BHARATH KISAN HELPLINE
Abstract The project develops machine learning-based strategies for precise gather yield statistics. The project makes the assumption that the rapid developments in machine learning (ML) and distinguishing calculation will provide practical and comprehensive solutions for improved harvest and environmental condition assessment. As we undoubtedly already know, India has the world's secondlargest population, and the majority of its citizens work in the horticulture industry. Farmers repeatedly produce the same harvests without trying new varieties of yields, and they apply manures in irregular amounts without realizing how much is missing in both substance and quantity. Thus, this directly affects agricultural yield in addition to causing the soil to ferment and harming the top layer. In this way, we developed the foundation for farmers' advancement using AI calculations.
Keywords - Crop recommendation, Machine learning algorithms,Accuracy.
I. Introduction
I. One of the important occupations practiced in India is farming. It is the largest banking sector and plays a major role in the advancement of the nation as a whole. To address the problems facing 1.3 billion individuals worldwide, more than 60% of the country's territory is usedforhorticultureadoptingnewagribusinesstoolsafter that. Based on Farmers' experience in a particular region, previous crop and yield expectations were made. The ongoing situation without a change in the harvest and the application of insufficient amounts of supplements to the soil causes a decrease in the output, soil contamination (soilfermentation),anddamagetothetoplayer.
II. Inordertocreatenewpossibilities,machinelearning,a componentofcomputerizedreasoning,hasemergedalong with big data advancements and improved execution registering. The proposed framework will make the best yieldrecommendationforagivenplotofproperty.Inlight of the soil's composition and factors affecting the environment,suchastemperature,stickiness,andpH.
II LITERATURE REVIEW

1. Crop Prediction using Machine Learning Approaches, Nischitha K, Dhanush Vishwakarma, Mahendra N, Ashwini, Manjuraju M.R,2022
As we are undoubtedly aware, India is the world's second most populous country, with agribusiness being the most common occupation for the majority of Indians. Farmers continuetodevelopthesameharvestswithouttryingnew varieties of yields, and they apply composts in arbitrary amounts without understanding the lack of substance and amount. Asa result,this directlyaffectscrop output while also causing dirt fermentation and harming the top layer. As a result, we designed the structure for rancher development using AI calculations. Our framework will offer the optimum suited yield for specific land in the context of its makeup and natural requirements. The framework also provides information on the necessary quantity and type of manure, in addition to the essential seedsforgrowth.Duetothewaywe'resetup,farmersmay produceawiderrangeofharvest,increasenetincome,and avoidsoilcontamination.
2.Enhancing Crop Yield Prediction Utilizing Machine Learning on Satellite- Based Vegetation Health Indices Hoa Thi Pham,Joseph Awange, Michael Kuhn,Binh Van Nguyen,LuyenK Bui,2022
Exact gather result determination is fundamental in the distinctivedesignofthefoodsector,whereestimatesfrom the agricultural condition document (VCI), the warm situationrecord(TCI),andthesimulatedintelligence(ML) are combined. The drawback is that a one-size-fits-all assumption framework is typically applied throughout a region as a whole, ignoring the spatial variance in subterritorial VCI and TCI brought on by environmental and weather conditions. Rehashed VCI/TCI data poses extra difficulties that have a detrimental effect on the models' predictions when nonlinear ML is used. To deal with the two upgrades, this study proposes a framework that (I) applies higher-demand spatial free part assessment and (ii) employs a mixture of key part assessment (PCA) and ML(i.e.,PCA-MLblend)(i.e.,PCA-MLblend).Thesuggested technique, like Vietnam, divides typical VCI/TCI spatial capriciousnessinto distinct subdistricts. Instead of a onesize-fits-all methodology, sub-local rice yield evaluation
models outperformed Vietnam by 20% to 60%. ML-only underperformed PCA-ML mixture by an average of 18.5% to 45%. The constancy of the structure is shown by the ability to anticipate rice production 1 to 2 months before harvestwithastandarderrorof5%.
3. Machine learning for large-scale crop yield forecasting panelDilli Paudel , Hendrik Boogaard , Allard deWit , Sander Janssen , Sjoukje Osinga , ChristosPylianidis, IoannisN.Athanasiadis ,2021
Withafocusonclearcontext-orientedrequirements,many studies have used computer-based intelligence to reduce yield gauging. They may not have used knowledge or techniques that are applicable to all yields or all geographical areas. However, practical large-scale frameworksdon'tuseartificialintelligence,suchtheMARS Gather Yield Expectation Structure (MCYFS) from the European Commission. A method that holds promise is man-made intelligence, especially when a lot of data is beingacquiredanddisseminated.Wecombinedcomputerbased intelligence with reap exhibiting agronomic principlestocreateacomputer-basedintelligencemeasure for extensive crop yield assessment. The standard is a working method that emphasises justice, objectivity, and reusability. In order to manage development and improvement,wefocusedonorganisingcoherentpointsor features.Toincreaseexactness,wethenappliedcomputerbased intelligence without information leakage. From the MCYFS informative index, we created features incorporating crop re-sanctioning discoveries as well as environmental, remote sensing, and soil information. We emphasised a detachable and adaptable work cycle to support various outputs and nations with minimal plan adjustments. The work cycle can be used to conduct repetitive The work cyclecanbeusedtorepeattests with standard information data in order to get reproducible results (for example, early season or end-of-season assumptions). We estimated average production for five harvests sensitive wheat, spring grain, sunflower, sugar beetroot, and potatoes and three countries the Netherlands (NL), Germany (DE), and France (FR). We compared the results to a fundamental technique that lackedassumptionmasteryandassumedeitheraconstant yielddesignortheaverageoftheplanningset.
4. Crop Recommendation System using Machine Learning Dhruvi
Hardik Jayswal4, Axat Patel,2021
Horticulture is considered to be an important profession byalargeportionofIndia'spopulation.Inournation,yield creation plays a significant role. Poor harvest quality is frequently caused by either excessive compost use or inadequatemanureapplication.ThesuggestedIoTandML arrangementallowsforsoiltestingusingsensors,whichis
dependent on estimating and noting soil boundaries. This structure reduces the possibility of soil degradation while maintaining crop health. In this framework, soil temperature,soilmoisture,pH,andothersensorsNPKare used to monitor temperature, stickiness, soil dampness, andsoilpHindividually,aswellasNPKsupplementsofthe earth. The data collected by these sensors is saved on the microcontroller and analysed using AI calculations like irregular backwoods, on the basis of which ideas for the growthof the reasonableharvest aredeveloped. This task alsohasastrategythatfocusesonutilisingaconvolutional brain network as an important approach to determining whetherornottheplantisindangerofasickness.
5. Efficient Crop Yeild Recommendation System Using Machine Learning For Digital Farmig. Dr.G.Suresh, Dr. A.Senthil Kumar, Dr.S.Lekashri,Dr.R.Manikandan,2021
Precision agriculture and digital farming enable the exact application of inputs such as seed, water, pesticides, and fertilisers to crops at the right time to maximise output, quality, and yields. Farmers can better comprehend their fields by deploying sensors for data collection and mapping fields, allowing them to conserve resources and minimisenegativeenvironmentaleffects.Mostfarmersuse conventionalfarmingpatternstodeterminewhichcropsto growinafield.Farmers,ontheotherhand,donotbelieve crop yield is affected by soil characteristics and climatic circumstances.Inlightofclimate,wetness,andseason,our computerised farming system may then advise a yield recommendation framework that assists farmers in selecting the greatest harvest to germinate on their land. AI approaches enable a machine to successfully make educated decisions. This application aids in herbicide selection, seed separation, and seed separation. seed profunditybyutilisingtheMLrecommendationmotor.
III. PROPOSED SYSTEM
1. Architectural Design:

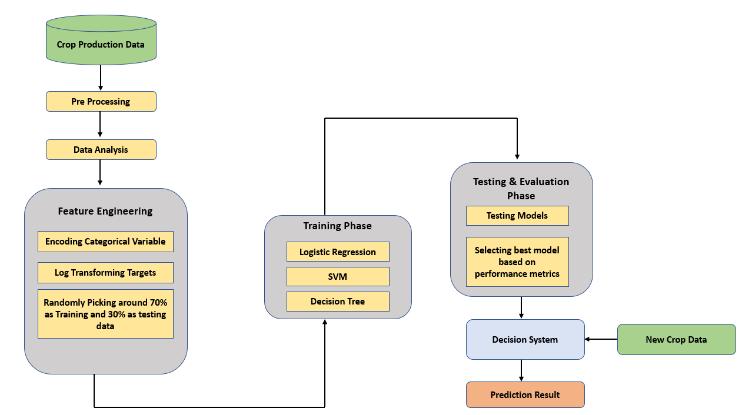
Information gathering and preparation are two key steps inensuringtheaccuracyofthedataset.Thereshouldbeno missing attributes in the dataset, and they should be replaced with the correct qualities. Additionally, the information needs to be examined to see if its characteristics follow a usual dispersion. Information investigation and representation are the preceding stage. Wemakeanefforttothoroughlystudyourdatainorderto spot any trends or standout instances in the dataset. We createdseveralrepresentationsofthematerialinorderto fully understand it. The following stage is highlight choosing; we must select only those components that will be expected to allow the type of product to grow. We createdacorrelationmatrixtoshowthelinearrelationship between one feature and each of the other features. Then comes data testing and instruction. Before we can start building the machine learning model, we must partition our dataset into training and test sets. The material was shared in a 70-30 split. Machine learning algorithms will be used for training, and performance matrices will be used to pick the model for testing. We are receiving the results, and the decision-making system will be able to extrapolatenewcropyielddataforcropyieldforecasts.To displaythe linear link amongone characteristic and every single one of the other features, we have constructed a correlation matrix. Testing the data will come next, then instruction. We must divide our information into training and test sets before creating the machine learning model. Thedistributionofthesubstanceis70to30.Performance matriceswillbeusedtochoosethemodelfortestingafter machine learning methods have been employed for training. We are receiving the results, and the decisionmaking For agricultural yield estimates, the methodology willbeabletoextrapolatefreshcropyielddata.
model and test the three AI models, wecreated the model andusedthetesteddatayieldchoiceframework.Actually, the choice framework will desire to summarise the initial harvestyielddatafortheanticipatedcropoutput.
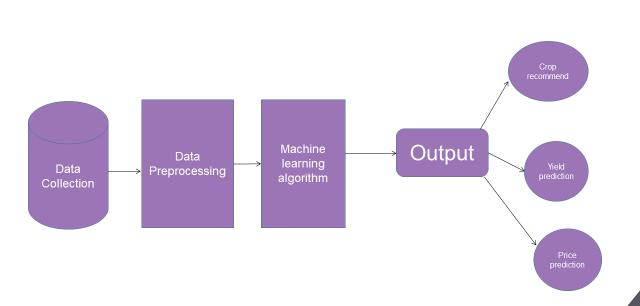

3.
Insoftwareengineering,theterm"classdiagram"refersto a specific kind of static structural diagram that illustrates the categories, properties, operations (or methods), and connectionsamong the classesto depict thestructure ofa system.Itdescribesthekindofdatathatispresent.
Webeganbycompilingmeasurementsoftheenvironment and crop creation from many sources into a focused data set. We usedseveral pre-handling techniques, followed by research and examination procedures, to decipher the information buried in the data. We used highlight designing to organise the information for planning. After the component designing phase, In order to develop a
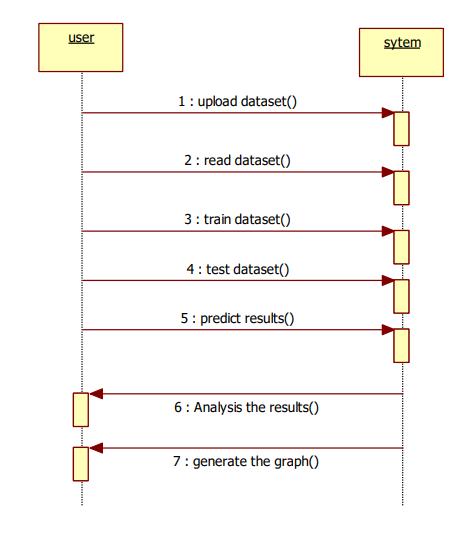
In the Unified Modelling Language (UML), A succession chart is a diagram that illustrates how and when cycles cooperate with one another. It is a strategy for message grouping. The names occasion charts, occasion circumstances,andtimingoutlinesarewidelyusedtorefer tosuccessiongraphs.
V. RESULTS
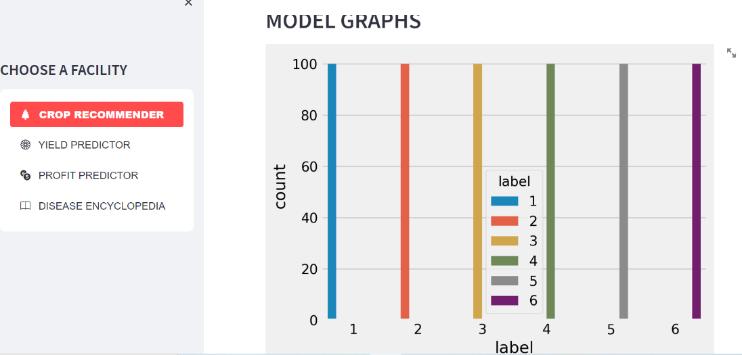
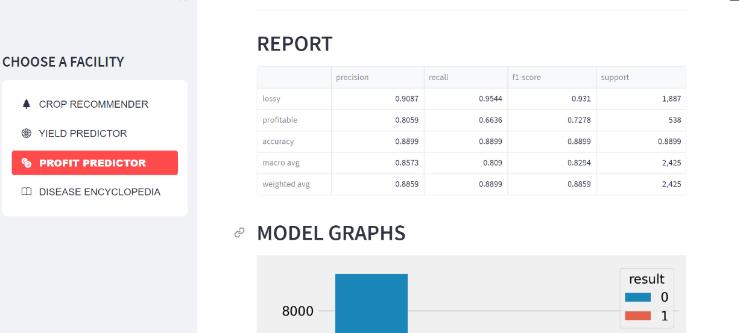
By uploading the data to the Bharath Kisan Helpline, the findings are dependent on the four parameters Crop recommendation, Yield predictor, Profit predictor, and Disease encyclopaedia. And when compared to other applications,ourapplicationhasachievedexcellentresults intermsofaccuracy,precision,anddiseasedetection.
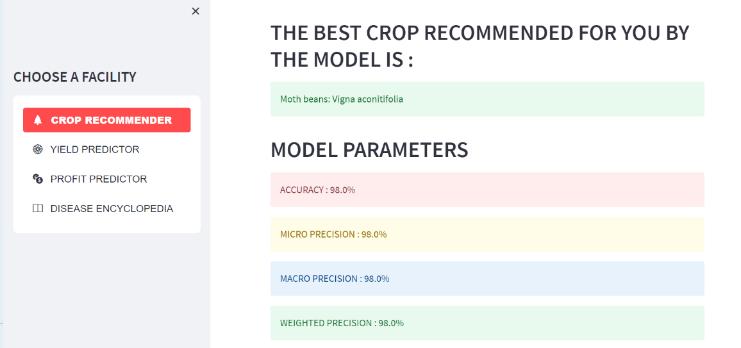
We enter the following factors into the Bharath Kisan Helplinetocalculatetheoutputofcroprecommendations:

N (nitrogen value), P (phosphorus value), K (potassium value),temperature, humidity,PH, rainfall,and we get the accuracy, Micro Precision, Macro precision and weighted precision.

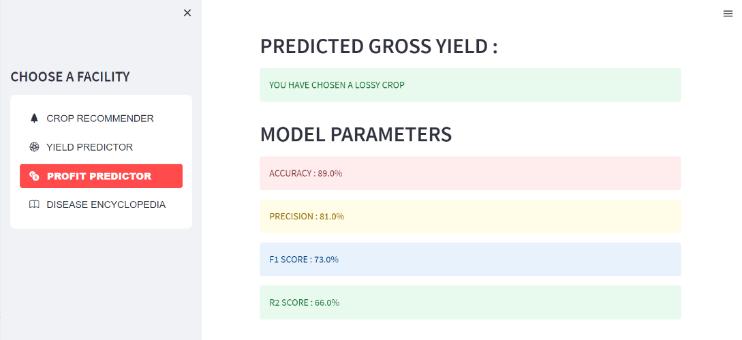
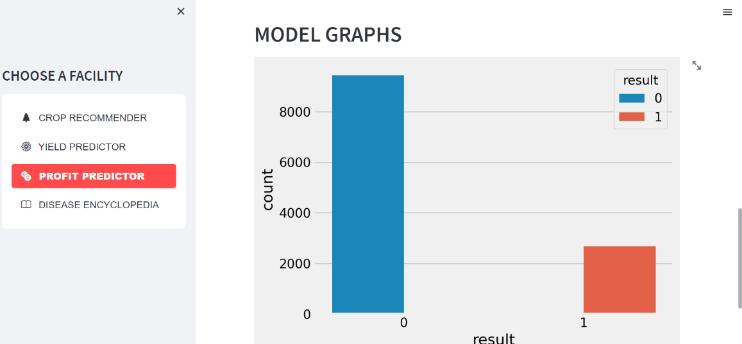
We take into account the following factors when computing the output of the yield predictor and the profit predictor: State_Name, District_Name, Crop_Year, Season, Crop, Area, Production, UnitPrice, Netprice, Unit Investment,NetInvestment,Profit,andwegettheresults.
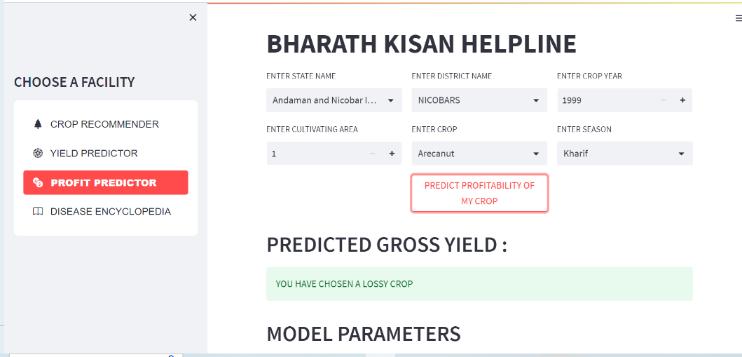
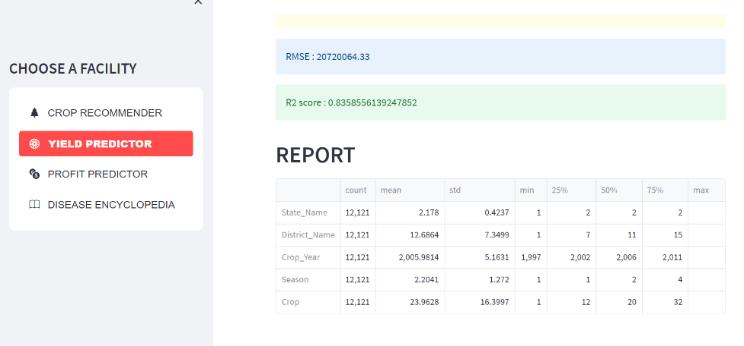
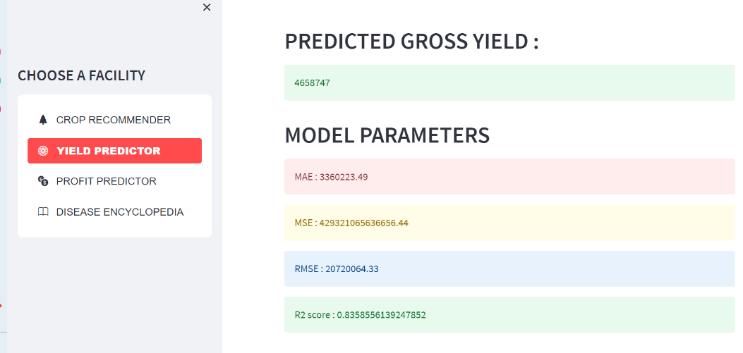
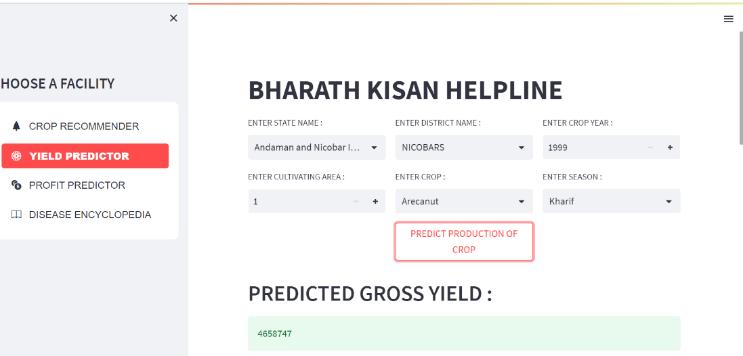

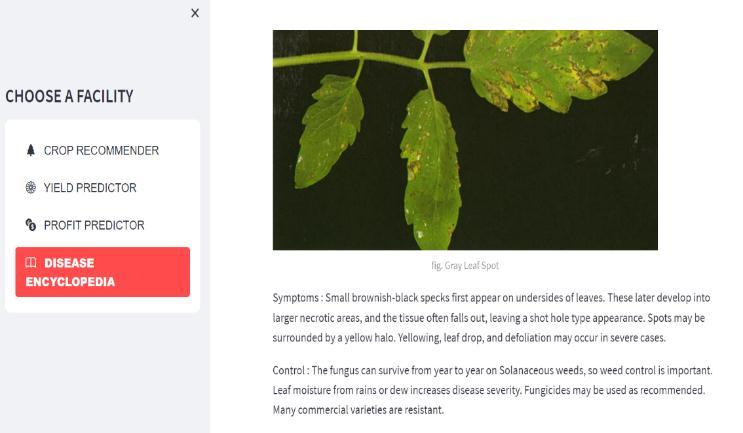
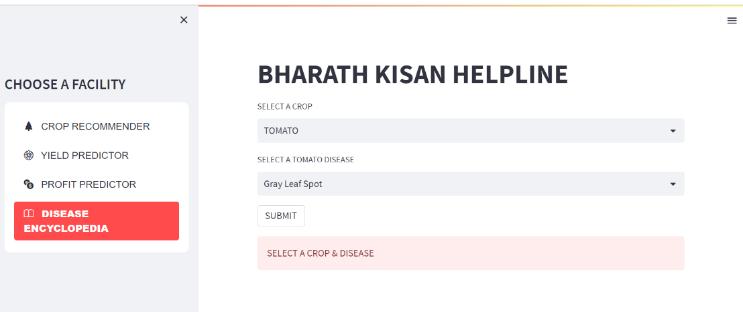
Fordiseaseencyclopedia,wehaveuploaded the images of leaveswithdiseasesandwehavechosen5plantsTomato, Potato,Cotton,Pumpkin,Cabbageandweareobtainingthe results.
VI. CONCLUSION
In this study, we made predictions using a variety of variables, such as crop yields, suggested fertiliser applications, and price forecasts. Agriculture is a sector that helps the economy of our country. This, however, is slow to adopt new machine learning technology. Our farmers should be acquainted with all of the most recent machine learning technologies and other methodologies. With the help of the algorithms that were used to predict yieldandprice,cropyieldandtheeffectiveuseoffertiliser were effectively predicted. Based on this philosophy, we createdasmartphoneapplicationthatissimpletouseand aids in the user's understanding of agriculture. These techniques help to resolve agricultural problems and increase agricultural yield, and we have improved agriculturaloutputasaresults.
REFERENCES
[1] Crop yield prediction using machine learning: A systematic literature review Thomas van Klompenburga , Ayalew Kassahuna , Cagatay Catalb, Computers and Electronics in Agriculture Volume 177,October 2020, 105709.
[2]AnnaChlingaryana,SalahSukkarieha,BrettWhelanb― Machinelearningapproachesforcropyieldpredictionand nitrogen status estimation in precision agriculture: A review, Computers and Electronics in Agriculture 151 (2018)61–69,Elisver,2018.
[3] Niketa Gandhi et al," Rice Crop Yield Forecasting of Tropical Wet and Dry Climatic Zone of India Using Data Mining Techniques", IEEE International Conference on AdvancesinComputerApplications(ICACA),2016.
[4] K.E. Eswari. L.Vinitha. “Crop Yield Prediction in Tamil Nadu Using Baysian Network ", International Journal of Intellectual Advancements and Research in Engineering Computations,Volume-6,Issue-2,ISSN:2348-2079.

[5] Shruti Mishra, Priyanka Paygude, Sinha Chaudhary, SonaliIdate“UseofDataMining inCropYieldPrediction” IEEE Xplore Compliant - Part Number:CFP18J06-ART, ISBN:978-1-5386-0807-4; DVD PartNumber: CFP18J06DVD,ISBN:978-1-5386-0806-7
[6]P. Parameswari, N. Rajathi, K. J. Harshanaa, “Machine Learning Approaches for Crop Recommendation”, International Conference on Advancements in Electrical, Electronics, Communication, Computing and Automation (ICAECA), 978-1-6654-2829-3/21 ©2021 IEEE, Coimbatore,India,2021.
[7]JeevaganeshR, Harish D, Priya B, “A MachineLearningbased Approach for Crop Yield Prediction and Fertilizer Recommendation”, International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI) 978-1-6654-83285/22©2022IEEE,Chennai,India,2022.

[8]Harendra Singh Negi, Bhawnesh Kumar, Anuj Singh, “Crop Prediction Based on Soil Properties using Machine Learning for Smart Farming”, International Conference on Computional Intelligence and Sustainable Engineering Solutions (CISES), 978-1-6654-8004-8/22 ©2022 IEEE, Dehradun,India,2022.
[9]M Sobhana, A H L Swaroop, Phani Kumar V, “KRISHI RAKSHAN - A Machine Learning based New Recommendation System to the Farmer”, International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems(ICICCS), 978-1-6654-1035-8/22 ©2022 IEEE, AndhraPradesh,India,2022.
[10]M. Sai Teja, T. Sai Preetham , S.Jancy, “Crop Recommendation and Yield Production using SVM Algorithm ”, International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems(ICICCS), 978-1-66541035-9/22©2022 IEEE,Chennai,India,2022.
