ECOFRIENDLY LIGHT-WEIGHT BRICK
2,3,4,5,6Diploma Students, Civil Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar, Maharashtra, India
1Professor, Dept. of Civil Engineering, Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Maharashtra, India ***

Abstract - The most common type of construction material worldwide is brick. Also, we are now having issues with waste that is produced in surrounding regions. So, the goal of our project is to try to find a solution to this issue by creating waste-based brick made up of paper cup and coconut coir. For waste clay is utilized as a binding agent. In addition to making bricks lighter, using coconut coir and paper cup follows best practices for handling solid waste. We tried to lower the percentage of clay in this brick. We try make this brick dam proof for this we are using the banana leaves as a damp proofing agent this method is called as ‘Decoction Method.’
Key Words: Bricks, Banana Leaves, Coconut Coir, Dam proofing, Decoction Method, Paper Cup, Waste Material
1. INTRODUCTION
Asitisacommonknowledge,bricksareakeycomponentof constructionproject.Bricksareproducedinapproximately over1400billionunitperyearthroughouttheworld,andit isanticipatedthatdemandwillcontinuetoincrease.Soiland otherelementmakeupthemajorityofconventionalbricks, whicharecreatedduringhigh-temperaturekilnfire.Alack ofsoilexistinmanynations.Sincesoilisanaturalresource, over extraction will have an adverse effect on the environment. Coconut fibre or coir is used in our brick. Coconutisversatilesubstancewith manyapplication.Use wastepapercupthatareproducedbycafes,restaurants,and hotels.Sothatwecandecreasethepercentageofdirtand alsoofferwastemanagementsolutions.Weworktoreduce manufacturingcostsandbrickweightatsametime.Alsowe trytomakethebrickmadebysuchingredientdamp-proof byusingliquidsolutionofbananaleaves.
2. OBJECTIVE
Theobjectivesofthisprojectareasfollows:-
1. Tocomparestrengthandweightofclaybrickwith2nd classconventionalbrick.
2. Tocomparecostofclaybrickwith2ndclassconventional brick.
3. Tomakedamproofbrickbyusingdecoctionofbanana leaves.
3. STUDY WORK
3.1 What exactly is brick?
The primary building material used to create walls, pavements,andothermasonryconstructionelementisthe brick,sand,lime,concrete,flyash,andclayaresomeofthe other element used. The dimensions of normal clay brick vary from country to country, but in India it is roughly 9 incheslong,4incheswideand3inchesthick.

3.2 Materials used in this brick:A. Alluvial Soil:-
Alluvialsoilisthosethathavebeendumpedalongthe banksandattheriver’sbottom.Thissoilcanbefoundin alluvialfans,floodplains,andnearrivers.Becausenew silt is frequently deposited at the surface by floods, alluvialsoilhasadistinctivelayeredappearance.Round gravelparticlescomeinavarietyofsizesanddarkand lighttints.
Manyfloodplainscreatethisdistinctivelayeringprocess, knownasstratification.Floodingisthesourceofalluvial soil.Thestreamisthesourceofnewlyaddedsediment, whichissusceptibletoshiftsinlandscapeuse.
Properties of soil:-
1. Riverloaddevelopeditasitflowedfromtheupperto lowerstream.
2. Itislightweightandporous,makingitconvenientto use.
3. Soil’s consistency refers to both its ability to resist deformationandadheretootherobjectsaswellasto itself.
B.
Paper cup: -

Forthepurposeofmanufacturingbricks,wecollectused coffee paper cup from hotels, restaurant, and another establishment. Paper cups are lightweight and easily incorporatedintothesoil.
D. Water: -
Itisaclearfluid.Itwillbecleananddevoidofanydust particles.
Water's qualities for producing bricks include:
1)Itmustbedrinkable.
2)Water'spHshouldn'tbelowerthan6.
3)Thereshouldbenocontaminantsinit.
3.3 Proportioning
Beforebeginningproduction,testsshouldbefinishedto ensurethegreatestqualitybricks.Theproductshould be mixed in the proper proportions for best results. Evenafterconductingextensiveresearch,westillhave no notion regarding proportion. So, we made the decision to create a trail sample based on the ratio of dirttopapercupandcocopeat.Weconductthreetrials forfindingProportion:-
First Trial: -
In first trial we continue with the proportion of 1:0.1:0.1. Thatis1partofsoil,0.1partofcocopeat,0.1partofpaper cup. Main thing that is used in this proportion is coconut peat. But as this proportion give good poor result in compressive strength so it breaks easily. So, we skip this proportion.

Thefibrouscoconuthuskisusedtomakecoconutwaste, also known as coir. It is utilized in brick to increase strengthofbrick.


Asweusecocopeatinfirsttrialwedecidedtousecoconut coirinsteadofcoconut peat bytakingsameproportion as 1:0.1:0.1. But after casting the brick we seen that the finishingofbrickisverypoorascomparedtoconventional brick.Thisiswhyweskipthistrialalso.
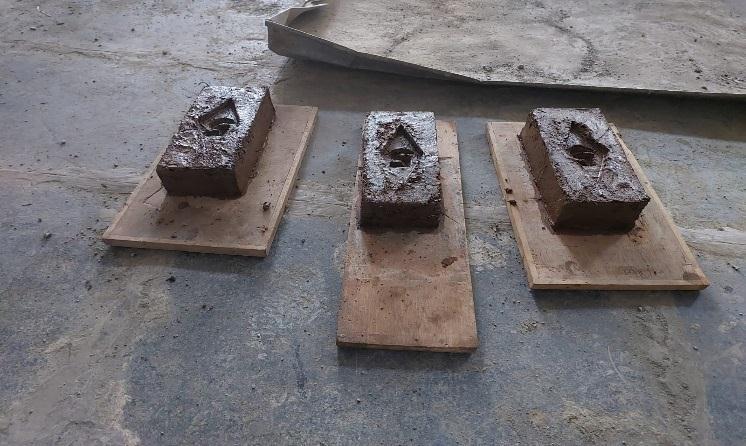



Trial:-

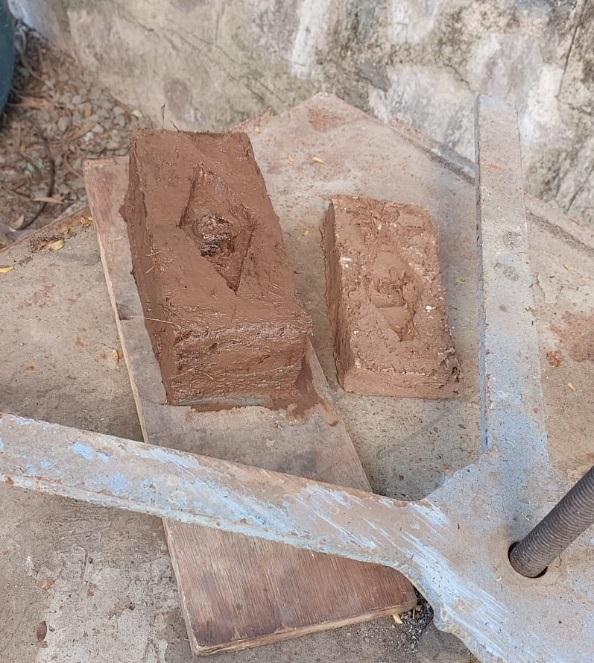
Forthirdtrialwedecidedtotake1partofsoil,0.0125part ofcoconutcoir,0.0125papercup.Aftertakingtwotrialwe understandthatthe%ofcoconutcoirandpapercupismuch moresowedecidedtoreduceit.Hencewetakeonly0.0125 partofbothcoconutcoirandpapercup.Aftercastingabrick weseethatthefinishingismuchbetterthantrialno.2.Also aftertakingcompressivestrengthtestitgivesbetterresult thantrialno.1.Sowedecidedtokeepthisproportionasour finalproportionforourproject.
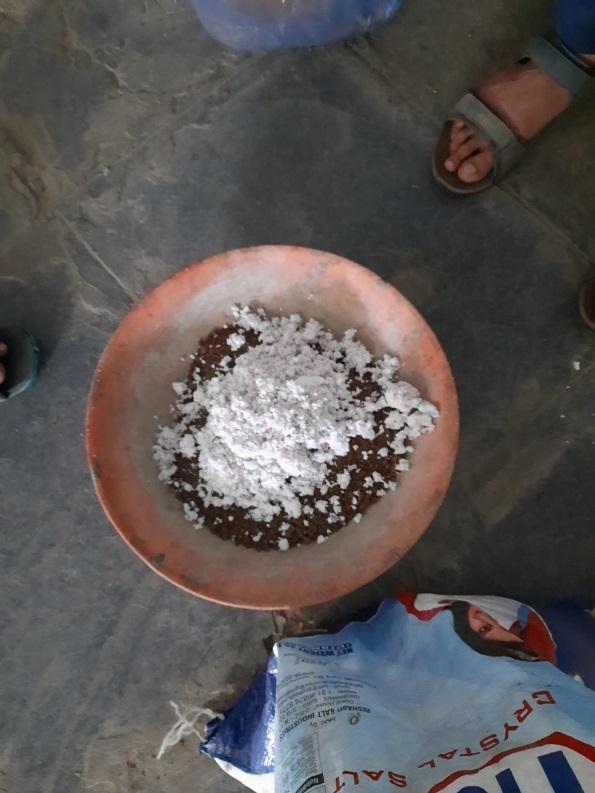

3.4 Mixing
Theblendingneedstobedonecorrectly.Handmixing shouldbeusedtocombineallcomponents.Theexpense ofhandmixingshouldbereasonableforsmallvolumes. Allofthematerialsweutilizedfortheexperimentare balanced.So,thecalculationforourrawmaterialshould be made. Three liters of water are used to make one brick.Anessentialcomponentofmixingisthebindingof thematerialstogether;theremovalofairgapsmustbe accomplishedthroughcompaction.Inorderforthebrick toreachitsmaximumstrength.Wheninspectingit,the finishing should be taken into consideration. Keeping thesurfaceflatwillreducetheplasteringexpense.
4. PREPARATION OF BRICK
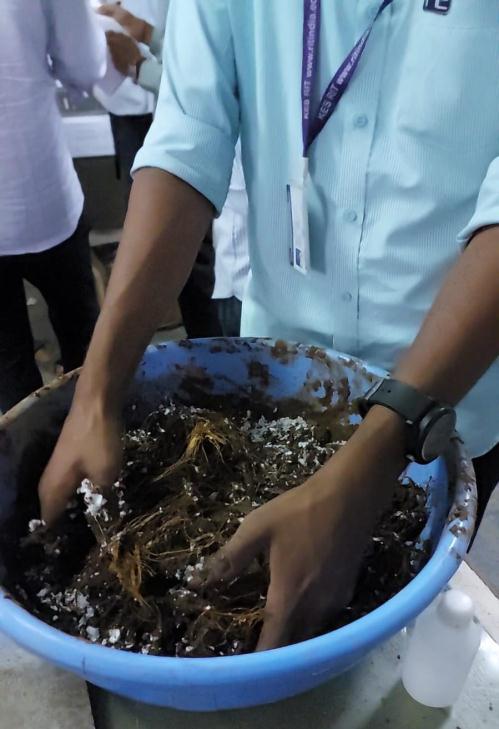
4.1 Actual Procedure of Brick Casting

1. Inordertomaintainthebestporosity,thebrick-making materials stored in the open air. The soil needs to be exposed to air for 24 hours. Then calculate the soil's weight.Itisimportanttoexaminethewater'sgravity, which should be roughly equivalent to the soil's moisture content, which was previously calculated through experiment. By taking numerous samples in different ratios, the water's composition should be chosen.

2. Wecreatethreebricksforourexperimentthathavethe same proportions of the ingredients as our brick. Use 25gofcococoir,25gmcupsofusedpaper,approximate water,and2Kgamountofsoiltomakeasinglebrick.To find compressive test we use three brick sample and taketheaverageofthem.

3. Ingredientswereaddedtothepanproportionately.The waterisaddedusingthesprinklingmethodafterithas been thoroughly mixed. To eliminate voids, prepared materialsareputintoamoldandcompacted.Itneedsto bepoundedwiththeblows.
4. Afterthebricksarecasted,theystoredforupto3days of air drying. For first brick we keep the brick more than 7 days in the air. (Note: - It totally depend upon weatheringcondition).Wetestedthebricksafterthey had dried out, first for dry density and then for
compressivestrength.Wetookthedrydensitytestfor onlyonesetofbrick.
5. Proportionusedforcastingbrickis1:0.0125:0.0125
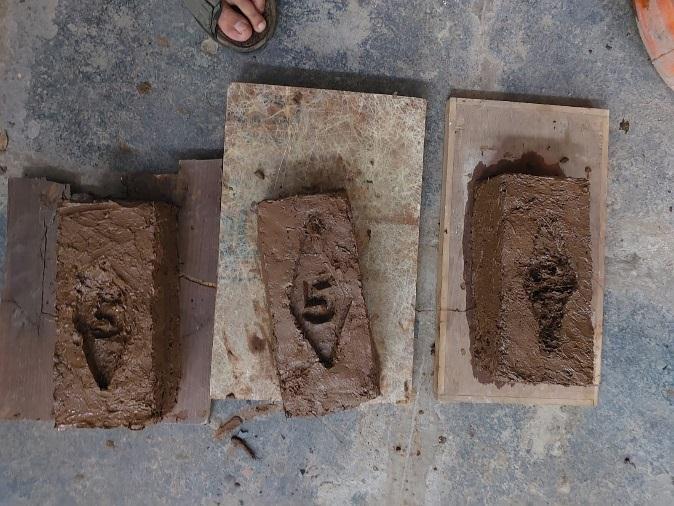
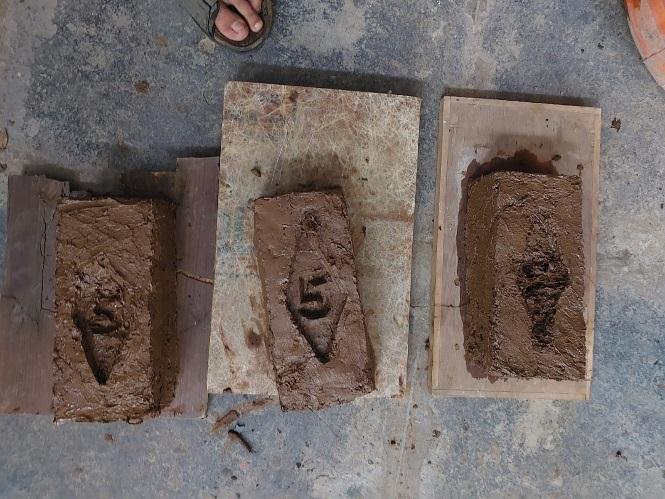
4.2 Comparison of Finishing
Belowisacomparisonoftraditionalbricksandourbricks. Ourbrickhasanidenticalfinishtoconventionalbrick
5.TESTING
A. Name of the test: - Compressive Test:-

Procedure of Compressive Test: -
1. Takethedimensionofthespecimentothenearest0.2m
2. Cleanthebearingsurfaceofthetestingmachine
3. Placethespecimeninthemachineinsuchamannerthat the load shall be applied to the opposite sides of the cubecast.
4. Align the specimen centrally on the base plate of the machine.

5. Rotate the movable portion gently by hand so that it touchesthetopsurfaceofthespecimen.
6. Apply the load gradually without shock and continuouslytillthespecimenfails
7. Record the maximum load and note any unusual featuresinthetypeoffailure.
Observation Table (Proportion – 1:0.1:0.1)
(Note: - Coconut Peat is used in this brick)
Table 1:- Compressive Strength
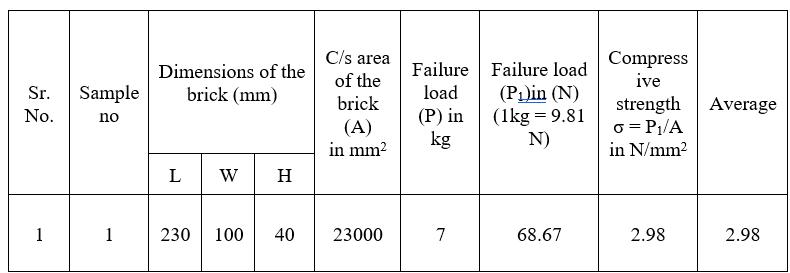
Conclusion: - After the test we saw that the compressive testofbrickthatwemakeinfirsttrialis2.98N/mm2 which isverylessthancompressivestrengthofconventionalbrick.
Observation Table (Proportion – 1:0.1:0.1)
(Note: - Coconut Coir is used in this brick)
Table 2:- Compressive Strength
Conclusion: - After the test we calculate the compressive strength of brick as 5.11 N/mm2 this is also less than compressivestrengthofconventionalbrick.
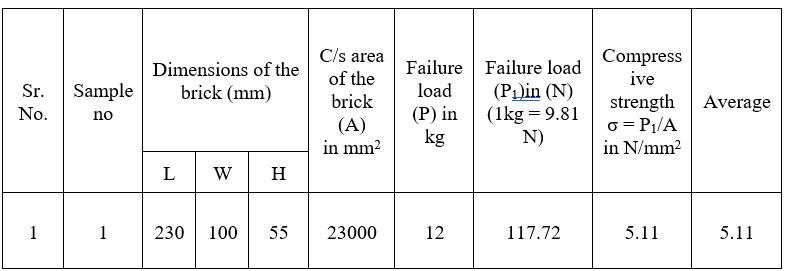
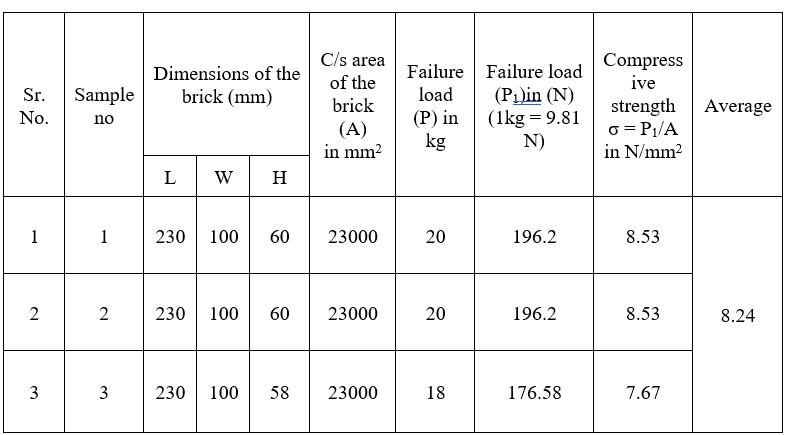
Observation Table (Proportion – 1:0.0125:0.0125)
Table 3:- Compressive Strength
Sample Calculation:ForSample1:-σ=P1/A
Result: - The average compressive strength of sample is 8.24 N/mm2
Conclusion:-Fromthisweconcludethatthecompressive strengthofeco-friendlybrickis8.24N/mm2 anditisvery goodascomparetoconventionalbrick.

6. RESULT
6.1
Result of Compressive Strength of Brick

AverageCompressiveStrengthofBrickPreparedinfirst trailis2.98N/mm2
Average Compressive Strength of Brick Prepared in secondtrailis5.11N/mm2
Average Compressive Strength of Brick Prepared in thirdtrailis8.24N/mm2
So the proportion that we fixed after taking test is 0.0125:0.0125:0.0125
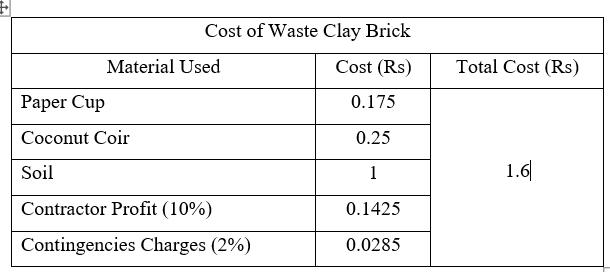
Waste Paper Cup:-
Onelabourtocollectwastepapercup=Rs.700/day
PaperCupcollectedinoneday=Approximately100Kg
Papercuprequireforonebrick=25gm.
Costofpapercupforonebrick=Rs.0.175
Cost of paper cup for 1 brick is Rs.0.175
Coconut Waste or Coir: -

Onelabourtocollectcoconutwaste=Rs.800/day
Coconutwastecollectedinoneday=Approximately80 Kg
Coconutwasterequireforonebrick=25gm.
Costofcoconutwasteforonebrick=Rs.0.25
Cost of coconut waste for 1 brick is Rs. 0.25
Soil :-
Soilrequiredfor1brick=2Kgor2000gm.
Cost of soil as per Indian mart = Rs 2000/ tonne ( 1 tonne=1000kg)
Costofsoilfor1brick=Rs.1
Cost of soil for 1 brick is Rs. 1
7. CONCLUSION
Throughtheprojectweconcludethat,
Themanufacturingcostofourbrickisminimumthan conventionalbrick.Also,itislightinweightandfinishingof our brick is equal to conventional brick. The compressive strengthofourbrickismorethanconventionalbrick.Itcan beusedforlowcostaswellasordinarybuilding.
8. REFERENCES
Currentmarketconventionalbrickprice:-Rs.8toRs.9
Table
Utilization of Waste Papers to Produce Ecofriendly Bricks,RohitKumarArya,RajeevKansal,International journalofInnovationsinEngineeringandScience,Vol5, No.1,2020
TheUtilizationofCoconutFibreintoFiredClayBrick.”, Aeslina Abdul Kadir1, a, Siti Noorhajar Mohd Zulkifly, InternationaljournalofInnovationsinEngineeringand Science,Vol5,No.1,2020
TheDevelopmentandStudyofFiberReinforcedFlyAsh Bricks, P.PrathyushaandKolliRamujee,Researchgate, March15,2012
