnology,vol.5, no.5,pp.268-272,May2016.
[6] R.Chaganti,F.Rustam,J.L.Mazón,C.L.RodríguezandI. Ashraf, "Thyroid Disease Prediction Using Selective FeaturesandMachineLearningTechniques,"Cancers, vol.14,no.16,p.3914,2022.
[7] G.Kaur,K.SidhuandE.Kaur,"Artificialneuralnetworks fordiagnosisofthyroiddisease,"InternationalJournal forTechnologicalResearchinEngineering,vol.2,no.1, pp.56-59,Sep.2014,ISSN:2347-4718.
[8] A.Shukla,R.Tiwari,P.KaurandR.R.Janghel,"Diagnosis ofThyroidDisordersusingArtificialNeuralNetworks," 2009 IEEE International Advance Computing Conference, 2009, pp. 1016-1020, doi: 10.1109/IADCC.2009.4809149.

[9] R.Chaganti,F.Rustam,I.DelaTorreDíez,J.L.Mazón,C. Rodríguez and I. Ashraf, "Thyroid Disease Prediction Using Selective Features and Machine Learning Techniques," Cancers, vol. 14, p. 3914, 2022. doi: 10.3390/cancers14163914.
[10] A.BanduniandR.Mehra,"InteractiveThyroidDisease PredictionSystemUsingMachineLearningTechnique," 2019 6th International Conference on Parallel, DistributedandGridComputing(PDGC),2019,pp.689693,doi:10.1109/PDGC.2018.8745910.
[11] V.Sarasvathi and Dr.A.Santhakumaran, “Towards Artificial Neural Network Model To Diagnose Thyroid Problems”, Global Journal of Computer Science and Technology,Vol.11,No.5,pp.53-55,2011.
[12] https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/8541thyroid-disease
