Glaucoma Screening Using Novel Evaluated CNN Architecture: An Automated Approach to Early Diagnosis
M. Madhumalini1 , J. Aparna2 , T. Diviya3, S. Nishanthini41Associate Professor, Dept. Electronics and Communication Engineering, P. A. College of Engineering and Technology Pollachi, Coimbatore, madhupavi.2007@gmail.com
2,3,4U. G. Scholars, Dept. Electronics and Communication Engineering, P. A. College of Engineering and Technology Pollachi, Coimbatore.
***
Abstract - Glaucoma is a collection of eye conditions which harms the optic nerve, that can result in vision loss and eventual blindness. The symptoms can start slowly leading to vision loss one may not notice them. Treatment at an early stage can prevent the further vision loss. A thorough dilated eye exam is the only approach to detect glaucoma. In this paper an eight-layer based Convolutional Neural Network architecture is proposed for the detection of glaucoma. For image distinction, CNN providesahierarchicalstructureofthe pictures. With a total of eight layers the proposed work canbe evaluated. The image is preprocessed using techniques like resizing, gray scaling, CLAHE. Further segmentation is done using canny edge detection. Using CNN the system classifies the images as normal eye or glaucoma eye based on the features extracted duringtraining.Theproposedmethodology manages to obtain high classification accuracy thus demonstrating the system's dependability and promise.
Key Words: Glaucoma, Convolutional Neural Network (CNN), Kaggle dataset, fundus images, classifier .
1. INTRODUCTION
The rear of the eye's interior is lined with a thin layer of tissuecalledtheretina.Itislocatedneartotheopticnerve. The retina's job is to collect the light that the lens has focused,transformitintoneuralsignals,andconveythose signalstothebrainforvisualidentification.
Thereisalayerofphotoreceptorcellsintheretinathat processlight.Inessence,thesearelight-sensitivecellsthat canrecognizecharacteristicslikecolorandlightintensity. After the photoreceptor cells collect the information, it is analyzedbytheretinaandtransmittedtothebrainthrough optic nerve. In general, the concentrated light creates an imagefortheretinatoanalyze,andthebrainisthenleftto determinewhatthevisualis.
Theretinaisnearly0.5mmthickthatextendsdownthe rearsideoftheeye.Theopticnervealsohasincomingblood arteriesthatflowintotheretinainadditiontotheganglion cell axons that proceeds to the brain. It vascularize the retinallayersandneurons.Thephotosensors,orrodsand cones, are situated next to the pigment epithelium and choroid, while the ganglion cells, which are the retina's
outputneurons,aresituatedintheradialpartoftheretina, whichisfontandnearertothelensoftheeye.Therefore,for lighttoreachandactivatetherodsandcones,itmustfirst passthroughtheretinaandactivatetherodsandcones,it mustfirstpassthroughtheretina'sthickness.
Followingthat,thephotonsthatareabsorbedbythevisual pigment of the photoreceptors are transformed into an electricalmessagethatcansubsequentlyactivateallofthe retina's succeeding neurons. The retinal communication regardingthephoticinputandsomepreliminarystructuring of the visual image into various sorts of emotion is transmitted to the brain via the ganglion cells' spiking dischargepattern.
1.1 Retinal diseases

Our eyes send our brain one-fifth of the information it receives.Manybothcommonanduncommoneyedisorders canimpaireyesight.Foreyesighttobeclear,theretinamust behealthy.Duetothefactthattheycanaffectanyareaofthe retina, retinal disorders are common. The following are possiblediseases.
DiabeticRetinopathy
Diabetes has a side effect called diabetic retinopathy, whichcandamagetheretinaandleadtoblindness.Theeye's essentialsustainingbloodvesselsdeteriorate,deviate,and multiplyinexplicably.Themostpopularformoftreatment todayforpreventingbloodvesselgrowthandfluidleaking intotheretinaislasertherapy.
Cataract
Cataractsarethetermfortheblindingoftheeye'slens. Normally, this region is unobstructed. Light rays are preventedfromgoingthroughthelensandfocusingonthe retinawhenthiscloudingtakesplace.Atissueliningthatis sensitivetolightistheretina.Itissituatedbehindtheeye. Whenaportionoftheproteinthatmakesuptheeye'slens
starts to change its structure, cloudiness develops. The visionisthenhamperedasaresult.
Acataract'searlyphasesmightnotbeproblematic.Onlya smallportionofthelensmaybeaffectedbythecloudiness. Ontheotherhand,thecataractcouldenlargewithtimeand covermoreofthelens.Itissignificantlymorechallengingto seewhenlesslightreachestheretina.Dullandfuzzyvision isexperienced.Unlikecataracts,whichcangofromoneeye totheother.However,alotofpeopledodevelopcataractsin botheyes.
RetinalMicroaneurysms
The most common lesions of diabetic retinopathy are retinal microaneurysms, although they can also occur in othermicrovessel-relatedillnesses.Capillarywallsnarrow slightlyasaresultofmicroaneurysms.Itisunclearwhether retinal microaneurysms are brought on by neovascularization or damage to blood vessel walls. However,theendoutcomeistheformationofsmallsaccular structures, roughly between 10 and 100 m in size, which appearasbrillianthypersensoryspotsonretinalfluorescein angiographybutasrounded,redspotsoncolouredfundal imaging.Becausebotharetiny,sphericalpatcheswithadark crimson colour and the same proportions, they cannot be distinguishedfromlittlebleeding.
Glaucoma
Glaucomaisachronic,progressiveeyeillnesscausedby opticnervedamage,which resultsinvisionfieldloss.It is oftencalled“silentthiefofsight”asithasnosymptoms.One of the primary risk factors is eye pressure. When the drainagesystemfails,fluidcanbuildupintheeye,whichcan causesignificantpressurethatdamagestheopticnerve.The optic nerve, which connects the retina and the brain, is a groupofnervefibres.Damagelikethisleadstovisionloss. Before gradually impairing the centre of the visual area, visionlossinitiallyaffectsitsedges.Thesymptomsmaynot appearformonthsorevenyearsafterthenervedamagehas happened.Oncelost,visioncannotberegained.
1.2 Types of Glaucoma
1)Open-AngleGlaucoma
2)AcuteAngle-ClosureGlaucoma
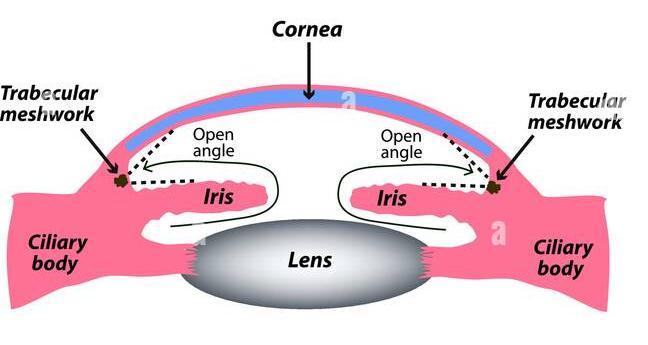
Open-AngleGlaucoma
When the eye is unable to adequately drain fluid, it causes intraocular pressure or IOP which is inner eye pressuretoincrease.Drainagecanalaperturesinopen-angle glaucomashouldbefunctioningandobvious.Theclogging problemspreadsdeeperintothedrainagecanals,muchlike a clogged pipe under a sink's drain. A large percentage of persons exhibit no symptoms or warning signals.. Openangleglaucomathatisundiagnosedanduntreatedcancause
a gradual vision loss. This glaucoma of this type develops slowly, occasionally for many years without any apparent sightloss.
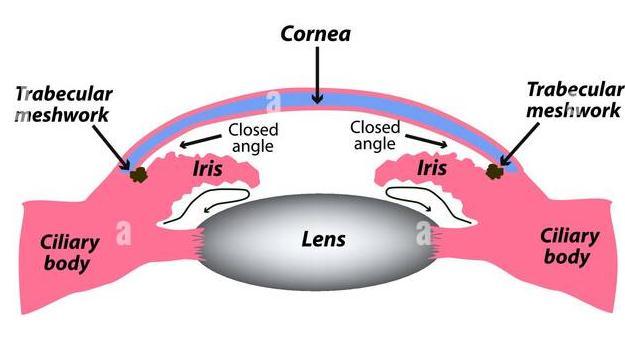
AcuteAngle-ClosureGlaucoma
The ocular emergency known as acute angle-closure glaucoma is brought on by a sudden rise in intraocular pressurebroughtonbyaqueoushumouroutflowrestriction. TherearemanyreasonsforthecauseofAcuteangle-closure glaucoma, but the anatomical anatomy of the anterior chamber,whichresultsiniris-corneaangletobeshallow,is themainriskfactor.Acuteangle-closureglaucomamanifests asasudden,intenseheadacheorpaininoneeye,alongwith nausea,vomiting,rainbow-coloredhalossurroundingbright lights,andblurredvision.Afixedmidwaypupilandafoggy or hazy cornea with obvious conjunctival injection are visibleonphysicalexamination.
2. EXISTING METHOD
Separating the picture samples into training and test samplesisthefirststepinthetechnique.Theinitialpicture processingperformedbythefundusimageaimstoenhance certain areas, improve the image information, and reduce deception.ThreesignificantConvNetarchitectures ResNet50, GoogLeNet and VGGNet-16 were trained on the preprocessedImageNetdataset.Toextractdeepfeatures, three ConvNet topologies are used. A prediction vector is createdusingtheresultof trainedneural networks,anda decision is made by majority vote. The final division of

fundusimagesintonormalandabnormal(glaucoma)images isclass0,whichdisplaysahealthyimage,andclass1,which displaysaglaucomaimage.Thearchitectureistestedusing the data sets from the PSGIMSR (Polygonal Shaped Image Microstructure), DRISHTIGS, DRIONS-DB, HRF (Head and NeckFracture)andcombinedimages.InthePSGIMSRdata set,471imagesarefoundtobenormal,and577imagesare discovered to be abnormal. There is cross-validation. 102 images have been inaccurately grouped. With ResNet-50, VGGNet-16,andGoogLeNetmodels,theaccuracy,precision, sensitivity,specificity,andF1scorewereallimproved.The accuracyratingsfortheGoogLeNet,VGGNet-16andResNet50,designs86.86%,87.04%and88.60%respectively.
2. PROPOSED METHOD
Thedetectionofglaucomaeyediseaseisbasedonfeature extractionfromfundusimages.Variousstepsaretakenlike pre-processing,segmentation,classificationanddetection.
2.1 Dataset
The Kaggle Dataset examines the manner and form in which data is frequently retrieved from the Kaggle repository.DataisintheMPEGor.JPEGformat.However,the fungalphotographsforthisresearcharein.JPEGformatand aredividedinto twofolders for the healthy andglaucoma images. The datasets that include screenshots of actual network environments are the most helpful for analysing Glaucomafundusimages.Giventhatitcontainsinformation onglaucoma,healthyeyes,aswellasimportantlysensitive data regarding the fundus images for the particular network'sexpertsystem,thisdatasetiseasilyaccessibleto the general public. Furthermore, it takes a tremendous amount of work to convert the raw network traces into a taggeddataset.Asaresult,researchersfrequentlyturntothe best dataset that may be made available to the research grouponKaggle.
2.2 Pre-Processing
Adjusting pixels is the main task of image processing. Modifying an image's pixels to take the desired shape. Preprocessing of data is typically done to lessen contrast, undesirable image noise, and luminous content. In preprocessing stage, the changes not connected to the glaucomaillnessareremovedfromthephotostoemphasize thedesirabletraits.
i. Grayscale
Grayscalerepresentationsareoftenusedforextracting descriptors rather than working directly with colour photographs since it is more straightforward and computationally efficient. In fact, adding extraneous information may increase the quantity of training data necessary to attain acceptable performance, while colour maybeofminimalutilityinmanyapplications.
ii. Medianblur filter

A nonlinear method for minimizing impulsive, or saltand-peppernoise,ismedianfiltering.Toeliminatenoise,all smoothingmethodsareemployed.LiketheGaussianfilter, themedianfilterisatypeofsmoothingtechnique,however the sole distinction between the two is the fact that the medianfilterretainsedgepropertywhiletheGaussianfilter will not. Because edges are crucial for look, edge preservation is a crucial characteristic. Median filters are frequently employed in digital image processing for edge preservation.
I'(x,y)=median(I(x+i,y+j)),
wherei,j=[-w/2,w/2]and(x+i,y+j)arethecoordinatesof theneighboringpixelswithinthewindowcenteredat(x,y).
iii. CLAHE
Contrast Limited Adaptive Histogram Equalization is a variedadaptivehistogramequalisation(AHE)whichhandles the issue of contrast overstimulation. CLAHE operates on separatesectionscalledtilesinsteadofprocessingtheentire image.Thefalsebordersaretheneliminatedbycombining theadjacenttilesusingbilinearinterpolation.Onecanuse thisalgorithmtomakephotographs'contrastbetter.
Just altering the brightness channel of an HSV image yieldsfarbetteroutcomesthanmodifyingtheBGRimage's several channels do. Although it is frequently used on the luminance channel, CLAHE may also be implemented to colourpictures.
TherearetwoconsiderationsforCLAHE.OneisClipLimit Thisvariable controlsthe contrastlimitingthreshold. The defaultvalueis40. TitleGridSize-Setsthenumberoftiles in the row and column. This defaults to being 8x8. It is utilizedforapplyingCLAHEwhiletheimageistiled.Interms ofimprovingedges,CLAHEisthemostsuccessful.
2.2 Segmentation
Theedgesofobjectsinphotosarefoundusinganimage processing technique called edge detection. Using a linear filter with Gaussian kernel, the canny edge detector first smooths the noise for calculating the edge strength and direction for each pixel in the smoothed image. Three parametersfromtheusermustbeprovidedintotheCanny edge detector. The Gaussian filter's pixel-based standard deviationisknownassigma,anditisthefirstfactor.Thelow threshold,whichisthesecondparameter,issuppliedasa percentageofthecalculatedhighthreshold.Thedistribution ofgradientmagnitudevaluesforthecandidateedgepixelsis usedtodeterminethethirdparameterhigh,whichspecifies the high threshold to apply in the hysteresis. The mathematical equation for the Canny edge detection algorithmcanbeexpressedasfollows:
Smoothing:ApplyaGaussianfiltertotheimageto reducenoiseandremovesmalldetails.
G(x,y)=(1/(2*pi*sigma^2))*exp(-(x^2+y^2)/(2* sigma^2))
Smoothed.Img=Image*G(x,y)
Gx=[-101;-202;-101]
Gy=[-1-2-1;000;121]
GradientMagnitude=sqrt(Gx^2+Gy^2)
GradientOrientation=atan2(Gy,Gx)
Non-Maximum Suppression: Suppress non maximumedgestoobtainthinedges.
For each pixel: If the pixel is a local maximum along the gradientdirection,keepit.Otherwise,suppressit.
HysteresisThresholding:Usetwothresholdvalues todistinguishbetweenstrongandweakedges.
An edge is said to be strong edge if the magnitude of the gradient is above the high threshold. Similarly it is not an edge if the magnitude of the gradient is below the low threshold. An edge is strong also if the magnitude of the gradient is between the low and high thresholds and connectedtoastrongedge.
Strong Edges = Pixels with Gradient Magnitude > High Threshold
Weak Edges = Pixels with Gradient Magnitude > Low Thresholdand<HighThreshold
Non-Edges = Pixels with Gradient Magnitude < Low Threshold
Final Edges = Strong Edges + Weak Edges (connected to strongedges)
2.4 Feature Extraction
The most vital and delicate task is feature extraction. Systemaccuracyismostlydependentonfeaturequality.The methodofglaucomadetectionisimprovedwiththeuseof several automatedfeatureextractionapproaches. Tofind features like the median, mean, and variance, a random pickletechniqueapproachwasemployed.
To detect features including brightness, translation invariance,papillarim,andcupsize,avarietyofextraction techniques were applied, including Pixel Intensity Value, Textures, FFT Coefficients Pixels intensity, and Histogram Model.Byextractingnewfeaturesfromthecurrentonesina dataset,featureextractionseekstolowertheoverallnumber
offeaturesinthedataset.Thus,themajorityofthedatain theoriginalsetoffeaturesshouldbeabletobesummarised bythisnewreducedsetofcharacteristics.
2.5 Classifier
Deep neural networks like the convolutional neural network (CNN) are frequently utilised in computer vision andimageclassificationapplications.ByimplementingCNN usingthePythonTensorFlowlibrary,thisarticlewillshow youhowtobuildyourownimageclassificationmodel.
AlexNet is a classic convolutional neural network architecture. Convolutions, max pooling, and dense layers make up its fundamental building elements. The model is fitted over two GPUs using grouped convolutions. The AlexNet has eight learnable layers. All five levels of the modeluseReLuactivation,exceptfortheoutputlayer,which utilizes max pooling and is proceeded by three fully connectedlayers.Thefirstconvolutionlayeristhenapplied, using96filterswithasizeof11x11andastrideof4.ReLuis the activation function utilized in this layer. The output featuremapis55X55.
4. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Retinal image offers a less expensive, simpler, and more practical way for non-clinical practitioners to identify glaucomainunderprivilegedindividuals.Usingabetterand smarter algorithm, we have created a system with more benefits. Ourproject'sgoalistouseadifferentalgorithmto increasethesystem'sefficiencyandaccuracy.

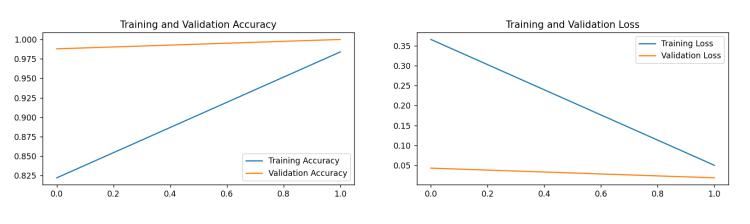
Figure - 3:TrainingandValidationaccuracy
The Figure 3 represents the training and validation accuracyandlossofaGlaucomadetection. Usingaspecific algorithmandconvolutionalneuralnetworkthevalidation accuracyisachievedto99%andtrainingaccuracyisreached to97.5%.Thetrainingandvalidationlossisdetectedandit is0.7%and0.2%.
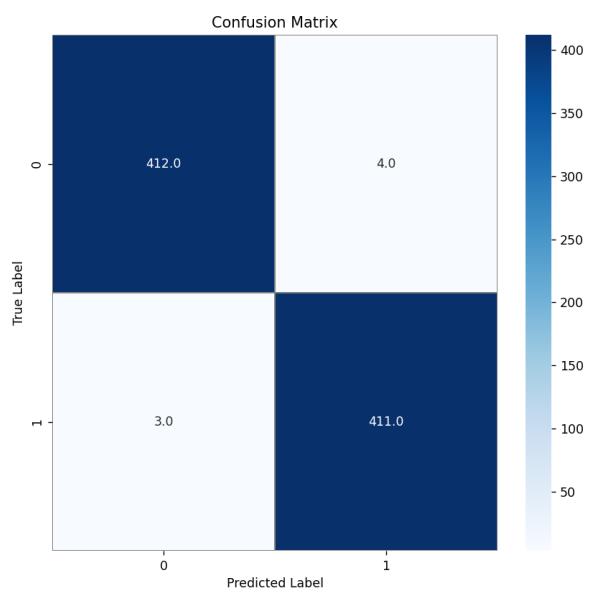
The above confusion matrix depicts the class 1 with normal images and class 0 with glaucoma images. A Confusion matrix is a table that is used to calculate the performance of a classification system by comparing the predictedandactualvaluesofthetargetvariable.Itisalso known as an error matrix or a contingency table. The Confusion matrix can be used to compute various performancematricesofaclassificationmodel,suchasF1score,precision,accuracy,recallandothers.Thesemetrics canhelptoevaluatethemodel’sperformanceandidentify areasforimprovement.
Aconfusionmatrixtypicallyconsistsoffourcategories:
TruePositives(TP):Thetotalcountofpositiveinstancesthat wereclassifiedcorrectlybythemodel.
False Positives (FP): The total count of negative instances thatwereclassifiedincorrectlyaspositivebythemodel.
FalseNegatives(FN):Thetotalcountofpositiveinstances thatwereclassifiedincorrectlyasnegativebythemodel.
TrueNegatives(TN):Thetotalcountofnegativeinstances thatwereclassifiedcorrectlybythemodel.
The model correctly identified normal eye 412 times (TruePositive)andglaucoma411times(TrueNegative),but incorrectly predictednormal eye4timesasglaucomaeye (False Positive) and glaucoma eye as normal eye 3 times (FalseNegative).
5. CONCLUSION
Amodelwascreatedintheproposedstudytoimprovethe earlydiagnosisofglaucoma.Themodelsuggeststheuseof convolutional neuralnetworktoextractfeaturedatafrom the images to distinguish between healthy images and
glaucomatousfundusimages.Avarietyofpublicandprivate data sets are used to test the proposed strategy. The proposedalgorithmperformsmoreeffectivelythanthemost recent method. Using the KAGGLE data set, the suggested model has a 99% accuracy. Theproposed model outperforms both the convolutional neural network architecture and traditional computer –aided diagnosismethods,accordingtoexperimentsonbothopensourceandclosed-sourcedatasets.Thefurtherinvestigation canbecarriedouttocreateafullyconvolutednetworkthat candifferentiatebetweentheopticdiscandopticcupinthe subsequently suggestedwork using a large experimental datacollection.
REFERENCES
[1] Afroze T, Akther S, Chowdhury, M.A., Hossain, E., Hossain, M.S., Andersson, K. (2021). “Glaucoma Detection Using Inception Convolutional Neural NetworkV3”.In:Mahmud,M.,Kaiser,M.S.,Kasabov,N., kharuddin,K.,Zhong,N.(eds)AppliedIntelligenceand Informatics. AII 2021. Communications in Computer andInformationScience,vol1435.Springer,Cham.
[2] Ahmed M.R.,Ahmed S. R., DuruA. D.,Uçan O.N. and Bayat O. (2021) , “An Expert System to Predict Eye Disorder Using Deep Convolutional Neural Network”,AcademicPlatform-JournalofEngineering andScience,vol.9,no.1,pp.47-52,Jan.2021
[3] AjithaS,Akkara,JohnD,JudyMV,(2021)“Identification ofglaucomafromfundus imagesusing deep learning techniques”.IndianJournalofOphthalmology69(10):p 2702-2709,October2021.
[4] Barros, D.M.S., Moura, J.C.C., Freire, C.R.et al.(2020) “Machinelearningappliedtoretinalimageprocessing for glaucoma detection”: review and perspective.BioMedEngOnLine19,20.
[5] Diaz-Pinto, A., Morales, S., Naranjo, V.et al.(2019)“CNNs for automatic glaucoma assessment usingfundusimages”:anextensivevalidation.BioMed EngOnLine18,29(2019).
[6] Gheisari, S., Shariflou, S., Phu, J.et al.(2021), “A combinedconvolutionalandrecurrentneuralnetwork forenhancedglaucomadetection”.SciRep11,1945.
[7] JoshiS,PartibaneB,HatamlehWA,TaraziH,YadavCS, Krah D. (2022), “Glaucoma Detection Using Image ProcessingandSupervisedLearningforClassification”, JHealthEng.2022Mar.
[8] Mahum R, Rehman SU, Okon OD, Alabrah A, Meraj T, RaufHT.(2022), “ANovel Hybrid ApproachBased on Deep CNN to Detect Glaucoma Using Fundus Imaging”.Electronics.

[9] Rutuja Shinde,(2021) “Glaucoma detection in retinal fundus images using U-Net and supervised machine learning algorithms”, Intelligence-Based Medicine, Volume5,2021,100038,ISSN 2666-5212.
[10] Saxena,A.,Vyas,A.,Parashar,L.andSingh,U. (2020),“A Glaucoma Detection using Convolutional Neural Network”,InternationalConferenceonElectronicsand Sustainable Communication Systems (ICESC), Coimbatore,India,2020,pp.815-820(2020)

